Additional And Relevant Useful Information For Nodular Basal Cell Carcinoma Of Skin:
There are multiple types of Basal Cell Carcinoma of Skin:
- Superficial Basal Cell Carcinoma of Skin
- Nodular Basal Cell Carcinoma of Skin
- Infiltrating Basal Cell Carcinoma of Skin
- Micronodular Basal Cell Carcinoma of Skin
- Fibroepithelial Basal Cell Carcinoma of Skin
- Basal Cell Carcinoma of Skin with Adnexal Differentiation
- Basosquamous Carcinoma
- Keratotic Basal Cell Carcinoma of Skin
Signs Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
Basal cell carcinomas can look like:
- A pimple that does not resolve after 2 months
- Open wounds that dont seem to heal or keep returning
- Shiny or pearly bumps on the skin that may be pink or red with brown, black, or blue spots
- Scar-like tissue that is firm, flat, pale, or yellowed
- Pinkish growths that look like a donut
- Pink patches which may be itchy or asymptomatic
These cancerous growths can often bleed after sustaining a minor injury, such as when you shave over them. If a cut from a razor reappears numerous times at the same site, it may be a basal cell carcinoma.
How Serious Is Basal Cell Skin Cancer
Basal cell skin cancer, also called basal cell carcinoma, is usually very curable, but it can cause disfigurement and complications if it’s not treated. In the majority of cases, basal cell carcinoma is very treatable.
It is unusual for basal cell carcinoma to cause death. Approximately 2,000 people in the U.S. die each year from basal and squamous skin cancers. In most cases, people who die from these types of skin cancer tend to be older, immunosuppressed, or have been diagnosed at a very late stage.
You May Like: What Is The Survival Rate For Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
How Can Nodular Basal Cell Carcinoma Of Skin Be Prevented
Currently, Nodular Basal Cell Carcinoma of Skin is a malignant skin cancer that has no preventive measures. However, the following factors may help reduce the risk for the condition:
- Avoid or minimize sun exposure
- Limit the use of tanning beds, tanning parlors
- Smoking cessation
- If it is caused by certain underlying disorders, then treating the underlying condition may help in the treatment and early cure of Nodular BCC of Skin
- Regular medical screening at periodic intervals with blood tests, scans, and physical examinations, are mandatory, due to its metastasizing potential and high possibility of recurrence. Often several years of active vigilance is necessary
What Are The Risks Of Treatment
Both surgery and medicated creams carry the risks of infection and pain or discomfort.
Both treatments have high cure rates, but the cure rate for creams is not as good as the cure rate for surgery.
Surgery usually leaves a scar. If a skin graft is used, it can tighten as it heals and make movement more difficult. Medicated creams dont leave scars. But there is a risk that they will leave some permanent patches of darker or lighter skin.
No matter which treatment you choose, theres always a risk that the cancer could come back.
Also Check: What Is The Survival Rate For Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
How Is Nodular Basal Cell Carcinoma Of Skin Diagnosed
Some of the tests that may help in diagnosing Nodular Basal Cell Carcinoma of Skin include:
- Complete physical examination with detailed medical history evaluation
- Examination by a dermatologist using a dermoscopy, a special device to examine the skin
- Woodâs lamp examination: In this procedure, the healthcare provider examines the skin using ultraviolet light. It is performed to examine the change in skin pigmentation
- Skin or tissue biopsy: A skin or tissue biopsy is performed and sent to a laboratory for a pathological examination, who examines the biopsy under a microscope. After putting together clinical findings, special studies on tissues and with microscope findings, the pathologist arrives at a definitive diagnosis
- Differential diagnosis of other tumors should be ruled out hence, biopsy is an important diagnostic tool
Many clinical conditions may have similar signs and symptoms. Your healthcare provider may perform additional tests to rule out other clinical conditions to arrive at a definitive diagnosis.
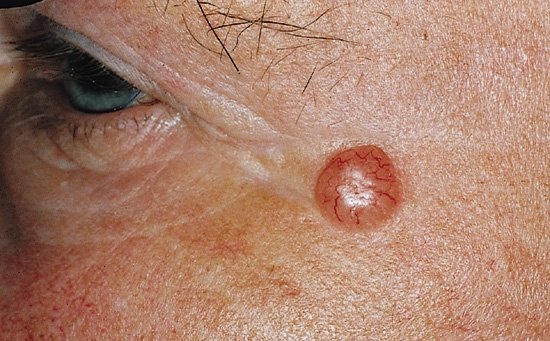
What Is Nodular Basal Cell Carcinoma Of Skin
- Basal Cell Carcinoma of Skin is a malignant cancer affecting the skin. It is a slow-growing tumor generally observed in older individuals, in both men and women
- This malignant carcinoma, which may be present as a lesion on the sun-exposed areas of the body, has the potential to metastasize to the lymph nodes
- Nodular Basal Cell Carcinoma of Skin is the most common type of BCC that is present as nodules on the skin, usually in the head and neck area
- Some nodules may grow to large sizes and ulcerate. They can also infiltrate into the adjoining soft tissues and nerves. Larger tumors also have a greater tendency to recur after treatment
- The cause of Nodular Basal Cell Carcinoma of Skin is unknown, but factors such as chronic sun exposure, smoking, and ionizing radiation, etc., are known to contribute towards its development. Also, fair-skinned Caucasians have a greater risk than dark-skinned Africans and Asians
- Any combination of chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and invasive procedures are used to treat Nodular Basal Cell Carcinoma of Skin. Small-sized tumors and tumors that have not metastasized can be cured through appropriate skin surgery
- The prognosis for metastatic tumors depends upon many factors including the stage of the tumor, health status of the individual, and treatment response. The prognosis may be guarded
Also Check: When Squamous Cell Carcinoma Spreads
How Are Basal Cell Carcinomas Treated
How we treat your basal cell carcinoma will often be dictated by its location. There are numerous treatment options.
Surgery is the typical treatment method. Depending on the size and location of the removed growth, the wound may be sutured closed, covered with a skin graft, or allowed to heal on its own.
These are the surgical procedures:
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Infiltrating Basal Cell Carcinoma Of Skin
Infiltrating Basal Cell Carcinoma of Skin signs and symptoms may include:
- Infiltrating BCC of Skin is a slow-growing malignant tumor. The tumor is a typical skin lesion, with thickened skin, presenting as a poorly-demarcated plaque
- The surface of the plaque may be red, if intact. Else, it may appear as an ulcer, if the surface is eroded
- It is typically observed on sun-exposed areas of the body common sites include the head and neck region, arms and legs, etc.
- The tumor may be solitary or many in number. In children, if it is associated with basal cell nevus syndrome, then multiple lesions may be observed
- Some Infiltrating BCC of Skin may have pigmented appearance and may resemble a melanoma
- Most lesions are less than 1-2 cm, but some may grow to larger sizes of even 10 cm
- The carcinoma has a tendency to penetrate deep into the subcutaneous tissue
- The lesion may grow and there may be itching sensation, ulceration, and bleeding
Don’t Miss: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Prognosis
Basal Cell Carcinoma Overview
Basal cell carcinoma, also called epithelioma, is the uncontrolled growth of the skin’s basal cells. These are the cells that line the deepest layer of the epidermis, the skin’s outermost layer. This type of cancer rarely spreads to other parts of the body.
It is mainly caused by repeated long-term exposure to sunlight. Light-skinned people who spent a lot of time in the sun as children, or who spend time in tanning booths, are especially susceptible. X-ray treatments for acne and exposure to industrial pollutants such as arsenic and hydrocarbons also increase the risk of developing basal cell carcinoma.
Basal cell carcinoma is the most common skin cancer in the United States, with nearly 3 million cases diagnosed each year.
How Quickly Should Basal Cell Carcinoma Be Removed
How long after diagnosis of basal cell carcinoma would a doctor recommend removing it? I am aware that basal cell carcinoma is very common and there is a %90 cure rate, as well as the fact that it rarely metastasizes. Will waiting several months after diagnosis to remove it decrease cure rate? Is this something that needs to be removed immediately to have the best prognosis?? Thank you so much for your time, you have no idea how much this will help me!
Also Check: Braf Melanoma Treatment
Can Basal Cell Carcinoma Turn Into Melanoma
Basal cell carcinomas cannot progress or turn into melanoma. Basal cell carcinoma forms in the basal cells in the epidermis. They occur when DNA in the cells is damaged by exposure to ultraviolet radiation from the sun or tanning beds. This triggers changes in basal cells in the outermost layer of the skin, resulting in uncontrolled growth. This is a basal cell carcinoma.
Melanoma begins in cells known as melanocytes. While they are also found in the epidermis, melanocytes are different than basal cells. Melanocytes produce a pigment, known as melanin, which gives the skin its color. When the skin is exposed to UV radiation, it causes skin damage that triggers the melanocytes to produce more melanin. This tanning of the skin is a protective mechanism. But when the burning of the skin causes DNA damage, mutations in the melanocytes result in uncontrolled cellular growth, melanoma.
How Is Infiltrating Basal Cell Carcinoma Of Skin Diagnosed
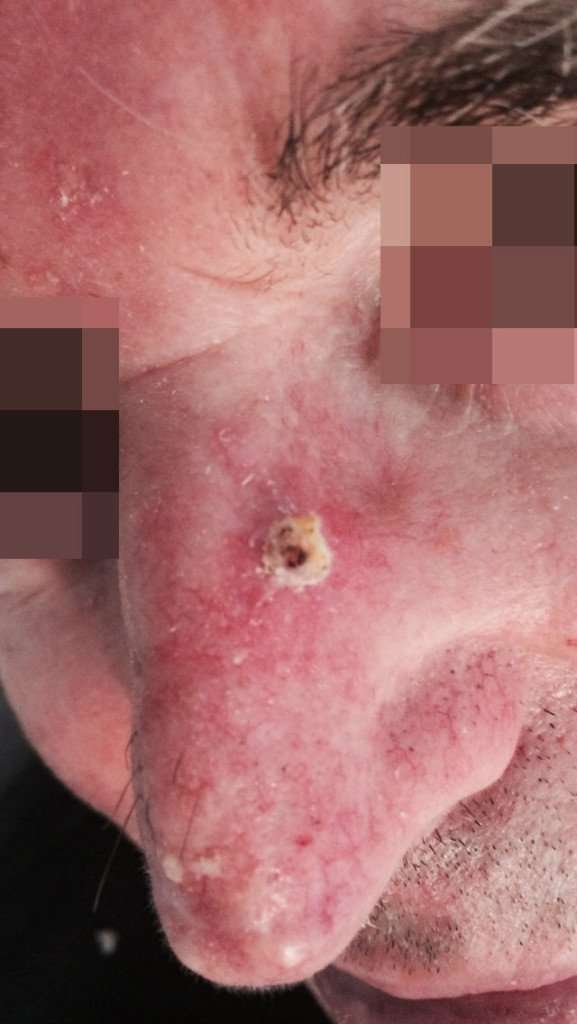
Some of the tests that may help in diagnosing Infiltrating Basal Cell Carcinoma of Skin include:
- Complete physical examination with detailed medical history evaluation
- Examination by a dermatologist using a dermoscopy, a special device to examine the skin
- Woodâs lamp examination: In this procedure, the healthcare provider examines the skin using ultraviolet light. It is performed to examine the change in skin pigmentation
- Skin or tissue biopsy: A skin or tissue biopsy is performed and sent to a laboratory for a pathological examination, who examines the biopsy under a microscope. After putting together clinical findings, special studies on tissues and with microscope findings, the pathologist arrives at a definitive diagnosis
- Differential diagnosis of other tumors should be ruled out hence, biopsy is an important diagnostic tool
Many clinical conditions may have similar signs and symptoms. Your healthcare provider may perform additional tests to rule out other clinical conditions to arrive at a definitive diagnosis.
Don’t Miss: Cancer Lesion Pictures
What Are The Risk Factors For Basal Cell Carcinoma
Basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma and melanoma are all skin cancers caused by exposure to damaging ultraviolet raysfrom natural and artificial sunlight. There’s also a genetic condition called basal cell nevus or Gorlin syndrome, which can cause people to develop hundreds of basal cell skin cancers, but it’s extremely rare, says Dr. Christensen.
People at the highest risk for basal cell carcinoma tend to have fair or light-colored skin, a history of sun exposure and a tendency to sunburn quickly. Fair-skinned people have a 50 percent risk of developing basal skin cancer at some point in their lives, Dr. Christensen says. The cancer is the result of cumulative damage of years spent in the sun, and may take 20 years to manifest.
Although it’s often more common in older people, it can occur in younger adults, too.
Basal cell carcinoma spreads very slowly and very rarely will metastasize, Dr. Christensen says. But if it’s not treated, basal cell carcinoma can continue to grow deeper under the skin and cause significant destruction to surrounding tissues. It can even become fatal. For example, an untreated basal cell carcinoma on the face can grow into the bones and, over time, directly into the brain, Dr. Christensen says.
Can Basal Cell Carcinomas Be Cured
Yes, BCCs can be cured in almost every case, although treatment can be more complicated if the BCC has been neglected for a long time, or if it occurs in an awkward place, such as close to the eye or on the nose or ear.
BCCs rarely spread to other parts of the body. Therefore, although it is a type of skin cancer it is almost never a danger to life.
Recommended Reading: Can You Die From Basal Cell Skin Cancer
How Can You Prevent Basal Cell Carcinoma
Being safe in the sun is the best way to prevent BCC and other skin cancers. Here are some tips:
- Avoid being in the sun from 10 am to 4 pm.
- Avoid tanning beds.
- Use a broad spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 15 or higher each day. If you will be outside for longer periods of time, use a broad spectrum sunscreen that is water-resistant and has an SPF of 30 or higher. Put the sunscreen on 30 minutes before going outside. Put sunscreen on again every two hours, or more frequently if you have been swimming or sweating a lot.
- Use protective clothing that has built-in sun protection, which is measured in UPF. Also, use broad-brimmed hats and sunglasses.
- Do your own skin self-exam about once per month and see a dermatologist about one time per year for a professional skin exam.
- Have any skin changes examined as soon as possible by a healthcare provider.
What Are The Treatments For Basal Cell Carcinoma
BCC is treated by removing it. The choice of treatment depends on many things, including patient health and age, the location of the tumor, and the extent and type of the cancer. Treatment may occur in many ways:
- Scratching off with a curette, an instrument that may end in a ring or a spoon, and then burning with a special electric needle. This method is called electrodessication and curettage.
- Surgical removal
- Mohs surgery: This is a specialized technique. The doctor first removes the visible cancer and then begins cutting around the edges. The tissues are examined during the surgery until no more cancer cells are found in tissues around the wound. If necessary, a skin graft or flap might be applied to help the wound heal.
- Excisional surgery: The growth and a bit of surrounding skin is removed with a scalpel.
If the BCC has advanced locally or spread to another location, which is very rare for BCC, the FDA has approved two medicines: vismodegib and sonidegib . These drugs are of a class called hedgehog inhibitors.
Recommended Reading: What Does Squamous Skin Cancer Look Like
Also Check: What Is The Survival Rate For Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Will I Need Chemotherapy For Basal Cell Carcinoma
Basal cell carcinoma, a type of nonmelanoma skin cancer, is very common and affects people of various age groups. If you have been diagnosed with basal cell carcinoma, you probably have questions about your next steps and what treatments can be used to address this type of cancer.
Every patient is different and requires an individualized treatment plan. With this said, chemotherapy is rarely used to eradicate basal cell carcinoma. This systemic treatment involves administering medicine into the bloodstream to attack cancer cells throughout the body. Because basal cell carcinoma usually affects an isolated area and seldom reaches an advanced stage, a systematic approach to treatment is typically not necessary.
Surgery For Basal Cell Carcinoma
Our dermatologic surgeons remove as little tissue as possible when treating your skin cancer, with the goal of preserving your appearance and minimizing scarring.
- Mohs surgery. Tumors in delicate areas like the face might require Mohs surgery, a technique performed by our highly trained doctors. During Mohs surgery, the tumor is removed layer by layer and microscopically examined each time during the procedure to ensure elimination of cancer while preserving as much healthy skin as possible.
- Curettage. Small superficial basal cell cancers can be scraped off using a curette , using local anesthesia. Your doctor then dessicates the tumor site with an electrocautery needle. This technique is best reserved for parts of the body where you wouldnt mind having a scar since it typically leaves a depressed whitish scar at the tumor site.
- Skin cancer excision. Basal cell carcinomas can be excised by a surgical excision right in the doctors office using local anesthesia. Each surgery is tailored specifically to each patient, depending on the site of the skin cancer, specific physical demands of the patient and personal preferences.
You May Like: What Stage Is Invasive Lobular Carcinoma
Ask The Expert: Why Am I Having Surgery To Remove A Small Basal Cell Carcinoma
Although the nonmelanoma skin cancer basal cell carcinoma is rarely life-threatening, it can be troublesome, especially because 80 percent of BCCs develop on highly visible areas of the head and neck. These BCCs can have a substantial impact on a persons appearance and can even cause significant disfigurement if not treated appropriately in a timely manner.
The fact is, BCCs can appear much smaller than they are. On critical areas of the face such as the eyes, nose, ears and lips, they are more likely to grow irregularly and extensively under the skins surface, and the surgery will have a greater impact on appearance than might have been guessed. Even a small BCC on the face can be deceptively large and deep the extent of the cancer cannot be seen with the naked eye.
If such a BCC is treated nonsurgically , the chance of the cancer recurring is high. Unfortunately, treating a BCC that has returned is usually much more difficult than treating it precisely and completely when initially diagnosed.
BCCs on the trunk, arms and legs that cause concern are typically larger in size, but even a small BCC in these areas can have an irregular growth pattern under the skin if the initial biopsy shows the tumor is aggressive. In addition, a small BCC in an area previously treated with radiation may be much more aggressive than it appears on the surface. Again, treating such a tumor nonsurgically is likely to leave cancer cells behind.
About the Expert: