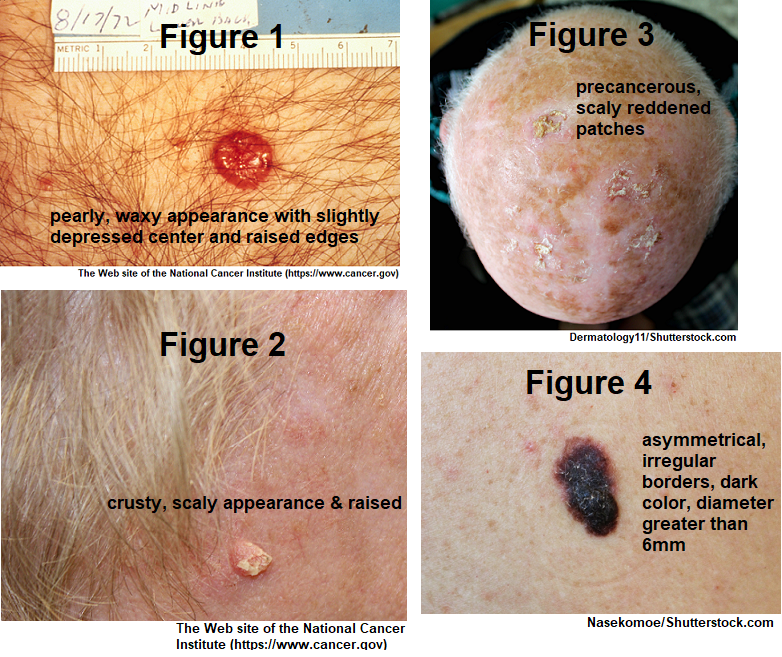
Precancerous Types Of Skin Cancer
Some precancerous growths, often attributable to sun exposure, can lead to skin cancer over time. However, if they are recognized and removed early, you could avoid a cancer diagnosis.;These growths include:
- Actinic keratosis: About 40-60% of squamous cell cancer cases began as actinic keratosis. Anywhere between 2-10% of these growths will develop into SCC, sometimes in as little as a couple of years. Actinic cheilitis is a type of actinic keratosis that appears on the lower lip, and is at higher risk for developing into skin cancer
- Bowens disease: This early, noninvasive form of SCC is at high risk of becoming skin cancer if not addressed. It presents as an eczema-like scaly patch and is usually red or brown in color. These growths have been linked to sun exposure, radiation, carcinogen exposure, genetics, and trauma;
- Leukoplakia: These white patches on the lips, tongue, and gums may be caused by alcohol and tobacco use, and can turn into squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer sites on the lips may be caused by sun damage
- Keratoacanthoma: This dome-shaped growth is usually found on sun-exposed skin and usually grows quickly at first, then slows down. Many shrink and go away on their own, but if they continue to grow, this tumor can turn into squamous cell carcinoma. They are usually removed surgically
Four Main Types Of Skin Melanoma
There are four main types of skin melanoma.
How Common Is Skin Cancer
Australia has one of the highest rates of skin cancer in the world. Skin cancer is the most common cancer diagnosed in Australia. About two in three Australians will be diagnosed with some form of skin cancer before the age of 70.
Almost 980,000 new cases of BCC and SCC are treated each year. BCC can develop in young people, but it is more common in people over 40. SCC occurs mostly in people over 50.
More than 13,000 people are diagnosed with melanoma in Australia every year. Australia and New Zealand have the highest rates of melanoma in the world.
| For an overview of what to expect during all stages of your cancer care, visit;Cancer Pathways Basal and squamous cell carcinoma. This is a short guide to what is recommended, from diagnosis to treatment and beyond. |
You May Like: How Bad Is Melanoma Skin Cancer
Rarer Types Of Skin Cancer
Basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, melanoma, and Merkel cell cancer make up the vast majority of all skin cancer cases. However, there are several other rare types of skin cancer:
- Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma can affect the skin, blood, lymph nodes, and internal organs, and presents as a dry, itchy red rash
- Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans causes a tumor in the deep layers of the skin and starts out as a patch of firm skin that raises over time. The tumors have a high rate of recurring or returning once treated;
- Kaposi sarcoma is a rare cancer caused by an infection with human herpesvirus-8 . It causes abnormal tissue growth under the skin, and looks like red and purple lesions. Those with a compromised immune system, such as people who are HIV-positive, are more at risk
- Sebaceous carcinoma is a rare, aggressive cancer that usually affects the skin on or around the eyelid. It presents as a small, round, painless tumor on the upper or lower eyelid
- Skin adnexal tumors are very rare tumors that grow in the sebaceous glands or hair follicles. They are often misdiagnosed as benign growth, and almost always require a pathologist to diagnose;
- Soft tissue sarcomas are cancerous growths that can develop in the deep layers of skin, as well as the bodys fat, muscle, nerves and blood vessels;
Cancer May Spread From Where It Began To Other Parts Of The Body
When cancer spreads to another part of the body, it is called metastasis. Cancer cells break away from where they began and travel through the lymph system or blood.
- Lymph system. The cancer gets into the lymph system, travels through the lymph vessels, and forms a tumor in another part of the body.
- Blood. The cancer gets into the blood, travels through the blood vessels, and forms a tumor in another part of the body.
The metastatic tumor is the same type of cancer as the primary tumor. For example, if skin cancer spreads to the lung, the cancer cells in the lung are actually skin cancer cells. The disease is metastatic skin cancer, not lung cancer.
Recommended Reading: Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma Slow Growing
Where Do Skin Cancers Start
Most skin cancers start in the top layer of skin, called the epidermis. There are 3 main types of cells in this layer:
- Squamous cells: These are flat cells in the upper part of the epidermis, which are constantly shed as new ones form. When these cells grow out of control, they can develop into squamous cell skin cancer .
- Basal cells: These cells are in the lower part of the epidermis, called the basal cell layer. These cells constantly divide to form new cells to replace the squamous cells that wear off the skins surface. As these cells move up in the epidermis, they get flatter, eventually becoming squamous cells. Skin cancers that start in the basal cell layer are called basal cell skin cancers or basal cell carcinomas.
- Melanocytes: These cells make the brown pigment called melanin, which gives the skin its tan or brown color. Melanin acts as the bodys natural sunscreen, protecting the deeper layers of the skin from some of the harmful effects of the sun. Melanoma skin cancer starts in these cells.
The epidermis is separated from the deeper layers of skin by the basement membrane. When a skin cancer becomes more advanced, it generally grows through this barrier and into the deeper layers.
Can You Prevent Skin Cancer
According to Dr. Dorsey, Skin cancer is an extremely serious condition, but with proactive care, most cases can be avoided altogether. In fact, taking a few small steps to limit sun damage and conducting regular skin self-exams is all you need to do to keep your skin healthy. Because sun exposure is the main underlying cause of skin cancer, sun protection is essential to prevent this condition. Patients need to apply sunscreen every day and reapply at least every two hours during prolonged sun exposure. Whenever possible, limit or avoid time spent outdoors during peak sun hours between 10 am and 4 pm. If patients need to be outdoors during these times, its important to wear protective coverings, seek shade, and reapply sunscreen frequently.
In addition to daily sun protection steps, patients also need to perform self-exams at least every month. Early detection is key to providing effective skin cancer treatment, so regular self-exams are an essential part of keeping people healthy. Your Board Certified Dermatologist can walk you through a self-exam when you visit the office, but the basic process involves carefully examining your skin, from the top of your head to the bottoms of your feet , and noting any spots, lesions, bumps, discoloration, or other skin changes or irregularities. When you know where marks are on your skin, youll be more likely to notice if they are growing or changing in ways that are concerning or that indicate skin cancer.
Read Also: Can You Get Skin Cancer From Radiation Treatments
Skin Color And Being Exposed To Sunlight Can Increase The Risk Of Basal Cell Carcinoma And Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of The Skin
Anything that increases your chance of getting a disease is called a risk factor. Having a risk factor does not mean that you will get cancer; not having risk factors doesnt mean that you will not get cancer. Talk with your doctor if you think you may be at risk.
Risk factors for basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma of the skin include the following:
- Being exposed to natural sunlight or artificial sunlight over long periods of time.
- Having a fair complexion, which includes the following:
- Fair skin that freckles and burns easily, does not tan, or tans poorly.
- Blue, green, or other light-colored eyes.
- Red or blond hair.
Although having a fair complexion is a risk factor for skin cancer, people of all skin colors can get skin cancer.
Older age is the main risk factor for most cancers. The chance of getting cancer increases as you get older.
Basal Cell Skin Cancer
BCC is the most common type of skin cancer. About 75 out of every 100;non melanoma skin cancers are BCCs. They develop from basal cells and these are found in the deepest part of the outer layer of the skin .
They develop mostly in areas of skin exposed to the sun, including parts of the face such as the nose, forehead and cheeks. Also, on your back or lower legs.
They are;most often diagnosed in people who are middle aged or older.
Doctors might also call;a basal cell cancer;a rodent ulcer.
There are;a number of different types of BCC.;Each type can look and behave differently. They;include:
- nodular basal cell skin cancer
- superficial basal cell skin cancer
- morphoeic basal cell skin cancer – also known as sclerosing or infiltrating basal cell skin cancer
- pigmented basal cell skin cancer
Nodular basal cell cancer is the most common subtype.
It’s very rare for basal cell skin cancer to spread to another part of the body to form a;secondary cancer. It’s possible to have more than one basal cell cancer at any one time and having had one does increase your risk of getting another.
Also Check: How To Know If You Have Melanoma Skin Cancer
Merkel Cell Carcinoma: A Rare Skin Cancer On The Rise
Merkel cell carcinoma is a rare type of skin cancer that affects about 2,000 people in the United States each year.
Though its an uncommon skin cancer, cases of Merkel cell carcinoma have increased rapidly in the last couple of decades.
This type of cancer starts when cells in the skin, called Merkel cells, start to grow out of control.
Merkel cell carcinomas typically grow quickly and can be difficult to treat if they spread.
They can start anywhere on the body, but Merkel cell carcinomas commonly affect areas exposed to the sun, such as the face, neck, and arms.
They may look like pink, red, or purple lumps that are firm when you touch them. Sometimes, they can open up as ulcers or sores.
Risk factors include:
Keeping Cancer In Check
Chronic exposure to the sun or intermittent sunburns can lead to skin cancer. Skin cancer risk doubles with five or more sunburns in a lifetime, but just one bad sunburn can double the risk of melanoma. While skin cancer is uncommon in African Americans, Latinos and Asians, it can also be more deadly because they are often diagnosed later in the course of the disease.
Its important to examine your skin regularly. You should report any changes in an existing mole or any new moles to your physician. People with fair complexions have the highest risk of developing skin cancer, but everyone should avoid the sun and practice safety measures to protect their skin.
The American Cancer Society;recommends the Slip, Slop, Slap and Wrap policy. When you go out in the sun, slip on a shirt, slop on sunscreen, slap on a hat and wrap on sunglasses to protect your eyes and the sensitive skin around them.
Exposure to the UV rays of tanning lamps is not safe. Tanning lamps give out UV rays, which can cause long-term skin damage and can contribute to skin cancer. Tanning bed use has been linked with an increased risk of melanoma, especially for people under 30. Most doctors and health organizations recommend not using tanning beds and sun lamps.
Recommended Reading: What Happens If I Have Skin Cancer
Who Is At Risk
Much like with BCC, the more time you spend in the sun, the more at risk you are for developing SCC. About 90% of nonmelanoma skin cancers are caused by sun exposure, and people who have tanned indoors have a 67% higher risk of developing squamous cell carcinoma.
Your risk for SCC is higher if you:
- Have a history of skin cancer
- Have a history of unprotected exposure to the sun or tanning beds
- Have a weakened immune system due to a chronic condition or medication
- Are over age 50
- Have a history of chronic skin infections, precancerous skin growths or human papillomavirus
What Happens If Basal Cell Carcinoma Is Left Untreated
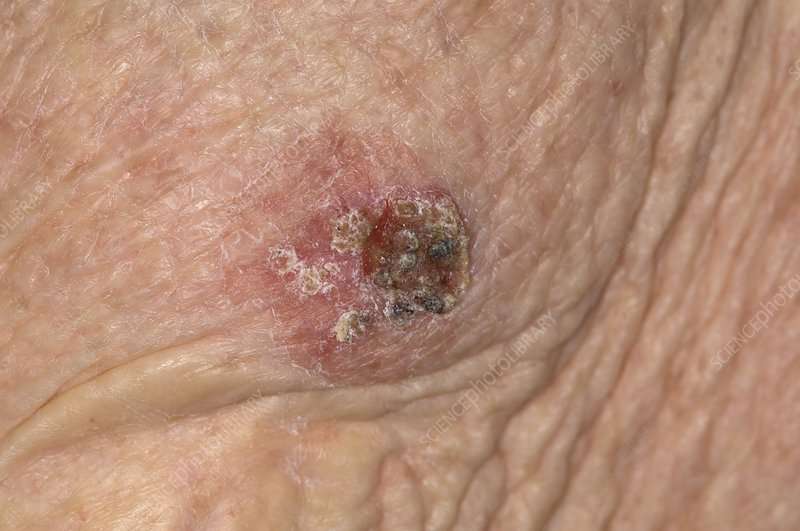
Basal cell carcinoma is the most common type of skin cancer, and it is considered very low risk for metastasizing and spreading to other parts of the body. It is typically very slow-progressing and is usually diagnosed and treated in very early stages. If left untreated, basal cell carcinomas can be locally destructive to the tissues where it grows, and it can invade deeper structures such as nerves, cartilage, and even bone. In most cases, basal cell carcinoma develops on the face, ears, neck, head, shoulders, hands, and other areas that receive frequent sun exposure. The tumors may look like raised bumps on the skin that are usually smooth and pearly/shiny in appearance. Blood vessels can sometimes be seen within the lesions, and in some cases, a wound may form and bleed easily.
Also Check: Is Basal Cell Carcinoma Life Threatening
Skin Cancer Pictures: What Does Skin Cancer Look Like
Skin cancer images by skin cancer type. Skin cancer can look different than the photos below.
Basal Cell Carcinoma;|;Squamous Cell Carcinoma;|;Bowens Disease;|;Keratoacanthoma;|;Actinic Keratosis;|;Melanoma
Skin cancer often presents itself as a change in the skins appearance. This could be the appearance of a new mole or other mark on the skin or a change in an existing mole.
Please remember that you should always seek advice from your doctor if you have any concern about your skin. Skin cancers often look different from skin cancer images found online.
Skin Cancer Symptoms And Signs
Basal Cell Carcinoma
BCC is the most common type of skin cancer and has a predilection for sun-exposed skin. Tumors may appear as a pearly or waxy bumps usually with visible blood vessels , or as a flat scaly reddish patch with a brown border, or as a hard or scar-like lesion . Frequently BCCs can be itchy, often bleed, or in more advanced cases, ulcerate.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Main Cause Of Skin Cancer
How Do You Know If A Spot Is Skin Cancer
To learn more you can read this article on the signs of skin cancer or this article on melanoma symptoms, but dont forget to get any skin concern you may have checked out by your doctor.
You can also read our guide on how to check your skin regularly, if you want to learn more about how to form a skin checking routine for yourself.
Squamous Cell Carcinomas Are More Likely To Spread
Like basal cell carcinomas, squamous cell carcinomas are curable and can usually be removed completely when caught in time. They are, however, more dangerous than BCC because of their higher likelihood to spread. SCC is more likely to grow into the deeper layers of skin and other tissues in the body than BCC. While basal cell carcinoma usually does not grow into other areas of the body, it can rarely grow into a large tumor on the skin.
Don’t Miss: How Many People Die From Skin Cancer Every Year
Medical Treatment For Skin Cancer
Surgical removal is the mainstay of skin cancer treatment for both basal cell and squamous cell carcinomas. For more information, see Surgery.People who cannot undergo surgery may be treated by external radiation therapy. Radiation therapy is the use of a small beam of radiation targeted at the skin lesion. The radiation kills the abnormal cells and destroys the lesion. Radiation therapy can cause irritation or burning of the surrounding normal skin. It can also cause fatigue. These side effects are temporary. In addition, topical chemotherapy creams have been FDA approved for the treatment of certain low-risk nonmelanoma skin cancers. Patients with advanced or many basal cell carcinomas are sometimes prescribed oral pills to block the growth of these cancers. Side effects include muscle spasms, hair loss, taste changes, weight loss and fatigue.
In advanced cases of melanoma, immune therapies, vaccines, or chemotherapy may be used. These treatments are typically offered as clinical trials. Clinical trials are studies of new therapies to see if they can be tolerated and work better than existing therapies.