How The Government Of Canada Protects You
The Public Health Agency of Canada monitors cancer in Canada. PHAC identifies trends and risk factors for cancer, develops programs to reduce cancer risks, and researches to evaluate risks from the environment and human behaviours. Health Canada also promotes public awareness about sun safety and the harmful effects of UV rays.
What You Can Do
Examine your skin once a month
Learn about the warning signs of skin cancer and know what to look for during a self-exam. If you spot anything that just doesnt look right, get it checked by your dermatologist as soon as possible.
See your dermatologist annually
Get a full-body, professional skin exam once a year or more often if you are at higher risk for skin cancer. Make the most of your appointment with these tips. If youve never seen a dermatologist, our physician finder can help you locate one.
Is There Anything Else I Need To Know About A Skin Cancer Screening
Exposure to the ultraviolet rays that come from the sun plays a major role in causing skin cancer. You are exposed to these rays anytime you are out in the sun, not just when you are at the beach or pool. But you can limit your sun exposure and help reduce your risk of skin cancer if you take a few simple precautions when out in the sun. These include:
- Using a sunscreen with a sun protection factor of at least 30
- Seeking shade when possible
- Wearing a hat and sunglasses
Sunbathing also increases your risk of skin cancer. You should avoid outdoor sunbathing and never use an indoor tanning salon. There is no safe amount of exposure to artificial tanning beds, sunlamps, or other artificial tanning devices.
If you have questions about reducing your risk of skin cancer, talk to your health care provider.
Also Check: How To Identify Basal Cell Carcinoma
Why Should I Start Skin Cancer Screening
In the UK the risk of melanoma increases with age however the the number of cases diagnosed in young people is disproportionately high. In fact melanoma is the most common cancer in people aged 15-34.
If you are exposed to the sun regularly, have a family history of skin cancer, have atypical mole syndrome or other predispositions that increase your risk of developing skin cancer, you should strongly consider skin cancer screening.
What Is My Skin Type
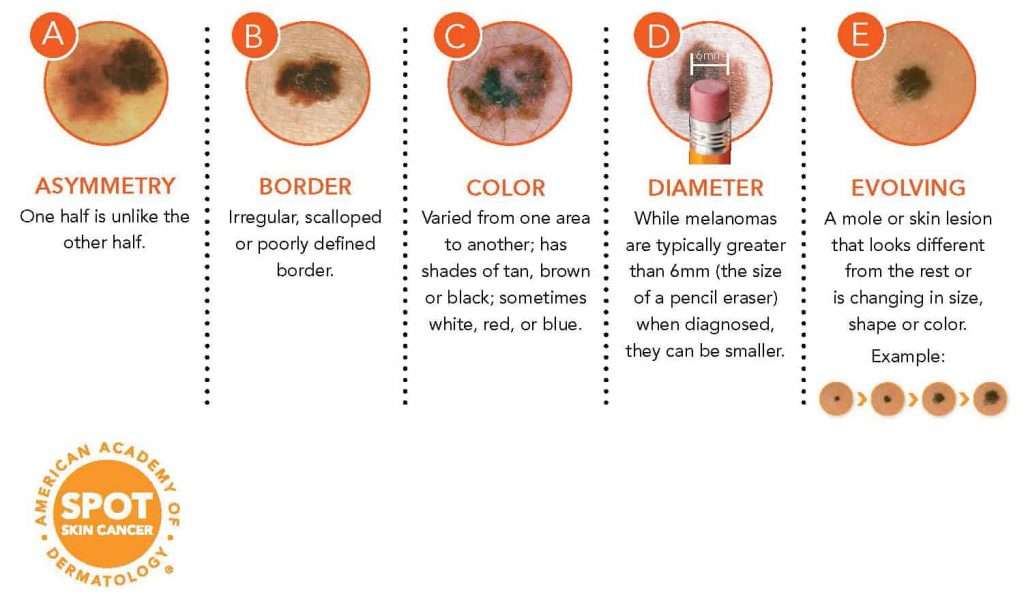
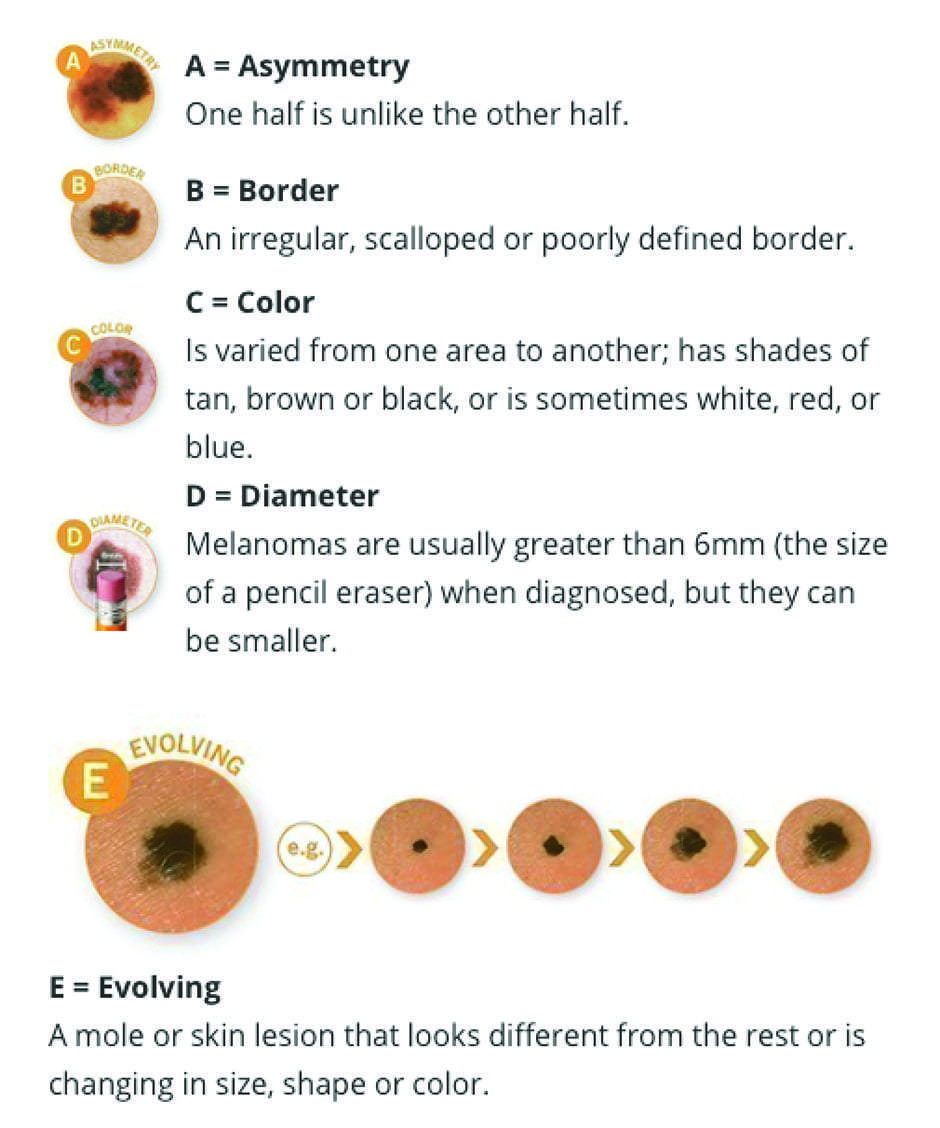
Skin types that are more sensitive to ultraviolet radiation burn more quickly and are at a greater risk of skin cancer.
All skin types can be damaged by too much UV radiation. Skin types that are more sensitive to UV radiation burn more quickly and are at a greater risk of skin cancer.
People with naturally very dark skin still need to take care in the sun even though they may rarely, if ever, get sunburnt. The larger amount of melanin in very dark skin provides natural protection from UV radiation. This means the risk of skin cancer is lower.
Eye damage can occur regardless of skin type. High levels of UV radiation have also been linked to harmful effects on the immune system.
Vitamin D deficiency may be a greater health concern for people with naturally very dark skin, as it is more difficult for people with this skin type to make vitamin D.
Read Also: What Is Braf Testing In Melanoma
Can I Opt To Have A Suspicious Lesion Watched Instead Of Getting A Biopsy
Sometimes that is a viable option, but it will depend on whether your dermatologist feels that there is a low or high suspicion of the lesion being cancerous or otherwise harmful.
If were monitoring a skin lesion, were watching for the area to grow, Aphale said. But the bigger the area becomes, the more difficult the treatment becomes, too.
Do You Still Need To See Your Dermatologist
Yes!!! While taking advantage of breakthrough technology like this model for a mobile app can be hugely beneficial to your skins health, this doesnt eliminate the need to check in with your dermatologist at least yearly. In addition to skin cancer screening, you should discuss issues with your doctor such as the best sunscreens for your Baumann Skin Type and preventative skincare and supplements.
Also Check: What Is The Survival Rate For Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
How To Perform A Self
1. Examine your face
Especially your nose, lips, mouth and ears front and back. Use one or both mirrors to get a clear view.
2. Inspect your scalp
Thoroughly inspect your scalp, using a blow-dryer and mirror to expose each section to view. Get a friend or family member to help, if you can.
3. Check your hands
Palms and backs, between the fingers and under the fingernails. Continue up the wrists to examine both the front and back of your forearms.
4. Scan your arms
Standing in front of the full-length mirror, begin at the elbows and scan all sides of your upper arms. Dont forget the underarms.
5. Inspect your torso
Take Matters Into Your Own Hands With Self
Regardless of how often you see your dermatologist, you should doyour best to monitor your own skin and that of your partner or close familymembers.
Grab a mirror and perform a skin exam of your own every three tosix months, Dr. Riley suggests.
Look for moles or spots that:
- Have changed in size, shape or color overtime.
- Bleed or do not heal after several weeks.
- Are asymmetrical or have irregular borders.
- Are larger than ¼ inch in size.
And, above all else, practice safe sun habits to prevent skin cancer from developing in the first place.
Read Also: What Is Stage 2 Melanoma Skin Cancer
Causes Of Skin Cancer
One of the main causes of skin cancer is being exposed to UV rays. UV rays are invisible, and are produced by the sun, and tanning equipment.
UV rays cause skin cancer by creating changes in the cells of your skin. In some cases, the UV rays cause direct damage to your cells. Tans and sunburns, for example, are both signs that UV rays have damaged your skin. In other cases, UV rays cause skin cancer indirectly, by weakening the immune system.
Many studies on skin cancer show that people who have suffered many severe sunburns in childhood are at greater risk of developing skin cancer. Family history, some chemical exposures, and immune dysfunction conditions can also create a greater risk of developing skin cancer.
Skin Cancer Screening Studies
For people without a history of skin cancer in their families, no studies have been done to test the effectiveness of routine screening for melanoma. Periodic skin examinations are the key to diagnosing skin cancer at its earliest stage, when it is most easily cured. Most cases of basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma first appear as changes in the skin, which, once noticed by the patient or primary care doctor, are then verified as skin cancer by a dermatologist after a skin examination and biopsy have been performed. Since basal cell and squamous cell carcinomas are almost always cured without specified screening, no studies have shown that such screening will improve the already high cure rates for those types of skin cancer.
Family history is a risk factor for melanoma. In addition, there is strong evidence that the risk of melanoma increases for individuals who have atypical moles or many common moles. Other melanoma risk factors include previous melanoma or non-melanoma skin cancers, skin that burns readily and fails to tan, freckling, blue eyes, red hair, and a history of blistering sunburns. To date, there is no evidence to show that screening individuals with any of these risk factors will reduce the number of melanoma deaths.
Read Also: What Is Melanoma In The Brain
How Often Should You Get A Skin Cancer Exam
Experts disagree on this question. Some medical groups say you should only get a screening if you have suspicious moles or you have a high chance of getting melanoma, the deadliest type of skin cancer.
Others recommend a yearly screening for people who are at high risk for skin cancer. A few things make you more likely to get it:
- Blond or red hair, light eye color, and skin that freckles or sunburns easily
- People in your family have had melanoma
- Youve had unusual moles in the past
- Youve had sunburns before, especially any that blistered
- Youve used tanning beds
- You have more than 50 moles or any that look irregular
Current Clinical Practice In The United States
Dermatologists tend to perform more skin screening examinations than family practice physicians or internists but lack the capacity to offer population screening. Potentially, to achieve skin screening of the general population, a two-step screening method with initial review of skin lesions in primary care and referral to dermatology for second review would be implemented. However, most primary care and general internists report not having sufficient training in skin cancer screening to feel confident in their skills to conduct whole body skin examinations on their patients. Hence, skin cancer screening in the United States among primary care physicians remains quite low. Primary care physicians in two counties in Connecticut and Florida indicate that only 31 percent perform skin cancer screening on their adult patients. The primary barrier to screening was the physician’s lack of confidence in identifying a suspected lesion. While there are several educational interventions to improve knowledge of and confidence in skin cancer screening in primary care, few tools have been rigorously tested for measured changes in clinical practice.
Despite no current screening guidelines, AAD has offered free skin cancer screening clinics since 1985, similar to its contemporary SPOTMe® screening campaign, and conducted 2.4 million screenings to date.
Also Check: What Is The Survival Rate For Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
How Is Skin Cancer Diagnosed
If your doctor believes you might have skin cancer, you will need a skin biopsy. During a biopsy, your doctor removes a small sample of skin from the affected area. Next, a pathologist will examine the tissue under a microscope to look for cancer cells. The your doctor recommends will depend on the type of skin cancer identified and whether it has spread, so accurate screening and diagnosis is important.
More common skin cancers like basal cell carcinoma dont usually spread, so your doctor may simply remove the entire growth during the biopsy without the need for more tests. However, if your biopsy shows melanoma, you may need surgery to remove surrounding tissue.
Depending on the results of the physical exam and biopsy, your doctor may also suggest additional imaging tests to verify a skin cancer diagnosis and whether the cancer has spread:
What Happens If They Find Something
If your doctor finds a spot that could be cancerous orpre-cancerous, theyll likely want to take a picture for your medical chart andperform a skin biopsy.
During a biopsy, the doctor will remove a small amount of tissueto be examined under a microscope by a pathologist. This is a simple procedurethat can be done right then and there, in the office. Theyll clean the area ofskin where the spot is located, numb it with an injection of anesthesia, anduse a blade or scalpel to take a sample of the skin. You shouldnt feel anypain, aside from the pinch from the injection.
That sample will be sent to the lab for testing, and your doctor willshare the results with you when they are available. This usually happens withina few days but could take up to a week or longer.
If the spot turns out to be cancerous, it may need to becompletely removed or treated with other methods, Dr. Riley says.
You May Like: Stage 3 Basal Cell Carcinoma Survival Rate
When Should I Get A Skin Cancer Screening
Most medical organizations in the United States dont have specific age recommendations for when to start getting visual skin exams. However, theres no wrong time to start screenings.
Anyone who has certain risk factors should get a baseline skin exam, said Abhishek Aphale, MD, a dermatologist at Fox Chase Cancer Center.
You may be at high risk of skin cancer if you have:
- Fair skin
- Skin that burns or freckles easily
- A history of sunburns
- A history of tanning bed use
- A job requiring a significant amount of time outdoors
- A family or personal history of skin cancer
- A large number of moles
If you find out a first-degree relative has skin cancer, Aphale recommends getting a baseline skin exam as soon as possible.
If you just found out that your mother was diagnosed with melanoma, even if youre 18 years old, go ahead and get screened, Aphale said. Or, if youve had melanoma, it would be beneficial for your children to have a skin exam.
Anyone who is concerned about a spot on their skin should get screened, tooeven if they arent at high risk.
Why Do A Biopsy
A biopsy is a tissue sample thats taken from a lesion that a dermatologist may believe contains cancerous cells and needs further evaluation. Its important to remember that having a biopsy done does not mean you necessarily have skin cancer.
The sample will be sent to a dermatopathologist to look at the skin cells more closely for the possible presence of cancerous cells.
Heres how a biopsy is usually done:
Biopsy results will usually come back within 2 weeks with a definitive answer as to whether the area is affected by skin cancer. If its been more than 2 weeks and you have not heard from the dermatologist, you can call their office to ask about your results.
Remember that its your right to receive your results, regardless of whether they are negative or positive for cancer cells.
You May Like: Ductal Breast Cancer Survival Rates
Early Detection Starts With You
When caught and treated early, skin cancers are highly curable. And in the early stages of skin cancer development, youre the one with the best chance to see changes.
Thats why we recommend that you examine your skin head-to-toe every month. Its a simple but powerful way to look at yourself with a new focus that can save your life.
What About A Skin Self
Whether youre at high risk or not, getting familiar with your own skin is very beneficial.
According to the American Cancer Society, regular skin self-exams are especially important if youve had skin cancer or are at higher risk.
Plan on doing your skin self-exam in a well-lit room after you bathe or shower.
While facing a mirror, check:
- your face, ears, neck, chest, abdomen
- underneath breasts
- underarms and both sides of arms
- your palms and the tops of your hands, between fingers, and under fingernails
Sit down to check:
- the front of your thighs and shins
- the top and bottom of your feet, between your toes, under toenails
With a hand mirror, check:
- the back of your calves and thighs
- your buttocks and genital area
- your lower and upper back
- the back of your neck and ears
- your scalp, using a comb to part your hair
If this is your first time doing a self-exam, take note of how moles, freckles, and blemishes look and feel. Get to know whats normal so youll notice when somethings abnormal.
You can even take photos if theres an area you want to watch. Repeat the exam once a month.
- a large brown spot with darker specks
- a mole that changes size, color, or feel
- a mole that bleeds
- a small lesion with irregular borders and variations in color
- a painful lesion with itching or burning
- dark lesions on your:
You May Like: What Is The Survival Rate For Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Get To Know Your Skin
Skin self-examination is a good way to detect early skin changes that may mean melanoma. Look for any abnormal skin growth or any change in the colour, shape, size, or appearance of a skin growth. Check for any area of injured skin that does not heal. Have your spouse or someone such as a close friend help you monitor your skin, especially places that are hard to see such as your scalp and back.
A careful skin examination may identify suspicious growths that may be cancer or growths that may develop into skin cancer . Adults should examine their skin regularly.
Skin cancer often appears on the trunk of men and on the legs of women.
- Get to know your moles and birthmarks, and look for any abnormal skin growth and any change in the colour, shape, size, or appearance of a skin growth.
- Check for any area of skin that does not heal after an injury.
- Have your doctor check your skin during any other health examinations.
- Tell your doctor about any suspicious skin growths or changes in a mole.
- Be aware of the risk of skin cancer and the steps you can take to prevent it, including using sunscreen, wearing protective clothing, and staying out of the midday sun.
For more information, see the topic Protecting Your Skin From the Sun.
Tests Are Used To Screen For Different Types Of Cancer When A Person Does Not Have Symptoms
Scientists study screening tests to find those with the fewest harms and most benefits. Cancer screening trials also are meant to show whether early detection helps a person live longer or decreases a person’s chance of dying from the disease. For some types of cancer, the chance of recovery is better if the disease is found and treated at an early stage.
Don’t Miss: Etiology Of Basal Cell Carcinoma