Sex Life And Fertility
Breast cancer treatments can have a direct effect on your sex life.
For example, surgery may affect how you think and feel about your body . It can take time to adjust to changes to your body. If you have a partner, it can help to talk openly with them about your feelings.
Some treatments for DCIS may cause menopausal symptoms. Doctors do not recommend hormone replacement therapy . This is because it contains oestrogen, which could encourage breast cancer cells to grow.
Your cancer doctor or breast care nurse will also advise you not to use contraception that contains hormones.
What Are Some Advantages Of Receiving Treatment For Dcis At Msk
At MSK, we have a very thoughtful approach to personalizing treatment for each person with DCIS. The doctors and patients make treatment decisions as a team. Much of the research determining risk factors for DCIS-related recurrence was done at MSK, and we have a computerized prediction model that can help calculate an individuals risk of recurrence, which helps us decide what treatments are best. Weve tried to figure out who really needs additional treatments, such as radiation or hormone therapy, and who may be able to avoid certain treatments. Our goal is to find the right treatment for each patient, so that they can remain cancer free with an excellent quality of life moving forward.
Dont Miss: Etiology Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
Current Controversies In The Treatment Of Ductal Carcinoma In Situ Of The Breast
Giorgia Garganese1*, Simona Maria Fragomeni1*, Sonia Bove1, Maria Teresa Evangelista1, Ida Paris2, Danilo Di Giorgio1, Daniela Andreina Terribile1, Riccardo Masetti1
1 Multidisciplinary Breast Center, Fondazione Policlinico Universitario Agostino Gemelli , Università Cattolica del Sacro Cuore , Division of Gynecologic Oncology, Fondazione Policlinico Universitario Agostino Gemelli , Università Cattolica del Sacro Cuore , , Italy
Contributions: Conception and design: G Garganese, SM Fragomeni, DA Terribile, I Paris, R Masetti Administrative support: MT Evangelista, S Bove, DD Giorgio Provision of study materials or patients: SM Fragomeni, MT Evangelista, S Bove, DD Giorgio Collection and assembly of data: G Garganese, SM Fragomeni Data analysis and interpretation: SM Fragomeni, G Garganese, DA Terribile, I Paris, R Masetti Manuscript writing: All authors Final approval of manuscript: All authors.
*These authors contributed equally to this work.
Correspondence to:
Keywords: Ductal carcinoma in situ treatment breast cancer review
Submitted Jul 01, 2017. Accepted for publication Aug 15, 2017.
doi: 10.21037/tcr.2017.08.33
You May Like: Metastatic Basal Cell Carcinoma Survival Rate
How Common Is Ductal Carcinoma In Situ
The American Cancer Society expects that 63,960 new cases of DCIS will be found in 2018. Today more and more women are aware of the importance of early detection and are getting mammograms each year. Because of this, the number of cases of DCIS has increased. In addition, mammography technology has greatly improved as well and is better able to detect problems at an earlier stage. An estimated 12.4% of women in the U.S. will develop invasive breast cancer at some time in their lives.
Overtreatment Of Ductal Carcinoma In Situ
9 out of ten ladies have no idea that some breast cancers by no means trigger issues or have turn into identified in the midst of their lives. This can be a downside that ductal carcinoma in situ has delivered to the fore.
The aim of most cancers screening is to establish life-threatening illnesses at an earlier, extra curable stage . So efficient most cancers screening packages improve each the incidence of most cancers thats detected at an early stage and the incidence of most cancers that presents itself at a late stage. Sounds cheap, as a result of in case you screened youll discover all of those tiny cancers that you may beforehand neglected, and have the ability to minimize it out and take away it from circulation. Nevertheless, this doesnt appear to be the case with mammograms as you may see at 0:30 in my video Overtreatment of Stage Zero Breast Most cancers DCIS . As mammography rose within the 1980s early-stage most cancers diagnoses really skyrocketed. What we then wish to see is a mirrored image of that surge, with the incidence of late-stage cancers falling. For those who found the most cancers early, it wouldnt be an choice for late-stage most cancers, wouldnt it? Not appropriate. The most cancers incidence within the late stage didnt appear to lower a lot in any respect.
Key to remove
How might somebody enhance their weight loss plan and life-style to cut back the chance of breast most cancers? See for instance:
Within the well being sector,
You May Like: What Are The Forms Of Skin Cancer
How Is Dcis Treated
The options for treating DCIS are: lumpectomy, lumpectomy and radiation, a combination of those with tamoxifen, or mastectomy. You dont have to rush into any one treatment because your doctor or your friend or anyone else says you should. Its your breast, and your life. Take the time to decide whats best for you.
How Likely Is Dcis To Come Back
The chance of the DCIS coming back depends on various factors. But after mastectomy DCIS almost never comes back. In women who have just the area of DCIS removed the chance of it coming back is a bit higher. But it depends on the grade and type of DCIS.
Your doctor can give you more information about the chance of the DCIS coming back in your case.
Don’t Miss: Does Amelanotic Melanoma Blanch When Pressed
Some Cases Of Dcis Will Progress Towards Invasive Breast Cancer If Left Untreated
There is a general consensus that DCIS may represent a transitional stage between the normal breast tissue and invasive breast carcinoma.
However, it is still largely unknown which types of DCIS are non-progressing towards invasive breast cancer if left untreated.
One recent study estimated that only between 100 to 270 cases of DCIS per 100000 will not progress to invasive breast cancer if left untreated.
A medical study from the United Kingdom examined 84 breast cancer screening units. This large research study looked at DCIS diagnoses between the years of 2003 and 2007 for women aged 50 to 64 years.
Data from over 5,243,658 was analyzed. The average frequency of DCIS detected was 1.60 per 1000 women. The study found that for every 3 cases of DCIS detected on screening there was one less case of invasive cancer in the next 3 years.
Is Surgery The Right Decision For Women With Dcis
Women with ductal carcinoma in situ face the difficult decision of howto treat the condition. Researchers at MD Anderson are studying ways tomake this tough choice easier.
Ligia Toro de Stefani, Ph.D., had just retired from a busy academic medical research career when a mammogram revealed a suspicious mass in her right breast. Her doctors in Brownsville, Texas, referred her to MD Anderson, where she was diagnosed with ductal carcinoma in situ, or DCIS, often called stage 0 breast cancer the very earliest stage.
Toro and her husband, Enrico Stefani, M.D., Ph.D., researched everything they could about the condition before meeting with MD Anderson surgeon Alastair Thompson, M.D., to discuss treatment options.
Investigating came naturally to the scientific couple. Toro is an emeritus professor of anesthesiology and molecular and medical pharmacology at the University of California, Los Angeles. Her husband is a former director of UCLAs anesthesiology division of molecular medicine.
We started reading a lot of papers, not just Googling the disease, but doing a serious literature search, Toro de Stefani says.
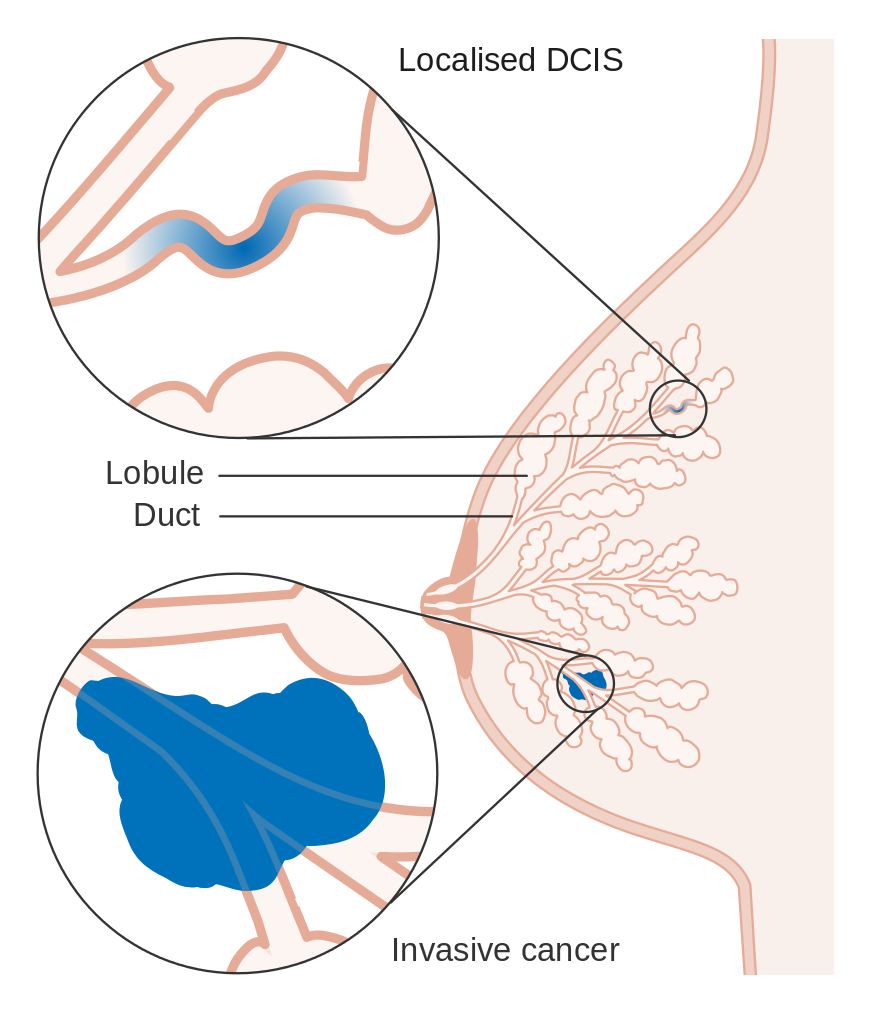
DCIS is a cluster of cancer cells inside a milk duct. The cells are held in place by the ducts wall, but they have the ability to break through the wall. Thats when they become invasive.
That wont happen to everyone, Toro de Stefani says, but theres no predicting when cells will break through the duct and spread, and when they wont.
Don’t Miss: Can Squamous Cell Carcinoma Metastasis
Stage 1b Breast Cancer Means One Of The Following Descriptions Applies:
Lymph nodes have cancer evidence with small clusters of cells between the approximate size of a pinprick to the approximate width of a grain of rice .
AND EITHER No actual tumor is found in the breast.
OR The tumor is smaller than the approximate size of a peanut .
Similar to stage 0, breast cancer at this stage is very treatable and survivable. When breast cancer is detected early, and is in the localized stage , the 5-year relative survival rate is 100%.
Will Dcis Return Or Spread
- Since DCIS is a noninvasive form of cancer, it does not spread throughout the body .
- For patients having a lumpectomy with radiation, the risk of local recurrence ranges from 5% to 15%.
- For those having mastectomy, the risk of local recurrence is less than 2%. Patients who receive hormonal therapy after surgery further reduce their risk of recurrence by half.
- Breast cancer may develop in the patients other breast, but only in about 5% of cases. If this happens, the cancer in the second breast is not considered a recurrence, but a new primary breast cancer. It can also be a different type of breast cancer.
Read Also: Melanoma Stage 4 Treatments
Younger Age At Diagnosis Of Dcis
A medical study published in 2015 set out to estimate the 10 and 20-year mortality rate after an initial diagnosis of ductal carcinoma in-situ.
The statistics were taken from the Surveillance, Epidemiology and End Results from 108,196 women diagnosed with DCIS between the years of 1988 to 2011.
The study found that the average age of diagnosis for DCIS was 53.8 years. In general the overall breast cancer death rate over a 20 year period was only 3.3%.
However, the mortality rate at 20 years increased to 7.8% in women who were diagnosed with DCIS before the age of 35 years old.
A further 2014 research study concluded that after 10 years the rates of local recurrence after breast conservative therapy and radiotherapy were as follows:-
- Women over 50 years at diagnosis: 11% recurrence rate
- For women between 45 and 50 years: 15% recurrence rate
- Women under 45 years: 25% recurrence rate
We can see from the above figures that the younger the age at diagnosis, the higher the percentage likelihood of recurrence.
However, this is often because younger women present with a higher grade tumor and are not as rigorously followed up by mammogram screening.
NOT
Factors At Diagnosis That Affect Prognosis For Ductal Carcinoma In Situ
Many people used to think that Ductal Carcinoma In-Situ was a precursor for invasive breast cancer or a pre-cancerous condition. However, researchers have struggled for many years to work out which ductal carcinomas in-situ develop into invasive breast cancer and why.
Indeed, not all of these early changes progress to a more invasive, problematic cancer. The high survival rates of 98% to 99% for Ductal Carcinoma In-Situ, in 2010 reflect the effectiveness of treatment.
At present, there does not seem to be onedefinitive prognostic marker. Indeed, it is difficult to find research on one single factor alone, such as age, or tumor grade, because they are all inter-linked.
This clearly shows that each individual case is different and outcome and prognosis is based upon many factors.
However, research suggests that 5 main factors of DCIS on diagnosis seem to predict a less favourable outcome. These include:-
- Younger age at Diagnosis
- Tumor Grade
- Large Tumor size or clinically palpable at diagnosis
Read Also: What Is The Survival Rate For Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Removing Breast Tissue Samples For Testing
During a core needle biopsy, a radiologist or surgeon uses a hollow needle to remove tissue samples from the suspicious area, sometimes guided by ultrasound or by X-ray . The tissue samples are sent to a lab for analysis.
In a lab, a doctor who specializes in analyzing blood and body tissue will examine the samples to determine whether abnormal cells are present and if so, how aggressive those abnormal cells appear to be.
Breast calcifications
Calcifications are small calcium deposits in the breast that show up as white spots on a mammogram. Large, round or well-defined calcifications are more likely to be noncancerous . Tight clusters of tiny, irregularly shaped calcifications may indicate cancer.
Stereotactic breast biopsy
During a stereotactic breast biopsy, your breast will be firmly compressed between two plates. Breast X-rays are used to produce stereo images â images of the same area from different angles â to determine the exact location for the biopsy. A sample of breast tissue in the area of concern is then removed with a needle.
Core needle biopsy
A core needle biopsy uses a long, hollow tube to obtain a sample of tissue. Here, a biopsy of a suspicious breast lump is being done. The sample is sent to a laboratory for testing and evaluation by doctors who specialize in analyzing blood and body tissue .
What If My Report On Ductal Carcinoma In Situ Mentions Margins Or Ink
When the entire area of DCIS is removed, the outside surface of the specimen is coated with ink, sometimes even with different colors of ink on different sides of the specimen. The pathologist looks at slides of the DCIS under the microscope to see how close the DCIS cells get to the ink . If DCIS is touching the ink , it can mean that some DCIS cells were left behind, and more surgery or other treatments may be needed. Sometimes, though, the surgeon has already removed more tissue to help make sure that this isnt needed. If your pathology report shows DCIS with positive margins, your doctor will talk to you about what treatment is best.
You May Like: Basal Cell Carcinoma Etiology
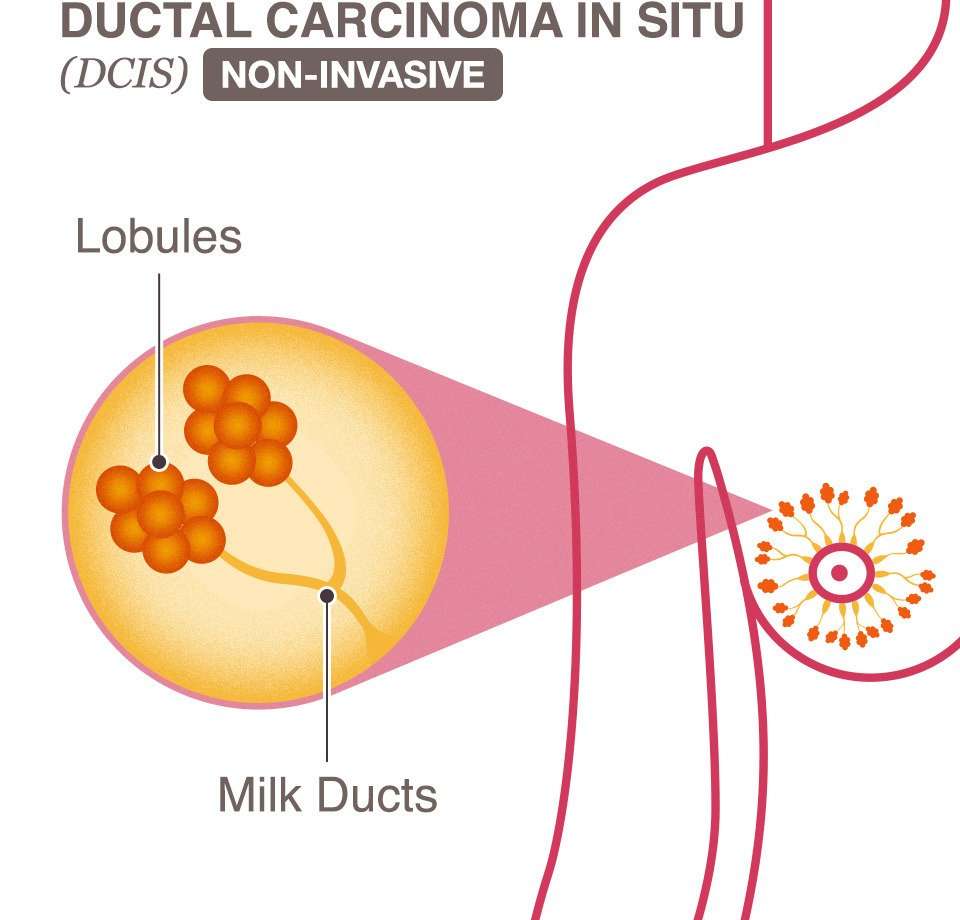
What Is Ductal Carcinoma In Situ
Ductal carcinoma in situ is a type of breast cancer. This is also called non-invasive or pre-invasive breast cancer. The cancer cells are found along the sides of the milk duct within the breast. Milk ducts are within each breast and are the tubes that let milk travel from the lobes to the nipple openings for breastfeeding.
DCIS is non-invasive, which means that the cancer cells are found only within the milk duct and have not spread through the walls of the ducts and to other nearby tissues in the breast. It is a Stage 0 breast cancer and is treatable. Doctors characterize cancer in stages, using Roman numerals from 0, or zero, to IV, or four. In order to determine the stage of a tumor, doctors must look at the original tumor and determine where it is located, its size, and if it has been noticed in other areas. The lower the stage number, the better chance for successful treatment of the disease and for the best results.
Although DCIS is always considered Stage 0, the tumor can be any size and may be found within several milk ducts inside the breast. With proper treatment, the prognosis is excellent.
Removal Of The Whole Breast
You might have a mastectomy if:
- the area of the DCIS is large
- there are several areas of DCIS
- you have small breasts and too much of the breast is affected by DCIS to make breast conserving surgery possible
You may have surgery to your armpit called a sentinel lymph node biopsy if you have a mastectomy. This means having about 1 to 3 lymph nodes removed.
If you want to, you can choose to have a new breast made at the time of the mastectomy, or some time afterwards.
Hormone therapy is recommended for 5 years if you have breast conserving surgery for DCIS and:
- your cancer calls have oestrogen receptors
- you do not have radiotherapy
Research shows that taking hormone therapy after breast conserving surgery for DCIS reduces the risk of it coming back .
Trials show that hormone therapy can reduce the number of further invasive breast cancers or DCIS. But in these trials, the people taking a hormone therapy tablet called tamoxifen did not live any longer than those who didn’t take it.
Also Check: Malignant Breast Cancer Survival Rate
Can Dcis Develop Into Invasive Breast Cancer
If DCIS is not treated, the cancer cells may develop the ability to spread outside the ducts, into the surrounding breast tissue. This is known as invasive breast cancer. Invasive cancer has the potential to also spread to other parts of the body.
In some cases, DCIS will never develop further or grows so slowly that it would never cause harm during a persons lifetime. Although the size and grade of the DCIS can help predict if it will become invasive, there is currently no way of knowing if this will happen. is more likely to become an invasive breast cancer and to do so over a shorter time than low-grade DCIS.
Lumpectomy Followed By Radiation Therapy
Most people with DCIS have a lumpectomy followed by radiation therapy. This is usually a very good option if the DCIS only appears in one area of the breast and can be completely removed with clear margins of healthy tissue. A clear margin is a rim of healthy tissue around the tumor that is completely free of cancer cells. How wide do these margins need to be? In February 2014, the American Society for Radiation Oncology and the Society of Surgical Oncology issued new guidelines saying that clear margins, no matter how small as long as there was no ink on the cancer tumor, should be the standard for lumpectomy surgery.
Lumpectomy, and in some cases a second procedure called re-excision lumpectomy, is used to completely remove the cancer.
- Lumpectomy removes the entire area of DCIS as well as a margin of normal, healthy breast tissue around it. The whole area that contained cancer cells is removed, even when there’s no lump present.
- Re-excision lumpectomy is a second surgery that may be necessary after lumpectomy to remove extra tissue in order to ensure that there is a clear margin of healthy tissue around the tumor.
If you’ve had lumpectomy, you may have a dent, bulge, or other distortion of the breast shape near the surgical site. Or your breast may have a different size or position compared to the other breast. Learn about options for reconstruction after lumpectomy.
You May Like: Braf And Melanoma