Does Squamous Cell Carcinoma Skin Cancer Hurt
Some people notice only a change to their skin, such as a sore that wont heal or heals and returns.
This skin cancer can also cause symptoms, such as:
-
Itching
-
Feeling sore or tender where you have the SCC
-
Numbness or a pins-and-needles sensation
Any sore, wart, or growth that isnt healing or heals and returns should be examined by a board-certified dermatologist.
How Serious Is A Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Id had a few skin cancers removed before, all basal cell carcinomas , the most common type. But when I was diagnosed with a squamous cell carcinoma on my scalp, it seemed different, and a little more scary. I asked C. William Hanke, MD, a Mohs surgeon at the Laser and Skin Surgery Center of Indiana and a senior vice president of The Skin Cancer Foundation, what we need to know about this second most common form of skin cancer.
Q: When people talk about nonmelanoma skin cancers, they tend to lump basal cell and squamous cell carcinomas together as the ones that are far less dangerous than melanoma. Should we take SCCs more seriously?
Dr. Hanke: Yes and no. BCCs hardly ever metastasize. Ive seen two cases in my entire career. But when SCCs that havent been treated early get big, then the chance of metastasis becomes real. Its uncommon, but its much more common than in BCC. We see it in our practice. But we dont want to scare people into thinking that just because they have squamous cell, Oh wow, Ive got a chance of metastasis. Remember, the rate is very low. Its just those big ones.
Q: OK, so its rare. But what happens when an SCC does spread?
Q: Whats the usual treatment for SCCs?
Q: How can we detect SCCs as early as possible?
What Are The Treatments For Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Your doctor will help you to decide on the best type of treatment. Factors in the decision include your overall health and age, the location of the cancer, and how invasive the cancer is.
Treatment options include:
- Scratching off with a curette, an instrument that may end in a ring or a spoon, and then burning with a special electric needle. This method is called electrodessication and curettage.
- Surgical removal:
- Mohs surgery: This is a specialized technique. The doctor first removes the visible cancer and then begins cutting around the edges. The tissues are examined during the surgery until no more cancer cells are found in tissues around the wound. If necessary, a skin graft or flap might be applied to help the wound heal.
- Excisional surgery: The growth and a bit of surrounding skin is removed with a scalpel.
If you have some type of advanced or very invasive SCC, you might find that it returns or metastasizes . There are several medications which have been approved to treat locally advanced cancers that cannot be simply treated or those that have spread to other areas of the body.
Recommended Reading: Melanoma Stage 3 Survival Rate
What Are The Types Of Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Squamous cell carcinoma develops when the flat cells in the toplayer of skin grow and divide in an uncontrolled way.
You can get an SCC wherever there are squamous cells which is in manydifferent parts of the body. However, typically they appear on parts of theskin that have been exposed to a lot of ultraviolet radiation from the sunor from tanning beds.
An early form of skin cancer, called Bowen’s disease, which looks like a red, scaly patch, can also develop into an SCC if nottreated.
An SCC can be quite an aggressive cancer if left untreated. If you evernotice a sore, scab or scaly patch of skin that doesnt heal within 2 months,see a doctor.
What Is Squamous Cell Skin Cancer Of The Head And Neck
Skin malignancies are the most common cancer in the United States, responsible for more than half of all new cancer cases. These can be broken down into melanoma and non-melanoma malignancies, which are squamous cell cancer and basal cell cancer. These skin malignancies are caused by ultraviolet radiation from exposure to the sun and tanning beds.
Squamous cell cancer is the second most common form of skin cancer. It is more aggressive and may require extensive surgery depending on location and nerve involvement. Radiation, chemotherapy and immunotherapy are used in advanced cases.
Also Check: Squamous Cell Carcinoma Skin Metastasis
Read Also: Stage 2 Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Survival Rate
What Is Skin Cancer
Cancer can start any place in the body. Skin cancer starts when cells in the skin grow out of control.
Skin cancer cells can sometimes spread to other parts of the body, but this is not common. When cancer cells do this, its called metastasis. To doctors, the cancer cells in the new place look just like the ones from the skin.
Cancer is always named based on the place where it starts. So if skin cancer spreads to another part of the body, its still called skin cancer.
The skin
You May Like: Does Amelanotic Melanoma Blanch When Pressed
Treating Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of The Skin
Treatment options for squamous cell skin cancer depend on the risk of the cancer coming back, which is based on factors like the size and location of the tumor and how the cancer cells look under a microscope, as well as if a person has a weakened immune system.
Most squamous cell skin cancers are found and treated at an early stage, when they can be removed or destroyed with local treatment methods. Small squamous cell cancers can usually be cured with these treatments. Larger squamous cell cancers are harder to treat, and fast-growing cancers have a higher risk of coming back.
In rare cases, squamous cell cancers can spread to lymph nodes or distant parts of the body. If this happens, treatments such as radiation therapy, immunotherapy, and/or chemotherapy may be needed.
Read Also: Invasive Breast Cancer Prognosis
Growth Factor Receptor Antagonists
EGFR
EGFR is a member of the ERBB family of trans-membrane tyrosine kinase receptors . EGFR and their receptors are involved in signal transduction and tumor growth, thus blockade of these systems provides a therapeutic approach, through neutralizing ligands, inhibiting ligand binding, or blocking the tyrosine kinases of the receptors. Examples of EGFR inhibitors include monoclonal antibodies against the extracellular domain of the receptor and receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors that target the intracellular domain . EGFR inhibitors have been applied in HNSCC, ESCC and extensively in NSCLC clinical trials. In HNSCC, patients with locally advanced disease have been shown to benefit from the addition of EGFR inhibition to radiotherapy . But, EGFR targeted therapy trials conducted in HNSCC to date still show various disadvantages such as low efficacy and significant toxicity . In ESCC, inhibition of EGFR-TK by erlotinib is promising through inducing growth inhibition and cell cycle arrest in human esophageal cancer cells and enhancing the antineoplastic effects of other targeted agents . Cetuximab and panitumumab are currently being investigated in NSCLC. Phase II trials showed that cetuximab improved survival in-chemo-naïve patients with advanced cancer and panitumumab is currently in phase II trial .
Other growth factor receptor antagonists
What Is Aggressive Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Aggressive SCC or high-risk SCC is cancer that is more likely to recur or metastasize . Features of high-risk SCC are:4,9
- Larger than 2 centimeters
- Deeper than 2 millimeters
- Near the lip and ear
- Located in a scar or other injured skin
- Spread into a nerve
- Poorly differentiated
Having a weakened immune system due to medications or infections increases the risk of aggressive SCC. History of radiation exposure or use of psoralen UVA treatment are other risk factors for aggressive SCC.9
You May Like: Does Melanoma Blanch When Pressed
Prognosis Of Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Typically, the prognosis for small tumors that are removed early and adequately is excellent. Treatment is usually effective, and most people survive. Most squamous cell carcinomas affect only the area around them, penetrating into nearby tissues. However, some spread to distant parts of the body, nearby skin and lymph nodes, and eventually to nearby organs and can be fatal. Tumors that are more than 2 centimeters in diameter or grow more than 2 millimeters deep, or tumors that occur near the ears and lips, in scars, or around nerves are more likely to spread. About one third of cancers on the tongue or elsewhere in the mouth have metastasized before diagnosis .
If the cancer is treated before it metastasizes, the person is usually cured. However, if the cancer has metastasized, the chance of surviving the next 5 years, even with treatment, is only 34%.
Know That Surgery Sites Heal In Time
Had basal cell on the side of my nose going toward the corner of my eye. Couldnt see anything on the skin, but thanks to the keen eye of my derm she saw it, and did a biopsy, and sent me to a Mohs specialist at UAB. He removed it along with surrounding tissue, sutured, sent me on my way looking, well, terrible! Within 1 year, the scare is completely gone & cant tell anything was done. Thankful for those yearly scans. Debbie
I had Mohs done on a very small spot on side of nose right by eye. They had to put me to sleep and did a flap on forehead. Also had Mohs on lip. It went about 2 inches outside of mouth and about an inch in mouth. Great results. Almost unnoticeable. Joy
Recommended Reading: Skin Cancer Perineural Invasion
Where Squamous Cell Carcinoma Occurs
SCC can be found anywhere on the body, but is most commonly seen in sun-exposed areas. Common SCC sites include the face, ears, lips, scalp, shoulders, neck, hands, and forearms. Its also possible to be diagnosed with SCC in areas without sun exposure, such as inside the mouth, under fingernails or toenails, on the genitals, or in the anus.
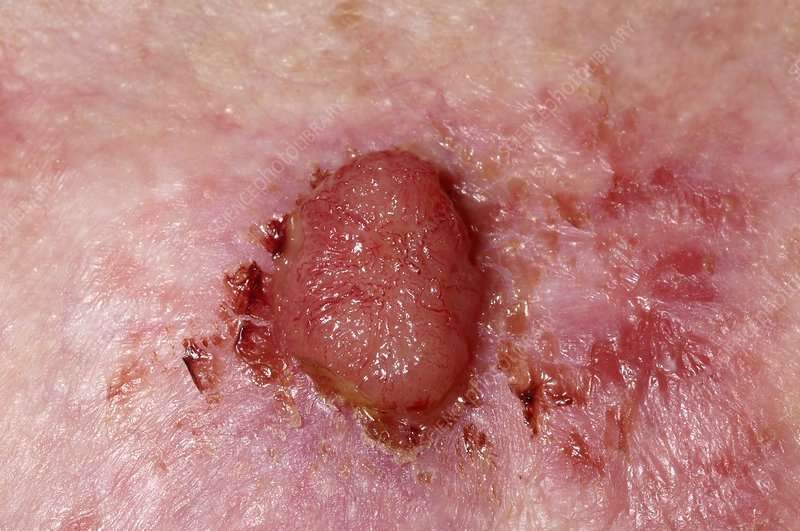
How To Identify A Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Squamous Cell Carcinomas appear most often on the face and neck, V-shaped area of the chest, and upper back. They are more likely than basal cell carcinomas to form on the top of the arms and hands. Sun exposure is a large contributor to the development of SCCs and hence they can occurr more frequently on the drivers-side arm.
Squamous cell carcinomas look like an inflamed , scaly growth. They can feel sore or tender and some may repeatedly break open, bleed, and crust never fully healing.
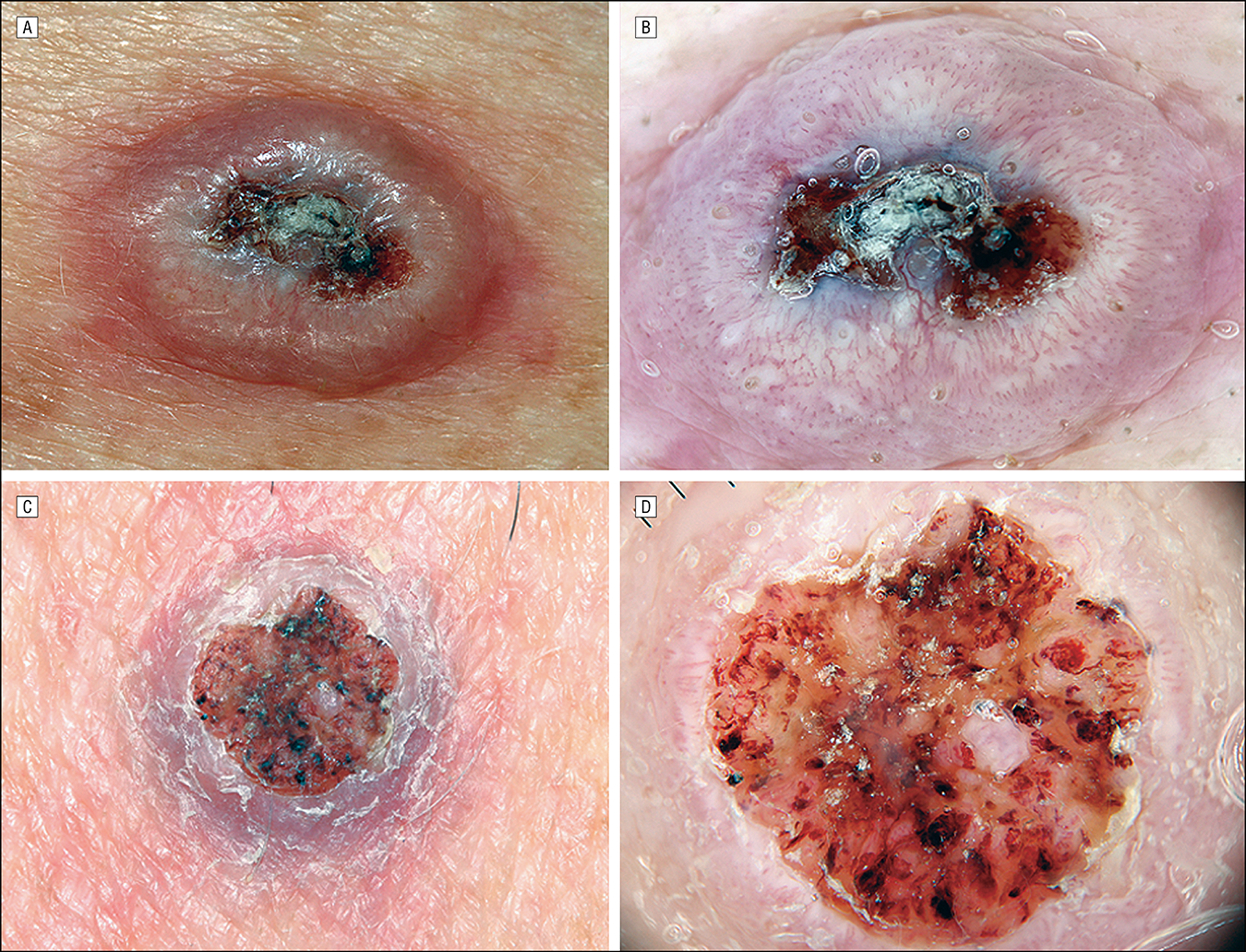
Four of the most typical characteristics of squamous cell carcinoma are shown below. Frequently, two or more of these features are present in one tumour.
| A wart-like growth that crusts and occasionally bleeds. |
| A persistent, scaly red patch with irregular borders that sometimes crusts or bleeds. |
| An open sore that bleeds and crusts and persists for weeks. |
| An elevated growth with a central depression that occasionally bleeds. A growth of this type mayrapidly increase in size. |
If you are concerned that you may have a squamous cell carcinoma it is important that you have it examined by a qualified physician as a matter of urgency. Curaderm is an effective treatment for SCCs in the skin, however in some cases they can metastasise, spreading to nearby lymph nodes or even to the lungs making treatment much more complicated.
Also Check: Late Stage Basal Cell Carcinoma
Potentially Malignant Disorders Transforming Into Oscc
Early detection of cancer is a key factor for improved prognosis and increased patient survival rate. Even though the oral cavity can be easily examined and assessed by direct visual inspection, most OSCC cases are not identified early. This most likely ensues because patients do not seek dental care on a regular basis and most oral cancers in the early stages are asymptomatic. Moreover, dentists may not be aware of the different clinical presentations of OSCC and misdiagnose cancers as reactive or benign lesions. In order to help early discovery and increase the prognosis of cancers, patient awareness about regularly visiting dentists and education of dental practice staff to carefully examine the patients should be raised.
There are many PMDs in the oral cavity that have the predisposition to transform into OSCC, a few of which are discussed below in detail.
Prevention Of Squamous Cell Carcinoma
The American Academy of Dermatology makes the following recommendations to help reduce the chances of developing SCC:
- When possible, wear protective clothing to minimize direct sun exposure to the skin
- Seek shaded areas especially between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m. when the suns ultraviolet radiation is most intense
- Apply a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher on all exposed skin. The sunscreen should be applied liberally and reapplied every 2 hours or more if excessively sweating or swimming.
- Avoid tanning beds
- Perform regular self-skin exams and note any changing moles or other skin lesions.
- Seek medical attention should you discover a new or changing skin growth.
Also Check: Metastatic Basal Cell Carcinoma Survival Rate
Don’t Miss: 3b Melanoma
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Detection Diagnosis And Treatment At The Center For Surgical Dermatology
At the Center for Surgical Dermatology, our exceptional board-certified dermatologists specialize in detecting, diagnosing, and treating squamous cell carcinoma, as well as basal cell carcinoma, melanoma skin cancer, and the precancer, actinic keratosis.
To learn more about how we treat skin cancer and other skin conditions, reach outto our clinic in Westerville, OH!
Center for Surgical Dermatology is the largest medical and surgical skin treatment and wellness facility in Central Ohio. Since 2007, our board-certified dermatologists, fellowship-trained Mohs surgeons, and caring professional staff have provided patients with treatment they can trust in an environment second to none. Learn more about our state-of-the-art Dermatology Center before booking your appointment today.
How Fast Does Squamous Cell Carcinoma Spread
Squamous cell carcinoma rarely metastasizes , and when spreading does occur, it typically happens slowly. Indeed, most squamous cell carcinoma cases are diagnosed before the cancer has progressed beyond the upper layer of skin. There are various types of squamous cell carcinoma and some tend to spread more quickly than others.
Read Also: Stage Iii Melanoma Treatment
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
Given the complexity of care required in the treatment of this condition, an interprofessional healthcare team, including primary clinicians, cardiothoracic surgeons, medical oncologists, radiation oncologists, surgical oncologists, and palliative care, are needed. Strong collaboration and communication within the interprofessional team are vital to improving outcomes.
When Should I Call The Doctor About Squamous Cell Carcinoma
If you have never had skin cancer or if you have had SCC, contact your doctor if:
- You have any skin changes that cause you worry, including a new lump, mole, or sore that does not heal, or changes in a mole or spot you have had for some time.
- You need to schedule your yearly skin check appointment.
- You have any issues related to your treatment for SCC that worry you, such as excessive pain, bleeding or itching.
Dont Miss: Stage 3 Basal Cell Carcinoma Survival Rate
Also Check: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Survival Rate Stage 4
Questions To Ask Your Doctor
- I spent a lot of time in the sun as a child. Am I at higher risk of developing skin cancer?
- One of my parents had skin cancer. Am I more likely to get it?
- What should I look for when I do a self-examination of my skin?
- I have darker skin. Can I still get skin cancer?
- What can I do to protect my child from the sun?
- Is there anything I can do to keep the cancer from coming back after treatment?
Skin Grafting And Reconstructive Surgery
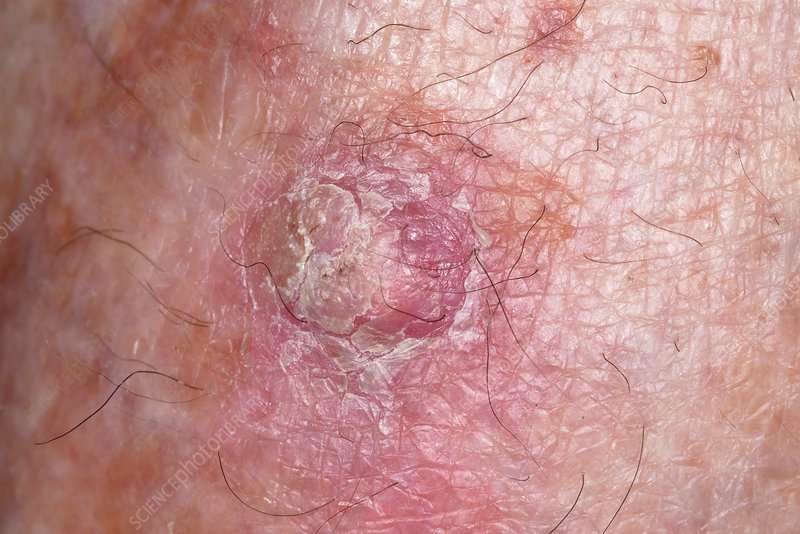
After surgery to remove a large basal or squamous cell skin cancer, it may not be possible to stretch the nearby skin enough to stitch the edges of the wound together. In these cases, healthy skin can be taken from another part of the body and grafted over the wound to help it heal and to restore the appearance of the affected area. Other reconstructive surgical procedures, such as moving flaps of nearby skin over the wound, can also be helpful in some cases.
Dont Miss: What Does Well Differentiated Squamous Cell Carcinoma Mean
You May Like: Well Differentiated Squamous Cell Carcinoma Prognosis
Treating Advanced Squamous Cell Cancers
Lymph node dissection:Removing regional lymph nodes might be recommended for some squamous cell cancers that are very large or have grown deeply into the skin, as well as if the lymph nodes feel enlarged and/or hard. The removed lymph nodes are looked at under a microscope to see if they contain cancer cells. Sometimes, radiation therapy might be recommended after surgery.
Immunotherapy: For advanced squamous cell cancers that cant be cured with surgery or radiation therapy, one option might be using an immunotherapy drug such as cemiplimab or pembrolizumab . However, these drugs havent been studied in people with weakened immune systems, such as people who take medicines for autoimmune diseases or who have had an organ transplant, so the balance between benefits and risks for these people isnt clear.
Systemic chemotherapy and/or targeted therapy:Chemotherapy and targeted therapy drugs might be other options for patients with squamous cell cancer that has spread to lymph nodes or distant organs. These types of treatment might be combined or used separately.
Deterrence And Patient Education
Education on avoiding or mitigating against risk factors such as tobacco products and causes of occupational disease can reduce SCC development. Education about early cancer screening with low dose CT scan of the chest is important for early recognization and treatment to prevent tumor burden. Counseling patients about stages of cancers and the chance of complete cure in case of early detection and counseling on palliative care in advanced stages is very important to reduce stress both for patients and loved ones.
You May Like: Stage 3 Melanoma Survival Rate