Can Melanoma Be Prevented
You can’t control how fair your skin is or whether you have a relative with cancerous moles. But there are things you can do to lower your risk of developing melanoma. The most important is limiting your exposure to the sun.
Take these precautions:
- Avoid the strongest sun of the day between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m.
- Use broad-spectrum sunscreen whenever you’re in the sun.
- Wear a wide-brimmed hat and cover up with long, loose cotton clothing if you burn easily.
- Stay out of the tanning salon. Even one indoor tanning session increases your risk of getting melanoma.
Also, be sure to check your moles often . Keep dated records of each mole’s location, size, shape, and color, and get anything suspicious checked out right away.
Not all skin cancer is melanoma, but every case of melanoma is serious. So now that you know more about it, take responsibility for protecting yourself and do what you can to lower your risk.
You can find more information online at:
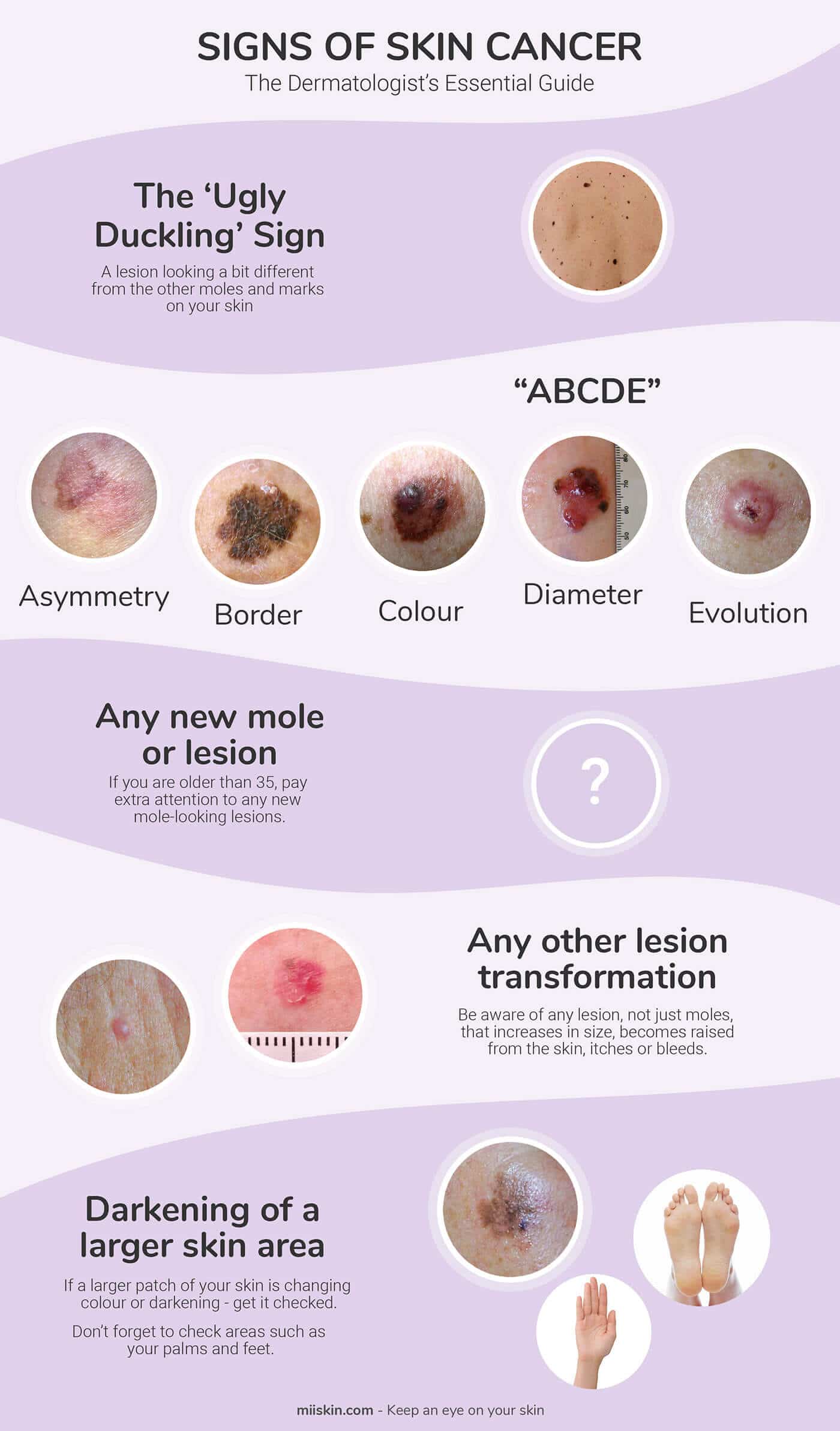
The Most Important And First Warning Sign Of Melanoma Is The Ugly Duckling Sign
The Ugly Duckling sign is one of the most important signs of melanoma. It is based on the concept that a melanoma can look different from the other moles and marks on your skin.
The ugly duckling sign of melanoma is any suspicious spot that looks different from other surrounding moles or marks on your skin .
Remember, critically evaluating your own skin lesions can be difficult. If you are concerned about a mole, you should see your doctor. Patient history is invaluable and can raise an early warning flag. Your doctor will help decide if further action is needed.
Red Flag #: Swollen Lymph Nodes
If melanoma spreads, it often goes to the lymph nodes first, says Melinda L. Yushak, M.D., assistant professor of hematology and medical oncology at Emory University School of Medicine in Atlanta. The cancer cells will first travel to the nodes closest to the original tumor, she says. Lymph nodes are located throughout your entire body, but large clusters are found in the neck, underarms, chest, abdomen, and groin. If the cancer has made its way to the lymph nodes, it usually wont be painful, but theyll feel swollen or even hard to the touch, Dr. Zaba says.
Read Also: What Is Melanoma In The Brain
The Abcde Rule Of Looking For Early Signs Of Melanoma:
- A Asymmetry of lesions
- C Color changes
- D Diameter greater than a pencil eraser 6 mm
- E Evolving lesions
The ABCDE Rule is used by physicians and patients for determining whether a lesion, mole or any other mark or growth on the skin may be suspicious for melanoma or even another type of skin cancer.
When you go through your full-body skin self-exam, use The ABCDE rule and look for lesions that present with one of the following melanoma signs.
Remember, just because a lesion has one of these signs DOES NOT make it a melanoma. These rules are useful in helping you to know what to report to your doctor when concerned about skin cancer.
Images supplied by DermNet NZ.
A Asymmetry of a lesion:
If the two halves of the lesion do not match it can be said to be asymmetric. Keep in mind that most moles that have some degree of asymmetry are not cancerous.
B Border irregularity:
The border is uneven in appearance and shows some irregularity it may seem to be more rugged or notched in the edges.
C Color changes or more than one colour:
Does the lesion present with different colours or shades of brown / black / red? Melanomas can also have areas that are white or blue.
A change in color of a lesion noticed by the patient may also be a potential melanoma sign.
D Diameter of the lesion:
E Evolution or Evolving:
MIISKIN PROMO
What You Can Do
Check yourself: No matter your risk, examine your skin head-to-toe once a month to identify potential skin cancers early. Take note of existing moles or lesions that grow or change. Learn how to check your skin here.
When in doubt, check it out. Because melanoma can be so dangerous once it advances, follow your instincts and visit your doctor if you see a spot that just doesnt seem right.
Keep in mind that while important, monthly self-exams are not enough. See your dermatologist at least once a year for a professional skin exam.
If youve had a melanoma, follow up regularly with your doctor once treatment is complete. Stick to the schedule your doctor recommends so that you will find any recurrence as early as possible.
Reviewed by:
Read Also: Large Cell Carcinoma Definition
How Does Metastatic Melanoma Spread
Melanoma occurs when melanocyte cells found in the epidermis start growing excessively and take over surrounding tissues. These cells can develop from existing moles or skin growths. But, more commonly, they start as new growth. Once melanoma has begun growing in the skin, it can become and spread to new sites through the lymphatic system or blood vessels.
When it has spread beyond the skin, and into the lymph nodes or distant organs. Like the liver, lungs, brain, bone or soft tissues, it is considered metastatic melanoma.
Metastatic melanoma can be treated through surgeries to remove the tumors with:
- chemotherapy
How Is Skin Cancer Of The Head And Neck Diagnosed
Diagnosis is made by clinical exam and a biopsy. Basal cell and squamous cell cancers are staged by size and extent of growth. Basal cell cancers rarely metastasize to lymph nodes, but they can grow quite large and invade local structures. Squamous cell cancers have a much higher incidence of lymph node involvement in the neck and parotid gland and can spread along nerves.
Melanoma is staged, based not on size but on how deeply it invades the skin layers. Therefore, a superficial or shave biopsy will not provide accurate staging information used to guide treatment. Melanomas can have a very unpredictable course and may spread to distant organs. Melanomas with intermediate thickness often require sentinel node biopsy, a surgical procedure performed by a head and neck surgeon, to determine if microscopic spreading to lymph nodes has occurred.
Also Check: How To Identify Basal Cell Carcinoma
Distinguishing Benign Moles From Melanoma
To find melanoma early, when it is most treatable, it is important to examine your skin on a regular basis, and become familiar with moles, and other skin conditions, in order to better identify changes. Certain moles are at a higher risk for changing into malignant melanoma. Large moles that are present at birth , and atypical moles , have a greater chance of becoming malignant.
Recognizing changes in your moles, is crucial in detecting malignant melanoma at its earliest stage. The warning signs are:
Normal mole / melanoma
When To See A Doctor
Many melanomas are dark brown or black and are often described as changing, different, unusual, or ugly looking. However, any skin abnormality that is growing or changing quickly and does not go away, whether colored or not, should be examined by a doctor. Bleeding may be a sign of more advanced melanoma. In addition, the appearance of a new and unusual mole is more likely to be melanoma.
If you are concerned about a new or existing mole, please talk with your family doctor or a dermatologist. Your doctor will ask how long and how often youve been experiencing the symptom, in addition to other questions. This is to help figure out the cause of the problem, called a diagnosis.
The next section in this guide is Diagnosis. It explains what tests may be needed to learn more about the cause of the symptoms. Use the menu to choose a different section to read in this guide.
Also Check: Can You Die From Basal Cell Skin Cancer
The 4 Stages Of Melanoma
Two main things determine the stage of melanoma: The thickness or depth of the tumor and how far it has spread when its diagnosed, explains David Polsky, M.D., dermatologist at NYU Langone Medical Center in New York City. In stages 0, 1, and 2, the melanoma is limited to the skin. In stage 3, its spread to the lymph nodes, small structures throughout your body that help filter fluids and fight infection. In the most advanced stage, stage 4, melanoma cells have broken away from the original tumor, traveled through the body and formed a new tumor somewhere else.
Possible Signs And Symptoms Of Melanoma
The most important warning sign of melanoma is a new spot on the skin or a spot that is changing in size, shape, or color.
Another important sign is a spot that looks different from all of the other spots on your skin .
If you have one of these warning signs, have your skin checked by a doctor.
The ABCDE rule is another guide to the usual signs of melanoma. Be on the lookout and tell your doctor about spots that have any of the following features:
- A is for Asymmetry: One half of a mole or birthmark does not match the other.
- B is for Border:The edges are irregular, ragged, notched, or blurred.
- C is for Color:The color is not the same all over and may include different shades of brown or black, or sometimes with patches of pink, red, white, or blue.
- D is for Diameter:The spot is larger than 6 millimeters across , although melanomas can sometimes be smaller than this.
- E is for Evolving: The mole is changing in size, shape, or color.
Some melanomas dont fit these rules. Its important to tell your doctor about any changes or new spots on the skin, or growths that look different from the rest of your moles.
Other warning signs are:
- A sore that doesnt heal
- Spread of pigment from the border of a spot into surrounding skin
- Redness or a new swelling beyond the border of the mole
- Change in sensation, such as itchiness, tenderness, or pain
- Change in the surface of a mole scaliness, oozing, bleeding, or the appearance of a lump or bump
You May Like: Does Amelanotic Melanoma Blanch When Pressed
How Is Melanoma Treated
Your melanoma treatment will depend on the stage of the melanoma and your general health.
Surgery is usually the main treatment for melanoma. The procedure involves cutting out the cancer and some of the normal skin surrounding it. The amount of healthy skin removed will depend on the size and location of the skin cancer. Typically, surgical excision of melanoma can be performed under local anesthesia in the dermatologist’s office. More advanced cases may require other types of treatment in addition to or instead of surgery.
Treatments for melanoma:
- Melanoma Surgery: In the early stages, surgery has a high probability of being able to cure your melanoma. Usually performed in an office, a dermatologist numbs the skin with a local anesthetic and removes the melanoma and margins .
- Lymphadenectomy: In cases where melanoma has spread, removal of the lymph nodes near the primary diagnosis site may be required. This can prevent the spread to other areas of your body.
- Metastasectomy: Metastasectomy is used to remove small melanoma bits from organs.
- Targeted cancer therapy: In this treatment option, drugs are used to attack specific cancer cells. This targeted approach goes after cancer cells, leaving healthy cells untouched.
- Radiation Therapy: Radiation therapy includes treatments with high-energy rays to attack cancer cells and shrink tumors.
- Immunotherapy: immunotherapy stimulates your own immune system to help fight the cancer.
Signs And Symptoms Of Melanoma Skin Cancer
How melanoma skin cancer looks can vary. Melanoma skin cancer often starts as an abnormal mole anywhere on the skin. A mole is a common non-cancerous growth. It is normally a small, round or oval spot that is usually brown, tan or pink. It may be raised or flat. Most people have a few moles.
A change in the colour, size or shape of a mole is usually the first sign of melanoma skin cancer. These changes can happen in a mole or spot that is already on your skin, or changes can appear as a new mole. Other health conditions can also look like melanoma skin cancer.
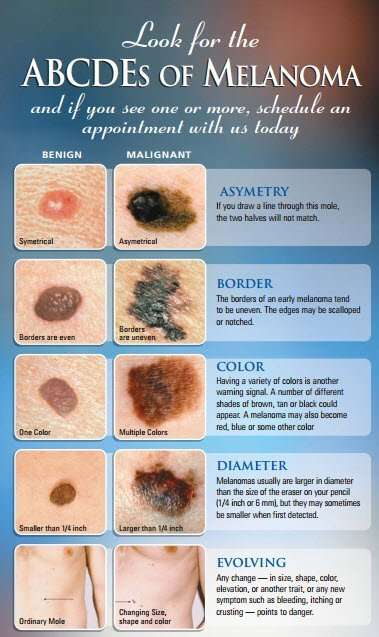
The ABCDE rule below can help you look for the common signs and symptoms of melanoma skin cancer. See your doctor if you have any of these changes on your skin:
A is for asymmetry One-half of a mole does not have the same shape as the other half.
B is for border The edge of a mole is uneven . It can look jagged, notched or blurry. The colour may spread into the area around the mole.
C is for colour The colour of a mole is not the same throughout. It could have shades of tan, brown and black. Sometimes areas of blue, grey, red, pink or white are also seen.
D is for diameter The size of a mole is larger than 6 mm across, which is about the size of a pencil eraser.
E is for evolving There is a change in the colour, size, shape or feel of the mole. The mole may become itchy or you may have a burning or tingling feeling.
Other signs and symptoms of melanoma skin cancer include:
Don’t Miss: Is Melanoma Cancer Curable
Tools That Can Help You Find Melanoma On Your Skin
To help you find melanoma early, the American Academy of Dermatology developed the following:
Melanoma can look different on a childs skin. Taking this short quiz can help you hone your skills at finding childhood melanoma.
ImagesImages 1,3,4,5,6,7,8,10: Images used with permission of the American Academy of Dermatology National Library of Dermatologic Teaching Slides.
Image 2: Developed by the American Academy of Dermatology
Image 9: Used with permission of the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
ReferencesBarnhill RL, Mihm MC, et al. Malignant melanoma. In: Nouri K, et al. Skin Cancer. McGraw Hill Medical, China, 2008: 140-167.
Gloster HM Jr, Neal K. Skin cancer in skin of color. J Am Acad Dermatol 2006 55:741-60.
National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN guidelines for patients: Melanoma. 2018. Last accessed February 12, 2019.
I’ve Been Diagnosed With Melanomawhat Happens Next
Doctors use the TNM system developed by the American Joint Committee on Cancer to begin the staging process. Its a classification based on three key factors:
T stands for the extent of the original tumor, its thickness or how deep it has grown and whether it has ulcerated.
What Is Breslow depth?
Breslow depth is a measurement from the surface of the skin to the deepest component of the melanoma.
Tumor thickness: Known as Breslow thickness or Breslow depth, this is a significant factor in predicting how far a melanoma has advanced. In general, a thinner Breslow depth indicates a smaller chance that the tumor has spread and a better outlook for treatment success. The thicker the melanoma measures, the greater its chance of spreading.
Tumor ulceration: Ulceration is a breakdown of the skin on top of the melanoma. Melanomas with ulceration are more serious because they have a greater risk of spreading, so they are staged higher than tumors without ulceration.
N indicates whether or not the cancer has already spread to nearby lymph nodes. The N category also includes in-transit tumors that have spread beyond the primary tumor toward the local lymph nodes but have not yet reached the lymph nodes.
M represents spread or metastasis to distant lymph nodes or skin sites and organs such as the lungs or brain.
After TNM categories are identified, the overall stage number is assigned. A lower stage number means less progression of the disease.
Don’t Miss: Invasive Ductal Breast Cancer Prognosis
Dermoscopy Of Superficial Melanoma
Superficial melanomas usually have one or more of the following dermoscopic features:
- Blue-white veil
- Multiple colours, especially red and blue
- Broad network
- Negative network
- Irregular vascularity
The blue-white veil is described as an irregular structureless area of confluent blue pigment with a ground glass haze, as if the image were out of focus. It is due to hyperkeratinisation over dense epidermal pigment. Uniform blue-white structures may be observed over some blue naevi and haemangiomas but in melanoma they are focal, asymmetrical and irregular.
Scar-like depigmentation due to regression of melanoma results in irregular white areas that must be distinguished from the uniform peripheral loss of pigment seen in benign halo naevi. It arises in about 50% of melanomas.
Negative network, although a feature of melanoma, may also be found in some benign melanocytic lesions and seborrhoeickeratoses.
Some of the structural features may be subtle in early melanoma, as in several examples shown here. Melanoma may be recognised when there are only 2-3 colours in the lesion on dermoscopy . Deeper melanomas reveal more colours.
Dermoscopic features of melanoma
Not all facial melanoma have these characteristics. In the absence of network, there may be amelanotic areas and irregular blotches.
Facial SSM
Symptoms If Cancer Has Spread To The Brain
You might have any of the following symptoms if your cancer has spread to your brain:
- headaches
- weakness of a part of the body
- fits
- personality changes or mood changes
- eyesight changes
-
J Tobias and D HochhauserJohn Wiley and Sons Ltd
-
TNM Staging ChartsLippincott Williams and Wilkins, 2009
-
Improving supportive and palliative care for adults with cancerNational Institute for Clinical Excellence , 2004
-
Oxford Textbook of Palliative MedicineEds D Doyle and othersOxford Universty Press, 3rd edition 2005
-
Cancer and its Management J Tobias and D HochhauserWiley Blackwell, 2015
Also Check: Can You Die From Basal Cell Skin Cancer
How To Prevent Melanoma
Most skin cancers, including melanoma are preventable. The following protective measures can help prevent skin cancer:
- Avoiding the sun during the hottest part of the day, which is typically 11 AM to 4 PM.
- Applying sunscreen throughout the year. Sunscreens don’t usually filter out all harmful UV radiation, especially radiation that can lead to melanoma but they are essential in providing overall protection from the sun. A broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30 should be used all year around and reapplied as required. Sunscreen is to be applied on all days including winter and cloudy days. It is advised to apply sunscreen over all exposed skin of the body and face, including the lips and ears. Special sunscreen is needed while swimming in the pools and beaches.
- Wearing protective clothing can provide protection against the sun and harmful UV radiation. Sunglasses are essential to protect the eyes and skin around the eyes, such as the eyelids, against UVB radiation.
- Avoid tanning beds because they emit UV rays that cause skin cancer.
- Consuming sun-sensitizing medications such as certain antibiotics or isotretinoin for acne can increase skin sensitivity to sun.
- Self examination of the skin regularly is important for diagnosis and treatment. Any new skin changes or changes in existing skin growths, patches or moles should be reported to a physician as soon as possible