Does Skin Cancer Look Like A Scab
4.6/5doWhat it looks likeskinfull detail here
“Squamous cell cancers, which can metastasize if left untreated, are often reddish marks that will scab, flake off, then scab again,” Bank says. If you draw a line through the middle of a benign mole, the two halves will line up. Cancerous cells don’t grow evenly.
Subsequently, question is, what does early signs of skin cancer look like? Melanoma signs include: A large brownish spot with darker speckles. A mole that changes in color, size or feel or that bleeds. A small lesion with an irregular border and portions that appear red, pink, white, blue or blue-black.
Just so, does skin cancer scab and bleed?
The skin features that frequently develop are listed below. For basal cell carcinoma, 2 or more of the following features may be present: An open sore that bleeds, oozes, or crusts and remains open for several weeks. A reddish, raised patch or irritated area that may crust or itch, but rarely hurts.
What is a scab that won’t heal?
Chronic wounds, by definition, are sores that don’t heal within about three months. They can start small, as a pimple or a scratch. They might scab over again and again, but they don’t get better.
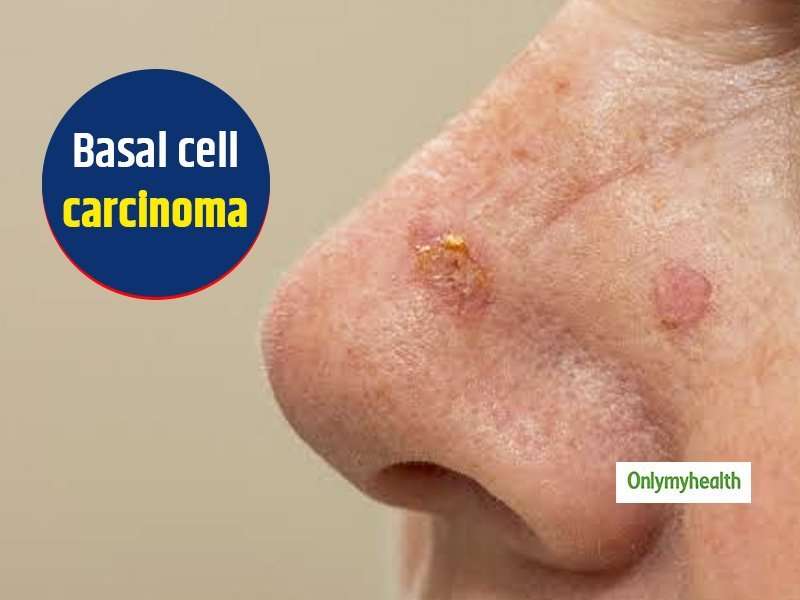
What Does Basal Cell Carcinoma Look Like
Basal cell carcinomalookbasal cell carcinomalikelooks like
People Also Asked, what is a basal cell carcinoma pictures?
Basal cell carcinoma often occurs on the face and neck, where the skin is exposed to sunlight. These tumors are locally invasive and tend to burrow in but not metastasize to distant locations.
Also know, how serious is basal cell skin cancer? The Most Common Skin Cancer BCCs arise from abnormal, uncontrolled growth of basal cells. Because BCCs grow slowly, most are curable and cause minimal damage when caught and treated early. Understanding BCC causes, risk factors and warning signs can help you detect them early, when they are easiest to treat and cure.
Contents
What Happens If Basal Cell Carcinoma Is Left Untreated
Basal cell carcinoma is a very slow growing type of non-melanoma skin cancer. If left untreated, basal cell carcinomas can become quite large, cause disfigurement, and in rare cases, spread to other parts of the body and cause death.
You may ask, What skin cancer looks like when it starts?
Squamous Cell Carcinoma This nonmelanoma skin cancer may appear as a firm red nodule, a scaly growth that bleeds or develops a crust, or a sore that doesnt heal. It most often occurs on the nose, forehead, ears, lower lip, hands, and other sun-exposed areas of the body.
You May Like: What Type Of Skin Cancer Spreads The Fastest
How To Diagnose Skin Cancer
First, a doctor will examine a personâs skin and take their medical history. They will usually ask the person when the mark first appeared, if its appearance has changed, if it is ever painful or itchy, and if it bleeds.
The doctor will also ask about the personâs family history and any other risk factors, such as lifetime sun exposure.
They may also check the rest of the body for other atypical moles and spots. Finally, they may feel the lymph nodes to determine whether or not they are enlarged.
The doctor may then refer a person to a skin doctor, or dermatologist. They may examine the mark with a dermatoscope, which is a handheld magnifying device, and take a small sample of skin, or a biopsy, and send it to a laboratory to check for signs of cancer.
How Skinvision Can Help With Bcc
Taking care of the skin is not just a matter of aesthetics, it is a matter of health. The earlier the skin cancer is detected, the easier it is to treat. Learning about the warning signs on your skin gives you the power to detect cancer early when its easiest to cure.
SkinVision can be used as an important tool in screening skin cancer or tracking changes in suspicious skin spots.
Always check your whole skin and look for new or changing lesions that increase in size, bleed or do not heal.
You May Like: What Are Some Treatments For Melanoma
What You Can Do
If youve already had a BCC, you have an increased chance of developing another, especially in the same sun-damaged area or nearby.
A BCC can recur even when it has been carefully removed the first time, because some cancer cells may remain undetectable after surgery and others can form roots that extend beyond whats visible. BCCs on the nose, ears and lips are more likely to recur, usually within the first two years after surgery.
Heres what you can do to detect a recurrence and safeguard yourself against further skin damage that can lead to cancer:
Reviewed by:
What Does Basal Cell Carcinoma Pictures Look Like
Since not all basal cell carcinomas have the same appearance, these images should serve as a general reference to what they may look like.
Basal cell carcinoma may resemble a slowly growing pink, skin-colored or light brown nodule on the skin, which gradually increases in size. Often a dark crust develops in the middle, which could bleed with a light touch. The tissue of the nodule can also look somewhat glassy, shiny and sometimes shows small blood vessels.
Wounds that do not heal can also be warning signs for skin cancer.
Early detection strategies are crucial for a successful outcome. Knowing your body and the signs and changes to look out for can give you the power to detect squamous cell carcinoma early when its easiest to treat.
You will notice that all these skin cancer pictures are quite different from one another. Note that not all basal cell cancers have the same appearance so these photos should serve as a general reference for what they can look like.
Don’t Miss: What Does Basal Cell Carcinoma Mean
Signs Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
BCC generally starts out in the upper layer of your skin. Thatâs called your epidermis. Hereâs what it may look like:
- A bloody or oozing sore that doesnât go away
- A rough patch of skin, usually in a sun-exposed area
- A reddish area that may hurt or itch
- A shiny bump thatâs clear, reddish, or white
- A flat white, yellow, or âwaxyâ area that looks like a scar
- A colored mole-like bump
BCC tends to grow slower than other kind of cancer, but thatâs not always the case. And if itâs advanced BCC, it can spread much deeper into your tissue. Call your doctor if you see any of these changes in your skin. Ask them about genetic conditions and other risk factors that can raise your chances of advanced BCC.
Tests Or Procedures That Examine The Skin Are Used To Diagnose Basal Cell Carcinoma And Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of The Skin
The following procedures may be used:
- Physical exam and health history: An exam of the body to check general signs of health, including checking for signs of disease, such as lumps or anything else that seems unusual. A history of the patients health habits and past illnesses and treatments will also be taken.
- Skin exam: An exam of the skin for bumps or spots that look abnormal in color, size, shape, or texture.
- Skin biopsy: All or part of the abnormal-looking growth is cut from the skin and viewed under a microscope by a pathologist to check for signs of cancer. There are four main types of skin biopsies:
- Shave biopsy: A sterile razor blade is used to shave-off the abnormal-looking growth.
- Punch biopsy: A special instrument called a punch or a trephine is used to remove a circle of tissue from the abnormal-looking growth. Enlarge Punch biopsy. A hollow, circular scalpel is used to cut into a lesion on the skin. The instrument is turned clockwise and counterclockwise to cut down about 4 millimeters to the layer of fatty tissue below the dermis. A small sample of tissue is removed to be checked under a microscope. Skin thickness is different on different parts of the body.
- Incisional biopsy: A scalpel is used to remove part of a growth.
- Excisional biopsy: A scalpel is used to remove the entire growth.
Also Check: What Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Mohs Microscopically Controlled Surgery
|
Because skin cancer cells often have spread beyond the edges of the visible patch on the skin, doctors sometimes use a special surgical technique to make sure they remove all of the cancer. In this technique, called Mohs microscopically controlled surgery or Mohs micrographic surgery, doctors first remove the visible tumor and then begin cutting away the edges of the wound bit by bit. During surgery, doctors examine pieces of tissue to look for cancer cells. Tissue removal from the area continues until the samples no longer contain cancer cells. This procedure enables doctors to limit the amount of tissue removed and thus is especially useful for cancers near such important sites as the eye. After removing all of the cancer, doctors decide how best to replace the skin that has been cut away. They may bring the edges of the remaining skin together with sutures or use a skin graft or skin flap. Or they may place dressings on top of the wound and let the skin heal on its own. Mohs surgery reduces recurrence rates for skin cancers. This surgery is useful for basal cell and squamous cell cancers but is less often used for melanoma. |
Basal Cell And Squamous Cell Carcinoma
The two most common kinds of skin cancer are basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma, which are sometimes called nonmelanoma skin cancer. These cancers are carcinomas that begin in the cells that cover or line an organ.
Basal cell carcinoma accounts for more than 90 percent of all skin cancers in the United States and is the most common of all cancers. Typically, it is a slow-growing cancer that seldom spreads to other parts of the body.
Squamous cell carcinoma also rarely spreads, but does so more often than basal cell carcinoma. It is important that skin cancers are found and treated early because they can invade and destroy nearby tissue. Organ transplant recipients have a 65-fold higher risk of developing squamous cell carcinoma than others. UCSF Medical Center offers a High Risk Skin Cancer Clinic for those at high risk for non-melanoma skin cancers, such as transplant recipients.
Recommended Reading: What To Do When You Get Skin Cancer
Recommended Reading: What Is Good For Skin Cancer
What Causes Basal Cell Carcinoma
Currently, about 8 in 10 diagnosed skin cancers are basal cell carcinoma. Because basal cell cancer grows slowly, most are curable and cause minimal damage when caught and treated early.
Understanding basal cell carcinoma causes, risk factors and warning signs can help you prevent the disease or detect it early, when it is easiest to treat.
Exposure to UV rays from the sun and indoor tanning is the major cause of basal cell carcinoma and most skin cancers. About 90% of non-melanoma skin cancers are associated with UV radiation.
Symptoms
What Are The Risk Factors For Basal Cell Carcinoma
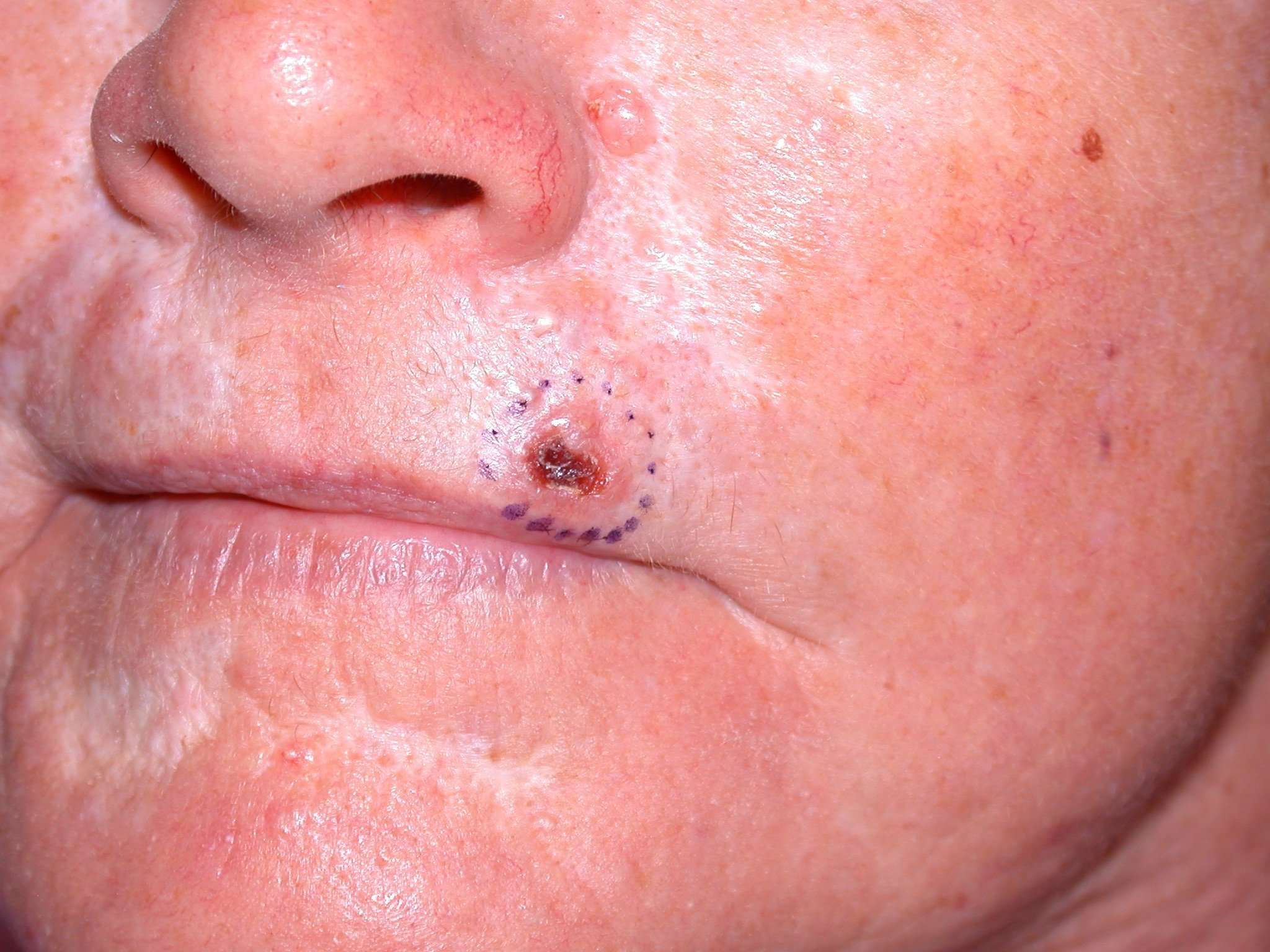
Basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma and melanoma are all skin cancers caused by exposure to damaging ultraviolet raysfrom natural and artificial sunlight. There’s also a genetic condition called basal cell nevus or Gorlin syndrome, which can cause people to develop hundreds of basal cell skin cancers, but it’s extremely rare, says Dr. Christensen.
People at the highest risk for basal cell carcinoma tend to have fair or light-colored skin, a history of sun exposure and a tendency to sunburn quickly. Fair-skinned people have a 50 percent risk of developing basal skin cancer at some point in their lives, Dr. Christensen says. The cancer is the result of cumulative damage of years spent in the sun, and may take 20 years to manifest.
Although it’s often more common in older people, it can occur in younger adults, too.
Basal cell carcinoma spreads very slowly and very rarely will metastasize, Dr. Christensen says. But if it’s not treated, basal cell carcinoma can continue to grow deeper under the skin and cause significant destruction to surrounding tissues. It can even become fatal. For example, an untreated basal cell carcinoma on the face can grow into the bones and, over time, directly into the brain, Dr. Christensen says.
Recommended Reading: Can I Die From Skin Cancer
What Should I Do If I Think I Have A Basal Cell Carcinoma
If you notice a change to or growth on your skin, make an appointment to see your doctor straight away. Your doctor will assess the size, location and look of the growth. They will also ask you how long you have had it, whether it bleeds or itches, etc.
If your doctor thinks the growth may be cancer, they may take a small sample of tissue . The tissue sample will be sent to a laboratory and examined under a microscope. Your doctor will let you know whether the sample showed any cancer cells, and will recommend appropriate treatment if necessary.
Recommended Reading: How Quickly Can Melanoma Metastasis
Pearls And Other Issues
The best treatment of basal cell carcinoma of any type is prevention with adequate protection from ultraviolet light exposure. The American Academy of Dermatology recommends a broad-spectrum sunscreen with a sun protection factor 30 or greater, reapplied every two hours while outdoors. Daily sunscreen should be encouraged to all patients, especially those who spend increased time outside. Many daily facial moisturizers and foundational makeup have SPF sun protection these cosmeceuticals should not replace regular sunscreen application when outside, but rather they should be viewed as an additional layer of protection. Other sun-protective measures include wearing a hat that shades the ears and neck and sunglasses. Tanning bed use should be strongly discouraged, as it greatly increases the risk for all types of skin cancer.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Survival Rate For Renal Cell Carcinoma
What Do I Need To Know
- AKs are evidence of sustained sun damage. Having them raises your lifetime risk for skin cancer. Since having one AK means that its likely you have already developed more, this may translate into an especially elevated risk for developing an SCC.
- An untreated SCC can become invasive and even life-threatening.
The Early Stages Of Skin Cancer
Some forms of cancer, especially melanoma, may appear suddenly and without warning. Most people become alarmed only when they develop a crust or sore that refuses to heal. Did you know that the early stages of cancer do not always look or feel so bad? Harmless-looking moles, skin lesions, or unusual skin growths may also be the signs of early stages.
Regular skin examination can help you spot these early clues. If you see anything suspicious or observe unusual appearances in your skin, we can help you get the right diagnosis and treatment immediately. Some forms of cancer in the skin can be life-threatening and spread without being given urgent attention.
Read Also: How Many Forms Of Skin Cancer Are There
Spotting Other Types Of Skin Cancer
While the big three are the most common types of skin cancer, theyre not the only ones you should be aware of.
Merkel Cell Carcinoma
After the big three, the next skin cancer you think about is Merkel cell carcinoma,Doris Day, a board-certified dermatologist in New York City and a spokesperson for the Skin Cancer Foundation, tells Allure. While its pretty uncommon about 40 times rarer than melanoma Day says its deadlier. Merkel cell carcinoma kills one in three patients , according to the Skin Cancer Foundation.
This type of cancer is incredibly hard to spot, which explains why its so deadly. Merkel cell can be tricky to diagnose because it doesnt always present the same way it can look like a cyst or just a little red bump, and it can occur anywhere on the body, says Day. This is one of the reasons why its super important to see a board-certified dermatologist for skin checks.
Merkel cell carcinomas typically dont occur in people under 50, but recent data suggests that could change. As we previously reported, rates of Merkel cell are estimated to be rising six times faster than other types of skin cancer something seriously concerning to dermatologists, given how aggressive this type of cancer can be. If a Merkel cell is not treated, its certainly deadlier than a melanoma, says McNeill.
Other Cancers
For these types of skin issues, a dermatologist would refer you to a specialist in treating that specific cancer.
Whats The Outlook For Stage 4 Melanoma
Once the cancer spreads, locating and treating the cancerous cells becomes more and more difficult. You and your doctor can develop a plan that balances your needs. The treatment should make you comfortable, but it should also seek to remove or slow cancer growth. The expected rate for deaths related to melanoma is 10,130 people per year. The outlook for stage 4 melanoma depends on how the cancer has spread. Its usually better if the cancer has only spread to distant parts of the skin and lymph nodes instead of other organs.
Also Check: What Are The Early Stages Of Skin Cancer
Mohs Micrographically Controlled Excision
Mohs micrographically controlled surgery involves examining carefully marked excised tissue under the microscope, layer by layer, to ensure complete excision.
- Very high cure rates achieved by trained Mohs surgeons
- Used in high-risk areas of the face around eyes, lips and nose
- Suitable for ill-defined, morphoeic, infiltrative and recurrent subtypes
- Large defects are repaired by flap or skin graft
Basal Cell And Squamous Cell Carcinomasigns And Symptoms
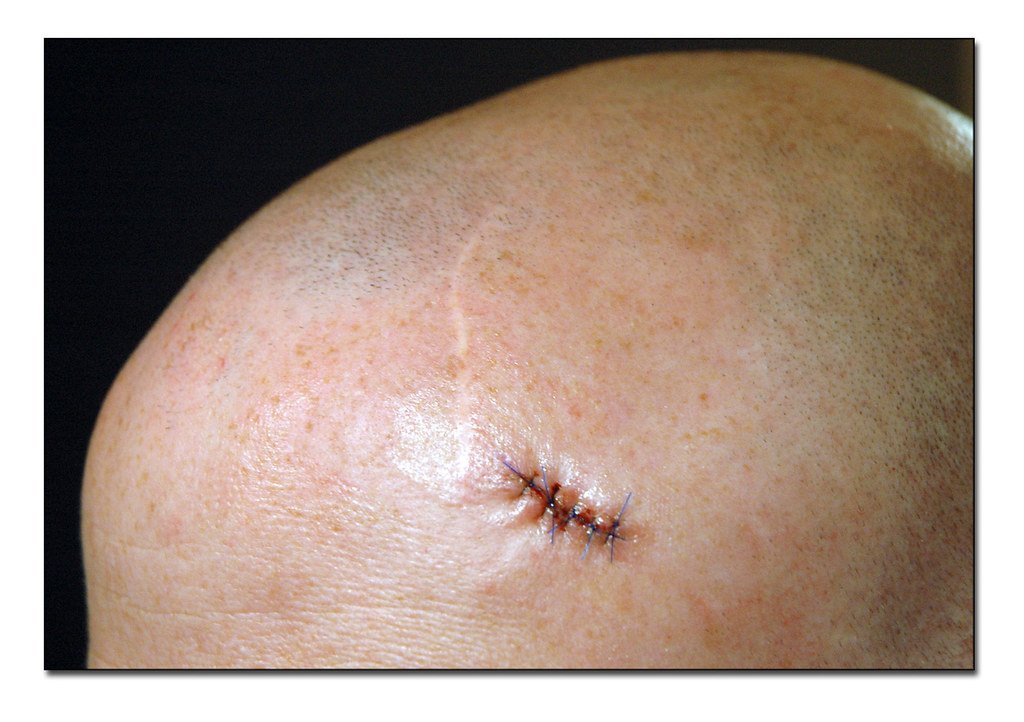
The most common warning sign of skin cancer is a change on the skin, especially a new growth or a sore that doesn’t heal. The cancer may start as a small, smooth, shiny, pale or waxy lump. It also may appear as a firm red lump. Sometimes, the lump bleeds or develops a crust.
Both basal and squamous cell cancers are found mainly on areas of the skin that are exposed to the sun the head, face, neck, hands and arms. But skin cancer can occur anywhere.
An early warning sign of skin cancer is the development of an actinic keratosis, a precancerous skin lesion caused by chronic sun exposure. These lesions are typically pink or red in color and rough or scaly to the touch. They occur on sun-exposed areas of the skin such as the face, scalp, ears, backs of hands or forearms.
Actinic keratoses may start as small, red, flat spots but grow larger and become scaly or thick, if untreated. Sometimes they’re easier to feel than to see. There may be multiple lesions next to each other.
Early treatment of actinic keratoses may prevent them from developing into cancer. These precancerous lesions affect more than 10 million Americans. People with one actinic keratosis usually develop more. Up to 1 percent of these lesions can develop into a squamous cell cancer.
Basal cell carcinoma is the most commonly diagnosed skin cancer. In recent years, there has been an upturn in the diagnoses among young women and the rise is blamed on sunbathing and tanning salons.
- Raised, dull-red skin lesion
Read Also: Where Does Skin Cancer Metastasis To