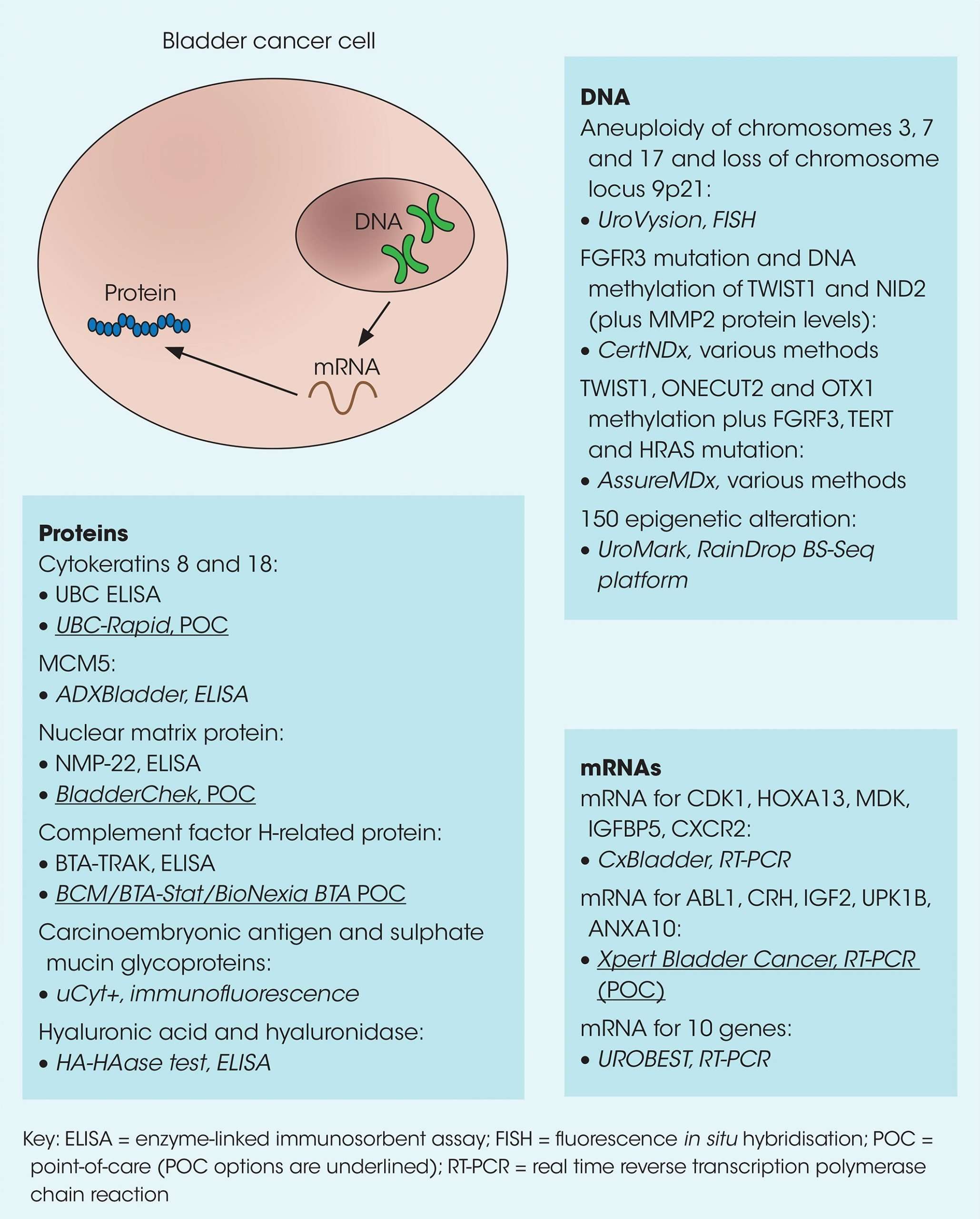
How Do I Check Myself For Melanoma
The first symptom of a melanoma is usually the appearance of a new spot, or a change in an existing freckle or mole. The change may be in size, shape or colour and is normally noticed over several weeks or months.
The ABCDE guidelines provide a useful way to monitor your skin and detect the early signs of melanoma. Please note that this is just a guide and melanoma may present with different characteristics. This is why regular skin checks from a professional are so important.
Please seek expert advice if you notice any of the following:
First Melanoma Test To Offer Reassurance Of Low Risk Of Cancer Spread
New test developed as mechanism of skin cancer growth understood
Newcastle University
image: Scientists at work in AMLo Biosciences lab to predict the spread or return of a melanomaview more
A pioneering test which reliably predicts the spread or return of the most deadly form of skin cancer has been developed by a team of Newcastle scientists and clinicians.
The technological advance came as they made a scientific breakthrough in understanding the mechanism of skin cancer growth.
Led by Professor Penny Lovat at Newcastle University, UK, in association with the University spin out company AMLo Biosciences, the test offers reassurance for patients diagnosed with an early stage melanoma.
With the support of the National Institute for Health Research to develop the provision and working with AMLo Biosciences, a referral service is now available where sections from a patients melanoma can be posted to a lab for analysis.The test identifies a patients true risk of disease progression and provides anyone diagnosed with a non-ulcerated early stage melanoma – accounting for around 75% of all new diagnoses – more accurate information about the risk of the disease spreading.Now the scientists have demonstrated the mechanism in the skin which underpins the test, publishing the research in the British Journal of Dermatology.
Melanoma growth
For further information and to obtain a test see the AMLo Biosciences referrals page.
Journal
Surgical Lymph Node Biopsy
This procedure can be used to remove an enlarged lymph node through a small incision in the skin. A local anesthetic is generally used if the lymph node is just under the skin, but the person may need to be sedated or even asleep if the lymph node is deeper in the body.
This type of biopsy is often done if a lymph nodes size suggests the melanoma has spread there but an FNA biopsy of the node wasnt done or didnt find any melanoma cells.
You May Like: How Fast Does Squamous Cell Carcinoma Spread
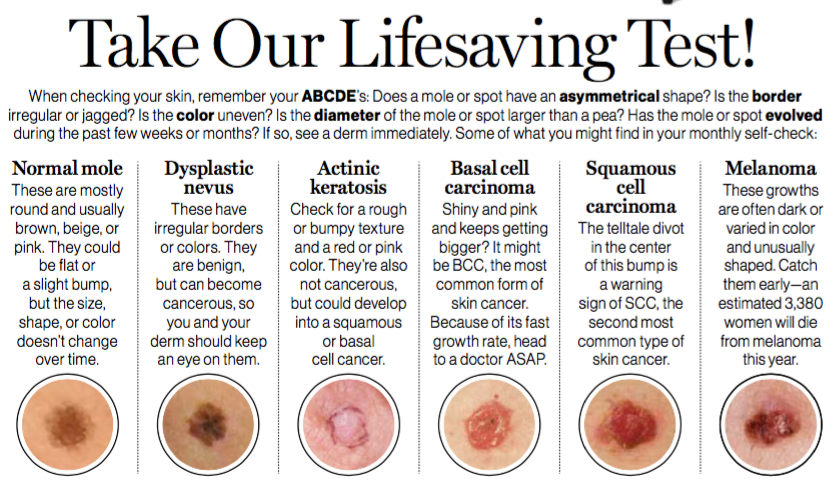
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Melanoma
There are often no symptoms of melanoma you wont feel anything. But there are signs.
One sign is a growing or changing mole, or something that looks like a mole, like a red spot or a pink bump. Generally I tell patients to look for an ugly duckling something on their body that doesnt look like anything else on their body, or something that stands out as a little different. Thats why its important to check your skin regularly so you get to know what your moles look like and if they are changing.
The Canadian Cancer Society recommends using the ABCDE approach to looking at your skin moles:
- A is for asymmetry. One-half of a mole does not have the same shape as the other half.
- B is for border. The edge of a mole is uneven . It can look jagged, notched or blurry. The colour may spread into the area around the mole.
- C is for colour. The colour of a mole is not the same throughout. It could have shades of tan, brown and black. Sometimes areas of blue, grey, red, pink or white are also seen.
- D is for diameter. The size of a mole is larger than 6 mm across, which is about the size of a pencil eraser.
- E is for evolving. There is a change in the colour, size, shape or feel of the mole. The mole may become itchy or you may have a burning or tingling feeling.
If any of your moles concern you, talk to your doctor.
People At Higher Risk Of Melanoma
Some people have a higher than normal risk of developing melanoma. This includes people who have:
- had a melanoma in the past
- a family history of melanoma
- many moles
- had an organ transplant
If you have any of these, your doctor can refer you to a skin specialist who can show you how to check your skin each month for abnormal moles.
Some people have a much higher than normal risk of melanoma and should have regular checks by a skin cancer specialist. This includes people who:
- have 2 family members with melanoma and also have a lot of large, irregularly shaped moles
- were born with a very large mole
- have 3 or more people in their family diagnosed with melanoma or pancreatic cancer
- have had more than 1 melanoma
Your skin cancer specialist or nurse can examine your skin. They are trained to look out for moles that may be starting to become cancerous. If you have any moles that could be a melanoma, they can remove them at the clinic. By removing suspicious moles early, they can prevent an invasive melanoma developing.
-
Revised guidelines for the management of cutaneous melanoma 2010JR Marsden and others
Read Also: What Does Melanoma In Situ Look Like
What Do We Mean By Stage Of Melanoma And Why Is It Important To Know
The stage of melanoma in the body is about how far advanced it is. This is important because:
-
Melanoma stages are determined by the thickness, depth and spread in the body. How far advanced the melanoma is when diagnosed influences a persons outcome.
-
For people who are treated early, when melanoma affects only the superficial layers of the skin, the prognosis is excellent and the disease is often curable. If the cancer spreads to other parts of the body it can be harder to treat.
StagesStage 0 – abnormal cells found in the epidermis. Stage 1 – the melanoma is not more than 2mm thickStage 2 – more than 2 to 4mm thick with no spread to the lymph vessels or lymph nodesStage 3 – any thickness that has spread to lymph vessels or lymph nodesStage 4 – the melanoma has spread to other parts of the body
What Are The Signs Of Melanoma
Knowing how to spot melanoma is important because early melanomas are highly treatable. Melanoma can appear as moles, scaly patches, open sores or raised bumps.
Use the American Academy of Dermatology’s “ABCDE” memory device to learn the warning signs that a spot on your skin may be melanoma:
- Asymmetry: One half does not match the other half.
- Border: The edges are not smooth.
- Color: The color is mottled and uneven, with shades of brown, black, gray, red or white.
- Diameter: The spot is greater than the tip of a pencil eraser .
- Evolving: The spot is new or changing in size, shape or color.
Some melanomas don’t fit the ABCDE rule, so tell your doctor about any sores that won’t go away, unusual bumps or rashes or changes in your skin or in any existing moles.
Another tool to recognize melanoma is the ugly duckling sign. If one of your moles looks different from the others, its the ugly duckling and should be seen by a dermatologist.
Don’t Miss: Invasive Ductal Breast Cancer Prognosis
What Is My Skin Type
Skin types that are more sensitive to ultraviolet radiation burn more quickly and are at a greater risk of skin cancer.
All skin types can be damaged by too much UV radiation. Skin types that are more sensitive to UV radiation burn more quickly and are at a greater risk of skin cancer.
People with naturally very dark skin still need to take care in the sun even though they may rarely, if ever, get sunburnt. The larger amount of melanin in very dark skin provides natural protection from UV radiation. This means the risk of skin cancer is lower.
Eye damage can occur regardless of skin type. High levels of UV radiation have also been linked to harmful effects on the immune system.
Vitamin D deficiency may be a greater health concern for people with naturally very dark skin, as it is more difficult for people with this skin type to make vitamin D.
Lymph Node Dissection Or Completion Lymphadenectomy
An operation to remove the remaining lymph nodes in the group is known as a completion lymph node dissection or completion lymphadenectomy. Again, you should discuss the pros and cons of the procedure with your surgeon.
Other tests you may have include:
Cancer Research UK has more information about test to diagnose melanoma and tests to stage melanoma.
Don’t Miss: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Grade 2 Survival Rate
The Ldh Test For Melanoma And Detection Of Metastasis
Rony Kampalath, MD, is a board-certified diagnostic radiologist specializing in imaging of the abdomen.
LDH is a blood test that measures the amount of lactate dehydrogenase , an enzyme, in your blood. Chemically, LDH works to convert pyruvate to lactate in your body. You may be familiar with lactate, as it is what accumulates in your body after a heavy workout and makes you feel sore.
Verywell / Brianna Gilmartin
Genomic Testing For Advanced Melanoma
Genomic testing is also called tumor sequencing or molecular profiling. It involves looking at the cells obtained from the melanoma to see if there are any genetic mutations that could be linked to the type of cancer.
For people with advanced disease, our experts use a testing approach called MSK-IMPACT. This test, developed by MSK experts, screens for mutations in more than 450 genes at once.
Based on which mutations we find, we may be able to recommend a targeted therapy that has been approved for the specific changes in the tumor. Some MSK patients may be able to join a melanoma clinical trial testing a new drug therapy.
Genetic information about the tumor can also help us predict the chances that the cancer will return after treatment and avoid treatments that wont work.
Almost all of these genetic changes are found only in cancer cells, not in normal cells, which means they cannot be passed on to your children.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Prognosis For Skin Cancer
Prognosis For Melanoma On The Nail
Like other forms of melanoma, subungual melanoma can metastasize to other parts of the body if left untreated.3,4 Because it can be difficult to see and is often mistaken for a bruise or other nail problem, this condition often goes undetected. However, checking your nails and showing any changes to your healthcare provider can help reduce your chances of an undetected subungual melanoma.
Can Blood Tests Or Scans Detect Skin Cancer
Currently, blood tests and imaging scans like MRI or PET are not used as screening tests for skin cancer. However, some national studies are underway to determine if concentrations of skin cancer DNA can be detected by blood tests. Occasionally, imaging detects signs of advanced disease. Sometimes, skin cancer that has spread to internal organs is detected incidentally when a patient is undergoing an imaging study such as MRI or PET scan for unrelated conditions.
Recommended Reading: Melanoma Bone Cancer Symptoms
New Melanoma Test To Offer The Reassurance Of Low Risk Of Cancer Spread
| Font : A-A+ |
A pioneering test that reliably predicts the spread or return of the deadliest form of skin cancer has been developed by a team of Newcastle scientists and clinicians.Led by Professor Penny Lovat at Newcastle University, UK, in association with the University spin-out company AMLo Biosciences, the test offers reassurance for patients diagnosed with early-stage melanoma.
British Journal of DermatologyMelanoma is increasing worldwide and every year more than 16,000 people in the UK and 96,000 people in the US are diagnosed with cancerThis test will aid clinicians to identify genuinely low-risk patients diagnosed with early-stage melanoma and to reduce the number of follow up appointments for those identified as low risk, saving NHS time and money
Biopsy For Melanoma That Has Spread
Your doctor may remove the suspicious growth, or a piece of it, for examination by a laboratory, where the pathologist will inspect the sample for cancerous cells.
Various biopsy methods are used in diagnosing skin cancers.
Melanoma biopsies can be excisional or incisional. An excisional biopsy takes off the entire lesion along with a small margin of normal skin around it, while an incisional biopsy removes only part of a suspicious lesion.
Skin biopsy: If your dermatologist notices a suspicious-looking mole, a skin biopsy is usually warranted. Your doctor will remove as much of the suspicious area as possible and send it to a lab for analysis. Its worth noting this procedure can leave a scar.
Shave biopsy: A shave biopsy involves removing or shaving off the top layers of the skin with a small blade. Because this type of biopsy doesnt remove deep layers of tissue, its an option when your melanoma risk is thought to be low. You may experience bleeding after a shave biopsy. Your doctor may control it with a special ointment or a small electrical current that cauterizes the wound.
Optical biopsies: Newer types of virtual biopsies can be done without needles, using a 3D imaging technique, called reflectance confocal microscopy, to capture images of suspicious lesions. This technology is both painless and non-invasive.
Recommended Reading: Well Differentiated
How Do Doctors Diagnose The Stage Of Melanoma
Doctors will recommend a number of testing methods to determine the existence and spread of the melanoma. Examples of these methods include:
- Physical exam. Melanoma can grow anywhere on the body. This is why doctors often recommend thorough skin checks, including on the scalp and in between the toes. A doctor may also ask about any recent changes in the skin or in existing moles.
- CT scan. Also called a CAT scan, a CT scan can create images of the body to identify potential signs of tumor and tumor spread.
- Magnetic resonance imaging scan. This scan uses magnetic energy and radio waves to generate images. A doctor can administer a radioactive material known as gadolinium that highlights cancer cells.
- Positron emission tomography scan. This is another imaging study type thattests for where the body is using glucose for energy. Because tumors consume glucose more significantly, they will often show up as bright spots on the imaging.
- Blood testing. People with melanoma may have higher-than-normal levels of the enzyme lactate dehydrogenase .
- Biopsy. A doctor may take a sample of a potentially cancerous lesion as well as nearby lymph nodes.
Doctors will consider the results of each of these tests when determining cancer stage.
What Should I Look For When Checking My Skin
Look for any new moles or changes in your skin, especially any of the following:
- A new lump, growth or spot
- A change in size, shape, and/or color of an existing mole, lump or growth
- A sore that doesnt heal
- A red or brown patch thats rough and scaly
- A pink pearly bump that bleeds easily
- Any mole or spot that is asymmetrical, or has an irregular border or uneven color
- Any mole or spot larger than ¼ of an inch
Recommended Reading: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Stage 3 Survival Rate
How Common Is Melanoma
Melanoma accounts for only about 1% of all skin cancers, but causes the great majority of skin cancer-related deaths. Its one of the most common cancers in young people under 30, especially in young women.
Melanoma incidence has dramatically increased over the past 30 years. Its widely accepted that increasing levels of ultraviolet exposure are one of the main reasons for this rapid rise in the number of melanoma cases.
Does The Ottawa Hospital Research And Treat Melanoma
Dr. Jennifer Beecker
Yes! The Ottawa Hospitals Cancer Program treats people who have been diagnosed with melanoma and many other types of cancer, and is among the most advanced cancer programs in Canada. From prevention and assessment to treatment, psychosocial support and follow-up, patients receive a full range of compassionate, world-class care. Our hospital also conducts world-leading cancer research and offers experimental therapies through clinical trials.
Read the inspiring story of Dan Collins, who was diagnosed with stage 4 melanoma at 62 and received immunotherapy treatment at The Ottawa Hospital. Or read the story of economics professor Dr. David Gray, who took part in a clinical trial to see whether an immunotherapy drug could keep his high-risk skin cancer from coming back. Taking part in these trials not only helped these individuals, but will also help future melanoma patients treated both at The Ottawa Hospital and around the world.
Dr. Jennifer Beecker is a dermatologist, clinical researcher and Director of Research for the Division of Dermatology at The Ottawa Hospital. She is also President-Elect of the Canadian Dermatology Association, and has been featured in The Globe & Mail, The Toronto Star, Todays Parent, Chatelaine, and others.
Read Also: How Long Does It Take For Melanoma To Metastasize
The Abcdes Of Melanoma
The first five letters of the alphabet are a guide to help you recognize the warning signs of melanoma.
A is for Asymmetry. Most melanomas are asymmetrical. If you draw a line through the middle of the lesion, the two halves dont match, so it looks different from a round to oval and symmetrical common mole.
B is for Border. Melanoma borders tend to be uneven and may have scalloped or notched edges, while common moles tend to have smoother, more even borders.
C is for Color. Multiple colors are a warning sign. While benign moles are usually a single shade of brown, a melanoma may have different shades of brown, tan or black. As it grows, the colors red, white or blue may also appear.
D is for Diameter or Dark. While its ideal to detect a melanoma when it is small, its a warning sign if a lesion is the size of a pencil eraser or larger. Some experts say it is also important to look for any lesion, no matter what size, that is darker than others. Rare, amelanotic melanomas are colorless.
E is for Evolving. Any change in size, shape, color or elevation of a spot on your skin, or any new symptom in it, such as bleeding, itching or crusting, may be a warning sign of melanoma.
If you notice these warning signs, or anything NEW, CHANGING or UNUSUAL on your skin see a dermatologist promptly.
A is for Asymmetry
D is for Diameter or Dark
E is for Evolving
E is for Evolving