What Does Aflac Pay You For
Accident Emergency Treatment Benefit Aflac will pay $120 for the insured and the spouse, and $70 for children if a covered person receives treatment for injuries sustained in a covered accident. If the covered person is admitted directly to an intensive care unit, Aflac will pay $2,000.
You may ask, How much does Aflac pay for broken bone?
ACCIDENT SPECIFIC-SUM INJURIES BENEFITS: When a Covered Person receives treatment under the care of a Physician for Injuries sustained in a covered accident, Aflac will pay specified benefits ranging from $35 $12,500 for dislocations, burns, skin grafts, eye injuries, lacerations, fractures, concussion, emergency
What Can I Do To Reduce My Risk Of Skin Cancer
Protection from ultraviolet radiation is important all year, not just during the summer.
Most skin cancers are caused by too much exposure to ultraviolet rays. UV rays come from the sun, tanning beds, and sunlamps. UV rays can damage skin cells.
To lower your risk of getting skin cancer, you can protect your skin from UV rays from the sun and from artificial sources like tanning beds and sunlamps.
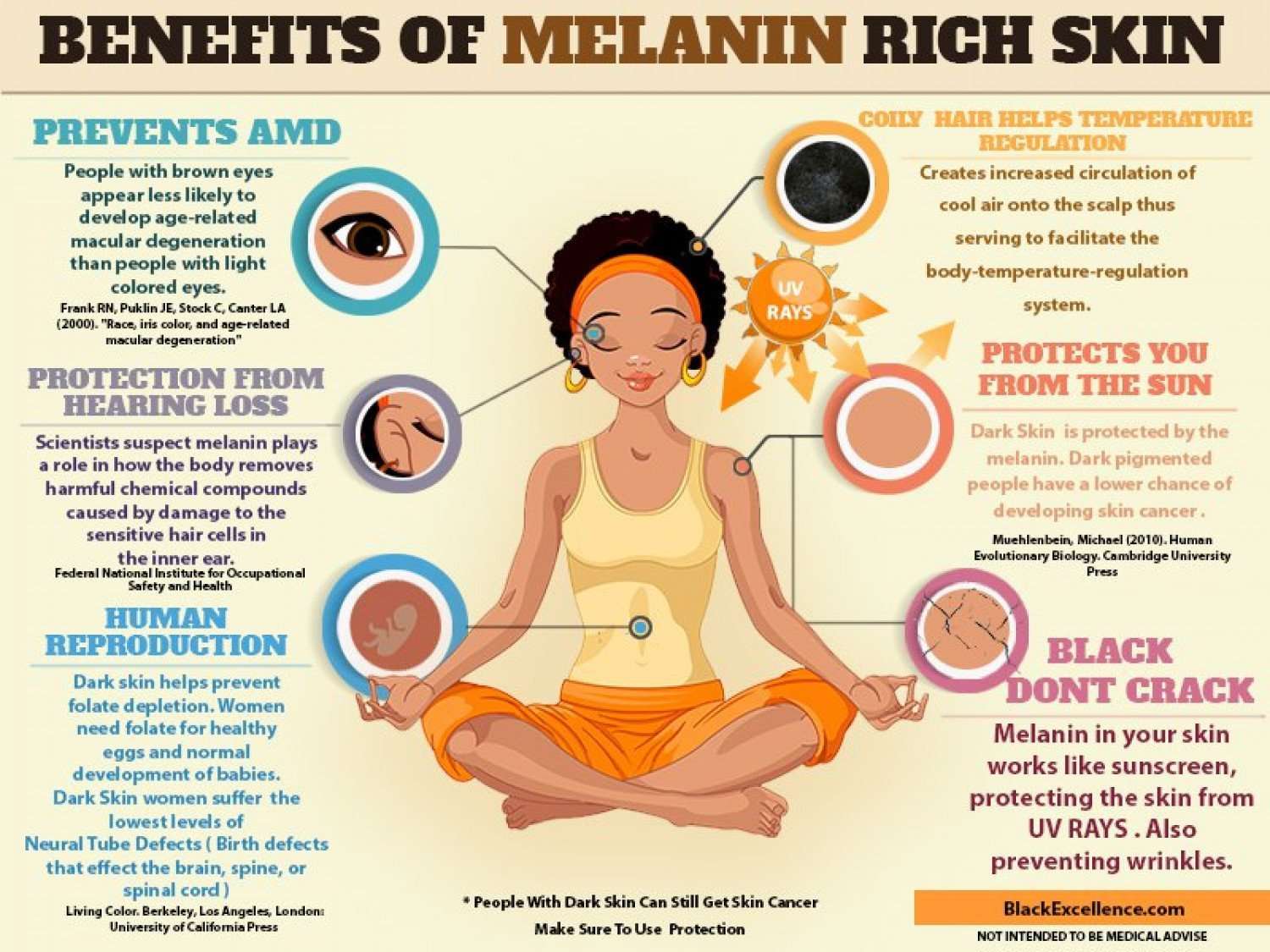
Do We All Have The Same Amount Of Melanin
Despite the many variations in human skin, hair, and eye color, almost all human beings have roughly the same number of melanocytes.
However, people with dark skin tones have melanosomes that are higher in number, larger in size, and more pigmented than those with light skin tones.
Interestingly, these melanosomes also seem to display specific distribution patterns based on skin color. These differences all contribute to the wide variety of skin colors and tones in human beings.
Don’t Miss: Treatment For Stage 3 Melanoma
How Melanin Can Hurt Us
Researchers say UV radiation generates reactive oxygen and nitrogen that energizes an electron in melanin.
That energy can cause DNA lesions, which can lead to cancer-causing mutations. The lesions typically appear less than one second after UV radiation exposure.
The researchers noted, however, that particular damage can also take place more than three hours after exposure to UVA radiation, which comes from the sun and from tanning beds.
You have two opposing things happening at the same time: Melanin protecting you and melanin damaging you, explained Dr. Doug E. Brash, a skin cancer researcher at the Yale School of Medicine. Youve got this race going on between melanin blocking and protecting you.
Brash said it is a simultaneous event melanin protects us at the same time sunlight is trying to damage our cells.
A consequence of these events is that melanin may be carcinogenic as well as protective against cancer, the new report stated.
We didnt see this coming, Brash added.
Wear Sunscreen Every Day
Yep, thats every single dayeven if its cloudy out. Choose a broad spectrum sunscreen that protects against both types of ultraviolet radiation, UVA and UVB, that comes from the sun, Dr. Dilworth recommends. Make sure it is water resistant and has a sun protection factor of 30 or higher. Other sunscreens may help keep you from getting sunburned, but they wont protect against skin cancer. The picks below are all melanin-friendly:
Recommended Reading: What Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of The Head And Neck
Sunlight Continues To Damage Skin In The Dark
Much of the damage that ultraviolet radiation does to skin occurs hours after sun exposure, a team of Yale-led researchers concluded in a study that was published online Feb. 19 by the journal Science.
Exposure to UV light from the sun or from tanning beds can damage the DNA in melanocytes, the cells that make the melanin that gives skin its color. This damage is a major cause of skin cancer, the most common form of cancer in the United States. In the past, experts believed that melanin protected the skin by blocking harmful UV light. But there was also evidence from studies suggesting that melanin was associated with skin cell damage.
In the current study, Douglas E. Brash, clinical professor of therapeutic radiology and dermatology at Yale School of Medicine and his co-authors first exposed mouse and human melanocyte cells to radiation from a UV lamp. The radiation caused a type of DNA damage known as a cyclobutane dimer , in which two DNA letters attach and bend the DNA, preventing the information it contains from being read correctly. To the researchers surprise, the melanocytes not only generated CPDs immediately but continued to do so hours after UV exposure ended. Cells without melanin generated CPDs only during the UV exposure.
The study was supported in part by Department of Defense CDMRP grants CA093473P1 and CA093473 , and NIH grant 2 P50 CA121974 .
Does Any One Have Aflac
| May 08, 2012 7:09 pm
I have Aflac. I actually have several of their policies. Thank goodness I got the cancer policy, I think.. Does anyone else have it & is it what I think it is? I am so overwhelmed with all the insurance lingo along with the medical lingo that my brain is mush! Just wanting to know if it helped anyone else. Thanks |
Read Also: Lobular Carcinoma Survival Rate
More Confusion About Niacinamide And Skin Cancer
Then something ELSE confusing popped up. It was a product called Tru Niagen that makes itself sound like the fountain of youth. This kind of thing makes me suspicious. I first got niacinamide for my skin cancer at my local Whole Foods. When I ran out, I checked it out on Amazon, and there are so many manufacturers I wasnt sure which one to get.
Vitamin D Benefits And Facts
Avoiding the sun can leave you without enough vitamin D. Sunlight triggers vitamin D production in your skin cells.
This vitamin is important for everyone but might be more important when you have vitiligo. So, while you want to protect your skin, its not good to avoid all sun exposure.
Vitamin D may help reduce autoimmune activity. Its also linked to the creation of melanin in your skin.
| Recommended Daily Allowance of Vitamin D |
|---|
| AGE |
Read Also: Basaloid Tumor
Neovax Remembers How To Kill Cancer
After four years, all eight patients on NeoVax were still alive and six showed no signs of the disease.
When study authors analyzed the groups T cells, they uncovered evidence that the cells not only remembered their initial target epitopes, but also recognized other melanoma epitopes. Two of the patients, whose cancers had spread to their lungs, also received an immune checkpoint inhibitor. This drug loosens some of the restraints the immune response has when fighting cancer.
With those two patients, researchers found signs that their T cells had made their way into the tumor tissue. This is where the cancer-fighters can be most lethal to melanoma cells.
We found evidence of everything we look for in a strong, sustained immune response, study co-leader Dr. Patrick Ott reports. T cells continued to specifically target melanoma cells and retained a memory of the epitopes they initially responded to. The T cells were activated to kill tumor cells and, critically, had diversified to target melanoma epitopes not included in the original vaccine.
The long-term persistence and expansion of the melanoma-targeting T cells is a strong indication that personal neoantigen peptide vaccines can help control metastatic tumors, particularly when combined with immune checkpoint inhibition, Ott adds.
The findings appear in the journal Nature Medicine.
SWNS writer Stephen Beech contributed to this report.
Myth: Skin Cancer Looks The Same In All Skin Types
Fact: Skin cancer symptoms differ depending on the type of cancer and skin color. Not sure what to look for? These are the three most common types of skin cancer in people of color.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Squamous cell carcinoma is the most common cancer in darker skin. Two things can cause it: Sun exposure and the human papillomavirus . If you have a compromised immune system, youre at greater risk for both UV radiation and HPV-induced skin cancers.
In pale skin, we tend to see this in chronically sun-exposed areas like the back of the arms, top of the hands, the tops of the ears or on a mans bald scalp, says Guffey.
Darker skin can get squamous cell in these places as well. But youre most likely to see it:
- In the genital area or another site not typically exposed to the sun
- In an area with chronic scarring due to a condition like lupus
Squamous cell carcinoma symptoms include:
- A painful or tender bump
- A growing warty lesion in the genital area
- A sore that fails to heal
- Thick scaly patches that crust or bleed
Basal Cell Carcinoma
Basal cell carcinoma looks basically the same in all skin colors. The signs of basal cell in darker skin include a non-painful bump that:
- Is translucent in appearance
- Bleeds easily
- Has flecks or globules of pigment, like a dark marble suspended in gelatin
Most of the cases of basal cell carcinoma in pigmented skin are directly related to sun exposure, says Guffey.
Melanoma
If you have darker skin, watch for these common melanoma symptoms:
Read Also: Does Amelanotic Melanoma Blanch When Pressed
The Real Risk Of Skin Cancer Regardless Of Race Or Ethnicity
Rates of all three skin cancers are drastically different when compared by race. The density of melanin appears to be the strongest predictor of skin cancer risk, with higher levels of skin melanin lending more protection against UV-induced skin damage. And melanin levels vary among individuals of all races and ethnicities, creating a wide range of potential risks.
Although research on the interactions between melanin and UV radiation can be understood apart from race, the data on skin cancer is often based on self-reported racial or ethnic identities or both. This makes it difficult to separate skin color, or melanin density, from race when discussing melanin, skin cancer and risk reduction options.
Because higher melanin density is associated with a lower risk of skin cancer development, skin cancer may be perceived as a non-issue by people with darker skin tones.
However, skin cancer in Black people, particularly melanoma, is associated with higher risks of illness and death, as well as delayed treatment.
A December 2006 study published in Pigment Cell Research examined increasing levels of sun exposure to skin with varying melanin densities. It found that DNA damage was absent in the basal cell layer the suspected origin of skin cancer of melanin-dense skin, even when sunburn developed. Conversely, damage occurred across all layers of less melanin-dense skin.
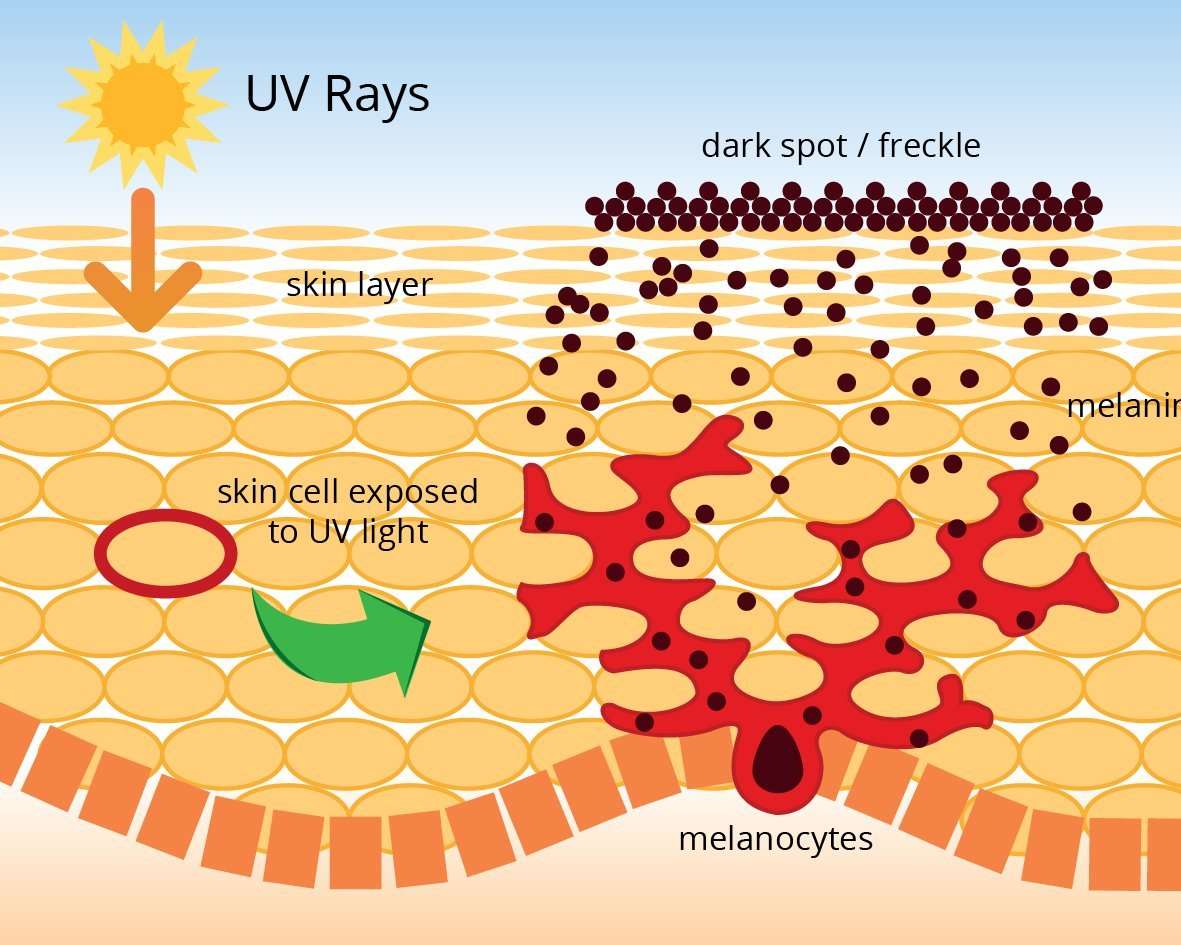
How Does Uv Light Impact Skin Pigmentation
Following DNA damage or repair from UV light exposure, we increase the production of melanin and this creates a tanning effect.2 How pigmentation of the skin is regulated is not well understood but will likely be the subject of future investigation. In mammals, it is known that more than 120 genes have a role in pigmentation.2
Also Check: Ductal Carcinoma Survival Rate
A Solarium Tan Is Not A Safe Tan
Due to the associated health risks, commercial solariums were banned in Victoria in January 2015. Before the ban, it was estimated that each year in Australia solarium use led to:
- 281 new melanoma cases
- 43 melanoma-related deaths
- 2,572 new cases of squamous cell carcinoma.
Solariums use UV radiation to tan the skin. They emit stronger UV radiation levels than the sun . This means they can damage your skin even faster than UV from the sun, and lead to cancer.
Solarium tans offer no protection against DNA damage to skin cells, which can occur without any visible signs of skin damage.
The International Agency for Research on Cancer has put UV-emitting tanning beds in its highest cancer risk category. Tobacco and asbestos are also in this category.
Solariums can cause:
Q: What About Vitiligo Which Is Sort Of Like The Flip Side Of Hyperpigmentation In That Its Primary Characteristic Is Patches Of Color
About 150,000 Americans are treated annually for vitiligo. While the condition affects people across all ethnic groups worldwide, it is of course more visually obvious in people of color. Vitiligo patients are at higher risk for sunburns, but their rates of melanoma and nonmelanoma skin cancers are lower than would be expected. Thats not to say that people with vitiligo wont get skin cancer, but the likelihood is no greater than among the population as a whole, thanks to various immunologic and genetic factors.
Read Also: Stage 3 Lobular Breast Cancer
Protecting Our Skin Inside And Outside
When we put on sunscreen during UV light exposure, it can stop the risk of sun damage.
After we leave the beach or the tanning bed, however, any exposure to UV radiation can still cause this harmful reaction with melanin.
Brashs team is looking to create a product that could suppress the reaction. It would be like an evening after sunscreen. People could apply it like they would a moisturizer when they come in from the sun.
Hopefully we can come up with a way to intervene, Brash said.
In the meantime, be careful with UV exposure, Brash warned.
I think its still true that its best not to go in the sun between 10 a.m. and 2 p.m., he said. Just be reasonable.
Uvr Dna Damage And Skin Cancer
Skin damage, particularly that derived from sunlight, constitutes a major public health problem. Non-melanoma skin cancers are the most frequent malignancies in the United States with more than 1,000,000 cases diagnosed annually . Melanoma skin cancer is the most rapidly increasing type of cancer. Additionally, actinic keratosis , skin lesions that can progress to NMSC are far more prevalent than skin cancers. DNA damage and cellular responses to DNA damage play a central role in skin damage . Sunlight is the major source of skin damage as it leads to DNA damage directly via formation of pyrimidine dimers and other photoproducts and indirectly via generation of reactive oxygen species and reactive carbonyl species by photooxidation and photosensitization reactions . UVR is a complete carcinogen. UVB which penetrates into the epidermis, is responsible for most of the direct DNA damage and is the most 10 Folate in Skin Cancer Prevention 183 effective at initiation of squamous cell carcinoma . UVA which penetrates into the dermis, induces ROS and causes SCC .
Sunlight-induced DNA damage pathways and opportunities for micronutrient modulation
Recommended Reading: How Long Does It Take Melanoma To Metastasize
Insurance Can Be Extremely Important But It Can Also Be Unnecessary
There are undoubtedly some types of insurance that everyone absolutely should have. Car insurance, health insurance and homeowners insurance are easily in the top three. Life insurance and long-term care insurance are also something you may want to consider as you shape your estate plan.
These types of insurance can help protect your health, life and property, while also providing financial reassurance for your loved ones. But there are some types of insurance that may be unnecessary for helping you to further your financial goals. As you assess your insurance needs, consider carefully whether to include these types of policies.
Types Of Tanning Products
The range of tanning products available includes:
- Topical dyes tanning lotions, creams, sprays, mousses, combined moisturiser and ‘fake tan’ products. These are generally made from vegetable dyes that stain the skin a darker colour. This gives a temporary appearance of a tan, which is why it is referred to as a ‘fake tan’. This colour does not stimulate the production of melanin, and it does not provide protection against UV radiation. The dye is shed, along with dead skin cells, after a few days.
- Bronzers and tinted sunscreens tinted cosmetic and sun protection products such as moisturisers, foundation, powders and sunscreen. Bronzers provide the skin with temporary colour that, unlike dyes, washes off with soap and water.
- Tan accelerators claim to speed up the natural tanning process by stimulating melanin production in the body. They come in tablet, injection or lotion form. Using tan accelerators for a long time has been associated with an increased risk of skin cancer. When taken by mouth, the possible side effects of tan accelerator products include nausea, headaches and itchy skin.
- Spray tanning booths these use mist spray guns to apply an even coat of fake tan solution to all, or parts of, the body. They are often found at beauty salons, hairdressers and some gymnasiums.
Also Check: Skin Cancer Spreading To Lymph Nodes
Variations In Human Skin Pigmentation
It has been long recognized that skin colors among indigenous populations show a direct relationship to the intensity of the local UV spectrum. Recently, Jablonski and Chaplin have dramatically advanced the study of the proposed relationships by correlation and regression analyses of quantitative skin color measurements obtained by skin reflectance spectrophotometry with newly available remotely sensed data on levels of UVR, total solar radiation, temperature, humidity, precipitation, and other environmental variables at the Earthâs surface . The strongest association to skin color was found to be latitude, which corresponds to an effect of UVR intensity. A strong correlation was found between latitude and annual average minimal erythemal dose of UVR , and thus between annual average UVMED and skin reflectance using UVMED data from the Earthâs surface . A subsequent study of the influence of minimum, maximum, and seasonal levels of UVR showed that skin reflectance was correlated with autumn levels of UVMED, and that skin reflectance could be almost fully modeled as a linear effect of this variable alone . Dark pigmentation was found to be primarily a function of UVMED , with regression analysis demonstrating that autumn UVMED levels have the strongest effect. Interestingly, their data indicated that skin color is more strongly correlated with UVA, which is consistently higher throughout the year at all latitudes, than with UVB .