Is There Anything Else I Should Know
The diagnosis of suspected diffuse iris melanoma relies on close monitoring of the early lesions and detection of changes that suggest progression. Monitoring is seldom, if ever, disadvantageous. Some iris melanomas grow very slowly, and the eye may not have to be removed for years. It is often difficult to think about removing your cats eye, even with the diagnosis of a life-threatening cancer, but enucleation can both prevent pain and save your cats life. Most cats will quickly adjust to the change in visual capacity and function very well.
Types Of Ocular Melanoma
Melanoma is a type of cancer that develops from cells called melanocytes.Melanocytes give the skin its pigment . Melanoma usually develops in the skin, but because there are melanocytes in different parts of the body, it can start in other places, such as the eye.
Most eye melanomas form in the area of the eye called the uvea, which includes the iris, ciliary body, and choroid. This is called uveal melanoma. While it is the most common type of cancer of the eye, it is still rare with an incidence of 5.1 cases per million people per year.
Very rarely, melanoma starts in the conjunctiva, which is the outer lining of the eye. This is called conjunctival melanoma.
How Does Radiation Therapy Treat Intraocular Melanoma
- Radiation therapy uses powerful doses of radiation to destroy tumors. Depending on the size and location of your tumor, your healthcare provider may recommend:
- External radiation therapy, which points beams of radiation at the tumor from outside the body. Special techniques such as proton beam radiation target the tumor. This minimizes damage to nearby eye and brain tissues.
- Internal radiation therapy, which implants seeds of radiation inside the eye, near the tumor. Providers call this technique radioactive plaque therapy. The seeds are inside a metal plaque to protect other parts of the eye.
Also Check: Lobular Breast Cancer Stage 3
Getting A Diagnosis Of Ocular Melanoma
My grandmother drove my mom to her appointment, where the ophthalmologist, Andrew Dahl, MD, looked carefully at Moms eyes. After the exam, he sent her back to his office and got my grandmother from the waiting room. Then he told my mother that she had a tumor in the back of her eye.
Thank God my mother was with me. She had the presence of mind to ask the doctor if it was malignant. I was just too stunned. I immediately started to wonder if I was going to die.
Dr. Dahl couldnt tell Mom if the tumor was cancerous. For that she would need more tests, so he recommended she see a tumor specialist at the Harkness Eye Institute at Columbia Presbyterian in New York City.
Within a week, Mom was admitted to the hospital for four days of tests and scans. One of the tests she remembers most vividly was called a radioactive phosphorous uptake test. She was injected with a radioactive dye and then monitored for 48 hours, while the dye traveled through her body. If cancer was present, the radioactive phosphorous would attach itself to the cancer cells. She was put under general anesthesia while doctors cut into a muscle alongside her eye and used a radiation detector to see if there was a higher uptake of the dye in the eye compared to surrounding tissue.
What Is The Cause Of Ocular Melanoma

Like other forms of melanoma, ocular melanoma occurs because of genetic changes within melanocytes that cause the cells to proliferate. Further changes in the cells cause them to invade surrounding tissues and to spread elsewhere round the body .
Many reports suggest exposure to sunlight may be an important factor in the development of ocular melanoma.
Also Check: Invasive Breast Cancer Prognosis
Squamous Cell Skin Cancer
Most squamous cell cancers are found on the skin and develop in areas that are exposed to the sun. This includes the eyelids.
Squamous cell cancers don’t often spread. If they do, it’s most often to the deeper layers of the skin. They can spread to nearby lymph nodes and other organs causing secondary cancers, but this is unusual.
Orbital And Adnexal Cancers
The orbit consists of the tissues surrounding the eyeball. These include muscles that move the eyeball in different directions and the nerves attached to the eye. Cancers of these tissues are called orbital cancers.
Adnexal structures include the eyelids and tear glands. Cancers that develop in these tissues are called adnexal cancers.
Cancers of the orbit and adnexa develop from tissues such as muscle, nerve, and skin around the eyeball and are like cancers in other parts of the body. For example:
Recommended Reading: Signs Of Stage 4 Cancer
How Does Surgery Treat Intraocular Melanoma
There are several types of surgery for intraocular melanoma:
- External resection to remove the tumor and some of the surrounding healthy tissue from outside-in.
- Enucleation to remove the eye and part of the optic nerve.
Some degree of vision loss is a risk with each type of surgery. You may choose to have a prosthetic eye after enucleation or exenteration, but this wont restore vision in that eye.
Clinical Features Predicting Prognosis
Although the influence of age on the prognosis of uveal melanoma is uncertain, recent studies indicate that a poor prognosis is more likely associated with increasing age. Lower metastatic rates in younger patients could be related to smaller tumors, more robust immune response, or fewer genetic mutational events within the melanoma compared with older adults., At 10 years, metastasis in patients aged 1120 years is estimated at 10%, for 4150 years is 21%, and for 7180 years is 30%. The COMS study showed no difference in uveal melanoma-related metastasis and death based on gender. However, some reports suggest a better prognosis in females compared with males, with a twofold higher rate of mortality in males compared with females in the first 10 years of posterior uveal melanoma diagnosis. Hormonal factors, especially estrogen, may cause direct or indirect inhibition of development of metastasis in females.
AJCC classification is an important prognostic factor of posterior uveal melanoma. In a study of 7731 patients with posterior uveal melanoma based on T category of AJCC classification, the risk for metastasis and death increased twofold with each increasing tumor category, and the 10-year metastatic rate was 15% for T1, 25% for T2, 49% for T3, and 63% for T4 tumors.
Also Check: How Long Does It Take For Melanoma To Metastasize
Who Is At Risk For Intraocular Melanoma
A risk factor is anything that may increase your chance of having a disease. The exact cause of someones cancer may not be known. But certain risk factors can make it more likely for a person to develop cancer. Some risk factors may not be in your control. But others may be things you can change.
Anyone can develop intraocular melanoma. But certain factors may make you more likely to get it. They include:
- Having fair skin and light-colored eyes
- Being older
- Exposure to UV light sources from the sun or tanning beds
- Certain inherited skin problems, such as dysplastic nevus syndrome
Talk with your healthcare provider about your risk factors for intraocular melanoma and what you can do about them.
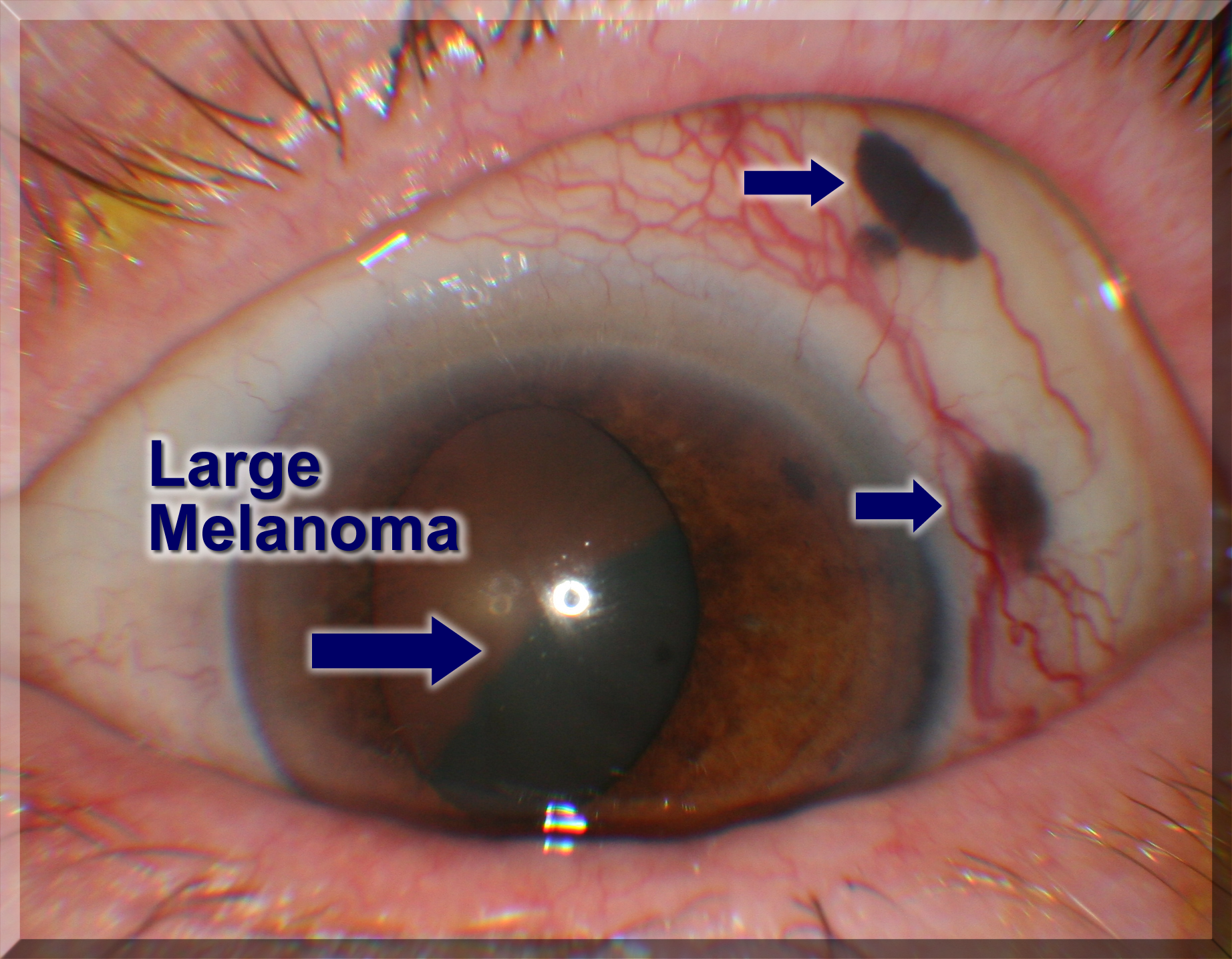
Signs Of Intraocular Melanoma Include Blurred Vision Or A Dark Spot On The Iris
Intraocular melanoma may not cause early signs or symptoms. It is sometimes found during a regular eye exam when the doctor dilates the pupil and looks into the eye. Signs and symptoms may be caused by intraocular melanoma or by other conditions. Check with your doctor if you have any of the following:
- Blurred vision or other change in vision.
- Floaters or flashes of light.
- A dark spot on the iris.
- A change in the size or shape of the pupil.
- A change in the position of the eyeball in the eye socket.
Read Also: What Does Cancer Look Like Outside The Body
Diagnosing Melanoma Of The Eye
If your GP or optician suspects you have a serious problem with your eyes, they will refer you to a specialist eye doctor called an ophthalmologist for an assessment.
If they suspect you have melanoma of the eye, they’ll refer you to a specialist centre for eye cancer. There are four centres in the UK, located in London, Sheffield, Liverpool, and Glasgow.
It’s likely you’ll have a number of different tests at the centre, including:
- an eye examination to look at the structures of your eyes in more detail and check for abnormalities
- an ultrasound scan of your eye a small probe placed over your closed eye uses high-frequency sound waves to create an image of the inside of your eye this allows your doctor to find out more about the position of the tumour and its size
- a fluorescein angiogram where photographs of the suspected cancer are taken using a special camera after dye has been injected into your bloodstream to highlight the tumour
Occasionally, a thin needle may be used to remove a small sample of cells from the tumour . The genetic information in these cells is analysed to give an indication of the chances of the cancer spreading or coming back.
Talk With Your Healthcare Provider
If you have questions about intraocular melanoma, talk with your healthcare provider. Your healthcare provider can help you understand more about this cancer.
The Johns Hopkins Proton Therapy Center
Proton therapy is used to treat certain tumors in children and adults. Our treatment center, located at Sibley Memorial Hospital in Washington, D.C., combines advanced proton therapy technology, the latest research and caring specialists.
Recommended Reading: 3b Melanoma
Key Points About Intraocular Melanoma
- Intraocular melanoma is cancer that starts in the melanocytes in your eyes.
- Its rare, but it’s still the most common type of cancer of the eye in adults.
- Risk factors for it are being older and having fair skin and light-colored eyes.
- Symptoms may include blurry vision, eye soreness, or floaters in your vision.
- Exposure to UV light is linked to this cancer. Protect your eyes with sunglasses with 99% to 100% ultraviolet A and B protection.
- Treatments for this cancer include surgery, radiation, and photocoagulation.
A Biopsy Of The Tumor Is Rarely Needed To Diagnose Intraocular Melanoma
A biopsy is the removal of cells or tissues so they can be viewed under a microscope to check for signs of cancer. Rarely, a biopsy of the tumor is needed to diagnose intraocular melanoma. Tissue that is removed during a biopsy or surgery to remove the tumor may be tested to get more information about prognosis and which treatment options are best.
The following tests may be done on the sample of tissue:
- Cytogenetic analysis: A laboratory test in which the chromosomes of cells in a sample of tissue are counted and checked for any changes, such as broken, missing, rearranged, or extra chromosomes. Changes in certain chromosomes may be a sign of cancer. Cytogenetic analysis is used to help diagnose cancer, plan treatment, or find out how well treatment is working.
- Gene expression profiling: A laboratory test that identifies all of the genes in a cell or tissue that are making messenger RNA. Messenger RNA molecules carry the genetic information that is needed to make proteins from the DNA in the cell nucleus to the protein-making machinery in the cell cytoplasm.
A biopsy may result in retinal detachment . This can be repaired by surgery.
Also Check: Non Invasive Breast Cancer Survival Rate
Can Intraocular Melanoma Be Prevented
Certain factors may make you more likely to get intraocular melanoma. Some factors you can’t change. While others you can control. For instance, repeatedly being exposed to sunlight or tanning beds over time may raise your risk. But experts don’t know this for sure.
Still, you shouldnt use tanning beds. Some healthcare providers say to wear sunglasses with 99% to 100% UVA and UVB protection when outside in sunlight.
Treating this cancer can cause eye damage. For this reason, your healthcare provider may recommend that you not start treatment right away. This is called “watchful waiting.” Your healthcare provider will check on you regularly and take pictures of the tumor to track its growth. If the tumor starts to grow, you may start treatment.
Diagnosis Of Ocular Melanoma
If your doctor or optometrist thinks that you may have ocular melanoma, they will carry out certain tests.
If the results suggest that you may have ocular melanoma, your doctor will refer you to a specialist doctor called an ophthalmologist who specialises in ocular oncology. The ophthalmologist will carry out more tests that may include:
Don’t Miss: Metastatic Skin Cancer Pictures
What Are The Symptoms Of Intraocular Melanoma
In some cases, intraocular melanoma may not cause symptoms. Or symptoms may be difficult to spot since the cancer is in part of the eye that isnt visible.
When symptoms do occur, they can include:
- Blind spots or a reduced field of vision.
- Floaters or flashes of light in your field of vision.
- Retinal detachment .
What Cancer Is
Your body is made up of billions of cells that can only be seen under a microscope. The cells group together to make up the tissues and organs of our bodies.
Normally, cells only divide to replace old and worn out cells. Cancer develops when something inside a single cell goes wrong, making the cell carry on dividing until it forms a lump or a tumour.
A tumour can be either non cancerous or cancerous . A benign tumour does not spread to other parts of the body. But a malignant tumour can spread.
Also Check: Survival Rate Of Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Who Gets It
Overall, the risk of developing an eye cancer increases as you get older. Almost 25 out of 100 people diagnosed with eye cancer in the UK are aged 75 and over. The exception to this is a type called retinoblastoma. This usually affects children under the age of 5.
-
Ross and Wilson Anatomy and Physiology in Health and Illness A Waugh and A Grant Churchill Livingstone, 2014
What Is A 5
A relative survival rate compares people with the same type and stage of cancer to people in the overall population. For example, if the 5-year relative survival rate for a specific stage of eye cancer is 80%, it means that people who have that cancer are, on average, about 80% as likely as people who dont have that cancer to live for at least 5 years after being diagnosed.
Don’t Miss: Lobular Carcinoma Survival Rate
Histopathology Features Predicting Prognosis
The histopathologic features predicting poor prognosis of uveal melanoma include epithelioid cell type, high mitotic activity, large mean diameter of the 10 largest nucleoli, high microvascular density, presence of microvascular loops and networks, increased tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and macrophages, and higher expression of insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor, and HLA class I and II antigens. Currently, most authorities rely on cytogenetic features rather than histopathologic features for prognostication.
How Is The Diagnosis Of Ocular Melanoma Made
Diagnosis of ocular melanoma is usually made by accurate clinical examination. The main indicators of disease in 90 patients described in a Canadian study were:
- partial loss of visual field
- sun sensitivity
- incidental finding on eye examination
Conjunctival melanoma presents as an increasingly irregular pigmented lesion on the external eye.
Other symptoms may include a protruding eye, change in colour of the iris, red or painful eye, and retinal detachment.
You May Like: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Grade 3 Life Expectancy
What Causes Ocular Melanoma
The exact cause of most eye cancer is unknown.
Risk factors for developing ocular melanoma include:
- Race/ethnicity
- The risk is higher in whites than it is in African Americans, Hispanics or Asian Americans
What Are The Treatments For This Type Of Tumor
The treatment of choice for diffuse iris melanoma will vary according to the initial appearance of the cancer, how it progresses over time, and your cats age. When there are only mild to moderate changes in the iris, most veterinary ophthalmologists prefer to monitor the progression of the cancer with periodic examinations, although laser surgery or partial iridectomy is possible. The intraocular pressure is also monitored. If the size and number of lesions substantially increase, the lesions become raised, the pupil changes shape, the pigment spreads to other areas of the eye, or the intraocular pressure rises, enucleation is recommended. Enucleation is always advised in cases of fast-growing, locally invasive melanoma, even in older cats.
“The treatment of choice for diffuse iris melanoma will vary according to the initial appearance of the cancer, how it progresses over time, and your cats age.”
Histopathology should always be done in cases of enucleation. This will provide a definitive diagnosis, assess whether the tumor has metastasized, and enable you and your veterinarian to form a long-term plan of care. If there is evidence of metastasis, your veterinarian may recommend periodic imaging to determine presence and extent of metastatic disease. Unlike many other cancers that metastasize, metastatic disease may not become evident for years.
Recommended Reading: Survival Rates For Invasive Ductal Carcinoma