Now What Percentage Of Melanomas Actually Arise From An Atypical Mole
Dr. Tsoukas says those who have dysplastic nevi without family history of melanoma face a 7 to 27 times higher risk for developing melanoma.
However, this doesnt mean that an atypical mole will necessarily transform into melanoma, although a severely atypical mole as just mentioned has the highest chance for melanoma transformation.
We carefully examine and thereafter remove atypical moles via biopsy or surgical excision techniques in the office.
Having many dysplastic nevi is one of the risk factors for melanoma.
Someone with many dysplastic nevi and personal history or with 1st-degree relatives who have had melanoma has an extremely higher lifetime risk of developing melanoma, than general population says Dr. Tsoukas.
Melanoma under magnification. Shutterstock/Nasekomoe
Additional risk factors include: fair skin, sunburn history, indoor tanning, advancing age and immunosuppression.
What Does A Precancerous Mole Look Like
Normal moles are usually smaller than 5 mm wide. They are round or oval, have a smooth surface with a distinct border, and are uniform in color .
In contrast, a precancerous mole has certain characteristics that are apparent to the naked eye. The National Cancer Institute describes a dysplastic nevus as appearing flat with a smooth, slightly scaly or pebbly surface, with an irregular edge that may fade into the surrounding skin. The institute also specifies that a dysplastic nevus may often be more than 6 mm wide.
According to the American Cancer Society , the signs to watch out for follow the mnemonic ABCDE:
- Asymmetry: One part of a mole does not match the other.
- Border: The edges are irregular, ragged, notched or blurred.
- Color: The color isnt uniform and may include patches of brown, black, pink, red, white or blue.
- Diameter: The mole is larger than a pencil eraser , though some can be smaller.
- Evolving: The mole is changing in size, shape or color.
The ugly duckling sign is another way of identifying the possibility of skin cancer. It simply means that any mole or freckle that differs in shape, size or color from any other on the skin is often the most suspicious and therefore warrants further examination.
What Are Atypical Moles
An atypical mole, also known as a dysplastic nevus, is a mole that looks different than common moles.
Characteristics of an atypical mole include:
- Size: typically, larger than a common molegreater than 5 millimeters
- Shape: shape may vary, but is usually asymmetrical
- Texture: may be pebbly, smooth, scaly, or rougher than common moles
- Edges: usually irregular and jagged, may fade in color around edges
- Protrusion: typically flat
- Color: may be a combination of several colors, from pink to dark brown
Atypical moles form anywhere on the body including the scalp, breasts, or legs, but are often found in areas that are frequently exposed to the sun. Most people with atypical moles also have more common moles than usual.
Atypical moles are very similar to melanoma: both are asymmetrical, multicolored, have an irregular border, and can grow over time. While not all atypical moles are precancerous moles, they can become cancerous moles or melanoma.
It is important to understand the characteristics of an atypical mole so that if you detect one on your body, you can seek the help of a professional to make a diagnosis and treatment plan if necessary.
Recommended Reading: What Is Metastatic Merkel Cell Carcinoma
What Are Precancerous Moles Or Precancerous Skin Lesions
Precancerous moles, more commonly referred to as precancerous skin lesions, are growths that have an increased risk of developing into skin cancer. Precancerous skin lesions, usually referred to as actinic keratosis or solar keratoses, can cause different types of skin cancer, including:
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma
- Basal Cell Carcinoma
- Melanoma
There are different causes of skin cancer and many of these involve sun exposure. When people are exposed to the sun, the ultraviolet radiation often damages the DNA of the skin cells themselves. As the DNA is damaged, the cells are unable to produce proteins and cannot correctly respond to the various signals of the body. As a result, they divide out of control and lead to the symptoms of cancer. Therefore, it is important to spot a precancerous lesion before it gets too big.
What Is A Common Mole
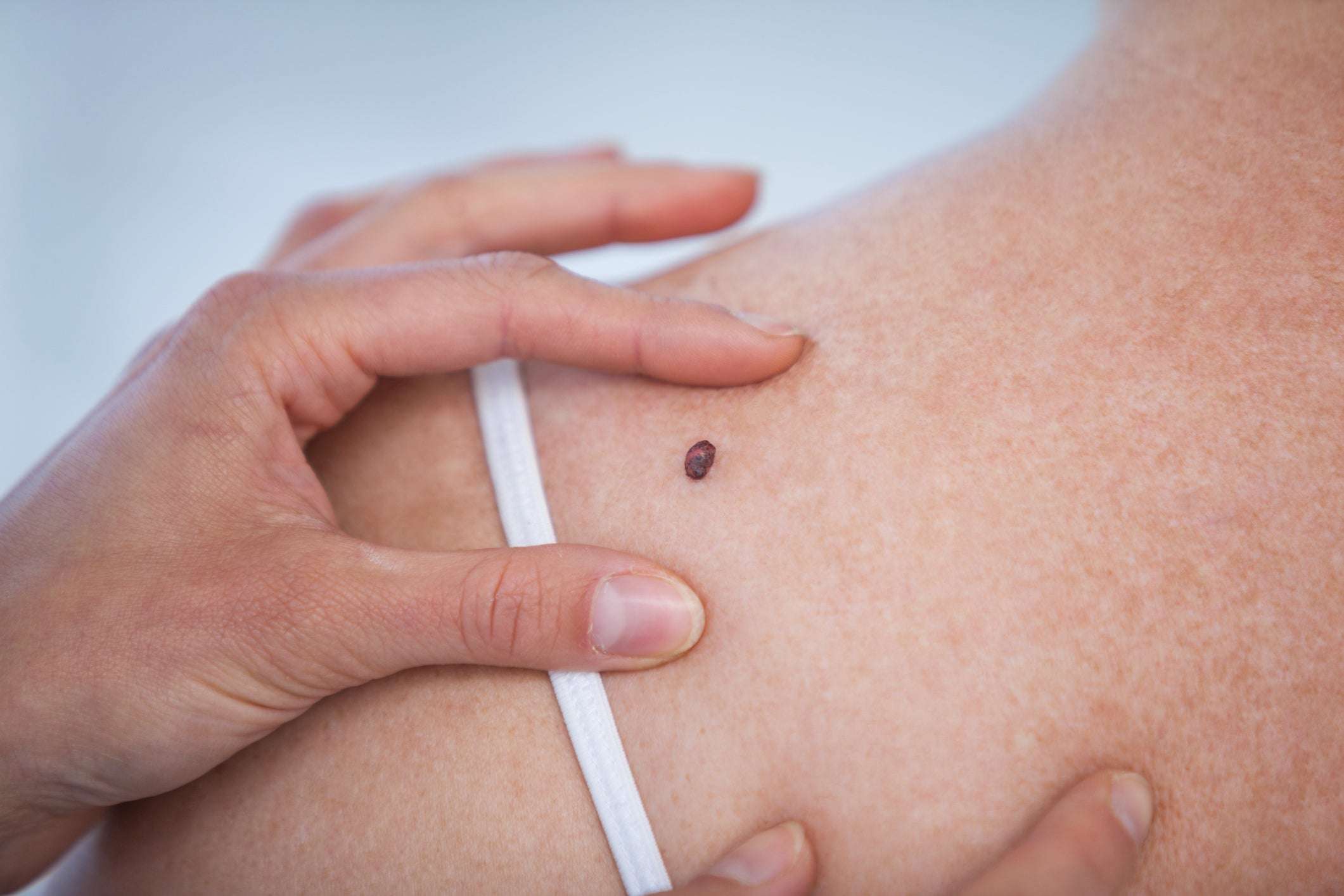
A common mole is a growth on the skin that develops when pigment cells grow in clusters. Most adults have between 10 and 40 common moles. These growths are usually found above the waist on areas exposed to the sun. They are seldom found on the scalp, breast, or buttocks.
Although common moles may be present at birth, they usually appear later in childhood. Most people continue to develop new moles until about age 40. In older people, common moles tend to fade away.
Another name for a mole is a nevus. The plural is nevi.
Don’t Miss: What Is Pre Melanoma Skin Cancer
Should People Have A Doctor Remove A Dysplastic Nevus Or A Common Mole To Prevent It From Changing Into Melanoma
No. Normally, people do not need to have a dysplastic nevus or common mole removed. One reason is that very few dysplastic nevi or common moles turn into melanoma . Another reason is that even removing all of the moles on the skin would not prevent the development of melanoma because melanoma can develop as a new colored area on the skin . That is why doctors usually remove only a mole that changes or a new colored area on the skin.
How Is Actinic Keratosis Diagnosed
Healthcare providers can often diagnose an actinic keratosis by looking at and feeling the area on your skin. But sometimes an actinic keratosis can be hard to tell apart from skin cancer. Your healthcare provider might remove the area of skin to have it checked under a microscope. This is known as a skin biopsy.
You May Like: Can Red Spots Be Skin Cancer
When Do Cells Become Cancerous
The answer is that most of the time, we dont know how long it takes for precancerous cells to become cancerous. In addition, the answer certainly varies depending on the type of cell studied.
In one study looking at 101 people with dysplasia of the vocal cords, 15 went on to develop invasive cancer .
In 73% of these patients, their precancerous lesions became invasive cancer of the vocal cords within one year, with the remainder developing cancer years later.
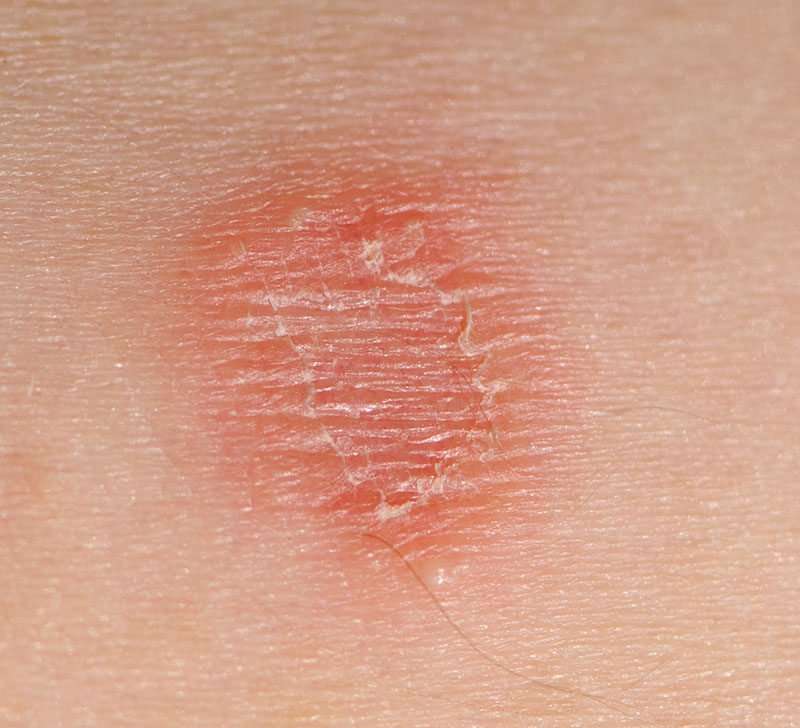
Actinic Keratosis On An Arm
This photo contains content that some people may find graphic or disturbing.
Actinic keratosis, also called solar keratosis, is a precancerous skin lesion usually caused by too much sun exposure. It can also be caused by other factors such as radiation or arsenic exposure.
If left untreated, actinic keratoses can develop into a more invasive and potentially disfiguring skin cancer called squamous cell carcinoma. They appear predominantly on sun-exposed areas of the skin such as the face, neck, back of the hands and forearms, upper chest, and upper back. You can also develop keratoses along the rim of your ear.
Actinic keratosis is caused by cumulative skin damage from repeated exposure to ultraviolet light, including that found in sunshine. Over the years, the genetic material in your cells may become irreparably damaged and produce these pre-cancerous lesions. The lesions, like those seen here on the arm, can later become squamous cell carcinoma, a more invasive cancer.
Read Also: What Happens When Melanoma Spreads
S Of Moles Nevus Actinic Keratosis Psoriasis
Doru Paul, MD, is triple board-certified in medical oncology, hematology, and internal medicine. He is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Weill Cornell Medical College and attending physician in the Department of Hematology and Oncology at the New York Presbyterian Weill Cornell Medical Center.
Not all skin blemishes are cancerous, nor will they all become cancerous in the future. If you are worried about a spot on your skin, this gallery of photographs can help you distinguish between cancerous, noncancerous, and precancerous lesions.
Of course, diagnosing skin cancer is far from straightforward, so if you have any doubts, contact your dermatologist or primary care physician as soon as possible.
What Is A Dysplastic Nevus
A dysplastic nevus is a type of mole that looks different from a common mole. A dysplastic nevus may be bigger than a common mole, and its color, surface, and border may be different. It is usually more than 5 millimeters wide . A dysplastic nevus can have a mixture of several colors, from pink to dark brown. Usually, it is flat with a smooth, slightly scaly, or pebbly surface, and it has an irregular edge that may fade into the surrounding skin. Some examples of dysplastic nevi are shown here. More examples are on the What Does a Mole Look Like? page.
Dysplastic Nevi Photos
This dysplastic nevus has a raised area at the center that doctors may call a fried egg appearance.
This dysplastic nevus is more than 5 millimeters in diameter.
This dysplastic nevus is more than 10 millimeters wide .
A dysplastic nevus may occur anywhere on the body, but it is usually seen in areas exposed to the sun, such as on the back. A dysplastic nevus may also appear in areas not exposed to the sun, such as the scalp, breasts, and areas below the waist . Some people have only a couple of dysplastic nevi, but other people have more than 10. People who have dysplastic nevi usually also have an increased number of common moles.
Don’t Miss: What Do Melanoma Spots Look Like
The Five Ss Of Sun Safety:
SLIP on a T-shirt
Intra-Epidermal Carcinoma
Bowens Disease is a precancerous skin lesion that has not yet penetrated the basement membrane, but can if left untreated, lead to Squamous Cell Carcinoma.
- Bowens disease = Intraepidermal Carcinoma = IEC = Squamous cell carcinoma in-situ.
- Bowens disease is a precancerous lesion. In-situ refers to the fact that the disease has not penetrated the basement membrane. Once this occurs, the lesion is a Squamous Cell Carcinoma a full blown skin cancer.
- Bowens disease typically presents as an asymptomatic, slow growing, sharply-demarcated, scaly erythematous patch or plaque. The border may be irregular.
- The surface may be flat, scaly, crusted, eroded, ulcerated, velvety or verrucous .
- Because of its asymptomatic nature, lesions may become very large by the time of presentation.
- Although Bowens disease can occur just about anywhere, common sites for presentation are the lower limbs and head and neck.
- Bowens disease occurs most commonly in later life and most patients aged over 60.
- Women are affected more than men.
- In approx. 3% of cases Bowens disease transforms to squamous cell carcinoma and about 1/3 of these will metastasise and become fatal.
The development of an ulcer or lump on a patch of Bowens disease may indicate the formation of invasive squamous cell cancer, so it is very important to seek professional advice with anything suspicious.
After Skin Cancer Treatment
Most skin cancer is cured surgically in the dermatologist’s office. Of skin cancers that do recur, most do so within three years. Therefore, follow up with your dermatologist as recommended. Make an appointment immediately if you suspect a problem.
If you have advanced malignant melanoma, your oncologist may want to see you every few months. These visits may include total body skin exams, regional lymph node checks, and periodic chest X-rays and body scans. Over time, the intervals between follow-up appointments will increase. Eventually these checks may be done only once a year.
Read Also: Can Apple Cider Vinegar Help With Skin Cancer
What Does A Common Mole Look Like
A common mole is usually smaller than about 5 millimeters wide . It is round or oval, has a smooth surface with a distinct edge, and is often dome-shaped. A common mole usually has an even color of pink, tan, or brown. People who have dark skin or hair tend to have darker moles than people with fair skin or blonde hair. Several photos of common moles are shown here, and more photos are available on the What Does a Mole Look Like? page.
Common Mole Photos
This common mole is 1 millimeter in diameter .
This common mole is 2 millimeters in diameter .
This common mole is about 5 millimeters in diameter .
This common mole is about 5 millimeters in diameter .
This common mole is about 5 millimeters in diameter .
What Should I Do About A Precancerous Mole
If there is concern that a skin lesion is precancerous, a doctor should take a look at it. In some cases, the lesion may need to be biopsied and placed under a microscope for more information.
Special stains can be used to try and differentiate a mole from a skin lesion. If the lesion is deemed to be cancerous, various treatment options can be discussed.
If melanoma is present, in some cases cancer can be removed in its entirety in a single appointment. In other cases, surgery may be used in combination with chemotherapy and radiation to kill the cancer cells. Radiation is also used as a primary treatment for some non-melanoma skin cancers. This decision should be made in conjunction with a cancer specialist.
In the end, it can be difficult for people to tell the difference between a simple mole and a precancerous skin lesion or precancerous mole. Because of this, it is important to conduct detailed skin exams regularly. If there are any questions or concerns, schedule an appointment with a trained health professional.
Also Check: How To Remove Skin Cancer Yourself
What Are The Different Kinds Of Precancerous Skin Lesions
There are several different kinds. Some of these are described below.
Congenital Melanocytic Nevi: These are birthmarks or large moles that are present at birth or that develop shortly afterward. Having one or more of these is associated with a higher risk of developing a form of skin cancer called melanoma. The appearance of these features can vary in terms of color, size, shape, and texture. Their pigmentation may be even or irregular, giving these patches a speckled appearance. Some are flat while others are distinctly raised from the skin surface. These may or may not have hair. Any change in the appearance of a congenital nevus, or any inflammation, pain or bleeding may be a sign of malignancy. Generally, the larger the patch, the greater its chances of developing into melanoma. In fact, a rare form known as the giant congenital melanocytic nevus is associated with a significant risk of melanoma.
What Is Precancerous Skin Growth
Precancerous skin growths develop on skin that has a lot of sun exposure over time without proper protection. While it’s not considered cancer yet, it can turn into it in the future. While many forms of precancerous skin growths form after the age of 40, it can happen at an earlier age, especially for those of us living in Florida where we are outside in a lot of sunshine.
Actinic keratosis is the most common type of precancerous growth. Some people say an AK feels rough, like a spot of sandpaper on the skin. Many oncologists consider AKs as early squamous cell cancers . If left untreated, AKs are likely to progress into nonmelanoma skin cancer.
If precancerous skin growths are left untreated, they may result in one of the following types of skin cancer:
Read Also: Does Basal Cell Skin Cancer Spread
Skin Cancer Support Groups And Counseling
Living with skin cancer presents many new challenges for you and for your family and friends. You will probably have many worries about how the cancer will affect you and your ability to “live a normal life,” that is, to care for your family and home, to hold your job, and to continue the friendships and activities you enjoy.
Many people with a skin cancer diagnosis feel anxious and depressed. Some people feel angry and resentful others feel helpless and defeated. For most people with skin cancer, talking about their feelings and concerns helps. Your friends and family members can be very supportive. They may be hesitant to offer support until they see how you are coping. Don’t wait for them to bring it up. If you want to talk about your concerns, let them know.
Continued
Some people don’t want to “burden” their loved ones, or prefer talking about their concerns with a more neutral professional. A social worker, counselor, or member of the clergy can be helpful. Your dermatologist or oncologist should be able to recommend someone.
Many people with cancer are profoundly helped by talking to other people who have cancer. Sharing your concerns with others who have been through the same thing can be remarkably reassuring. Support groups for people with cancer may be available through the medical center where you are receiving your treatment. The American Cancer Society also has information about support groups throughout the U.S.
Diagnosis & Prevention Of Precancerous Skin Conditions
Skin is the bodys primary barrier to infection and harmful environmental stressors. In order to protect and preserve this barrier, its important to actively monitor skin for any signs of skin cancer. When discovered and treated during the early stages of development, skin cancer is highly curable. At Advanced Dermatology and Skin Cancer Center, our dermatologists in Boardman and Howland, OH, can diagnose and treat a myriad of precancerous skin conditions. We likewise provide treatment for skin with signs of sun damage. If youre concerned about the health of your skin, contact our office today to schedule a skin care appointment.
Recommended Reading: What Are The Types Of Skin Cancer
Keeping Cancer In Check
Chronic exposure to the sun or intermittent sunburns can lead to skin cancer. Skin cancer risk doubles with five or more sunburns in a lifetime, but just one bad sunburn can double the risk of melanoma. While skin cancer is uncommon in African Americans, Latinos and Asians, it can also be more deadly because they are often diagnosed later in the course of the disease.
Its important to examine your skin regularly. You should report any changes in an existing mole or any new moles to your physician. People with fair complexions have the highest risk of developing skin cancer, but everyone should avoid the sun and practice safety measures to protect their skin.
The American Cancer Society recommends the Slip, Slop, Slap and Wrap policy. When you go out in the sun, slip on a shirt, slop on sunscreen, slap on a hat and wrap on sunglasses to protect your eyes and the sensitive skin around them.
Exposure to the UV rays of tanning lamps is not safe. Tanning lamps give out UV rays, which can cause long-term skin damage and can contribute to skin cancer. Tanning bed use has been linked with an increased risk of melanoma, especially for people under 30. Most doctors and health organizations recommend not using tanning beds and sun lamps.