Key Points About Merkel Cell Cancer
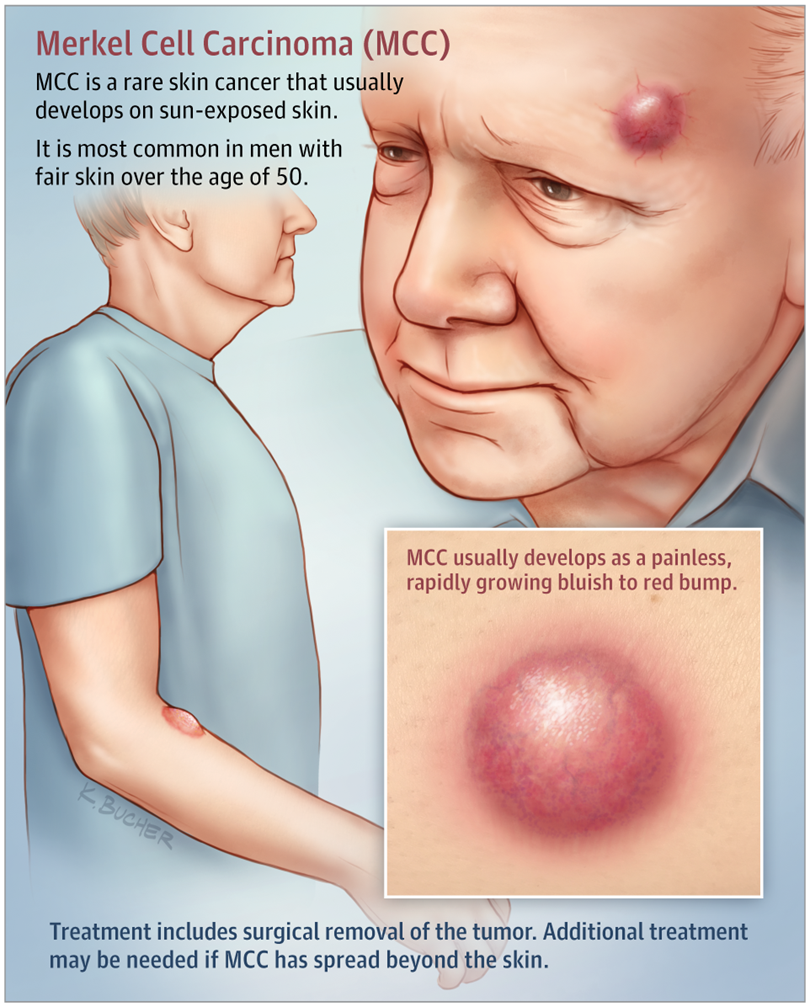
- Merkel cell cancer is a rare type of skin cancer. It forms in the Merkel cells. These cells are found in the outer layer of the skin.
- Merkel cells are very close to nerve endings. They help the skin sense light touch.
- Being exposed to a lot of UV light can raise your risk for this cancer.
- Merkel cell cancer often looks like firm, shiny lumps on your skin that dont hurt. They may be red, pink, or blue.
- This cancer grows and spreads quickly.
- Treatment includes surgery, radiation, chemotherapy, and immunotherapy. One type of treatment or a combination of treatments may be used.
Mcc That Comes Back After Initial Treatment
If MCC comes back after treatment, further treatment depends on where it comes back and what types of treatment were used before.
If the cancer comes back on the skin where it first started, surgery can often be done to try to remove it. This might be followed by radiation therapy to the area if it hasnt been given before. If the nearby lymph nodes haven’t been treated, they might be removed and/or treated with radiation. Some doctors might consider giving chemotherapy as well, but its not clear how helpful this might be.
If the cancer comes back in the nearby lymph nodes and they have not been treated before, they might be removed and/or treated with radiation. Some doctors might consider giving chemotherapy too, but, again, its not clear how helpful this is.
Cancers that come back in distant parts of the body can be hard to treat. Surgery and/or radiation therapy might be used, but the goal is usually to ease symptoms rather than try to cure the cancer. Chemotherapy can often shrink or slow the growth of the cancer for a time and can help relieve symptoms. But chemotherapy can also cause side effects that need to be taken into account. Treatment with one of the newer immunotherapy drugs, such as avelumab or pembrolizumab might be another option. These drugs have been shown to be helpful against some advanced MCCs.
Patients Can Enter Clinical Trials Before During Or After Starting Their Cancer Treatment
Some clinical trials only include patients who have not yet received treatment. Other trials test treatments for patients whose cancer has not gotten better. There are also clinical trials that test new ways to stop cancer from recurring or reduce the side effects of cancer treatment.
Clinical trials are taking place in many parts of the country. Information about clinical trials supported by NCI can be found on NCIs clinical trials search webpage. Clinical trials supported by other organizations can be found on the ClinicalTrials.gov website.
Also Check: What Is The Most Aggressive Skin Cancer
Permission To Use This Summary
PDQ is a registered trademark. The content of PDQ documents can be used freely as text. It cannot be identified as an NCI PDQ cancer information summary unless the whole summary is shown and it is updated regularly. However, a user would be allowed to write a sentence such as NCIs PDQ cancer information summary about breast cancer prevention states the risks in the following way: .
The best way to cite this PDQ summary is:
PDQ® Adult Treatment Editorial Board. PDQ Merkel Cell Carcinoma Treatment. Bethesda, MD: National Cancer Institute. Updated < MM/DD/YYYY> . Available at: . Accessed < MM/DD/YYYY> .
Images in this summary are used with permission of the author, artist, and/or publisher for use in the PDQ summaries only. If you want to use an image from a PDQ summary and you are not using the whole summary, you must get permission from the owner. It cannot be given by the National Cancer Institute. Information about using the images in this summary, along with many other images related to cancer can be found in Visuals Online. Visuals Online is a collection of more than 3,000 scientific images.
Regional Lymph Node Surgery
In some case series, local-regional recurrence rates are high when pathologic nodal staging is omitted. Surgical nodal staging in clinically negative patients has identified positive nodes in at least 25% to 35% of patients. In one retrospective series of 213 patients who underwent surgical treatment of the primary tumor and evaluation of the draining nodes, nodal positivity was found in 2 of 54 patients with small tumors and 51 of 159 patients with tumors larger than 1.0 cm.
The role of elective lymph node dissection in the absence of clinically positive lymph nodes has not been studied in formal clinical trials. In small case series, ELND has been recommended for larger primary tumors, tumors with more than ten mitoses per high-power field, lymphatic or vascular invasion, and the small-cell histologic subtypes.
Sentinel lymph node biopsy has been suggested as a preferred initial alternative to complete ELND for the proper staging of MCC. SLN biopsy has less morbidity than complete nodal dissection. Furthermore, for MCC sites with indeterminate lymphatic drainage, such as those on the back, SLN biopsy techniques can be used to identify the pertinent lymph node bed. If performed, SLN biopsy is done at the time of the wide resection when the local lymphatic channels are still intact.
Several reports have found the use of SLN biopsy techniques in MCC to be reliable and reproducible. However, the significance of SLN positivity remains unclear.
You May Like: Does Skin Cancer Burn And Itch
Coping With Merkel Cell Cancer
Many people feel worried, depressed, and stressed when dealing with cancer. Getting treatment for cancer can be tough on your mind and body. Keep talking with your healthcare team about any problems or concerns you have. Work together to ease the effect of cancer and its symptoms on your daily life.
To help ease your stress:
- Talk with your family or friends.
- Ask your healthcare team or social worker for help.
- Speak with a counselor.
- Talk with a spiritual advisor, such as a minister or rabbi.
- Ask your healthcare team about medicines for depression or anxiety.
- Keep socially active.
- Join a cancer support group.
Cancer treatment is also hard on the body. To help yourself stay healthier, try to:
- Eat a healthy diet, with a focus on high-protein foods.
- Drink plenty of water, fruit juices, and other liquids.
- Keep physically active.
- Rest as much as needed.
- Talk with your healthcare team about ways to manage treatment side effects.
- Take your medicines as directed by your team.
Sun Exposure And Having A Weak Immune System Can Affect The Risk Of Merkel Cell Carcinoma
Anything that increases your risk of getting a disease is called a risk factor. Having a risk factor does not mean that you will get cancer not having risk factors doesn’t mean that you will not get cancer. Talk with your doctor if you think you may be at risk. Risk factors for Merkel cell carcinoma include the following:
- Being exposed to a lot of natural sunlight.
- Having an immune system weakened by disease, such as chronic lymphocytic leukemia or HIVinfection.
- Taking drugs that make the immune system less active, such as after an organ transplant.
- Having a history of other types of cancer.
- Being older than 50 years, male, or White.
Also Check: Stage 3 Basal Cell Carcinoma Survival Rate
Merkel Cell Carcinoma Is A Very Rare Disease In Which Malignant Cells Form In The Skin
Merkel cells are found in the top layer of the skin. These cells are very close to the nerve endings that receive the sensation of touch. Merkel cell carcinoma, also called neuroendocrine carcinoma of the skin or trabecular cancer, is a very rare type of skin cancer that forms when Merkel cells grow out of control. Merkel cell carcinoma starts most often in areas of skin exposed to the sun, especially the head and neck, as well as the arms, legs, and trunk.
Merkel cell carcinoma tends to grow quickly and to metastasize at an early stage. It usually spreads first to nearby lymph nodes and then may spread to lymph nodes or skin in distant parts of the body, lungs, brain, bones, or other organs.
Merkel cell carcinoma is the second most common cause of skin cancer death after melanoma.
What You Need To Know
Merkel cell carcinoma is rare and dangerous but treatable, especially when found at an early stage. Be watchful for any new or changing lesions on your skin and look out for these warning signs.
If youve been treated for a previous MCC, pay close attention to the site and the surrounding region. Contact your medical team immediately if you see any suspicious changes.
How to spot a Merkel Cell Carcinoma
APPEARANCE Painless shiny or pearly lesions or nodules
SIZE Dimensions vary, but the average size at detection is 1.7 cm, about the diameter of a dime.
COLOR Skin-colored, red, purple or bluish-red
LOCATION Frequently on sun-exposed areas, often on the head and neck, particularly the eyelids.
While rare, Merkel cell carcinomas are often aggressive and can advance rapidly which is why early detection and removal are especially important. Memorial Sloan Kettering oncologist Sandra DAngelo, MD, shares some important warning signs you should never ignore.
Read Also: Does Amelanotic Melanoma Blanch When Pressed
What Are The Symptoms Of Merkel Cell Carcinoma
In most cases, MCC causes a small reddish or purplish lump or bump to form on areas of skin often exposed to ultraviolet light, such as the face, neck, arms, and hands. The lumps usually do not cause pain. In some cases, bumps appear inside the nostrils or esophagus. Lumps or bumps may crack open and bleed.
How Is Merkel Cell Cancer Treated
Your treatment choices depend on the number of Merkel cell cancer tumors, test results, and the stage of the cancer. The goal of treatment may be to cure you, control the cancer, or to help ease problems caused by cancer. Talk with your healthcare team about your treatment choices, the goals of treatment, and what the risks and side effects may be.
Types of treatment for cancer are either local or systemic. Local treatments remove, destroy, or control cancer cells in one area. Surgery and radiation are local treatments. Systemic treatment is used to destroy or control cancer cells that may have traveled around your body. When taken by pill or injection, chemotherapy and targeted therapy are systemic treatments. You may have just one type of treatment or a combination of treatments.
Sometimes more than 1 type of treatment is used. Treatment may include:
Talk with your healthcare providers about your treatment options. Make a list of questions. Think about the benefits and possible side effects of each option. Some treatments may affect your ability to have children in the future. Talk about your concerns with your healthcare provider before making a decision.
Read Also: Soderstrom Skin Cancer Screening
Treatment Options By Stage
While various considerations help determine the best approach to treatment, the stage of MCC is often the most important factor.Below, learn about the stages and the recommended treatments.
MCC without obvious spread
After having an SLNB to check whether the cancer has spread, most people undergo a wide local excision. This procedure removes the cancerous cells from the skin.
If MCC is on the face or other sensitive areas, a person may instead undergo Mohs micrographic surgery, which helps preserve more healthy skin.
Some people may also, or alternately, undergo radiation therapy, especially targeting the surrounding lymph nodes.
MCC with spread
This can be very difficult to cure. A person may need:
- surgery to remove affected cells
- radiation therapy
- immunotherapy drugs, such as pembrolizumab or avelumab
Recurring MCC
When MCC comes back, doctors often recommend a combination of:
- surgery to remove more of the affected tissue, possibly with surrounding lymph nodes
- radiation therapy
- chemotherapy
- immunotherapy drugs, such as Keytruda or Bavencio
Recurring MCC can be very difficult to treat, especially if it comes back in different areas. If this happens, doctors tend to focus on reducing symptoms, not curing the disease.
Some people also try complementary therapies for MCC, including:
- naturopathic medicine
Radiation For Merkel Cell Carcinoma
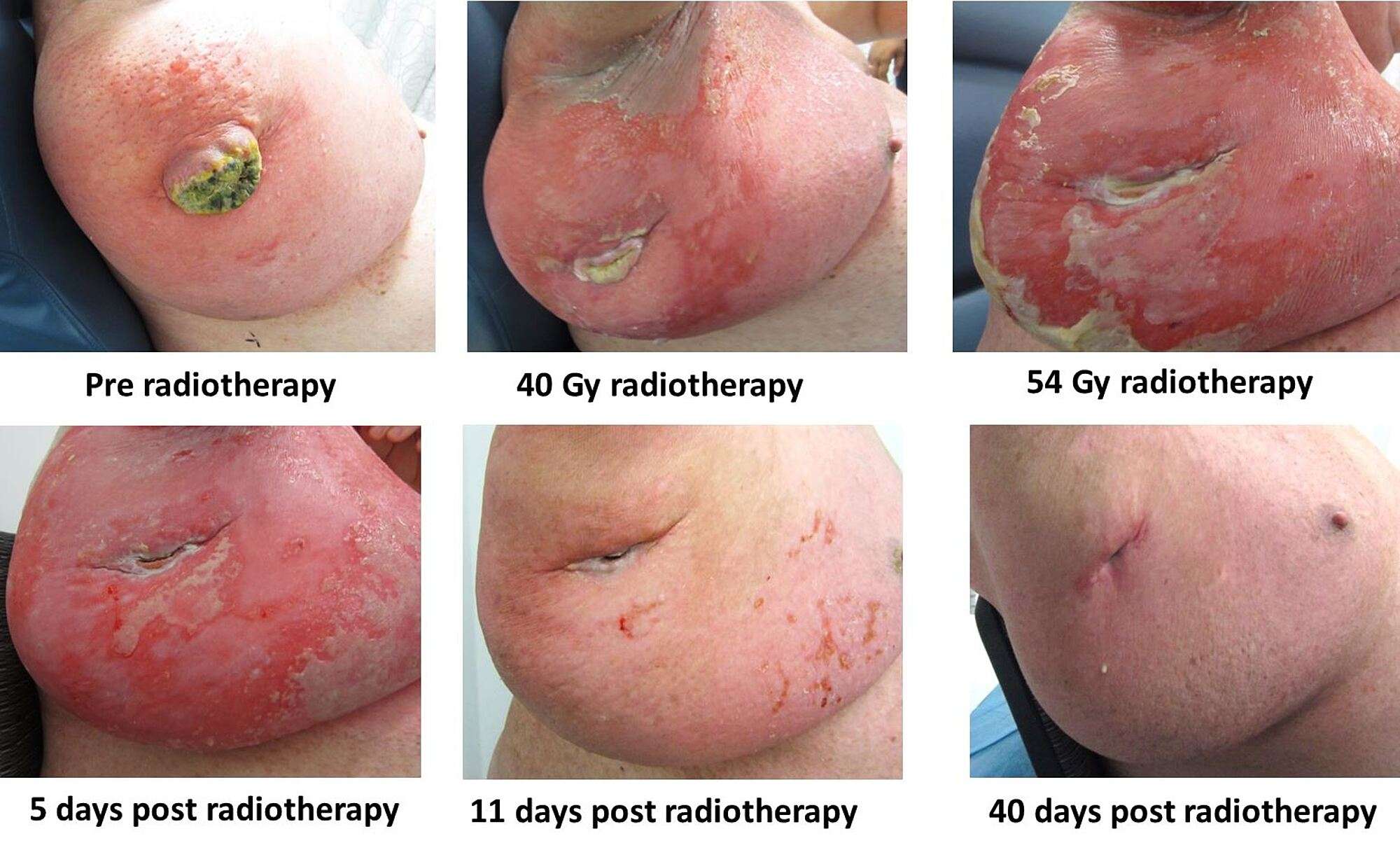
Our experienced radiation oncologists partner with our dermatologic oncologists to deliver the latest radiation therapy high-energy rays or special radioactive sources that damage cancer cells and stop them from growing.
-
External Beam Radiation Therapy: External beam radiation uses a large machine to aim high-energy radiation beams at your cancer from outside your body. Our specialists treat as small an area as possible to avoid causing unnecessary damage to your healthy tissue.
-
High-Dose Rate Brachytherapy: This is a method of brachytherapy that delivers radiation to the lesion at the surface of the skin. In HDR brachytherapy, a radioactive wire is attached to a highly specialized robotic machine. The robotic machine carefully guides the delivery of the radiation directly into the tumor and removes the wire after the session.
-
Total Skin Electron Therapy: Rotational Total Skin Electron Therapy and static Total Skin Electron Irradiation are advanced approaches to treating this skin disorder. During TSEI, a patient’s entire skin is treated with low-energy electrons. This radiation penetrates very superficially, protecting internal organs and other structures.
Merkel Cell Carcinoma can respond well to radiation therapy, and we may recommend it when:
Recommended Reading: Squamous Cell Carcinoma Skin Metastasis
How Can I Help Prevent Merkel Cell Cancer
Early diagnosis and treatment of Merkel cell cancer is important to prevent it from spreading. Be aware of any lumps, growths, moles, or other abnormal areas on your skin. Watch for new spots or areas that are changing. This can include skin marks that grow larger, bleed, crust, or itch. Your healthcare provider may recommend you do a skin self-exam once a month or more. See your healthcare provider if you have any new or changing marks on your skin.
What Is Merkel Cell Carcinoma
MCC is an uncommon form of skin cancer. It begins in the epidermis, the top layer of the skin, near nerve endings. MCC usually progresses quickly. It can be difficult to treat if it metastasizes beyond the skin.
MCC shows up as a discolored bump or lump on an area of skin frequently exposed to the sun. It is also called trabecular carcinoma or neuroendocrine carcinoma of the skin.
Recommended Reading: Does Amelanotic Melanoma Blanch When Pressed
Current Treatment Options In Mcc
The choice of treatment depends on the tumor characteristics, such as the stage at presentation, regional lymph node involvement, location of the disease, comorbidities and performance status of the patient . Current treatment strategies that incorporate surgery and/or radiotherapy achieve high rates of locoregional control, but they are commonly associated with the development of distant metastases. Chemotherapy has demonstrated limited efficacy in the treatment of metastatic disease, but advances in immunotherapeutics are likely to have a major impact on the management and outcomes of MCC. As treatment options for the loco-regional form have already been standardized, there are no therapeutic agents specifically approved for the treatment of the advanced form of MCC, and treatment choice is often based on data available from retrospective series and prospective randomized controlled trials . In the metastatic setting, chemotherapy has limited efficacy, but advances in immunotherapeutics are likely to have a major impact on the management and outcomes of MCC.
What Is Merkel Cellcarcinoma Of The Skin
Merkel cell carcinoma of the skin is a rare form of skin cancer. It may be very aggressive and often metastasises to other parts of the body. It has also been called Toker tumour, cutaneousneuroendocrine carcinoma, trabecular cell carcinoma, and primary small-cell carcinoma of the skin.
Merkel cell carcinoma
Also Check: What Is The Most Aggressive Skin Cancer
What Causes Merkel Cell Cancer
Experts arent exactly sure what causes Merkel cell cancer. But it occurs when Merkel cells in the body change and grow out of control. These abnormal cells may grow to form a lump or mass called a tumor. If the tumor is cancerous, it can grow into nearby areas. It can even spread to other parts of the body .
What Are The Risk Factors For Merkel Cell Carcinoma
The known risk factors for Merkel cell carcinoma include:
-
Exposure to UV rays. Like many other types of skin cancer, the risk of Merkel cell carcinoma is higher in people who have been exposed to a lot of UV rays from the sun or from other sources like tanning beds. People who are treated for psoriasis with UV rays may also have a higher risk.
-
Weakened immune system. People with weakened immune systems, such as people who have had an organ transplant, are at increased risk for this cancer.
-
Light-colored skin. People with lighter skin are at higher risk.
-
Older age. People older than 50 are more likely to get this cancer.
-
Being male. Men are more likely to get Merkel cell carcinoma.
Researchers have found that Merkel cell carcinoma almost always shows infection with a virus known as Merkel cell polyomavirus . It is not known how the virus may contribute to the growth of this cancer. Most people are infected with this virus at some point. But very few people develop this cancer.
Read Also: Does Skin Cancer Make You Lose Hair
How Dangerous Is Mcc
While MCC is about three to five times more likely to be deadly than melanoma, with early detection, MCC can be treated successfully. If you think you might have MCC, see your doctor. Treatment becomes increasingly difficult once the disease has spread, but new options are now available. Thanks to advances in the field of immunotherapy, MCC survival rates are improving.
How Is Merkel Cell Carcinoma Treated
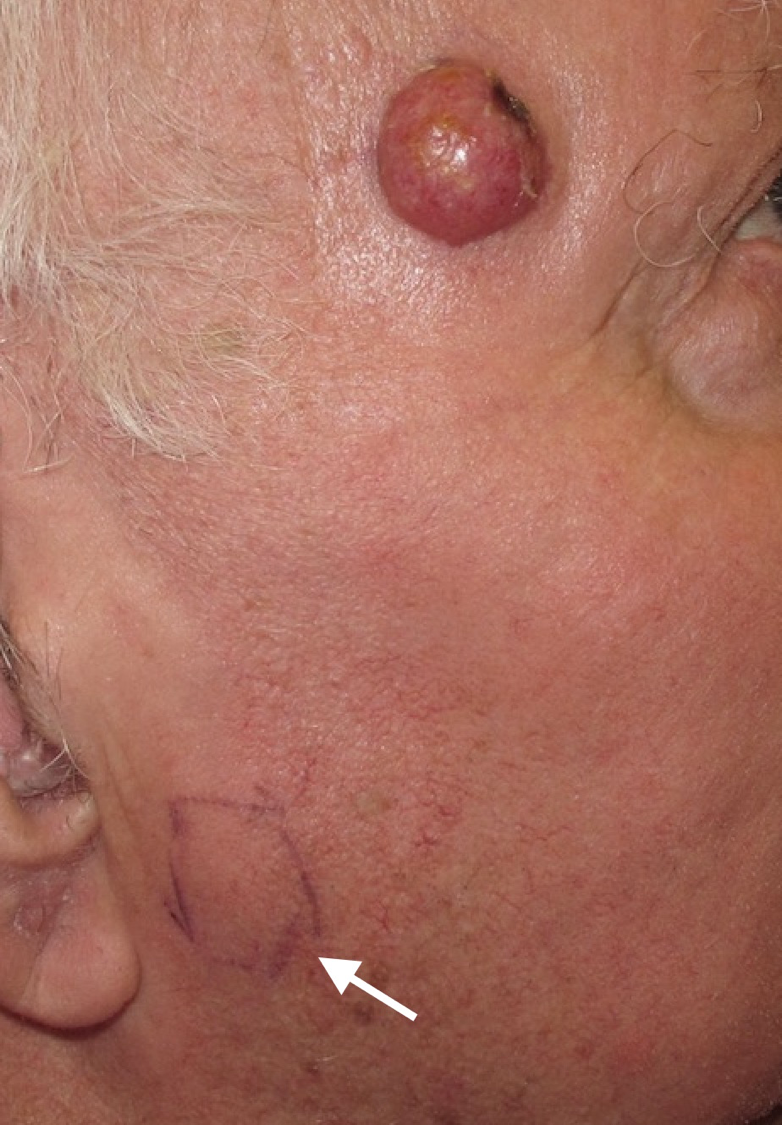
Your medical team will consider the stage of the cancer and your health when creating your treatment plan, which may include one or more of the following:
Surgery: This treatment is often recommended for MCC in stage O, I, II, or III. Also called surgical removal because it seeks to remove the cancer, your team may recommend excision or Mohs.
After surgery, some patients need reconstructive surgery because MCC can grow deep. Reconstructive surgery can often be performed immediately after the surgery to remove the cancer.
To lower the risk of the cancer returning after surgery, doctors often recommend having another type of treatment. Called adjuvant therapy, this helps to kill any remaining cancer cells. Radiation therapy is often the treatment given after surgery for MCC.
Radiation treatments: Some studies show that radiation treatments reduce the risk of MCC returning. Most patients begin radiation treatments within 4 weeks of having surgery.
If you have MCC in stage I, II, or III that surgery cannot remove, you may receive only radiation treatments.
Observation: If you are in poor health and the MCC is growing slowly, your medical team may recommend this approach. Observation means that doctors will watch rather than treat you. If the cancer starts to grow quickly, treatment will be considered.
-
Radiation
-
Chemotherapy
Immunotherapy: When MCC spreads, doctors often recommend this type of treatment. These medications can target and destroy cancer cells.
Also Check: Etiology Of Basal Cell Carcinoma