How To Check For Skin Cancer
This article was medically reviewed by . Dr. Litza is a board certified Family Medicine Physician in Wisconsin. She is a practicing Physician and taught as a Clinical Professor for 13 years, after receiving her MD from the University of Wisconsin-Madison School of Medicine and Public Health in 1998.There are 15 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been viewed 786,826 times.
Early detection of skin cancer is important and can be lifesaving, especially for certain types of skin cancer such as melanoma and squamous cell carcinoma. It is estimated that 76,380 new cases of melanoma will be diagnosed in 2016 and over 13,000 will die from the skin cancer.XTrustworthy SourceAmerican Cancer SocietyNonprofit devoted to promoting cancer research, education, and supportGo to source Given that timing is so crucial to diagnosing and treating skin cancer, you should follow a few simple steps to learn how to detect skin cancer on your skin.
What Should I Look For When Examining My Moles
Examine your skin with a mirror. Pay close attention to areas of your skin that are often exposed to the sun, such as the hands, arms, chest, and head.
The following ABCDEs are important signs of moles that could be skin cancer. If a mole displays any of the signs listed below, have it checked immediately by a dermatologist:
- Asymmetry: One half of the mole does not match the other half
- Border: The border or edges of the mole are ragged, blurred, or irregular
- Color: The mole has different colors or it has shades of tan, brown, black, blue, white, or red
- Diameter: The diameter of the mole is larger than the eraser of a pencil
- Evolving: The mole appears different from others and/or changing in size, color, shape
Keep in mind that some melanomas may be smaller or not fit other characteristics.You should always be suspicious of a new mole. If you do notice a new mole, see your dermatologist as soon as possible. They will examine the mole and take a skin biopsy . If it’s skin cancer, a biopsy can show how deeply it has penetrated the skin. Your dermatologist needs this information to decide how to treat the mole.
The most common location for melanoma in men is the back in women, it is the lower leg.
Continued
Biopsies Of Melanoma That May Have Spread
Biopsies of areas other than the skin may be needed in some cases. For example, if melanoma has already been diagnosed on the skin, nearby lymph nodes may be biopsied to see if the cancer has spread to them.
Rarely, biopsies may be needed to figure out what type of cancer someone has. For example, some melanomas can spread so quickly that they reach the lymph nodes, lungs, brain, or other areas while the original skin melanoma is still very small. Sometimes these tumors are found with imaging tests or other exams even before the melanoma on the skin is discovered. In other cases, they may be found long after a skin melanoma has been removed, so its not clear if its the same cancer.
In still other cases, melanoma may be found somewhere in the body without ever finding a spot on the skin. This may be because some skin lesions go away on their own after some of their cells have spread to other parts of the body. Melanoma can also start in internal organs, but this is very rare, and if melanoma has spread widely throughout the body, it may not be possible to tell exactly where it started.
When melanoma has spread to other organs, it can sometimes be confused with a cancer starting in that organ. For example, melanoma that has spread to the lung might be confused with a primary lung cancer .
Biopsies of suspicious areas inside the body often are more involved than those used to sample the skin.
Also Check: Etiology Of Skin Cancer
The Risks The Causes What You Can Do
Skin cancers like melanoma have damaged DNA in skin cells that lead to uncontrolled growth of these cells. Ultraviolet rays from the sun or tanning beds damage DNA in your skin cells. Your immune system repairs some of this damage but not all. Over time, the remaining DNA damage can lead to mutations that cause skin cancer. Many other factors also play a role in increasing the risk for melanoma, including genetics , skin type or color, hair color, freckling and number of moles on the body.
Understanding what causes melanoma and whether youre at high risk of developing the disease can help you prevent it or detect it early when it is easiest to treat and cure.
These factors increase your melanoma risk:
- Unprotected or excessive UV exposure from the sun or indoor tanning.
- Weakened immune system due to a medical condition or medications.
- Many moles: The more moles you have on your body, the higher your risk for melanoma. Also, having large moles , or any atypical moles, increases the risk for melanoma.
- Fair skin: Melanoma occurs more frequently in people with fair skin, light eyes and light or red hair.
- Skin cancer history: People who have already had melanoma or nonmelanoma skin cancers run a greater risk of developing melanoma in the future.
- Genetics: Melanoma can run in families one in every 10 patients has a family member who also has had the disease.
Melanoma Can Be Tricky
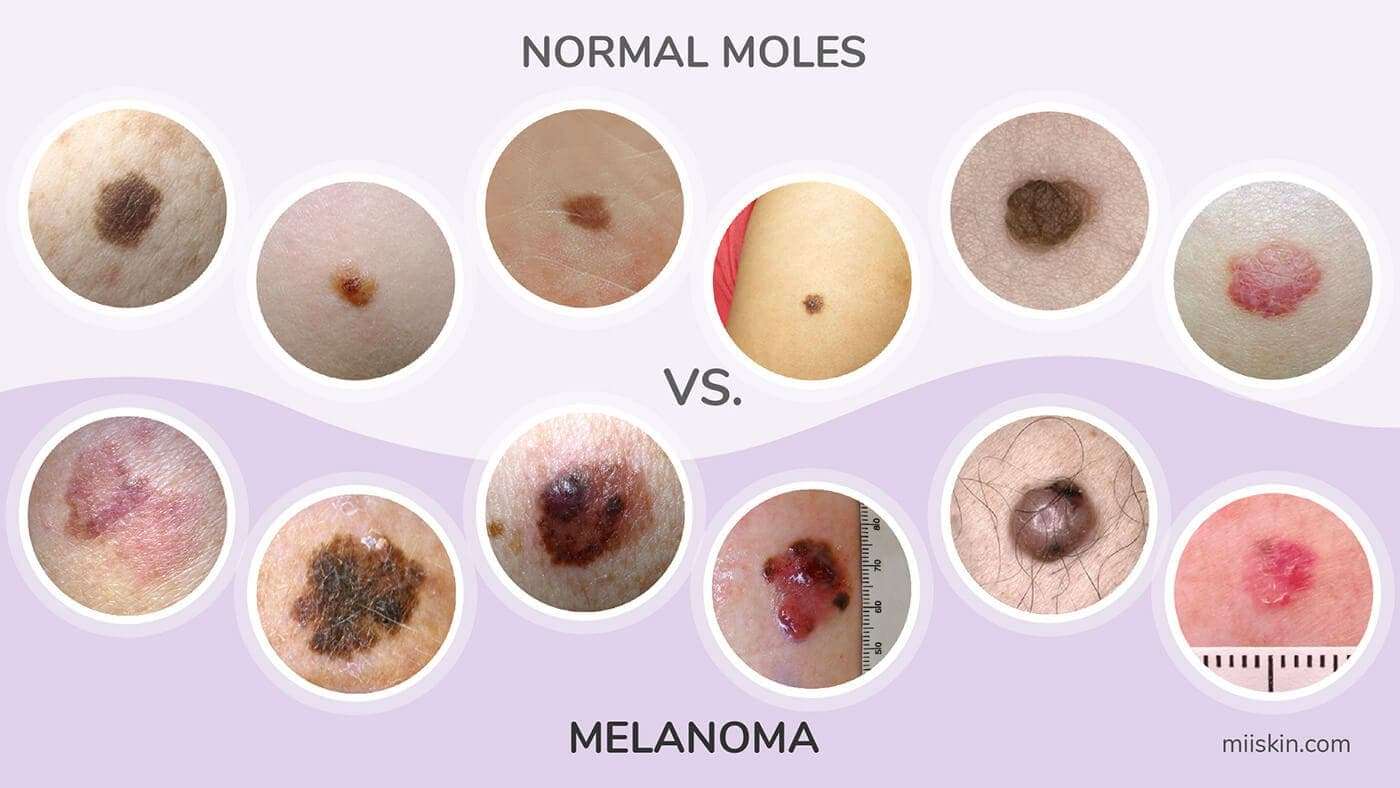
Identifying a potential skin cancer is not easy, and not all melanomas follow the rules. Melanomas come in many forms and may display none of the typical warning signs.
Its also important to note that about 20 to 30 percent of melanomas develop in existing moles, while 70 to 80 percent arise on seemingly normal skin.
Amelanotic melanomas are missing the dark pigment melanin that gives most moles their color. Amelanotic melanomas may be pinkish, reddish, white, the color of your skin or even clear and colorless, making them difficult to recognize.
Acral lentiginous melanoma, the most common form of melanoma found in people of color, often appears in hard-to-spot places, including under the fingernails or toenails, on the palms of the hands or soles of the feet.
The takeaway: Be watchful for any new mole or freckle that arises on your skin, a sore or spot that does not heal, any existing mole that starts changing or any spot, mole or lesion that looks unusual.
Acral lentiginous melanoma is the most common melanoma found in people of color.
Don’t Miss: Invasive Ductal Breast Cancer Prognosis
Medical History And Physical Exam
Usually the first step your doctor takes is to ask about your symptoms, such as when the mark on the skin first appeared, if it has changed in size or appearance, and if it has been painful, itchy, or bleeding. You may also be asked about your possible risk factors for melanoma skin cancer, such as your history of tanning and sunburns, and if you or anyone in your family has had melanoma or other skin cancers.
During the physical exam, your doctor will note the size, shape, color, and texture of the area in question, and whether it is bleeding, oozing, or crusting. The rest of your body may be checked for moles and other spots that could be related to skin cancer .
The doctor may also feel the lymph nodes under the skin in the neck, underarm, or groin near the abnormal area. When melanoma spreads, it often goes to nearby lymph nodes first, making them larger.
If you are being seen by your primary doctor and melanoma is suspected, you may be referred to a dermatologist, a doctor who specializes in skin diseases, who will look at the area more closely.
Along with a standard physical exam, many dermatologists use a technique called dermoscopy to see spots on the skin more clearly. The doctor uses a dermatoscope, which is a special magnifying lens and light source held near the skin. Sometimes a thin layer of alcohol or oil is used with this instrument. The doctor may take a digital photo of the spot.
Risk Of Further Melanomas
Most people treated for early melanoma do not have further trouble with the disease. However, when there is a chance that the melanoma may have spread to other parts of your body, you will need regular check-ups. Your doctor will decide how often you will need check-ups everyone is different. They will become less frequent if you have no further problems. After treatment for melanoma it is important to limit exposure to the sun’s UV radiation. As biological family members usually share similar traits, your family members may also have an increased risk of developing melanoma and other skin cancers. They can reduce their risk by spending less time in the sun and using a combination of sun protection measures during sun protection times. It is important to monitor your skin regularly and if you notice any changes in your skin, or enlarged lymph glands near to where you had the cancer, see your specialist as soon as possible.
Read Also: Stage Iii Melanoma Prognosis
Complementary And Alternative Treatments
It’s common for people with cancer to seek out complementary or alternative treatments. When used alongside your conventional cancer treatment, some of these therapies can make you feel better and improve your quality of life. Others may not be so helpful and in some cases may be harmful. It is important to tell all your healthcare professionals about any complementary medicines you are taking. Never stop taking your conventional treatment without consulting your doctor first.All treatments can have side effects. These days, new treatments are available that can help to make many side effects much less severe than they were in the past.
Security Of Personal Information
AMRF regards the security of personal information as a priority and takes a number of precautions to protect peoples personal information from loss, misuse, unauthorised access, modification or disclosure. Specific security precautions are in place for processing online payments through payment gateway providers Stripe and PayPal which include the use of encrypted links, dedicated private connections and Secure Sockets Layer encryption. However, the Internet is not a secure environment and although all care is taken, we cannot guarantee the security of information people provide to us via electronic means such as email.
If people become aware of any inaccuracy in the personal information, we hold about themselves, they are encouraged to contact AMRF so we can update any personal information we hold.
Don’t Miss: Ductal Breast Cancer Survival Rates
When Should I Call My Doctor
You should have a skin examination by a doctor if you have any of the following:
- A personal history of skin cancer or atypical moles .
- A family history of skin cancer.
- A history of intense sun exposure as a young person and painful or blistering sunburns.
- New or numerous large moles.
- A mole that changes in size, color or shape.
- Any mole that itches, bleeds or is tender.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Receiving a diagnosis of melanoma can be scary. Watch your skin and moles for any changes and seeing your doctor regularly for skin examinations, especially if youre fair-skinned, will give you the best chances for catching melanoma early when its most treatable.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 06/21/2021.
References
How To Perform A Self
1. Examine your face
Especially your nose, lips, mouth and ears front and back. Use one or both mirrors to get a clear view.
2. Inspect your scalp
Thoroughly inspect your scalp, using a blow-dryer and mirror to expose each section to view. Get a friend or family member to help, if you can.
3. Check your hands
Palms and backs, between the fingers and under the fingernails. Continue up the wrists to examine both the front and back of your forearms.
4. Scan your arms
Standing in front of the full-length mirror, begin at the elbows and scan all sides of your upper arms. Dont forget the underarms.
5. Inspect your torso
You May Like: What Stage Is Invasive Lobular Carcinoma
Can I Lower My Risk Of The Melanoma Progressing Or Coming Back
If you have melanoma, you probably want to know if there are things you can do that might lower your risk of the cancer coming back, or of getting a new skin cancer.
At this time, not enough is known about melanoma to say for sure if there are things you can do that will be helpful. We do know that people who have had melanoma are at higher risk for developing another melanoma or other type of skin cancer. Because of this, its very important to limit your exposure to UV rays and to continue to examine your skin every month for signs of melanoma coming back or possible new skin cancers. Skin cancers that are found early are typically much easier to treat than those found at a later stage.
Adopting healthy behaviors such as not smoking, eating well, being active, and staying at a healthy weight might help as well, but no one knows for sure. However, we do know that these types of changes can have positive effects on your health that can extend beyond your risk of melanoma or other cancers.
How To Spot Skin Cancer
Skin cancer is by far the most common type of cancer. If you know what to look for, you can spot warning signs of skin cancer early. Finding it early, when its small and has not spread, makes skin cancer much easier to treat.
Some doctors and other health care professionals include skin exams as part of routine health check-ups. Many doctors also recommend that you check your own skin about once a month. Look at your skin in a well-lit room in front of a full-length mirror. Use a hand-held mirror to look at areas that are hard to see.
Use the ABCDE rule to look for some of the common signs of melanoma, one of the deadliest forms of skin cancer:
AsymmetryOne part of a mole or birthmark doesnt match the other.
BorderThe edges are irregular, ragged, notched, or blurred.
ColorThe color is not the same all over and may include shades of brown or black, sometimes with patches of pink, red, white, or blue.
DiameterThe spot is larger than ¼ inch across about the size of a pencil eraser although melanomas can sometimes be smaller than this.
EvolvingThe mole is changing in size, shape, or color.
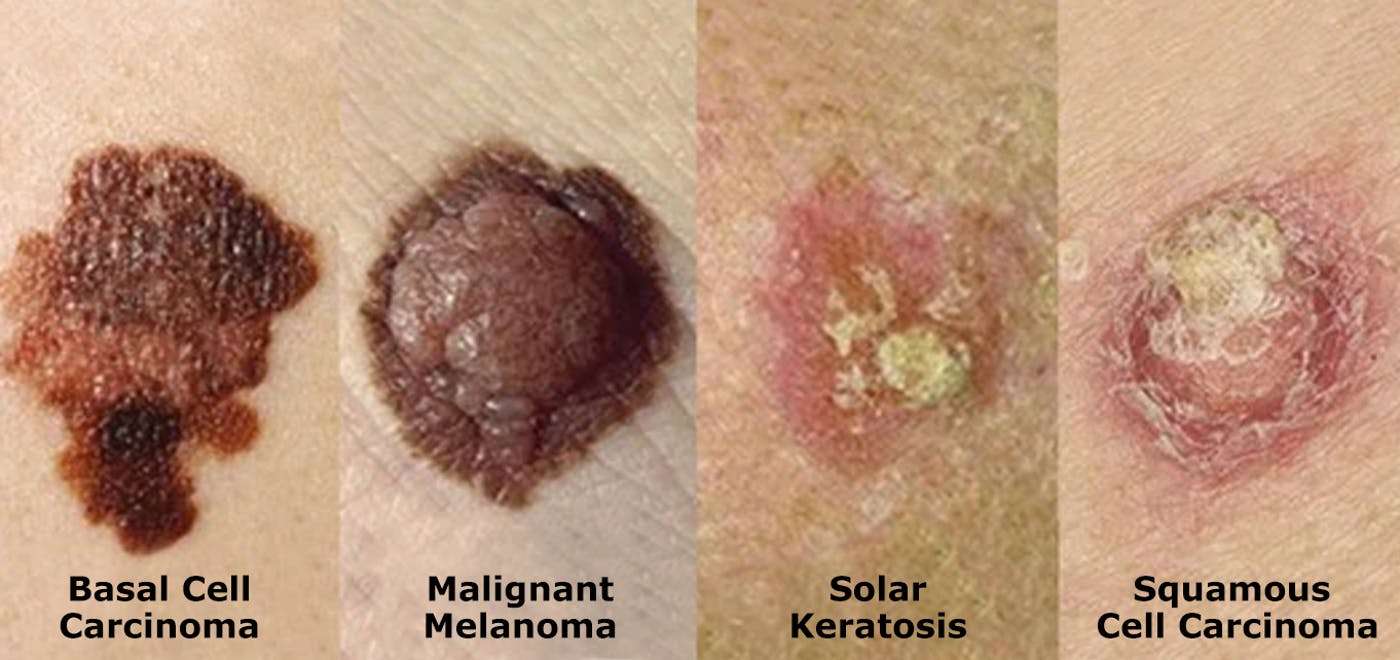
Basal and squamous cell skin cancers are more common than melanomas, but they are usually very treatable.
Both basal cell carcinomas and squamous cell carcinomas, or cancers, usually grow on parts of the body that get the most sun, such as the face, head, and neck. But they can show up anywhere.
Basal cell carcinomas: what to look for:
Squamous cell carcinomas: what to look for:
Read Also: What Is The Survival Rate For Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Ask Your Doctor For A Survivorship Care Plan
Talk with your doctor about developing a survivorship care plan for you. This plan might include:
- A suggested schedule for follow-up exams and tests
- A schedule for other tests you might need in the future, such as early detection tests for other types of cancer, or tests to look for long-term health effects from your cancer or its treatment
- A list of possible late- or long-term side effects from your treatment, including what to watch for and when you should contact your doctor
- Diet and physical activity suggestions
How Is Melanoma Treated
Your melanoma treatment will depend on the stage of the melanoma and your general health.
Surgery is usually the main treatment for melanoma. The procedure involves cutting out the cancer and some of the normal skin surrounding it. The amount of healthy skin removed will depend on the size and location of the skin cancer. Typically, surgical excision of melanoma can be performed under local anesthesia in the dermatologist’s office. More advanced cases may require other types of treatment in addition to or instead of surgery.
Treatments for melanoma:
- Melanoma Surgery: In the early stages, surgery has a high probability of being able to cure your melanoma. Usually performed in an office, a dermatologist numbs the skin with a local anesthetic and removes the melanoma and margins .
- Lymphadenectomy: In cases where melanoma has spread, removal of the lymph nodes near the primary diagnosis site may be required. This can prevent the spread to other areas of your body.
- Metastasectomy: Metastasectomy is used to remove small melanoma bits from organs.
- Targeted cancer therapy: In this treatment option, drugs are used to attack specific cancer cells. This targeted approach goes after cancer cells, leaving healthy cells untouched.
- Radiation Therapy: Radiation therapy includes treatments with high-energy rays to attack cancer cells and shrink tumors.
- Immunotherapy: immunotherapy stimulates your own immune system to help fight the cancer.
You May Like: Can You Die From Basal Cell Skin Cancer
How To Do A Skin Self
You dont need x-rays or blood tests to find skin cancer early just your eyes and a mirror. If you have skin cancer, finding it early is the best way to make sure it can be treated successfully.
Although the American Cancer Society does not have guidelines for the early detection of skin cancer, many doctors recommend checking your own skin regularly, typically once a month.
Regular skin self-exams are especially important for people who are at higher risk of skin cancer, such as people with reduced immunity, people who have had skin cancer before, and people with a strong family history of skin cancer. Talk to your doctor about how often you should examine your skin.
A skin self-exam is best done in a well-lit room in front of a full-length mirror. You can use a hand-held mirror to look at areas that are hard to see, such as the backs of your thighs. A spouse, partner, or close friend or family member may be able to help you with these exams, especially for those hard-to-see areas like your back or scalp.
The first time you examine your skin, spend time carefully going over the entire surface. Learn the pattern of moles, blemishes, freckles, and other marks on your skin so that youll notice any changes next time. Be sure to show your doctor any areas that concern you.
Follow these step-by-step instructions to examine your skin: