Rarer Types Of Non Melanoma Skin Cancer
There are other less common types of skin cancer. These include:
- Merkel cell carcinoma
These are all treated differently from basal cell and squamous cell skin cancers.
Merkel cell carcinoma
Merkel cell carcinoma is very rare. Treatment is with surgery or radiotherapy, or both. This usually works well, but sometimes the cancer can come back in the same place. And sometimes it spreads to nearby lymph nodes.
Sebaceous gland cancer
Sebaceous gland cancer is another rare type of skin cancer affecting the glands that produce the skinâs natural oils. Treatment is usually surgery for this type of cancer.
Kaposiâs sarcoma
Kaposis sarcoma is a rare condition. Itâs often associated with HIV but also occurs in people who donât have HIV. Itâs a cancer that starts in the cells that form the lining of lymph nodes and the lining of blood vessels in the skin. Treatment is surgery or radiotherapy, and sometimes chemotherapy.
T cell lymphoma of the skin
T cell lymphoma of the skin can also be called primary cutaneous lymphoma. Itâs a type of non Hodgkin lymphoma. There are a number of different types of treatment for this type of cancer.
Prevention Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
Because basal cell carcinoma is often caused by sun exposure, people can help prevent this cancer by doing the following:
-
Avoiding the sun: For example, seeking shade, minimizing outdoor activities between 10 AM and 4 PM , and avoiding sunbathing and the use of tanning beds
-
Wearing protective clothing: For example, long-sleeved shirts, pants, and broad-brimmed hats
-
Using sunscreen: At least sun protection factor 30 with UVA and UVB protection used as directed and reapplied every 2 hours and after swimming or sweating but not used to prolong sun exposure
In addition, any skin change that lasts for more than a few weeks should be evaluated by a doctor.
Painful Skin Lesions May Signal Squamous Cell Carcinoma
When dermatology patients report painful skin lesions, their doctors may want to look for squamous cell carcinoma, according to the latest research findings from Wake Forest Baptist Medical Center.
Gil Yosipovitch, M.D., professor of dermatology at Wake Forest Baptist Medical Center, has conducted the first study of its kind to assess the prevalence of pain related to common skin cancers. Because there are nearly four million new cases of non-melanoma skin cancers diagnosed each year, Yosipovitch said there was a need to look at the prevalence rates of common symptoms, including pain and itch, associated with the two most common types of skin cancer – basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma .
“Our findings reveal that pain and itch are common symptoms of non-melanoma skin cancers,” Yosipovitch said. “To our knowledge, this is the first study to assess the prevalence of pain and itch and their intensities in non-melanoma skin cancers.”
Yosipovitch discussed his findings in a letter to the Archives of Dermatology, a Journal of American Medicine Association network, publishing online Dec. 17.
Data for the study was collected over a nine-month period from 478 patients treated at Wake Forest Baptist who had either basal cell carcinoma or squamous cell carcinoma . A total of 576 biopsy-proven NMSCs were involved. Patients rated their pain and itch intensity on a visual analog scale from 0 to 10 .
Also Check: How Long For Squamous Cell Carcinoma To Spread
What Should I Do If I Think I Have A Basal Cell Carcinoma
If you notice a change to or growth on your skin, make an appointment to see your doctor straight away. Your doctor will assess the size, location and look of the growth. They will also ask you how long you have had it, whether it bleeds or itches, etc.
If your doctor thinks the growth may be cancer, they may take a small sample of tissue . The tissue sample will be sent to a laboratory and examined under a microscope. Your doctor will let you know whether the sample showed any cancer cells, and will recommend appropriate treatment if necessary.
Recommended Reading: How Quickly Can Melanoma Metastasis
When To Visit A Podiatrist
Podiatrists are uniquely trained as lower extremity specialists to recognize and treat abnormal conditions on the skin of the lower legs and feet. Skin cancers affecting the feet may have a very different appearance from those arising on the rest of the body. For this reason, a podiatrist’s knowledge and clinical training is of extreme importance for patients for the early detection of both benign and malignant skin tumors.
Learn the ABCDs of melanoma. If you notice a mole, bump, or patch on the skin that meets any of the following criteria, see a podiatrist immediately:
- Asymmetry – If the lesion is divided in half, the sides don’t match.
- Borders – Borders look scalloped, uneven, or ragged.
- Color – There may be more than one color. These colors may have an uneven distribution.
- Diameter The lesion is wider than a pencil eraser .
To detect other types of skin cancer, look for spontaneous ulcers and non-healing sores, bumps that crack or bleed, nodules with rolled or donut-shaped edges, or scaly areas.
Also Check: What Happens If I Have Melanoma
Is Mohs Right For Me
Mohs surgery is the gold standard for treating many basal cell carcinomas and squamous cell carcinomas , including those in cosmetically and functionally important areas around the eyes, nose, lips, ears, scalp, fingers, toes or genitals. Mohs is also recommended for BCCs or SCCs that are large, aggressive or growing rapidly, that have indistinct edges, or have recurred after previous treatment. Some surgeons are also successfully using Mohs surgery on certain cases of melanoma.
Staging For Merkel Cell Cancer
Doctors use the TNM system to describe the stage of Merkel cell cancer. Doctors use the results from diagnostic tests and scans to answer these questions:
-
Tumor : How large is the primary tumor? Where is it located?
-
Node : Has the tumor spread to the lymph nodes? If so, where and how many?
-
Metastasis : Has the cancer spread to other parts of the body? If so, where and how much?
The results are combined to determine the stage of Merkel cell cancer for each person.
There are 5 stages: stage 0 and stages I through IV . The stage provides a common way of describing the cancer, so doctors can work together to plan the best treatments.
Stage 0: This is called carcinoma in situ. Cancer cells are found only in the top layers of the skin. The cancer does not involve the lymph nodes, and it has not spread.
Stage I: The primary tumor is 2 centimeters or smaller at its widest part. The cancer has not spread to the lymph nodes or to other parts of the body.
Stage IIA: The tumor is larger than 2 cm and has not spread to the lymph nodes or other parts of the body.
Stage IIB: The tumor has grown into nearby tissues, such as muscles, cartilage, or bone. It has not spread to the lymph nodes or elsewhere in the body.
Stage III: The cancer has spread to the lymph nodes. The tumor can be any size and may have spread to nearby bone, muscle, connective tissue, or cartilage.
Stage IV: The tumor has spread to distant parts of the body, such as the liver, lung, bone, or brain.
Recommended Reading: How Do You Know If Melanoma Has Spread
My First Squamous Cell Skin Cancer
The morning of surgery, my doctor had me point out everything to him that needed to be removed. He compared it with the body map he had made in his office to make sure we would be getting everything.
As I pointed out the areas, he circled each one on me with a purple marker. The picture had 23 purple circles on my body I looked pretty funny. He counted the circles and told me we had ended up with one extra purple mark. I explained that the place on the tip of my nose had just shown up two days prior. He assumed that one would be squamous cell because they tend to show up rather quickly. And, unfortunately, pathology during surgery confirmed he was correct. This was my first squamous cell skin cancer.
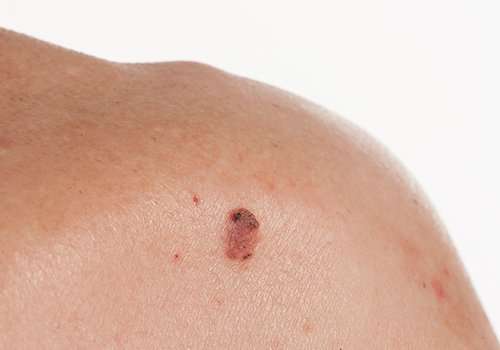
Basal Cell And Squamous Cell Carcinomasigns And Symptoms
The most common warning sign of skin cancer is a change on the skin, especially a new growth or a sore that doesn’t heal. The cancer may start as a small, smooth, shiny, pale or waxy lump. It also may appear as a firm red lump. Sometimes, the lump bleeds or develops a crust.
Both basal and squamous cell cancers are found mainly on areas of the skin that are exposed to the sun the head, face, neck, hands and arms. But skin cancer can occur anywhere.
An early warning sign of skin cancer is the development of an actinic keratosis, a precancerous skin lesion caused by chronic sun exposure. These lesions are typically pink or red in color and rough or scaly to the touch. They occur on sun-exposed areas of the skin such as the face, scalp, ears, backs of hands or forearms.
Actinic keratoses may start as small, red, flat spots but grow larger and become scaly or thick, if untreated. Sometimes they’re easier to feel than to see. There may be multiple lesions next to each other.
Early treatment of actinic keratoses may prevent them from developing into cancer. These precancerous lesions affect more than 10 million Americans. People with one actinic keratosis usually develop more. Up to 1 percent of these lesions can develop into a squamous cell cancer.
Basal cell carcinoma is the most commonly diagnosed skin cancer. In recent years, there has been an upturn in the diagnoses among young women and the rise is blamed on sunbathing and tanning salons.
- Raised, dull-red skin lesion
You May Like: Is Skin Cancer Always Visible
Lump With Small Depression
Some basal cell carcinoma lesions have small indentations in the center, similar to a canker sore. These depressions in the skin may weep and crust. The temptation to pick at a sore is normal, but it is important not to disrupt these growths and to see a doctor if they appear to grow or spread or do not heal promptly.
General Principles In Outer Nose Repair
Most of nasal skin is of the sebaceous type. Whenever possible, scar lines should be placed along relaxed skin tension lines. Aesthetic units of the nose need consideration although tumours do not respect their borders. Aging affects the nose anatomy. Characteristic symptoms are frown lines , transverse crease on the nasal root, drooping of tip of nose, and deepened nasolabial folds. Skin diseases of elderly, like rosacea and rhinophyma can interfere with surgical techniques.
The skin covering the bony parts is highly movable, while the skin over cartilage parts is thicker, tighter and bound to the cartilage. Healing by second ary intention of convex surfaces like the nose tip should be avoided since healing often is delayed and may lead to uneven scars.
You May Like: How Fast Does Squamous Cell Carcinoma Spread
Read Also: How Can You Get Skin Cancer From The Sun
There Actually Are Cases In Which Basal Cell Carcinoma Sometimes Called A Non
Youve probably read that basal cell carcinoma cant spread or doesnt spread, but does cause local destruction if not treated.
But basal cell carcinoma CAN spreadand kill.
Unlike melanomas, basal cell carcinomas usually do not metastasize but instead spread locally, says Dr. Tess Mauricio, MD, FAAD, a leading board certified dermatologist from Stanford University Medical School and CEO of MBeautyClinic.com.
However, if BCCs are allowed to spread without treatment, there could be a chance for metastasis, warns Dr. Mauricio.
What are the chances of basal cell carcinoma metastasis?
The chances, in terms of percent, have not been determined. However, check out the following:
Metastasis of basal cell carcinoma rarely occurs. Few cases have been reported in the literature.
the occurrence of BCC metastasis is exceedingly rare, with an average rate of approximately 0.03%, typically involving a large, long-standing, locally destructive, recalcitrant tumor of the head or neck.
Cutis, July 2007
To put this in more perspective, here are intriguing excerpts from DermatologyTimes .
A search of the current literature shows that only about 350 cases of metastatic BCC have been reported.
However, with 1 million new cases of BCC every year in the United States alone, Dr. Giannelli says it is very hard to believe, and highly unlikely, that these metastases do not occur more frequently than they are actually reported.
From the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology :
Treatment Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
-
Removal of the tumor
Doctors may remove the cancer in the office by scraping and burning it with an electric needle or by cutting it out. Doctors may destroy the cancer by using extreme cold .
Certain chemotherapy drugs may be applied to the skin. Photodynamic therapy , in which chemicals and a laser are applied to the skin, also may be used. Occasionally, radiation therapy is used.
A technique called Mohs microscopically controlled surgery may be required for some basal cell carcinomas that are large or regrow or occur in certain areas, such as around the nose and eyes.
People whose cancer has spread to nearby tissues or spread to other parts of the body and who are not candidates for surgery or radiation therapy may be given the drug vismodegib or sonidegib taken by mouth.
Don’t Miss: How Common Is Renal Cell Carcinoma
What Happens During Mohs Surgery
The procedure is done in stages, all in one visit, while the patient waits between each stage. After removing a layer of tissue, the surgeon examines it under a microscope in an on-site lab. If any cancer cells remain, the surgeon knows the exact area where they are and removes another layer of tissue from that precise location, while sparing as much healthy tissue as possible. The doctor repeats this process until no cancer cells remain.
Step 1: Examination and prep
Depending on the location of your skin cancer, you may be able to wear your street clothes, or you may need to put on a hospital gown. The Mohs surgeon examines the spot where you had your biopsy and may mark it with a pen for reference. The doctor positions you for best access, which may mean sitting up or lying down. A surgical drape is placed over the area. If your skin cancer is on your face, that may mean you cant see whats happening, but the doctor talks you through it. The surgeon then injects a local anesthesia, which numbs the area completely. You stay awake throughout the procedure.
Step 2: Top layer removal
Using a scalpel, the surgeon removes a thin layer of visible cancerous tissue. Some skin cancers may be the tip of the iceberg, meaning they have roots or extensions that arent visible from the surface. The lab analysis, which comes next, will determine that. Your wound is bandaged temporarily and you can relax while the lab work begins.
Step 3: Lab analysis
Step 4: Microscopic examination
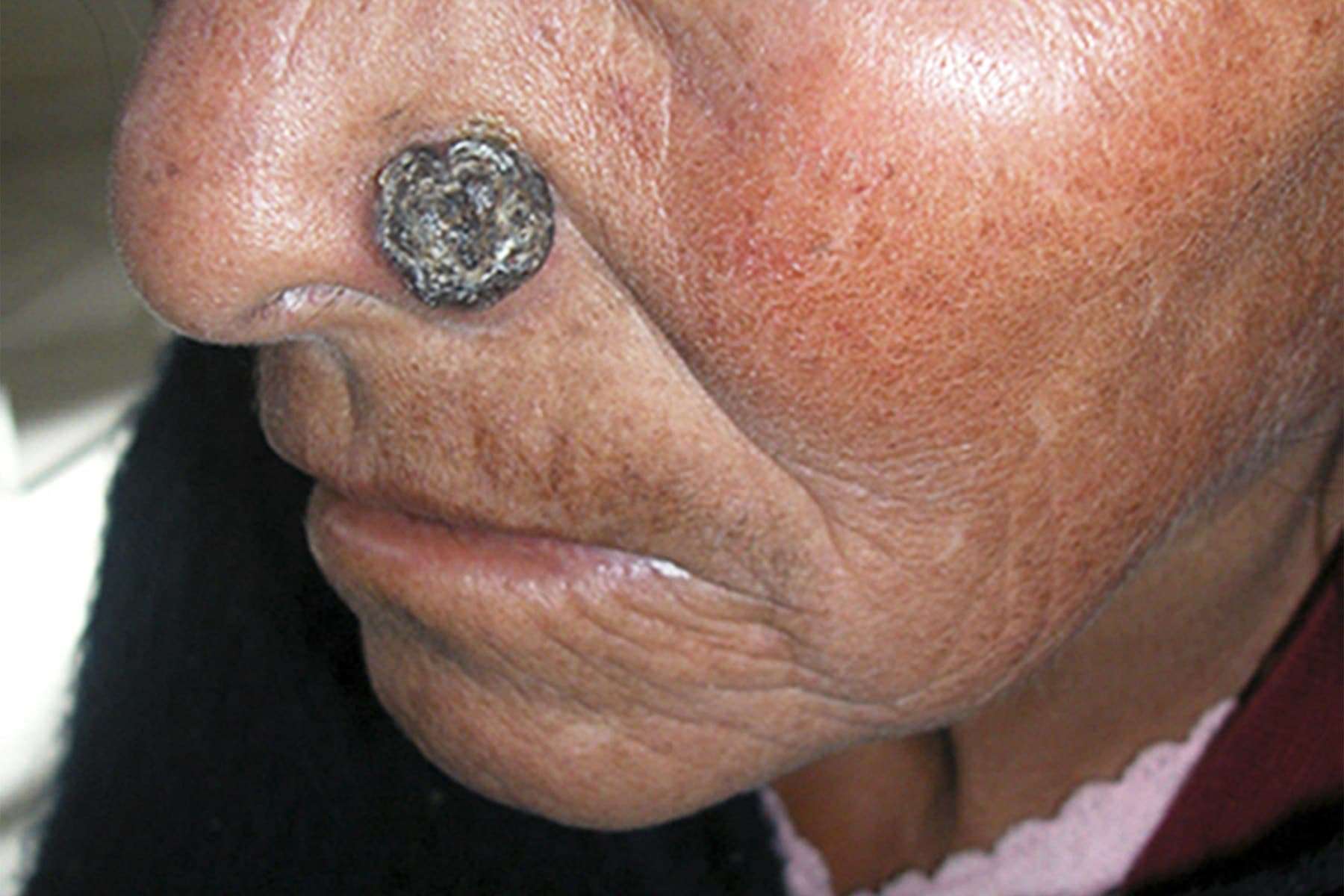
What Is Advanced Bcc
An estimated 1% of all BCC cases will progress to advanced BCC and either invade the surrounding tissue or spread to other parts of the body . This may result in debilitating effects, severe deformities and even death.
Advanced BCCs are often open lesions that may bleed, become infected, and produce unpleasant odours.
Donât Miss: How Do You Know If You Have Melanoma
Read Also: What Are The Early Stages Of Melanoma
What Is The Prognosis Of Superficial Basal Cell Carcinoma Of Skin
- In general, the prognosis of Superficial Basal Cell Carcinoma of Skin is excellent, if it is detected and treated early.
- Stage of tumor: With this lower-stage tumor, the prognosis is usually excellent with appropriate therapy
- The surgical resectability of the tumor
- Overall health of the individual: Individuals with overall excellent health have better prognosis compared to those with poor health
- Age of the individual: Older individuals generally have poorer prognosis than younger individuals
- Whether the tumor is occurring for the first time, or is a recurrent tumor. Recurring tumors have a poorer prognosis compared to tumors that do not recur
Is Basal Cell Carcinoma Serious Lets Ask Hugh Jackman
Hugh Jackman is no stranger to skin cancer. In August, 2021 the Australian actor posted an after having a second skin biopsy in two years. He urged fans to get their skin checked. A couple of notes please get skin checks often, please dont think it wont happen to you and, above all, please wear sunscreen.
Jackman is committed to raising awareness by using social media to discuss his skin cancer history. In a follow-up post, he explains If by posting about this I remind one person to go see their dermatologist, Im happy.
In 2017, the last time Jackman dealt with basal cell carcinoma , he posted a photo of himself on Instagram showing the aftermath of skin cancer surgery. He assured fans he was okay in his posts caption, thanking frequent skin checks and amazing doctors.
Basal cell carcinoma is the most common form of skin cancer, with more than 3.6 million cases diagnosed in the U.S. each year. BCC almost never spreads beyond the original tumor site though, and the cure rate after excisional surgery is above 95 percent in most body areas. So, is this form of cancer even something to worry about?
Basal cell carcinoma is not something to be taken lightly, says Deborah S. Sarnoff, MD, president of The Skin Cancer Foundation. Once youve been diagnosed with a BCC, its very likely that you will develop more over the years, leading to continuous treatment and possibly even disfiguration.
Read Also: What Does Stage 2 Melanoma Look Like