Basal Cell Carcinoma Early Stages
Basal cells are found within the skin and are responsible for producing new skin cells as old ones degenerate. Basal cell carcinoma starts with the appearance of slightly transparent bumps, but they may also show through other symptoms.
In the beginning, a basal cell carcinoma resembles a small bump, similar to a flesh-colored mole or a pimple. The abnormal growths can also look dark, shiny pink, or scaly red in some cases.
How Can I Tell If I Have Skin Cancer
¿Cómo se ve el cáncer de la piel? ¿Cómo puedo prevenir el cáncer de piel?¿Estoy en riesgo de desarrollar melanoma?Cáncer de piel en personas de colorCómo examinar sus manchasNoe Rozas comparte su
Skin cancer is actually one of the easiest cancers to find. Thats because skin cancer usually begins where you can see it.
You can get skin cancer anywhere on your skin from your scalp to the bottoms of your feet. Even if the area gets little sun, its possible for skin cancer to develop there.
You can also get skin cancer in places that may surprise you. Skin cancer can begin under a toenail or fingernail, on your genitals, inside your mouth, or on a lip.
Basal Cell And Squamous Cell Survival Rates
Because basal cell and squamous cell carcinomas are lower-risk skin cancers, theres little information on survival rates based on stage.
Both types of cancer have a very high cure rate. According to the Canadian Cancer Society, the five-year survival rate for basal cell carcinoma is 100 percent. The five-year survival rate for squamous cell carcinoma is 95 percent.
Don’t Miss: Can You Die From Basal Cell Skin Cancer
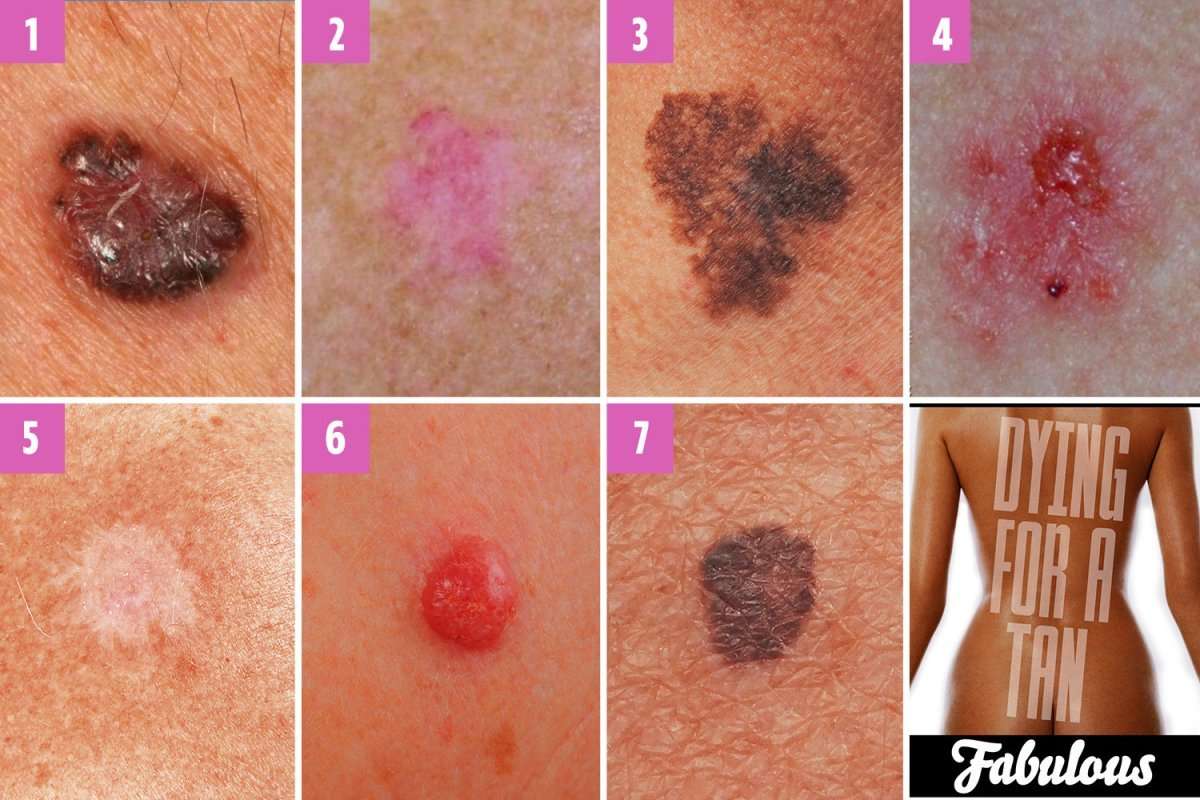
How To Spot A Bcc: Five Warning Signs
Check for BCCs where your skin is most exposed to the sun, especially the face, ears, neck, scalp, chest, shoulders and back, but remember that they can occur anywhere on the body. Frequently, two or more of these warning signs are visible in a BCC tumor.
Please note: Since not all BCCs have the same appearance, these images serve as a general reference to what basal cell carcinoma looks like.
An open sore that does not heal
A reddish patch or irritated area
A small pink growth with a slightly raised, rolled edge and a crusted indentation in the center
A shiny bump or nodule
A scar-like area that is flat white, yellow or waxy in color
Who Is Most At Risk For Skin Cancer
Although anyone can develop skin cancer, those that are most at risk for skin cancer are people who:
- Have had an organ transplant
- Tan or use tanning beds
- Get easily sunburned
- Have fair or freckled skin
- Have a family history of skin cancer
- Have blue eyes
- Take medications that suppress/weaken the immune system
People who work or spend more time outdoors have an increased risk for skin cancer, especially those in sunny climates. People with darker skin are still able to get skin cancer, but the risk is substantially lower. Organ transplant patients are up to 100 times more likely to develop squamous cell carcinoma skin cancer when compared to the general population, largely because they take medications that suppress their immune systems.
Risk factors unique to melanoma include a history of severe sunburns and an abundance of large and irregular moles.
Don’t Miss: Ductal Breast Cancer Survival Rates
What Does Skin Cancer Look Like On Your Face
Are you wondering what skin cancer looks like on your face? Is there a spot that is new or changing? For starters, let us just say kudos on paying attention! It is so vital to watch yourself for these things because early detection truly saves lives. Secondly, skin cancer has a variety of appearances so we will need to start by explaining exactly what skin cancer is and the types it can occur as.
What is Skin Cancer?Skin cancer is an abnormal growth of skin cells. It most often develops on areas of the skin exposed to the suns rays. Skin cancer affects people of all colors and races, although those with light skin who sunburn easily have a higher risk. Research has estimated that one in five Americans will develop skin cancer in their lifetime. According to the American Cancer Society, about 3.3 million basal and squamous cell skin cancers are diagnosed in America each year with an estimated 87,000+ new cases of melanoma predicted for 2020.
While rare types of skin cancer do exist, there are four main types of skin cancer:
Squamous cell carcinoma is the second most common type of skin cancer. SCC often appears as a red firm bump, scaly patch, or a sore that heals and then re-opens. SCC tends to form on skin that gets frequent sun exposure, such as the rim of the ear, face, neck, arms, chest, and back. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent this and stop SCC from spreading to other areas of the body.
What Is A Biopsy
A proper diagnosis of cancer in the skin is made possible through biopsy. We will remove a skin tissue sample and send it to a laboratory. A pathologist will then examine your samples and look for abnormal cells that could be cancerous. Through a biopsy, you can also get accurate information about the stage of skin cancer you might have.
For advanced melanoma, we request imaging tests and lymph node biopsy to see whether cancer has affected other parts of the body. Additional evaluation is made possible using any or a combination of the following methods:
- Computed tomography
- Measurement of lactate dehydrogenase levels
Read Also: What Is Large Cell Carcinoma
What Happens If You Let Skin Cancer Go Untreated
Many patients who are diagnosed with skin cancer, especially in the earliest stages, find themselves wondering whether treatment is really necessary. Skin cancer, like other forms of cancer, is serious and requires proper treatment. According to Dr. Valerie Truong of U.S. Dermatology Partners in Dallas, Plano, Sherman, and Corsicana, Texas, The visible part of skin cancer can often be like the tip of an iceberg. What you see on the surface is only a small percentage of the actual cancer. Even if the skin cancer appears to be negligible, there is always a risk that it will grow and spread. I recommend that people who suspect they have skin cancer get a skin check for an earlier diagnosis, and therefore, earlier treatment. In this blog, Dr. Truong talks more about what happens if you let skin cancer go untreated and the potential risks that may arise for skin health as well as overall health and well-being.
Basal Cell And Squamous Cell Carcinomasigns And Symptoms
The most common warning sign of skin cancer is a change on the skin, especially a new growth or a sore that doesn’t heal. The cancer may start as a small, smooth, shiny, pale or waxy lump. It also may appear as a firm red lump. Sometimes, the lump bleeds or develops a crust.
Both basal and squamous cell cancers are found mainly on areas of the skin that are exposed to the sun the head, face, neck, hands and arms. But skin cancer can occur anywhere.
An early warning sign of skin cancer is the development of an actinic keratosis, a precancerous skin lesion caused by chronic sun exposure. These lesions are typically pink or red in color and rough or scaly to the touch. They occur on sun-exposed areas of the skin such as the face, scalp, ears, backs of hands or forearms.
Actinic keratoses may start as small, red, flat spots but grow larger and become scaly or thick, if untreated. Sometimes they’re easier to feel than to see. There may be multiple lesions next to each other.
Early treatment of actinic keratoses may prevent them from developing into cancer. These precancerous lesions affect more than 10 million Americans. People with one actinic keratosis usually develop more. Up to 1 percent of these lesions can develop into a squamous cell cancer.
Basal cell carcinoma is the most commonly diagnosed skin cancer. In recent years, there has been an upturn in the diagnoses among young women and the rise is blamed on sunbathing and tanning salons.
- Raised, dull-red skin lesion
Recommended Reading: Does Amelanotic Melanoma Blanch When Pressed
Abcde Melanoma Detection Guide
A is for Asymmetry
Look for spots that lack symmetry. That is, if a line was drawn through the middle, the two sides would not match up.
B is for Border
A spot with a spreading or irregular edge .
C is for Colour
Blotchy spots with a number of colours such as black, blue, red, white and/or grey.
D is for Diameter
Look for spots that are getting bigger.
E is for Evolving
Spots that are changing and growing.
These are some changes to look out for when checking your skin for signs of any cancer:
- New moles.
- Moles that increases in size.
- An outline of a mole that becomes notched.
- A spot that changes colour from brown to black or is varied.
- A spot that becomes raised or develops a lump within it.
- The surface of a mole becoming rough, scaly or ulcerated.
- Moles that itch or tingle.
- Moles that bleed or weep.
- Spots that look different from the others.
What Are The Symptoms Of Skin Cancer
Talk to your doctor if you notice changes in your skin such as a new growth, a sore that doesnt heal, a change in an old growth, or any of the A-B-C-D-Es of melanoma.
A change in your skin is the most common sign of skin cancer. This could be a new growth, a sore that doesnt heal, or a change in a mole.external icon Not all skin cancers look the same.
For melanoma specifically, a simple way to remember the warning signs is to remember the A-B-C-D-Es of melanoma
- A stands for asymmetrical. Does the mole or spot have an irregular shape with two parts that look very different?
- B stands for border. Is the border irregular or jagged?
- C is for color. Is the color uneven?
- D is for diameter. Is the mole or spot larger than the size of a pea?
- E is for evolving. Has the mole or spot changed during the past few weeks or months?
Talk to your doctor if you notice changes in your skin such as a new growth, a sore that doesnt heal, a change in an old growth, or any of the A-B-C-D-Es of melanoma.
Don’t Miss: Can You Die From Basal Cell Skin Cancer
Skin Cancer Of The Head And Neck Treatment
Many early-stage small basal cell cancers or squamous cell cancers can be removed by Mohs surgery, a technique that spares normal tissue through repeated intraoperative margin testing, removing only the cancer and leaving adjacent normal tissue. Tumors with nerve involvement, lymph node involvement or of a large size are not suitable for Mohs surgery. They require a multimodality approach to treatment, with formal surgical resection and adjuvant radiation or chemotherapy.
Melanoma is more likely to spread, and aggressive surgical resection with wide margins is required, in addition to radiation and/or chemotherapy.
Johns Hopkins Head and Neck Cancer Surgery
Johns Hopkins Head and Neck Cancer Surgery provides comprehensive surgical care and treatment for head and neck cancers. Our surgeons are at the leading edge of head and neck cancer treatment. You will benefit from the skilled care of head and neck surgeons, guiding clinical advancements in the field of head and neck cancer care.
The 6 Best Treatments For Skin Cancer On The Face
Posted on May 1, 2017 in Skin Cancer, Mohs Micrographic Surgery, Skin Tumor, Basal Cell Carcinoma, Squamous Cell Carcinoma, Melanoma, Treatments, malignancy
Skin cancer, the most common form of cancer in the U.S., affects a growing number of people each year, raising public awareness and concern as we seek better ways to both prevent and treat the disease.
In the U.S., over three million people receive a non-melanoma skin cancer diagnosis each year, with rates of malignant melanoma, one of the most serious forms of the disease, rising significantly in recent years, with more than 87,000 people expected to receive a diagnosis in 2017. People who experience skin cancer may even develop multiple cases of it each year.
In fact, skin cancer has become so prevalent that the number of new cases annually exceeds the number of breast, colon, lung, and prostate cancer diagnoses combined, reveals Dr. Adam Mamelak, a board certified Dermatologist and Mohs surgeon at Sanova Dermatology in Austin, Texas.
While exposure to dangerous ultraviolet rays from the sun usually receives the blame for causing skin cancer, particularly malignant melanoma, the disease has also been linked to chemicals and other exposures as well.
One of the more common areas where skin cancer manifests is the face, including the lips, cheeks, forehead, scalp, eyelids, and nose. These areas also prove challenging to treat.
Three common types of skin cancer include:
Contact Us
Read Also: Cancer Spread All Over Body
Less Common Skin Cancers
Uncommon types of skin cancer include Kaposi’s sarcoma, mainly seen in people with weakened immune systems sebaceous gland carcinoma, an aggressive cancer originating in the oil glands in the skin and Merkel cell carcinoma, which is usually found on sun-exposed areas on the head, neck, arms, and legs but often spreads to other parts of the body.
How Do You Treat Skin Cancer On The Nose
The nose is a relatively common spot for skin cancer to develop. Skin cancer often starts on the face because it’s usually the body part that’s exposed to the sun. The two most common types of skin cancer that develop on the nose are basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma . While both types of skin cancer should be addressed right away, BCC is usually slow-growing and SCC grows more quickly. Basal cell carcinoma is the most common type of skin cancer ,with about 80% of cases occurring on the face and 25 to 30% on the nose.
The third type of skin cancer, melanoma, is rare and much more serious. It almost always requires excisional surgery to remove it. Fortunately, most forms of skin cancer are very treatable, especially when caught early. Treatment may include surgery, radiation, topical treatments, and more.
Don’t Miss: Etiology Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
Oral Medications For Advanced Bcc
It is rare for skin cancer to reach advanced stages, but when it does, oral medications may help. In addition to chemotherapy, targeted drugs may be used to treat advanced skin cancer. Targeted therapy means that the medication is able to directly target the cancer cells without destroying healthy cells. This can help to reduce side effects from treatment.
Vismodegib and sonidegib are hedgehog pathway inhibitors that work to prevent cancer cells from growing and spreading. The capsules are taken once per day and may be considered after surgery and other treatments. These medications come with several possible side effects and should never be taken during pregnancy since they can affect fetal growth.
Cetuximab is an EGFR inhibitor that can help to stop the spread of cancerous squamous cells. Its possible side effects include skin infections, diarrhea, mouth sores, and loss of appetite.
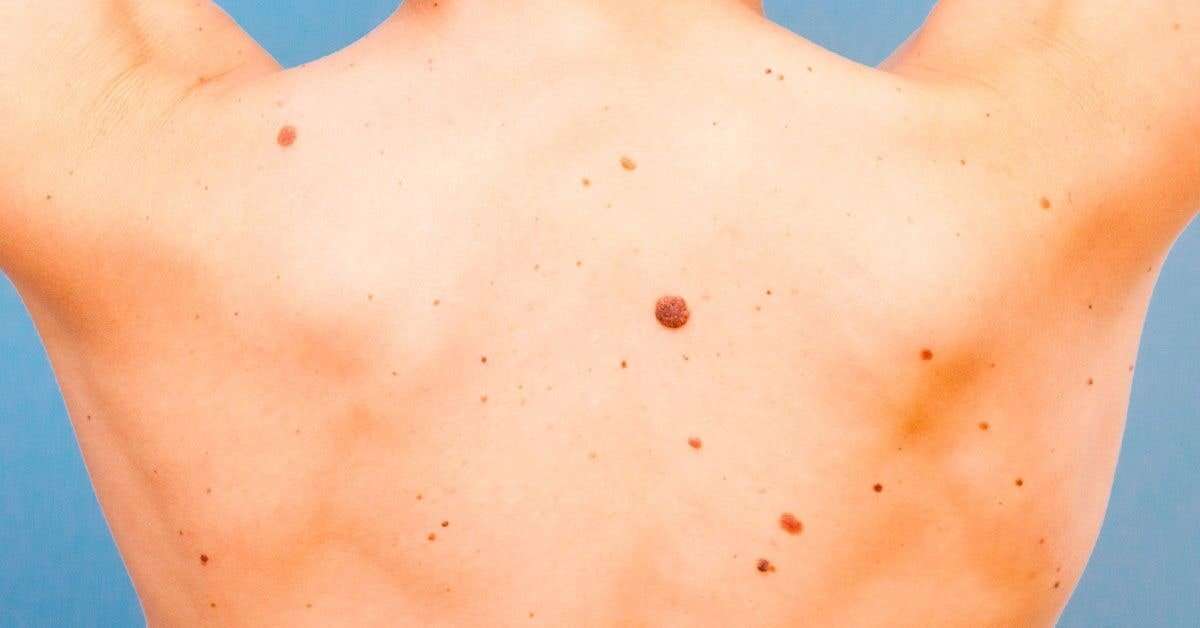
Signs That Your Mole Can Be Suspicious
If your mole starts to show some strange characteristics, it is probably time to ask a doctors opinion. Visit your doctor if your mole:
- develops a crust or a scab
- sometimes bleeds
- is getting bigger or swelling
- is strangely shaped
- has borders that are irregular
- includes lots of different colours or shades
- is bigger than the size of a pencil eraser in diameter
- has appeared recently
Non-melanoma skin cancer symptoms
While melanoma is the most dangerous form of skin cancer, it is still important to pay attention to non-melanoma skin cancers and understand the forms they can take.
According to the UK National Health Service, one of the first non-melanoma skin cancer symptoms is a persisting lump or discolored patch on the skin that doesnt heal after a few weeks and keeps progressing over months or even years. The two most common types of non-melanoma skin cancer are basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma. Find out how to identify these types of skin cancer below.
Don’t Miss: Squamous Cell Stage 4
How Serious Is My Cancer
If you have skin cancer, the doctor will want to find out how far it has spread. This is called staging.
Basal and squamous cell skin cancers don’t spread as often as some other types of cancer, so the exact stage might not be too important. Still, your doctor might want to find out the stage of your cancer to help decide what type of treatment is best for you.
The stage describes the growth or spread of the cancer through the skin. It also tells if the cancer has spread to other parts of your body that are close by or farther away.
Your cancer can be stage 0, 1, 2, 3, or 4. The lower the number, the less the cancer has spread. A higher number, like stage 4, means a more serious cancer that has spread beyond the skin. Be sure to ask the doctor about the cancer stage and what it means for you.
Other things can also help you and your doctor decide how to treat your cancer, such as:
- Where the cancer is on your body
- How fast the cancer has been growing
- If the cancer is causing symptoms, such as being painful or itchy
- If the cancer is in a place that was already treated with radiation
- If you have a weakened immune system