How Do You Know If A Spot Is Skin Cancer
To learn more you can read this article on the signs of skin cancer or this article on melanoma symptoms, but dont forget to get any skin concern you may have checked out by your doctor.
You can also read our guide on how to check your skin regularly, if you want to learn more about how to form a skin checking routine for yourself.
Melanoma: The Deadliest Skin Cancer
Melanoma is the most serious type of skin cancer, because it tends to spread if its not treated early.
This cancer starts in the melanocytes cells in the epidermis that make pigment.
About 100,350 new melanomas are diagnosed each year.
Risk factors for melanoma include:
- Having fair skin, light eyes, freckles, or red or blond hair
- Having a history of blistering sunburns
- Being exposed to sunlight or tanning beds
- Living closer to the equator or at a higher elevation
- Having a family history of melanoma
- Having many moles or unusual-looking moles
- Having a weakened immune system
Melanoma can develop within a mole that you already have, or it can pop up as a new dark spot on your skin.
This cancer can form anywhere on your body, but it most often affects areas that have had sun exposure, such as the back, legs, arms, and face. Melanomas can also develop on the soles of your feet, palms of your hands, or fingernail beds.
Signs to watch out for include:
- A mole that changes in color, size, or how it feels
- A mole that bleeds
RELATED: The Difference Between Chemical and Mineral Sunscreen
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
Basal cell carcinomas can appear anywhere on the body but the most common sites are sun exposed areas such as the face and arms. Its important to keep a close eye on your skin to try and identify early basal cell carcinoma, as its easier to treat if identified early on.
Typical Basal cell carcinoma symptoms are:
- New skin lesion
- Change in colour of a lesion
The typical lesions to watch out for are as follows:
- Pink or translucent, shiny bumps or pearly nodules, sometimes with dark spots or black, blue, or brown surface
- Growths, pink in color, with raised edges and sunken center, usually with irregular blood spoke-wheel vessels on its surface
- Pale or yellow scar-like areas
- Elevated reddish patches
- Oozing, crusted, scaly and open sores that dont heal over time
Don’t Miss: Stage 2 Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Survival Rate
More Pictures Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
While the above pictures show you some common ways that BCC can appear on the skin, this skin cancer can show up in other ways, as the following pictures illustrate.
Scaly patch with a spot of normal-looking skin in the center
On the trunk, BCC may look like a scaly patch with a spot of normal-looking skin in the center and a slightly raised border, as shown here.
Basal cell carcinoma can be lighter in some areas and darker in others
While BCC tends to be one color, it can be lighter in some areas and darker in others, as shown here.
Basal cell carcinoma can be brown in color
Most BCCs are red or pink however, this skin cancer can be brown, as shown here.
Basal cell carcinoma can look like a group of shiny bumps
BCC can look like a group of small, shiny bumps that feel smooth to the touch.
Basal cell carcinoma can look like a wart or a sore
The BCC on this patients lower eyelid looks like a wart* in one area and a sore** in another area.
If you see a spot or growth on your skin that looks like any of the above or one that is growing or changing in any way, see a board-certified dermatologist.
Why Is Basal Cell Carcinoma The Most Common
One of three main types of cells in the top layer of the skin, basal cells shed as new ones form. BCC most often occurs when DNA damage from exposure to ultraviolet radiation from the sun or indoor tanning triggers changes in basal cells in the outermost layer of skin , resulting in uncontrolled growth.
You May Like: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Grade 3 Survival Rate
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Pictures
Squamous cell carcinoma also appears in areas most exposed to the sun and, as indicated in the pictures below, often presents itself as a scab or sore that doesnt heal, a volcano-like growth with a rim and crater in the middle or simply as a crusty patch of skin that is a bit inflamed and red and doesnt go away over time.
Any lesion that bleeds or itches and doesnt heal within a few weeks may be a concern even if it doesnt look like these Squamous cell carcinoma images.
What Are The Advantages Of Mohs Surgery
The technique offers the highest possible cure rate for the treatment of skin cancer, compared to other therapeutic modalities. Mohs surgery also allows the physician to remove as little normal tissue as possible around the tumor, and thus in many cases can provide a superior cosmetic result. Our doctors also offer a variety of laser treatments to improve the appearance of scars after Mohs surgery. Another advantage is that with many large skin cancers, hospitalization can be avoided by performing Mohs surgery on an out-patient basis.
You May Like: Tumor Calcification
Warning Signs Of Basal Cell Carcinoma That You Could Mistake As Harmless
Warning sign: A pink or reddish growth that dips in the centerCan be mistaken for: A skin injury or acne scar
A pink or reddish growth that dips in the center
The BCC on this patients cheek could be mistaken for a minor skin injury.
Warning sign: A growth or scaly patch of skin on or near the earCan be mistaken for: Scaly, dry skin, minor injury, or scar
A growth or scaly patch of skin on or near the ear
BCC often develops on or near an ear, and this one could be mistaken for a minor skin injury.
Warning sign: A sore that doesn’t heal and may bleed, ooze, or crust overCan be mistaken for: Sore or pimple
A sore that doesn’t heal, or heals and returns
This patient mistook the BCC on his nose for a non-healing pimple.
Warning sign: A scaly, slightly raised patch of irritated skin, which could be red, pink, or another colorCan be mistaken for: Dry, irritated skin, especially if it’s red or pink
A scaly, slightly raised patch of irritated skin
This BCC could be mistaken for a patch of dry, irritated skin.
Warning sign: A round growth that may be pink, red, brown, black, tan, or the same color as your skinCan be mistaken for: A mole, wart, or other harmless growth.
A round growth that may be same color as your skin
Would you recognize this as a skin cancer, or would you dismiss it as a harmless growth on your face?
What Is The Treatment For Advanced Or Metastatic Basal Cell Carcinoma
Locally advanced primary, recurrent or metastatic BCC requires multidisciplinary consultation. Often a combination of treatments is used.
- Radiotherapy
- Targeted therapy
Targeted therapy refers to the hedgehog signalling pathway inhibitors, vismodegib and sonidegib. These drugs have some important risks and side effects.
Read Also: Lobular Breast Cancer Stage 3
Basal Cell Carcinoma Pictures
Below are basal cell carcinoma pictures of typical lesions on various sites of the body. These photos and images of basal cell carcinomas are not exhaustive but are examples of common lesions.
Basal Cell Carcinoma on Face:
Basal Cell Carcinoma on Nose:
Basal Cell Carcinoma on Scalp:
Basal Cell Carcinoma on Ear:
Basal Cell Carcinoma on Eyelid:
Basal Cell Carcinoma on Trunk:
Images in this article were sourced from DermNet NZ, Waikato District Health Board, Raimo Suhonen and Dr Richard Ashton.
MIISKIN PROMO
Symptoms Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
The various types of basal cell carcinoma can take many different forms. Often, it may seem like a small bump that grows very slowly. Other symptoms are a:
- Pink, reddish spot that dips in the center
- Scaly patch, especially near the ears
- Sore that resembles a pimple, but that either doesnt heal or heals but keeps returning
- Round growth that can be pink, red, brown, tan, black, or skin-colored
- Scar-like skin that isnt from an injury
Its important to note that the color and shape of the tumor may not be uniform. The spot may be flat or raised, it can be dipped in the center or not, and it can even appear shiny. Often, BCCs do not cause pain, but the area can be numb, sensitive, or itchy. Its hard to self-diagnose a basal cell carcinoma because they can take so many different shapes. If you have a concerning spot, its best to schedule a dermatological appointment right away.
You May Like: What Is Nodular And Infiltrating Basal Cell Carcinoma
How Can A Basal Cell Carcinoma Be Treated
How can a basal cell carcinoma be treated? The commonest treatment for BCC is surgery. Usually, this means cutting away the BCC, along with some clear skin around it, using local anaesthetic injection to numb the skin. The skin can usually be closed with a few stitches, but sometimes a skin graft is needed.
How Do People Find Bcc On Their Skin
Many people find it when they notice a spot, lump, or scaly patch on their skin that is growing or feels different from the rest of their skin. If you notice any spot on your skin that is growing, bleeding, or changing in any way, see a board-certified dermatologist. These doctors have the most training and experience in diagnosing skin cancer.
To find skin cancer early, dermatologists recommend that everyone check their own skin with a skin self-exam. This is especially important for people who have a higher risk of developing BCC. Youll find out what can increase your risk of getting this skin cancer at, Basal cell carcinoma: Who gets and causes.
Images used with permission of:
-
The American Academy of Dermatology National Library of Dermatologic Teaching Slides.
-
J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019 80:303-17.
You May Like: Can You Cure Stage 4 Melanoma
Additional And Relevant Useful Information For Infiltrating Basal Cell Carcinoma Of Skin:
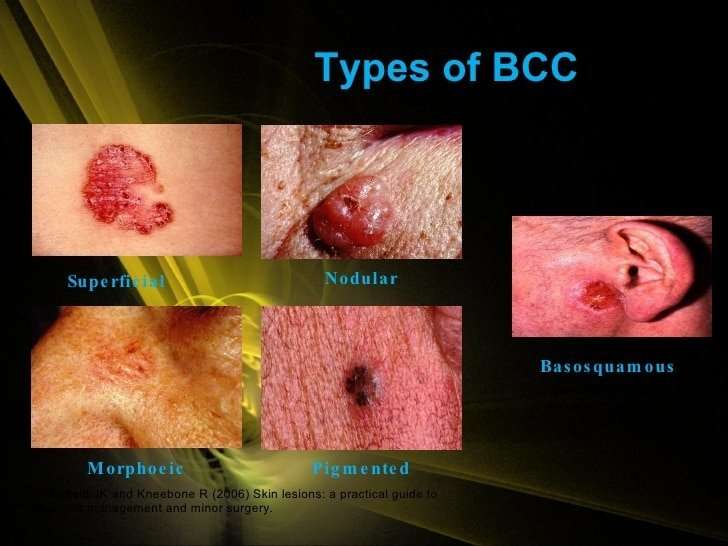
There are multiple types of Basal Cell Carcinoma of Skin:
- Superficial Basal Cell Carcinoma of Skin
- Nodular Basal Cell Carcinoma of Skin
- Infiltrating Basal Cell Carcinoma of Skin
- Micronodular Basal Cell Carcinoma of Skin
- Fibroepithelial Basal Cell Carcinoma of Skin
- Basal Cell Carcinoma of Skin with Adnexal Differentiation
- Basosquamous Carcinoma
- Keratotic Basal Cell Carcinoma of Skin
Treating Basal Cell Carcinoma
Several types of treatment can be used to remove or destroy basal cell skin cancers. The options depend on factors such as the tumor size and location, and a persons age, general health, and preferences. These cancers very rarely spread to other parts of the body, although they can grow into nearby tissues if not treated.
All of the treatments listed here can be effective when used in appropriate situations. The chance of the cancer coming back ranges from less than 5% after Mohs surgery to up to 15% or higher after some of the others, but this depends on the size of the tumor. Small tumors are less likely to recur than larger ones. Even if a tumor does recur, it can often still be treated effectively.
Read Also: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Grade 2 Survival Rate
Mohs Micrographically Controlled Excision
Mohs micrographically controlled surgery involves examining carefully marked excised tissue under the microscope, layer by layer, to ensure complete excision.
- Very high cure rates achieved by trained Mohs surgeons
- Used in high-risk areas of the face around eyes, lips and nose
- Suitable for ill-defined, morphoeic, infiltrative and recurrent subtypes
- Large defects are repaired by flap or skin graft
What Is Infiltrating Basal Cell Carcinoma Of Skin
- Basal Cell Carcinoma of Skin is a malignant cancer affecting the skin. It is a slow-growing tumor generally observed in older individuals, in both men and women
- This malignant carcinoma, which may be present as a lesion on the sun-exposed areas of the body, has the potential to metastasize to the lymph nodes
- Infiltrating Basal Cell Carcinoma of Skin occurs as an irregular plaque and has the tendency to infiltrate deep into the body tissue, making them difficult to treat. It is an uncommon subtype of BCC of Skin
- Some lesions may grow to large sizes and ulcerate. They can also infiltrate into the adjoining soft tissues and nerves. Larger tumors also have a greater tendency to recur after treatment
- The cause of Infiltrating Basal Cell Carcinoma of Skin is unknown, but factors such as chronic sun exposure, smoking, and ionizing radiation, etc., are known to contribute towards its development. Also, fair-skinned Caucasians have a greater risk than dark-skinned Africans and Asians
- Any combination of chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and invasive procedures are used to treat Infiltrating Basal Cell Carcinoma of Skin. Small-sized tumors and tumors that have not metastasized can be cured through appropriate skin surgery
- The prognosis for metastatic tumors depends upon many factors including the stage of the tumor, health status of the individual, and treatment response. The prognosis may be guarded
You May Like: How Do You Die From Melanoma
What Are The Treatments For Basal Cell Carcinoma
BCC is treated by removing it. The choice of treatment depends on many things, including patient health and age, the location of the tumor, and the extent and type of the cancer. Treatment may occur in many ways:
- Scratching off with a curette, an instrument that may end in a ring or a spoon, and then burning with a special electric needle. This method is called electrodessication and curettage.
- Surgical removal
- Mohs surgery: This is a specialized technique. The doctor first removes the visible cancer and then begins cutting around the edges. The tissues are examined during the surgery until no more cancer cells are found in tissues around the wound. If necessary, a skin graft or flap might be applied to help the wound heal.
- Excisional surgery: The growth and a bit of surrounding skin is removed with a scalpel.
If the BCC has advanced locally or spread to another location, which is very rare for BCC, the FDA has approved two medicines: vismodegib and sonidegib . These drugs are of a class called hedgehog inhibitors.
How Is Infiltrating Basal Cell Carcinoma Of Skin Treated
In general, the treatment of Basal Cell Carcinoma of Skin depends upon a variety of factors including:
- The subtype of BCC
- The location of the tumor
- The number of tumors
- The size of the tumor
- Whether the tumor has metastasized
A combination of treatment methods may be used to treat Infiltrating Basal Cell Carcinoma of Skin. The type of surgery may include:
- Shave biopsy of skin: This procedure is used for small tumors. There is no requirement of sutures after the surgery
- Excision of tumor: In this procedure, the tumor and surrounding tissue are removed with clear margins. Depending upon the amount of skin removed, surgical sutures may be necessary
- Mohs surgery: In this procedure, the tumor is removed layer by layer precisely, until clear margins are achieved. Each layer removed is examined under a microscope through a âfrozen sectionâ procedure, for the presence of residual tumor
In most cases, a surgical removal of the entire tumor is the preferred treatment option. This can result in a cure. However, since the tumor infiltrates deep into the body, it is very difficult to completely remove them through a surgical excision
Other techniques to treat this skin cancer may include:
Note: If multiple lesions occur in children, then the possibility of basal cell nevus syndrome should be eliminated.
Recommended Reading: What Is Large Cell Carcinoma
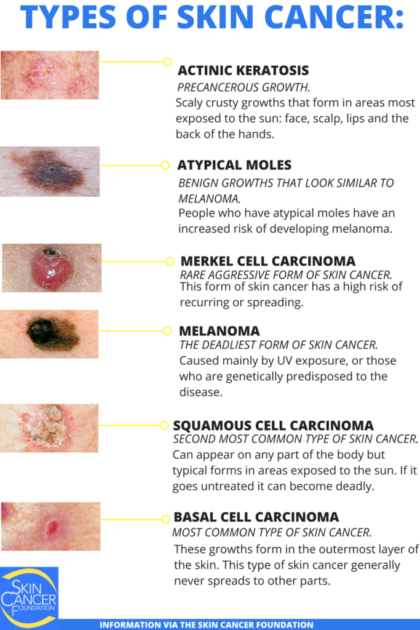
Different Types Of Skin Cancer
On this page
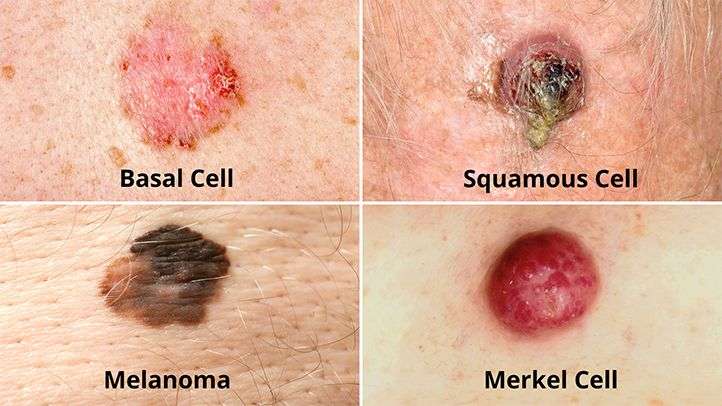
The different types of skin cancer are named after the type of skin cell they start from. There are three main types of skin cancer:
- basal cell carcinoma
- squamous cell carcinoma of the skin
- melanoma.
BCCs and SCCs are different from melanoma. They are called non-melanoma skin cancers.We have separate information about melanoma.
See also
The skin does many things. It:
- protects the body from injury and infection
- helps to control body temperature
- helps to control fluid loss
- gets rid of waste substances through the sweat glands.
The skin is divided into 2 main layers. The outer layer is the epidermis and the layer underneath is the dermis. Below these is a deeper layer of fatty tissue.
The epidermis contains several types of cells. Most of the epidermis is filled with cells called keratinocytes, also called squamous cells.
The lowest layer of the epidermis is called the basal layer. It contains rounder cells called basal cells.
The basal layer also contains skin cells called melanocytes which produce melanin. Melanin gives skin its natural colour.
What Are The Causes Of Infiltrating Basal Cell Carcinoma Of Skin
- The exact cause of development of Infiltrating Basal Cell Carcinoma of Skin is not completely known, in a majority of cases
- Although, genetic mutations have been detected in Basal Cell Carcinomas, which are currently being characterized
- Most BCCs are sporadic in origin i.e., they occur in a random fashion
Don’t Miss: Can You Die From Basal Cell Skin Cancer
Basal Cell And Squamous Cell Carcinoma
The two most common kinds of skin cancer are basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma, which are sometimes called nonmelanoma skin cancer. These cancers are carcinomas that begin in the cells that cover or line an organ.
Basal cell carcinoma accounts for more than 90 percent of all skin cancers in the United States and is the most common of all cancers. Typically, it is a slow-growing cancer that seldom spreads to other parts of the body.
Squamous cell carcinoma also rarely spreads, but does so more often than basal cell carcinoma. It is important that skin cancers are found and treated early because they can invade and destroy nearby tissue. Organ transplant recipients have a 65-fold higher risk of developing squamous cell carcinoma than others. UCSF Medical Center offers a High Risk Skin Cancer Clinic for those at high risk for non-melanoma skin cancers, such as transplant recipients.