What Is Squamous Cell Cancer
Squamous cell carcinoma of the skin is a common skin cancer that typically develops in chronic sun-exposed areas of your body. This type of skin cancer is usually not nearly as aggressive as melanoma and is uncontrolled growth of cells in the epidermis of your skin.
It can become disfiguring and sometimes deadly if allowed to grow. Squamous cell carcinomas are at least twice as frequent in men as in women. They rarely appear before age 50 and are most often seen in individuals in their 70s.
An estimated 700,000 cases of SCC are diagnosed each year in the United States, resulting in approximately 2,500 deaths.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Screening
Diagnosis and management of Squamous Cell Carcinoma is best performed via a Full Body Scan. In the first incidence, this process includes
- Digitally Mapping a patients entire body for any suspicious skin damage or lesion
- Followed by a detailed Dermoscopic Examination by a trained skin cancer Specialist
- Recording and combining all images and skin metrics into the patient record
Our expert Doctors at Bondi Junction Skin Cancer Clinic will then clearly identify and diagnose any skin cancers. Having a digital molemap or a baseline of all your skins sun damage for all family members with
- any suspicious sun damage,
- those with a large number of moles, or
- have been diagnosed with melanoma is recommended.
Any changes can be more easily spotted and understood.
You May Like: Do You Die From Skin Cancer
Lung Cancer Screening Criteria
The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommends annual screenings using CT for people who:
- Are 50 to 80 years old
- Have a 20 pack-year history of smoking
- Currently smoke or have quit smoking within the past 15 years
- Are healthy enough overall to tolerate and benefit from treatment if diagnosed with lung cancer
Don’t Miss: How Serious Is Skin Cancer
Can Better Detection Mean A Cure
With better screening, some people want to know if there’s a certain tumor size that suggests the lung cancer can be cured. In 2017, researchers created a simulation model. They found that the most aggressive NSCLCs would need to be diagnosed at only 10 mm in size in males and 15 mm in females. The average size of a lung tumor at diagnosis without screening is 33 mm.
When To Seek Medical Care
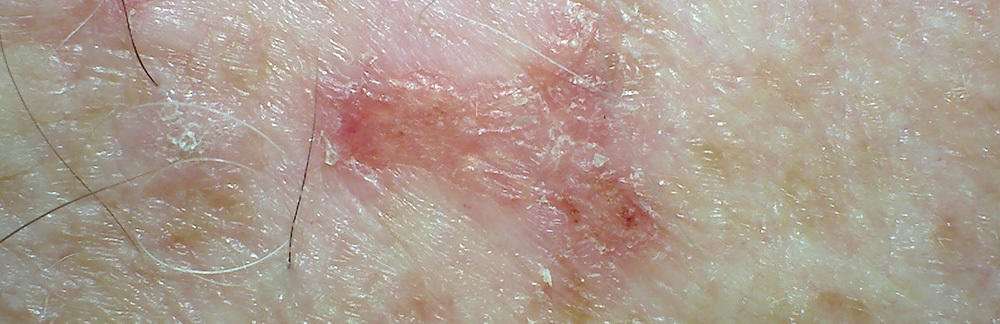
If you develop a new bump on sun-exposed skin, or if you have a spot that bleeds easily or does not seem to be healing, then you should make an appointment with your primary care physician or with a dermatologist. You should also make an appointment if an existing spot changes size, shape, color, or texture, or if it starts to itch, bleed, or become sore to the touch.Try to remember to tell your doctor when you first noticed the lesion and what symptoms, if any, it has. Also, young adults should ask adult family members whether or not they have ever had a skin cancer and relay this information to their physician.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Difference Between Age Spots And Skin Cancer
What Is Squamous Cell Skin Cancer Of The Head And Neck
Skin malignancies are the most common cancer in the United States, responsible for more than half of all new cancer cases. These can be broken down into melanoma and non-melanoma malignancies, which are squamous cell cancer and basal cell cancer. These skin malignancies are caused by ultraviolet radiation from exposure to the sun and tanning beds.
Squamous cell cancer is the second most common form of skin cancer. It is more aggressive and may require extensive surgery depending on location and nerve involvement. Radiation, chemotherapy and immunotherapy are used in advanced cases.
How Can You Prevent Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Practicing sun safety is the best way to prevent SCC and other skin cancers. Here are some tips:
- Avoid being in the sun from 10 am to 4 pm.
- Avoid tanning beds.
- Use a broad spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 15 or higher each day. If you will be outside for longer periods of time, use a broad spectrum sunscreen that is water-resistant and has an SPF of 30 or higher. Put the sunscreen on 30 minutes before going outside. Put sunscreen on again every two hours, or more frequently if you have been swimming or sweating a lot.
- Use protective clothing that has built-in sun protection, which is measured in UPF. Also, use broad-brimmed hats and sunglasses.
- Do your own skin self-exam about once per month, and see a dermatologist about one time per year for a professional skin exam.
- Have any skin changes examined as soon as possible by a healthcare provider.
Also Check: What Are The Signs Of Skin Cancer On The Scalp
How Is Squamous Cell Skin Cancer Treated
Although squamous cell cancers usually grow slowly, it is important to see a dermatologist quickly. “The sooner you see your doctor and the cancer is diagnosed and treated, the less complicated the surgery to remove it will be, and the faster you will make a complete recovery, Dr. Leffell explains. The treatment for squamous cell cancer varies according to the size and location of the lesion. The surgical options are the same as those for basal cell cancer:
- Surgical excision: Removing a squamous cell lesion is a simple procedure that typically takes place in the dermatologist’s office. After numbing the cancer and the area around it with a local anesthetic, the doctor uses a scalpel to remove the tumor and some of the surrounding skin to make sure all cancer is eliminated. Estimating how much to take requires skill and expertise, Dr. Leffell notes. The risk of taking too little tissue is that some cancer remains taking too much leaves a larger scar than is necessary. Shaped like a football, the wound is stitched together, using plastic surgery techniques. If dissolvable stitches are used, they will disappear on their own as the area heals. Though the procedure leaves some redness and a small scar, it tends to become less noticeable over time. “The cure rate for this type of excision is typically about 90 to 93 percent,” says Dr. Leffell. But, of course, this is dependent on the skill and experience of the doctor.”
Do You Need Chemotherapy For Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Because just about all squamous cell carcinoma is usually localized it is typically not treated with chemotherapy. Chemotherapy is used for widespread cancer cell eradication, not localized growths. Chemotherapy could be used for a very small percentage of these cases, typically if the cancer has spread.
About 95 percent of squamous cell carcinomas are detected early, and this makes them easy to treat. All treatment options are highly successful, but Mohs micrographic surgery is the most successful while taking the least amount of healthy skin.
Also Check: What Do Skin Cancer Sores Look Like
Also Check: What Does Squamous Cell Carcinoma Look Like On The Face
How Fast Does Skin Cancer Grow
Skin cancer starts when cells in the skin grow out of control. Some forms of skin cancer tend to grow in a matter of weeks, while others grow over months or longer. While a number of factors determine how fast or slow skin cancer may grow in any one individual, some types of skin cancer are more aggressive than others. In the space below, we look at typical growth rates for some specific types of cancer.
Are You At Risk
The skin is the largest organ of the body. It is also our bodys first line of defense. There are numerous factors which may increase your risk of skin cancer:
- Genetics: Individuals with fair complexions are at the greatest risk. Your risk is also increased if your parents, children, or siblings have had skin cancer.
- Sun Exposure: Over the course of a lifetime, exposure to the sun can lead to a higher risk of skin cancer. Tanning beds and other false sunlight are no exception.
- Immunosuppression: Immunosuppression therapy following organ transplants, chemotherapy, AIDS, and other treatments can put you at a significant risk for skin cancer.
- Lifespan: Human life expectancy has increased from forty-two years in 1904 to close to eighty years today. As a result, the number of skin cancers being seen around the world is increasing.
You May Like: Can Basal Cell Carcinoma Turn Into Melanoma
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Recurrence
Over the next two years, while I had other basal cell areas, I had no other squamous cell areas…..until November 2017.
I realized while at work one afternoon that an area on my chest felt painful, and after work, I saw that I had a new bump on it that wasnt there the day before. It wasnt bleeding or scabbing, though, and I was more bothered by the pain of it.
Surgical Removal Of Squamous Cell Carcinoma
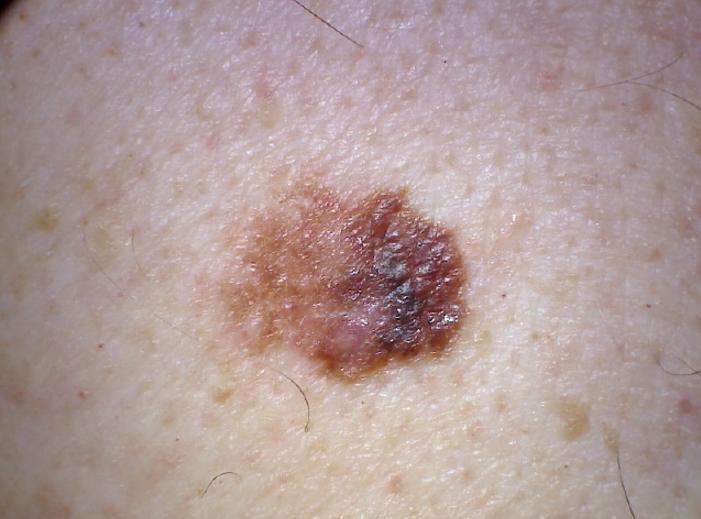
Surgical removal or excision of the Squamous Cell Carcinoma is the most common treatment.
Non-melanoma skin cancers are almost always surgically removed under local anaesthetic and this is the safest form of treatment due to the potential of Squamous Cell Carcinomas to spread. This approach offers:
- high cure rates
- Is immediate,
- Lesion margins are checked to ensure complete clearance
- In more advanced skin cancers, some of the surrounding tissue may also be removed to make sure that all of the cancerous cells are cleared.
Excision Treatment Process – After careful administration of local anaesthetic, the Doctor uses a scalpel to remove the entire growth, along with surrounding apparently normal skin as a safety margin. The wound around the surgical site is then closed with sutures .
Excision Treatment Recovery – For a few days post excision there may be minor bruising and swelling. Scarring is usually minimal. Pain or discomfort is minor. Typically, where sutures are used, they are removed soon afterwards.
Surgical Excision Prognosis – Studies indicate the cure rate for primary tumours with this technique is around 92 percent. Clearance rates for recurrent Squamous Cell Carcinomas are lower around 77 percent. A repeat excision may be necessary on a subsequent occasion if evidence of skin cancer is found in the specimen.
Read Also: How Many People Die From Skin Cancer
When Does Lung Cancer Begin
A different question looks at when the lung cancer first began. People may think of a stressful time in their life, or a specific chemical exposure, and wonder if it could have been the “cause” of their cancer. There isn’t a precise answer, but there are some theories.
One idea is to look at the patterns of mutation. A 2017 study published in the New England Journal of Medicine suggested that it takes along time for a lung cancer to develop, perhaps decades, especially for lung adenocarcinomas.
Predictions Based On Doubling Times
Looking at doubling times of tumors is helpful only if the estimated doubling times can be used to predict the growth of a person’s tumor. One study looked at predicted survival times of people who had inoperable lung cancers and found that there was a close correlation between survival predicted from doubling time and actual survival.
Recommended Reading: Is Squamous Skin Cancer Dangerous
Untreated Squamous Cell Carcinomas
The incidence of Squamous Cell Carcinoma is rising and can be life-threatening.
While Squamous Cell Carcinomas seldom spread to vital organs, Squamous Cell Carcinomas respond well to early treatment. If untreated the consequences could include:
- Disfigurement
- Nerve, or muscle injury, or other injury to nearby structures like eyelids or nostrils
- Certain rare, aggressive forms can be lethal if not treated promptly.
The larger the tumour has grown, the more extensive any surgical treatment would be. This could result in scarring.
In 2016 it is estimated that there were 560 deaths in Australia from non-melanoma skin cancers. It is not possible to identify how many of these are Squamous Cell Carcinomas as this data is not separately recorded.
How To Improve Your Odds
Even if youve exhausted all of your treatment options, you dont have to give up. Researchers are always testing new SCC treatments in clinical trials. Getting into one of these studies could give you access to a drug or therapy that might slow or stop your cancer.
To avoid the worsening of your skin cancer or a new cancer in a different area, protect yourself from the suns damaging UV rays. Wear sun-protective clothing and a wide-brimmed hat whenever you go outdoors. Apply a layer of broad-spectrum sunscreen that protects against both UVA and UVB rays.
Also check your own skin for any new growths on a regular basis. Report any skin changes to your doctor right away.
Recommended Reading: What Does Melanoma Look Like On Your Face
Prevention Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
Because basal cell carcinoma is often caused by sun exposure, people can help prevent this cancer by doing the following:
-
Avoiding the sun: For example, seeking shade, minimizing outdoor activities between 10 AM and 4 PM , and avoiding sunbathing and the use of tanning beds
-
Wearing protective clothing: For example, long-sleeved shirts, pants, and broad-brimmed hats
-
Using sunscreen: At least sun protection factor 30 with UVA and UVB protection used as directed and reapplied every 2 hours and after swimming or sweating but not used to prolong sun exposure
In addition, any skin change that lasts for more than a few weeks should be evaluated by a doctor.
How Is Squamous Cell Skin Cancer Of The Head And Neck Diagnosed
Diagnosis is made by clinical exam and a biopsy. Squamous cell cancers are staged by size and extent of growth. Squamous cell cancers can metastasize to nearby lymph nodes or other organs, and can invade both small and large nerves and local structures.
Biopsy can help determine if the squamous cell cancer is a low-risk tumor or a high-risk tumor that requires more aggressive treatment. Low-risk tumors are less than 10 millimeters in size, less than or equal to 5 millimeters deep and do not involve structures beyond the surrounding fat. High-risk tumors in the head and neck are those that involve the central face, nose and eye area, as well as those tumors that are greater than or equal to 10 millimeters on the cheeks, scalp and neck, tumors that are more than 5 millimeters thick or involve adjacent structures, tumors that invade nerves, tumors that are recurrent or arising from previously radiated tissue, and tumors arising in patients who are immunosuppressed.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Latest Treatment For Melanoma
How Fast Lung Cancer Grows
The doubling time for lung cancer can help you to get an idea about proliferation, or how fast lung cancer cells grow. But it’s important to look at the science of cancer cell growth, because there are limits to the math and the models used to estimate it. These limits mean that estimates of the true growth rate may be far too high or too low. In other words, there is no simple formula.
More Information About Basal Cell Carcinoma
The following are some English-language resources that may be useful. Please note that THE MANUAL is not responsible for the content of these resources.
See the following sites for comprehensive information about basal cell carcinoma, including detection, prevention, treatment options, and other resources:
Don’t Miss: How Successful Is Immunotherapy For Melanoma
Symptoms Of Squamous Cell Carcinoma
A key factor used to identify a Squamous Cell Carcinomas is any ongoing change that persists beyond a few weeks in a lesion on the skin.
Squamous Cell Carcinomas typically appear as persistent, thick, rough, scaly patches that can bleed if bumped, scratched or scraped.
If you observe two or more of the signs below, you should consult the Bondi Junction Skin Cancer Clinic immediately.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma can sometimes resemble non-cancerous skin conditions such as psoriasis or eczema.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Causes
Exposure to ultraviolet rays, like the ones from the sun or a tanning bed, affects the cells in the middle and outer layers of your skin and can cause them to make too many cells and not die off as they should. This can lead to out-of-control growth of these cells, which can lead to squamous cell carcinoma.
Other things can contribute to this kind of overgrowth, too, like conditions that affect your immune system.
You May Like: What Is Melanoma Skin Cancer
Recommended Reading: Does Sunburn Cause Skin Cancer
Scc Is Mainly Caused By Cumulative Uv Exposure Over The Course Of A Lifetime
If youve had a basal cell carcinoma you may be more likely to develop a squamous cell skin carcinoma, as is anyone with an inherited, highly UV-sensitive condition such as xeroderma pigmentosum.
Chronic infections, skin inflammation, HIV and other immune deficiency diseases, chemotherapy, anti-rejection drugs used in organ transplantation, and excessive sun exposure can all lead to a risk of squamous cell carcinoma.
Occasionally, squamous cell carcinomas arise spontaneously on what appears to be normal, healthy skin. Some researchers believe the tendency to develop these cancers can be inherited.
SCCs may occur on all areas of the body including the mucous membranes and genitals, but are most common in areas frequently exposed to the sun:
- Ears
- Previous BCC or SCC
- Chronic inflammatory skin conditions or chronic infections
But anyone with a history of substantial sun exposure is at increased risk. Those whose occupations require long hours outside or who spend their leisure time in the sun are also at risk.
What Are The Stages Of Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Squamous cell carcinoma is classified into the following stages, which are partly based on how far the cancer has spread throughout the body:
- Stage 0 Squamous cell carcinoma develops in the squamous cells, which are located in the epidermis . During Stage 0, the cancer hasnt spread beyond the epidermis.
- Stage 1 When squamous cell carcinoma progresses to Stage 1, it means that the cancer has spread deeper into the skin, but not into any lymph nodes or healthy tissues.
- Stage 2 A Stage 2 classification means that, in addition to progressing deeper into the skin, the cancer also displays at least one high-risk feature. This might include metastasizing to the lower skin layers or the nerves. However, at this stage, the cancer still hasnt spread to lymph nodes or healthy tissues.
- Stage 3 Once squamous cell carcinoma reaches Stage 3, the cancer has spread into lymph nodes but not any other tissues or organs.
- Stage 4 This is the final stage of squamous cell carcinoma, where the cancer has spread to at least one distant organ, whether that be the brain, the lungs or a separate area of skin.
If you think you might have squamous cell carcinoma, its important to seek prompt medical attention to minimize the risk of cancer spread. The specialists in Moffitt Cancer Centers Cutaneous Oncology Program can provide you with the comprehensive diagnostic and treatment services you need. Call or complete our new patient registration form online to request an appointment.
- BROWSE
Don’t Miss: What Is The Blue Light Treatment For Skin Cancer