Who Gets Metastatic Melanoma
Melanoma usually starts as a single lesion on the skin or mucous membrane. This lesion can progress to the formation of metastases if it is not recognised and treated effectively at an early stage.
Risk factors for the development of melanoma include:
- Age
- A history of previous skin cancer
- A family history of melanoma
- Having large numbers of moles especially atypical moles
- Having fair skin which burns easily
- Having sun-damaged skin.
The risk of melanoma metastasising is highest in an individual with an aggressive rapidly growing melanoma, an unrecognised melanoma, advanced primary melanoma, melanoma that was not completely excised , and/or is immunosuppressed.
Symptoms If Cancer Has Spread To The Brain
You might have any of the following symptoms if your cancer has spread to your brain:
- headaches
- weakness of a part of the body
- fits
- personality changes or mood changes
- eyesight changes
-
J Tobias and D HochhauserJohn Wiley and Sons Ltd
-
TNM Staging ChartsLippincott Williams and Wilkins, 2009
-
Improving supportive and palliative care for adults with cancerNational Institute for Clinical Excellence , 2004
-
Oxford Textbook of Palliative MedicineEds D Doyle and othersOxford Universty Press, 3rd edition 2005
-
Cancer and its Management J Tobias and D HochhauserWiley Blackwell, 2015
Box 1detection Of Melanoma: Summary Of Different Aspects Of Occult Melanoma Detection
Before melanoma cells metastasize they extend into the adjacent epidermis. Field cells were characterized by Bastian et al. . Epidermis adjacent to the acral lentiginous melanoma can harbor cells with a high level of DNA amplifications that can be detected by fluorescent in situ hybridization. Genetic analysis of these cells suggests that they precede melanoma in situ. They also extend significantly into normal skin without a correlation to tumor thickness or size .
Another potential step in the evolution of a primary tumor into its metastasis to lymph nodes is local lymphatic invasion. This is usually only assessed in the excisions of the primary tumor on hematoxylin and eosin slides. In a recent study, immunohistochemical stains with antibodies against podoplanin and S-100 were combined with multispectral imaging analysis. This increased the sensitivity of detection of lymphatic invasion sevenfold. Dadras et al. used the antibody against lymphatic endothelial hyaluronan receptor -1 to decorate lymphatic vessels in the tumor and its close proximity to its border . Additionally, they assessed expression of VEGF-C and VEGF-D in melanomas. As it turned out, VEGF-C and not VEGF-D correlated with a higher frequency of melanoma metastases to sentinel lymph nodes. The relative area of vascular invasion of primary melanomas correlated with metastasis to sentinel lymph nodes to a greater extent than did tumor thickness , as determined by the Wilcoxon rank test.
You May Like: What Does Melanoma In Situ Look Like
How Do Doctors Diagnose Metastasis
If you already had cancer treatment for non-metastatic cancer, you probably have a follow-up care plan. You will see your doctor for regular checkups. Specific tests may be done to look for metastases.
Alternatively, some people already have metastases when they are first diagnosed with cancer. In this situation, the metastases are usually found during the initial tests to stage the cancer.
Cancer may cause symptoms such as pain or shortness of breath. Sometimes these symptoms will lead your doctor to do necessary tests to find the metastases.
Also Check: How Bad Is Basal Cell Skin Cancer
What Is Metastatic Melanoma
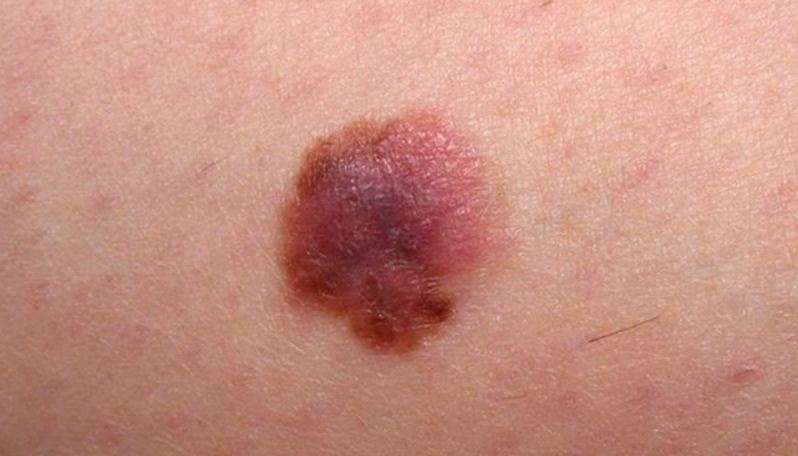
Metastatic melanoma occurs when the cancerous cells from the original tumor get loose, travel through the lymph or blood circulation, and start a new tumor somewhere else. Once it spreads, or metastasizes, the disease is known as metastatic melanoma. This type of melanoma may typically occur during stage III or stage IV. Common sites for metastases include the lymph nodes, lungs, liver, bones and brain.
About 106,110 adults in the United States will be diagnosed with melanoma in 2021, according to the American Society of Clinical Oncology . Approximately 4 percent of people are diagnosed with melanomas that have spread to distant parts of the body, according to the ASCO. This is the most advanced stage of metastatic melanoma.
The percentage of people diagnosed with melanoma that has spread to nearby lymph nodes is 8.5 percent, according to the National Cancer Institute . These cases have a slightly better prognosis.
From 2014 to 2018, the incidence rate of melanoma that had spread to distant parts of the body was 0.9 per 100,000 people, according to the NCI.
Melanoma tumors that have metastasized to other parts of the body are still considered melanoma. For example, melanoma found in the lungs is called metastatic melanoma of the lung or melanoma with lung metastases.
Read Also: Well-differentiated
Doctors Want To Give Their Cancer Patients Every Chance But Are They Pushing Off Hard Talks Too Long
His team then gave mice implanted with human melanomas a weeklong regimen of an MCT1 blocker, AstraZenecas investigational AZD3965. Result: The animals had fewer melanoma cells in the blood and fewer metastases.
Inhibiting MCT1 doesnt have much effect on the primary tumor or on established metastases, Morrison said. But for cells in between, it can prevent metastasis and, at least in the mice, extend survival.
Although AstraZenecas MCT1 inhibitor is being tested in an early-stage clinical trial, the participants have solid tumors that have already metastasized. Morrison thinks thats too late: Oxidative stress kills cancer cells in the bloodstream, not once theyve reached their destination. If blocking MCT1 and thereby exposing tumor cells to oxidative stress in the bloodstream has any benefit, he said, it will be around stage 3, when cancer cells have reached the bloodstream and lymph nodes but not beyond.
Our prediction is that blocking MCT1 wont have much activity against stage 4 melanoma, but if used as an adjuvant therapy in stage 3, it might decrease the percentage of patients who progress to stage 4, Morrison said.
His discovery might extend beyond melanoma. Lung and pancreatic tumor cells also use MCT1 to grab lactate from the bloodstream, presumably enabling those cancers, too, to metastasize.
How Does Melanoma Spread
Melanoma is a type of cancer. It develops in the cells that produce pigment, which is responsible for the skin’s color. Melanoma is considered the most lethal of the cancers that affect the skin. Unfortunately, melanoma spread can cause cancer to move from the skin cells to the internal organs. Melanoma spread can also cause cancer to develop in a persons lymph nodes.
Often, skin cancers do not spread this is because they are basal cell carcinomas, which dont usually spread. This type of skin cancer is often easier to cure. However, melanoma is different, and it spreads when cancerous cells get into the blood vessels near the melanoma or they make their way into lymphatic vessels. When the cells move into the blood vessels, they may be carried to other parts of the body, where they can develop in the organs. When they invade the lymphatic vessels, they are transported by the lymph fluid and drained, along with the fluid, into the lymph nodes.
Don’t Miss: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Stage 3 Survival Rate
Can Metastasis Be Prevented
Melanoma can spread “silently,” meaning that you may not experience any symptoms of metastasis. Therefore, if you’ve been treated for early-stage melanoma in the past, it is extremely important to perform regular self-examinations of your skin and lymph nodes, to keep all your appointments for checkups, and practice sun safety. There is nothing else an individual can do to prevent metastasis from being very diligent.
Catching a recurrence early greatly increases your chances of successful treatment. If the melanoma does spread, it is important to remain positive: remember that while the average prognosis is poor, some people do survive stage IV melanoma.
Skin Cancer Doctor Discussion Guide
Get our printable guide for your next doctor’s appointment to help you ask the right questions.
Merkel Cell Carcinoma: A Rare Skin Cancer On The Rise
Merkel cell carcinoma is a rare type of skin cancer that affects about 2,000 people in the United States each year.
Though its an uncommon skin cancer, cases of Merkel cell carcinoma have increased rapidly in the last couple of decades.
This type of cancer starts when cells in the skin, called Merkel cells, start to grow out of control.
Merkel cell carcinomas typically grow quickly and can be difficult to treat if they spread.
They can start anywhere on the body, but Merkel cell carcinomas commonly affect areas exposed to the sun, such as the face, neck, and arms.
They may look like pink, red, or purple lumps that are firm when you touch them. Sometimes, they can open up as ulcers or sores.
Risk factors include:
Read Also: Stage Iii Melanoma
What Are Metastatic Melanoma Symptoms And Signs
When melanoma spreads through the bloodstream, the signs and symptoms will depend upon which organ system is involved and how much the tumor has grown there. Metastatic melanoma may be initially painless and symptom-free or may demonstrate ongoing problems according to the site. With lymphatic spread, swollen lymph glands or a string of nodules in the skin may be the presentation. These also are usually painless.
Tumor metastasis into the liver may cause weight loss, nausea, a swollen liver, and abnormal blood tests. Tumor in lymph nodes may cause swelling of the extremities and enlarged glands. Tumor in the lungs may cause shortness of breath, cough, and bloody sputum. Tumor in the brain may cause headaches, dizziness, and seizures. Tumor in bone may cause bone pain or unusual fractures.
Melanoma may spread to other areas of the skin and may be bluish-gray or flesh-colored nodules depending upon the amount of melanin in the tumor and depth in the skin. In staging melanoma, stage 3 is defined as local spread through lymphatic drainage , and stage 4 is defined as distant spread to other organs, presumably by spread through the bloodstream.
How Does Metastatic Melanoma Differ From Melanoma
Melanoma is any cancer that originates in the melanocytes, while metastatic melanoma is melanoma that spreads from the skin to other parts of the body, such as the lymph nodes, liver, lungs, bones, and brain.
Most people who develop melanoma around 4 in 5 get their diagnosis at an early stage, while the cancer is still localized.
Treatment at this point is straightforward and extremely effective, with a five-year survival rate of over 98 percent.
Metastatic melanoma is much harder to treat and more life-threatening, killing an estimated 9,300 people in the United States each year.
Don’t Miss: Well-differentiated Squamous Cell Carcinoma Prognosis
How Is Melanoma Of The Head And Neck Diagnosed
Diagnosis is made by clinical exam and a biopsy. Melanoma is diagnosed by the presence of abnormal melanocytes.
Melanoma of the skin is staged based on how deeply it invades the skin layers and whether or not it has spread. A superficial or shave biopsy will not provide the accurate staging information used to guide treatment. The depth of invasion determines the risk of spread to lymph nodes or other organs. Ulceration and microsatellitosis are additional diagnostic features that, when present, are associated with a higher risk of spread. In patients without clinically enlarged lymph nodes, sentinel lymph node biopsy is used to determine if microscopic spread to lymph nodes in the neck has occurred, and is used for all but very thin melanomas unless other high-risk features are present.
This information is used for staging, to guide prognosis and further treatment. Thick melanomas are associated with a higher risk of spread to other organs, which is evaluated by pretreatment imaging. When enlarged lymph nodes are detected on clinical exam, a fine needle aspiration biopsy is performed to determine whether melanoma is present in nodes.
Some subtypes of melanoma may be less likely to spread: lentigo maligna and desmoplastic melanoma. The role of sentinel node biopsy is controversial in these cases, and will be discussed with you by your treatment team.
Red Flag #: Abdominal Pain And Tenderness
Early on, there may be no noticeable symptoms that melanoma has spread to the liver. When symptoms do show up, they commonly include an enlarged, hard, or tender liver and pain in the upper right area of your abdomen, just below your ribs. Other signs cancer has spread to the liver are similar to symptoms of liver disease: fluid buildup in the belly and yellowing of the skin and eyes .
Recommended Reading: Is Stage 3 Melanoma Curable
How Does Metastasized Melanoma Works
Melanoma begins in melanocytes cells in the deepest layer of skin. This is also known as the hypodermic or subcutaneous tissue. When these cells become damaged, mutations can occur and the mutated cells can reproduce themselves rapidly. Eventually, the cells start forming a tumor and taking over surrounding tissues.
Melanoma can develop from existing moles or skin growths, but, more commonly, they will start as new growth. In a further stage, it is possible that the melanoma grows into metastatic melanoma.
Topical Diphencyprone For Melanoma
Topical diphenylcyclopropenone or diphencyprone in various concentrations in solution or cream may be useful for small cutaneous melanoma metastases. The first application sensitises the patient to the chemical over about 10 days. Further applications applied to the lesions at weekly intervals cause allergic contact dermatitis, which can be very itchy and uncomfortable and may generalise. When effective, existing treated lesions stop enlarging and may shrink or disappear. Dramatic responses have been reported including regression of involved lymph nodes.
Intralesional immunotherapy for melanoma metastases using T-VEC, Allovectin-7® and Rose Bengal is under investigation.
Read Also: How Fast Does Squamous Cell Carcinoma Spread
Spreading To The Lymph Nodes
When a tumor gets too big, it requires more oxygen and nutrients to survive.
This is when the tumor sends out signals that cause new blood vessels to grow into the tumor , bringing the nutrients and oxygen it needs. After angiogenesis occurs, cancer cells are now able to break off and enter the bloodstream.
They can also break off and spread through the lymphatic system . When this happens, the cancer cells can now settle and take root in a new area of the body. Once the cancer cells have spread to the lymph nodes its considered stage three melanoma.
Diagnosis Of Metastatic Melanoma
Your care team may use several tests to diagnose metastatic melanoma.
If theres evidence of a primary tumor, a biopsy may be taken. For this, a small section of suspected cancerous skin is removed with a razor, scalpel or small punch tool. The removed tissue is examined under a microscope to determine whether its melanoma.
Additional tests are needed to determine whether the cancer is metastatic melanoma, or if theres no visible primary tumor. To test for metastatic melanoma, or melanoma that has spread to lymph nodes or distant parts of the body, your care team may perform the following tests.
- Lymph node mapping and sentinel lymph node biopsy : Your doctor may perform a physical exam of your lymph nodes and check for swelling or physical masses. If no tumors are found , an SLNB may be done. For an SLNB, a radioactive dye is injected to locate the primary tumor. Then, the doctor will remove the lymph nodes that the dye traveled to and check them for melanoma.
- Computed tomography scan, positron emission tomography scan, magnetic resonance imaging scan or ultrasound exam: Each of these scans is a noninvasive way to look inside your body and check for tumors.
- Blood chemistry studies: Cancer may cause elevated or abnormal levels of certain substances in your blood. A laboratory test can identify if your blood chemistry shows signs of a cancerous tumor.
Don’t Miss: Skin Cancer Perineural Invasion
Treatment Of Metastatic Melanoma
Metastatic melanomas can be difficult to treat. The five-year survival rate for people diagnosed with melanoma that has spread to nearby lymph nodes is 66 percent, according to the American Cancer Society. When cancer has spread to distant parts of the body, there may also be other metastases too small to detect by scans. For people diagnosed with stage 4 melanoma, or melanoma that has spread to distant parts of the body, the five-year survival rate is 27 percent.
For stage 3 and 4 melanomas, the following treatments may be used:
Multiple therapies can be used at any given time, and your care plan is a dynamic process. You and your care team should discuss all the options and decide on a treatment plan. Each treatment has different side effects, and its important to feel fully informed of all the associated risks. Other medications and options may help manage the symptoms of your cancer treatment, so you can live the highest quality of life possible throughout the course of your treatment and disease.
Expert
Treating Stage Ii Melanoma
Wide excision is the standard treatment for stage II melanoma. The width of the margin depends on the thickness and location of the melanoma.
Because the melanoma may have spread to nearby lymph nodes, many doctors recommend a sentinel lymph node biopsy as well. This is an option that you and your doctor should discuss.
If an SLNB is done and does not find cancer cells in the lymph nodes, then no further treatment is needed, although close follow-up is still important.
If the SLNB finds that the sentinel node contains cancer cells, then a lymph node dissection will probably be done at a later date. Another option might be to watch the lymph nodes closely by getting an ultrasound of the nodes every few months.
If the SLNB found cancer, adjuvant treatment with an immune checkpoint inhibitor or targeted therapy drugs might be recommended to try to lower the chance the melanoma will come back. Other drugs or perhaps vaccines might also be options as part of a clinical trial.
Recommended Reading: Lobular Breast Cancer Survival Rates