Preventing Basal Cell Carcinoma
Basal cell carcinoma prevention is the same as prevention methods for all skin cancers, with the goal of protecting skin from harmful UV rays.
The number one thing people can do is to practice good sun protection and sun avoidance, meaning wear sunscreen and protect the skin from getting sun damage, says Stevenson. Its also important to get skin checks regularly for early detection.
Stevenson says if someone is prone to skin cancers for example, has very fair skin, sunburns as a child, or a history of skin cancer in the family its better to go out in the late afternoon or early morning when the sun isnt as strong, or stay primarily in the shade.
Anyone spending time in the sun, regardless of complexion, should practice sun protective behaviors, including wearing sunscreen.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends a sunscreen with a minimum sun protection factor of 15, and UVA and UVB broad spectrum protection. It also advises people to stay in the shade as much as possible and wear protective clothing including brimmed hats and sunglasses. Stevenson suggests looking for a SPF over 30.
Lebwohl says the SPF number directly correlates with the amount of protection it gives you. He says to divide the amount of time in the sun by the SPF number. For example, if someone is in the sun for 60 minutes, and wearing SPF 30, its as if they were exposed to two minutes of damaging rays rather than the full 60 minutes.
Warning Signs Of Basal Cell Carcinoma That You Could Mistake As Harmless
Warning sign: A pink or reddish growth that dips in the centerCan be mistaken for: A skin injury or acne scar
A pink or reddish growth that dips in the center
The BCC on this patients cheek could be mistaken for a minor skin injury.
Warning sign: A growth or scaly patch of skin on or near the earCan be mistaken for: Scaly, dry skin, minor injury, or scar
A growth or scaly patch of skin on or near the ear
BCC often develops on or near an ear, and this one could be mistaken for a minor skin injury.
Warning sign: A sore that doesn’t heal and may bleed, ooze, or crust overCan be mistaken for: Sore or pimple
A sore that doesn’t heal, or heals and returns
This patient mistook the BCC on his nose for a non-healing pimple.
Warning sign: A scaly, slightly raised patch of irritated skin, which could be red, pink, or another colorCan be mistaken for: Dry, irritated skin, especially if it’s red or pink
A scaly, slightly raised patch of irritated skin
This BCC could be mistaken for a patch of dry, irritated skin.
Warning sign: A round growth that may be pink, red, brown, black, tan, or the same color as your skinCan be mistaken for: A mole, wart, or other harmless growth.
A round growth that may be same color as your skin
Would you recognize this as a skin cancer, or would you dismiss it as a harmless growth on your face?
Basal Cell Carcinoma Early Stage Perianal Skin Cancer Pictures / Invasive Orbital Basal Cell Carcinoma
The general term “lung cancer” actually covers a few very different versions of the disease. A cancer diagnosis can leave you unable to comprehend anything else your doctor says, but it’s important to pay attention to what stage of cancer you have. According to the american cancer society, just over 100,000 new cases of skin cancer are diagnosed in the united states each year. Information is a powerful weapon against uncertainty and fear, and you can use this to your advantage. Having fun in the sun sounds like a great idea.
Read Also: How To Identify Basal Cell Carcinoma
Staging For Merkel Cell Cancer
Doctors use the TNM system to describe the stage of Merkel cell cancer. Doctors use the results from diagnostic tests and scans to answer these questions:
-
Tumor : How large is the primary tumor? Where is it located?
-
Node : Has the tumor spread to the lymph nodes? If so, where and how many?
-
Metastasis : Has the cancer spread to other parts of the body? If so, where and how much?
The results are combined to determine the stage of Merkel cell cancer for each person.
There are 5 stages: stage 0 and stages I through IV . The stage provides a common way of describing the cancer, so doctors can work together to plan the best treatments.
Stage 0: This is called carcinoma in situ. Cancer cells are found only in the top layers of the skin. The cancer does not involve the lymph nodes, and it has not spread.
Stage I: The primary tumor is 2 centimeters or smaller at its widest part. The cancer has not spread to the lymph nodes or to other parts of the body.
Stage IIA: The tumor is larger than 2 cm and has not spread to the lymph nodes or other parts of the body.
Stage IIB: The tumor has grown into nearby tissues, such as muscles, cartilage, or bone. It has not spread to the lymph nodes or elsewhere in the body.
Stage III: The cancer has spread to the lymph nodes. The tumor can be any size and may have spread to nearby bone, muscle, connective tissue, or cartilage.
Stage IV: The tumor has spread to distant parts of the body, such as the liver, lung, bone, or brain.
Staging Basal Cell Carcinoma
In most cases, basal cell carcinoma does not require staging because it rarely spreads. Staging is only applicable if your cancer is very large or has spread. It determines how severe the cancer is and how to treat it.
The TNM system is used most often to stage cancer:
- Tumor: Takes into consideration tumor size and if it has infiltrated into other structures nearby, such as bone.
- Node: Describes cancer spread to the lymph nodes.
- Metastases: Identifies if cancer has spread to other distant body parts.
Read Also: Does Skin Cancer Make You Lose Hair
Different Types Of Cancer Start In The Skin
Skin cancer may form in basal cells or squamous cells. Basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma are the most common types of skin cancer. They are also called nonmelanoma skin cancer. Actinic keratosis is a skin condition that sometimes becomes squamous cell carcinoma.
Melanoma is less common than basal cell carcinoma or squamous cell carcinoma. It is more likely to invade nearby tissues and spread to other parts of the body.
This summary is about basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma of the skin, and actinic keratosis. See the following PDQ summaries for information on melanoma and other kinds of cancer that affect the skin:
Treatment Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
-
Removal of the tumor
Doctors may remove the cancer in the office by scraping and burning it with an electric needle or by cutting it out. Doctors may destroy the cancer by using extreme cold .
Certain chemotherapy drugs may be applied to the skin. Photodynamic therapy , in which chemicals and a laser are applied to the skin, also may be used. Occasionally, radiation therapy is used.
A technique called Mohs microscopically controlled surgery may be required for some basal cell carcinomas that are large or regrow or occur in certain areas, such as around the nose and eyes.
People whose cancer has spread to nearby tissues or spread to other parts of the body and who are not candidates for surgery or radiation therapy may be given the drug vismodegib or sonidegib taken by mouth.
You May Like: Amelanotic Melanoma Blanch
What Are The Possible Complications Of Superficial Basal Cell Carcinoma Of Skin
The complications of Superficial Basal Cell Carcinoma of Skin could include:
- If the tumor becomes big, or ulcerates, it can get secondarily infected with bacteria or fungus
- If left untreated, Superficial Basal Cell Carcinomas can become invasive
- Superficial BCC of Skin can cause cosmetic issues
- Recurrence of the tumor after a period of time recurrences are frequently noted with large tumors
- Effects of surgical or topical treatments, which involve scarring, redness, or secondary infection
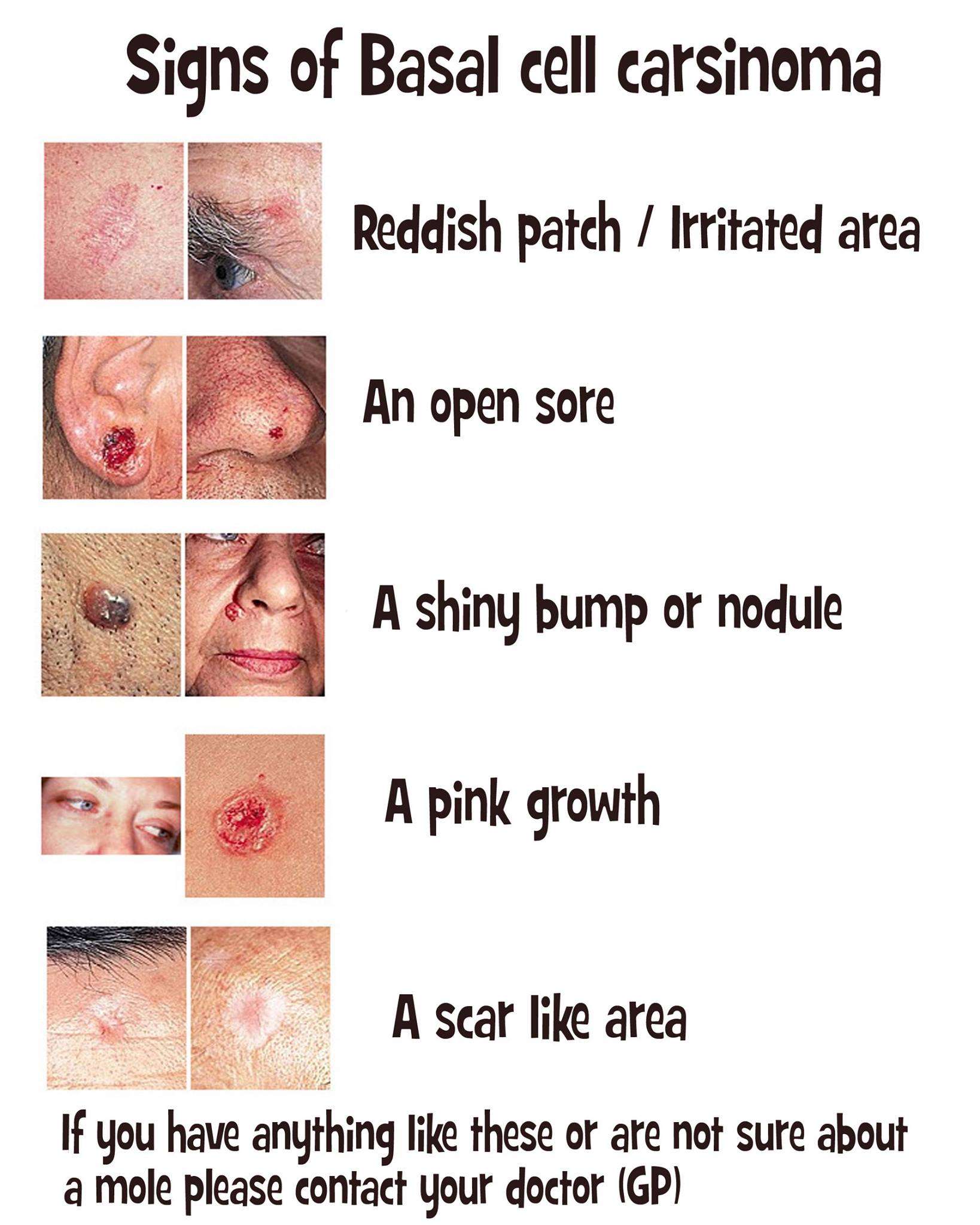
Symptoms Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
The various types of basal cell carcinoma can take many different forms. Often, it may seem like a small bump that grows very slowly. Other symptoms are a:
- Pink, reddish spot that dips in the center
- Scaly patch, especially near the ears
- Sore that resembles a pimple, but that either doesnt heal or heals but keeps returning
- Round growth that can be pink, red, brown, tan, black, or skin-colored
- Scar-like skin that isnt from an injury
Its important to note that the color and shape of the tumor may not be uniform. The spot may be flat or raised, it can be dipped in the center or not, and it can even appear shiny. Often, BCCs do not cause pain, but the area can be numb, sensitive, or itchy. Its hard to self-diagnose a basal cell carcinoma because they can take so many different shapes. If you have a concerning spot, its best to schedule a dermatological appointment right away.
Read Also: Can Squamous Cell Carcinoma Metastasis
A Cancer Diagnosis Can Leave You Unable To Comprehend Anything Else Your Doctor Says But It’s Important To Pay Attention To What Stage Of Cancer You Have
According to the american cancer society, just over 100,000 new cases of skin cancer are diagnosed in the united states each year. A diagnosis of lung cancer naturally causes some overwhelming emotions, but you don’t have to let those emotions get the best of you. It affects people of all races, genders and ages, which is why it’s absolutely critical for americans to learn about. Skin cancer is the most common type of cancer in the united states by a pretty large margin, and it does not discriminate. Basal cell carcinoma is the most common type of skin cancer. In the united states, it’s estimated that doctors diagnose over 100,000 new skin cancer cases each year. Lung cancer has two broad types: Having fun in the sun sounds like a great idea. Information is a powerful weapon against uncertainty and fear, and you can use this to your advantage. The general term “lung cancer” actually covers a few very different versions of the disease. Skin cancer is the most common type of cancer in the united states, with basal and squamous cell skin cancer being the most common carcinoma types. Some types of skin cancer are more dangerous than others, but if you have a spot. There are roughly 5.4 million diagnoses of these two types every year.
Skin Cancer Is A Disease In Which Malignant Cells Form In The Tissues Of The Skin
The skin is the bodys largest organ. It protects against heat, sunlight, injury, and infection. Skin also helps control body temperature and stores water, fat, and vitamin D. The skin has several layers, but the two main layers are the epidermis and the dermis . Skin cancer begins in the epidermis, which is made up of three kinds of cells:
- Squamous cells: Thin, flat cells that form the top layer of the epidermis.
- Basal cells: Round cells under the squamous cells.
- Melanocytes: Cells that make melanin and are found in the lower part of the epidermis. Melanin is the pigment that gives skin its natural color. When skin is exposed to the sun, melanocytes make more pigment and cause the skin to darken.
Skin cancer can occur anywhere on the body, but it is most common in skin that is often exposed to sunlight, such as the face, neck, and hands.
Recommended Reading: Does Skin Cancer Itch And Burn
How Is Superficial Basal Cell Carcinoma Of Skin Treated
In general, the treatment of Superficial Basal Cell Carcinoma of Skin depends upon a variety of factors including:
- The location of the tumor
- The number of tumors
- The size of the tumor
- Any health considerations of the patient
A number of treatment methods may be used to treat Superficial Basal Cell Carcinoma of Skin. The treatment types may include:
Topical medications can be used to treat Superficial Basal Cell Carcinoma. This is because the thinness of the tumor permits permeation of the active ingredient to the full depth of the carcinoma. The two most frequently used active ingredients are imiquimod and 5-Flurouracil.
- Imiquimod is an immune system signal which calls for the migration of T-cells into the area of the tumor, which actively kill the cancer cells
- 5-Flurouracil is a metabolic agent which toxically kills the more basal cell carcinoma cells. The surrounding normal skin does not absorb the medication and hence is safe from the toxicity
Both these topical applications take at least a few weeks to treat a typically sized lesion, longer for larger lesions. The actions will lead to redness, irritation, sometimes crusting and possibly secondary infection
One advantage of these creams is that it is sometimes possible to treat the Superficial Basal Cell Carcinoma without affecting the underlying skin at all, so after healing, little to no scarring is detectable.
Other techniques to treat this skin cancer may include:
Basal Cell Carcinoma Treatment And Diagnosis
Basal cell carcinoma diagnosis is a frequent and daily occurrence across the UK. Fortunately, the vast majority are very easy to cure and very few people diagnosed with BCC will see it spread from its starting site or suffer serious ill-health. However, this relies on early detection. As described and illustrated above most of these lesions are easy to notice and this usually prompts early medical review and treatment. This limits the number of people that present for basal cell cancer treatment at a late stage.
Diagnosis is often by inspection but sometimes confirmation is required by a simple skin biopsy which is then assessed under a microscope. Lesions in a single site are usually removed with minor surgical procedures. Basal cell carcinoma removal and surgery often only requires local anaesthetic. Some very small lesions can be treated with topical chemotherapy type creams.
Further details of basal cell carcinoma treatment can be foundhere.
You May Like: Basal Skin Cancer Survival Rates
What Are The Causes Of Superficial Basal Cell Carcinoma Of Skin
- The exact cause of development of Superficial Basal Cell Carcinoma of Skin is not completely known, in a majority of cases
- Although, genetic mutations have been detected in Basal Cell Carcinomas, which are currently being characterized
- Most BCCs are sporadic in origin i.e., they occur in a random fashion
What Are The Symptoms Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
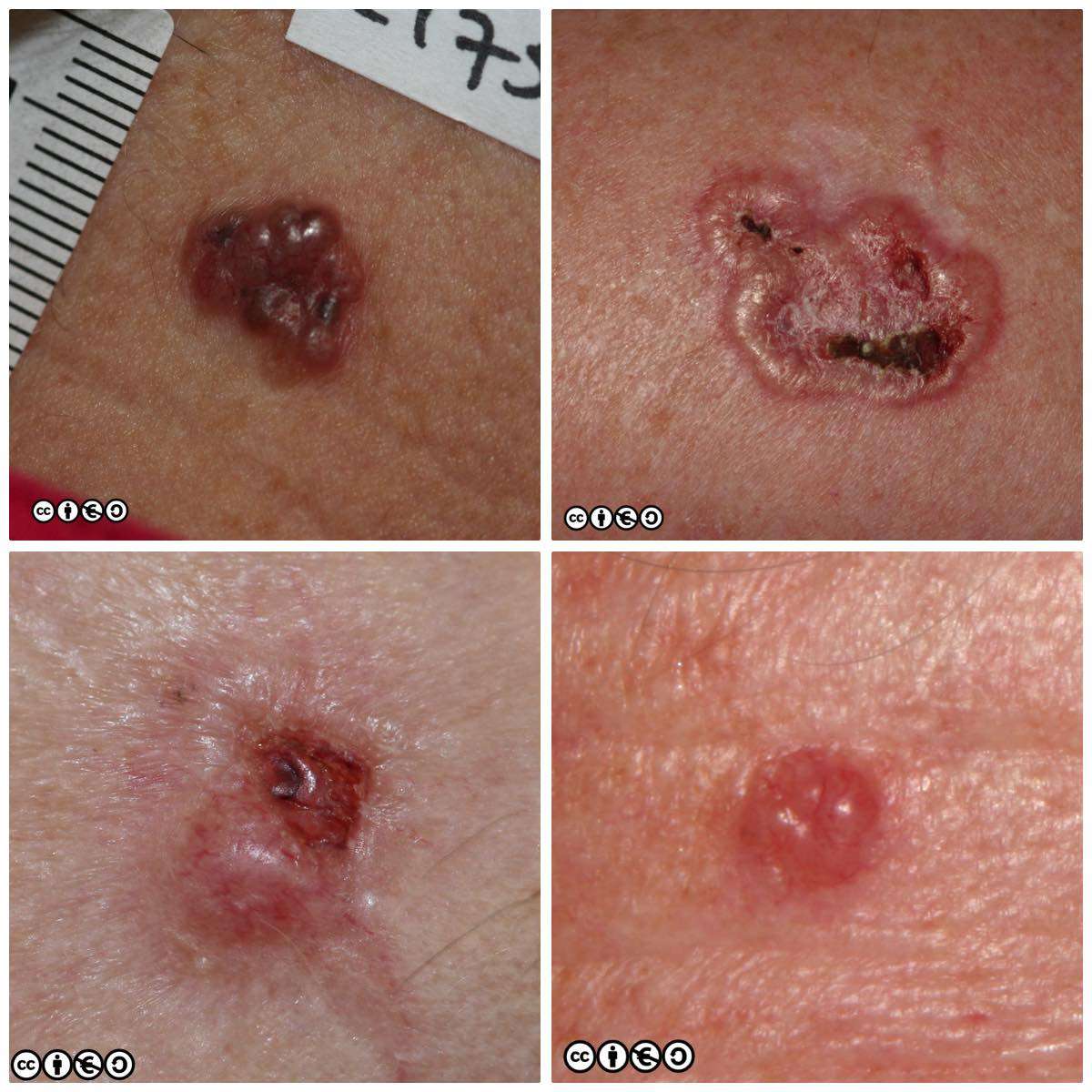
A basal cell carcinoma is a stubborn, persistent spot that usually appears on areas that have been exposed to the sun, such as the head, neck, chest, arms and legs. The spot may take one of several forms: an open sore, a reddish irritated patch, a shiny red bump or nodule, a pink growth, or a small scar-like patch. In some people, the condition may resemble psoriasis or eczema. The spot will sometimes bleed, scab and heal up after a week or two, then bleed or become irritated again.
The main warning sign for basal cell carcinoma is that the spot doesn’t go away on its own. Patients often mistake basal cell carcinomas for minor injuries, says Dr. Christensen. They dont realize that an ordinary cut or scratch will heal within a month or so. So if something hasnt healed within a month, it should be examined by a dermatologist.
Don’t Miss: Does Insurance Cover Skin Cancer Screening
Who Gets Basal Cell Carcinoma
Risk factors for BCC include:
- Age and sex: BCCs are particularly prevalent in elderly males. However, they also affect females and younger adults
- Repeated prior episodes of sunburn
- Fair skin, blue eyes and blond or red hairnote BCC can also affect darker skin types
Also Check: What Does Skin Cancer Look Like On Your Head
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
Basal cell carcinomas can appear anywhere on the body but the most common sites are sun exposed areas such as the face and arms. Its important to keep a close eye on your skin to try and identify early basal cell carcinoma, as its easier to treat if identified early on.
Typical Basal cell carcinoma symptoms are:
- New skin lesion
- Change in colour of a lesion
The typical lesions to watch out for are as follows:
- Pink or translucent, shiny bumps or pearly nodules, sometimes with dark spots or black, blue, or brown surface
- Growths, pink in color, with raised edges and sunken center, usually with irregular blood spoke-wheel vessels on its surface
- Pale or yellow scar-like areas
- Elevated reddish patches
Don’t Miss: How To Identify Basal Cell Carcinoma
Basal Cell Carcinoma Survival Rate
Basal cell carcinoma has an excellent survival rate especially when the cancer is detected early. Most tumors respond favorably to treatment. Statistics show that:
- The earlier basal cell carcinoma is diagnosed, the better the patients chance of survival.
- The therapies that are currently used for basal cell carcinoma offer an 85 to 95 percent recurrence-free cure rate. This means that the specific lesion being treated is effectively cured by the first round of treatment.
- The mortality rate for nonmelanoma skin cancers has been decreasing steadily in recent years.
Although basal cell carcinoma is often curable, people who are diagnosed with one basal cell carcinoma may develop additional lesions elsewhere on their skin later on in life. Recurrent basal cell carcinomas are also highly treatable oncologists may use the same therapies that they used for the first cancer, or they may recommend different approaches if they believe other options might be more effective.
Patients never need a referral to seek care from Moffitts Cutaneous Oncology Program. To speak with one of our experienced oncologists about the basal cell carcinoma survival rate and the most appropriate treatments, call or complete a new patient registration form.
- BROWSE