Is Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma Aggressive
Like all carcinomas, ccRCC can spread, or metastasize, to other parts of your body. Metastatic cancer is more difficult to treat. Compared to other kidney cancers, the clear cell type of renal cell carcinoma tends to be more aggressive and spread faster.
Renal cell carcinoma most commonly spreads to the:
- Lymph nodes .
Is Chromophobe Renal Cell Carcinoma Hereditary
This rare type of cancer can run in families as part of a rare genetic disorder called Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome. The disorders genetic nature has allowed researchers a small window of opportunity to study it however, very little is known about the genetic basis of sporadic chromophobe kidney cancer.
How Is Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma Diagnosed
Kidney cancer rarely causes symptoms. Thats why healthcare providers discover more than half of kidney tumors while looking for a cause of other conditions. They may see a tumor on imaging tests like MRIs or CT scans to check for problems like kidney stones.
While imaging tests can detect a tumor, they cant show whether the mass is benign or malignant. For an accurate diagnosis, youll undergo a biopsy or surgery to remove the tumor.
After surgery, healthcare providers take a biopsy of the tumor tissue. The results can confirm a cancer diagnosis and determine whether its the clear cell subtype. As many as 4 in 10 small kidney tumors turn out to be noncancerous tumors like renal oncocytomas.
Read Also: Grade 3 Cancer Treatment
When Should I Call The Doctor
- Blood in your urine.
- Lump or pain in your side that doesnt go away.
- Unexplained fever or weight loss.
What should I ask my healthcare provider?
You may want to ask your healthcare provider:
- What type of kidney cancer do I have?
- What is the best treatment for me?
- What are the treatment side effects?
- Am I at risk for metastatic cancer? How can I lower this risk?
- Are other family members at risk for kidney cancer?
- Should I look out for signs of complications?
Other Types Of Non Clear Cell Kidney Cancer

- Transitional cell carcinoma : They are also known as urothelial carcinomas. TCCs do not start in the kidney but in the transitional cells in the lining of the renal pelvis. This cancer can look like other types of urothelial cancer such as bladder cancer. However, people with TCC will often have the same symptoms as people with kidney cancer, like blood in the urine and back pain. TCC is rare and can be aggressive.
- Wilms tumor : This tumor almost always occurs in children and is very rare in adults. About 90% of kidney cancers in children are Wilms tumors.
- Renal sarcoma: This is a rare type of kidney cancer that begins in the blood vessels or connective tissue of the kidney.
You May Like: Stage 3 Cancer Symptoms
How Is Ccrcc Diagnosed
Patients with ccRCC may have pain or feel tired. Sometimes, patients do not have any noticeable symptoms. Symptoms can include:
- Blood in the urine
- Fever
- A lump in the side
For people without symptoms, these tumors can be discovered if the person has an imaging test for another reason.
Imaging: If are suspected to have clear cell renal cell carcinoma, your doctor will use imaging scans such as X-rays, CT or MRI to look at the size of the tumor. They will also check for signs that the tumor has spread to other parts of the body.
Biopsy: To check if the tumor is ccRCC your doctor will perform a biopsy, taking a small sample from the tumor with a needle. An expert, called a pathologist, will study cells from the sample under the microscope to see what kind of tumor it is.
Living With Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma
Your medical team will develop a treatment plan to help you fight ccRCC, but there are some very important parts of your care that cant happen in an operating room.
Managing your everyday life with ccRCC can feel like a huge challenge. But there are some simple steps you can take at home, with friends, and with other healthcare professionals. Great ways to take care of yourself during treatment include:
- Eating healthier. There isnt a set diet plan for ccRCC, but eating healthy can help you feel better during treatments and recovery. Talk with your doctor before making any major changes to your diet.
- Taking time for mental health. It can be hard to talk about a cancer diagnosis, even with family and friends. Mental health professionals such as counselors and psychologists can help you sort through the stress and emotions of managing ccRCC.
- Asking for help. Its a good idea to turn to friends, family, loved ones, or other supportive people when youre managing ccRCC. Local charities and cancer support groups can help you find support if youre in need.
You May Like: Melanoma 3c
Molecular Basis Of Clear Cell Rcc
Recent advances in the understanding of cancer as a genetic disease have allowed the identification of clonal genetic and epigenetic alterations, which accumulate during cancer progression, often in a general temporal order. However, relatively little is known about the secondary and later genetic alterations which drive progression after the initiating event of inactivation of VHL in clear cell RCC. Even less is known about the alterations that underlie the initiation and progression of sporadic papillary or chromophobe RCC, or the importance of different tumor suppressor and signaling pathways in renal cancer. It remains that much of what we know of the molecular basis of sporadic RCC arose from identification of the genes predisposing to inherited RCC .
With the exception of VHL, all these tumor suppressor genes appear to be inactivated in a minority of RCC, Indeed the number with clear evidence of inactivation of the retained allele by point mutation, homozygous deletion or hypermethylation is substantially less than the number with LOH. This may simply be due to not looking hard enough. The case of germline mutation of VHL is instructive because as investigators searched deeper for the second mutation, more were found . The target suppressor gene on several of the more frequently deleted chromosomal arms e.g. 6q, 8p or 14q in RCC have not yet been identified. Subtyping of RCC by tumor suppressor inactivation may prove important for prognostic stratification.
The Stages Of Kidney Cancer
Kidney cancer staging relies on the TNM system. This system was created by the American Joint Committee on Cancer:
- T: Size and localized spread of the original tumor
- N: How much spread has occurred in lymph nodes located near the original tumor
- M: Metastasis outside of the kidney into other organs and distant lymph nodes
Stage 1: Stage 1 is the first stage of kidney cancer. When kidney cancer is found during stage 1, youll have the most optimistic five-year relative survival rate. A stage 1 tumor is smaller than 7 centimeters and has not spread outside of the kidney. There is no cancer in the lymph nodes and no metastasis.
Stage 2: In this stage, the tumor is larger than 7 centimeters, but still hasnt spread outside of the kidney.
Stage 3: Stage 3 is a more aggressive cancer. In this stage, the tumor has either spread into a large vein and nearby tissue, or it is a tumor of any size that has spread outside of the kidney into lymph nodes located nearby.
Stage 4: Stage 4 renal cancer has the least favorable prognosis. Kidney cancer is stage 4 if the primary tumor has entered the adrenal gland, located on top of the kidney. Kidney cancer may also be considered stage 4 if it is a tumor of any size and has metastasized to other parts of the body, including distant lymph nodes or other organs.
Recommended Reading: Lobular Breast Cancer Stage 1
Prognosis And Predictive Factors
Patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma tend to have a worse prognosis than patients with other histologic subtypes of RCC, with 5-year disease-specific survival rates of 50-69%, compared with 67-87% for papillary RCC and 78-87% for chRCC. However, analysis of 1000 patients showed very similar 5-year disease-specific survival rates for CCRCC and papillary RCC once metastatic disease was present.
Multivariate analyses indicate that histologic RCC subtype has no significant independent value for predicting cancer-specific survival because prognosis is primarily dependent upon TNM stage and Fuhrman nuclear grade. Multivariate analysis specifically of CCRCC cases shows that in addition to the 3 separate components of tumor staging , other significant independent predictors of poor prognosis are nuclear grade, tumor size, and the presence of histologic necrosis or sarcomatoid differentiation.
Rhabdoid differentiation is also observed in CCRCC and seems to impart a poor outcome similar to sarcomatoid change however, this factor has not yet been tested in predictive models. Interestingly, histological necrosis is seen more commonly in papillary RCC but is not a significant predictor of poor prognosis for papillary RCC, even in univariate analyses.
References
Delahunt B, Eble JN. History of the development of the classification of renal cell neoplasia. Clin Lab Med. 2005 Jun. 25:231-46, v. .
Pascual D, Borque A. Epidemiology of kidney cancer. Adv Urol. 2008. 782381. .
Risk Prevention And Early Detection Of Rcc
Individuals with inherited syndromes that predispose to RCC and long-term dialysis patients are at high risk but account for a minority of RCC cases. Algorithms of relative risk of RCC according to smoking status, body mass index and blood pressure have been investigated and a decrease in risk was observed for men who had stopped smoking for 30 years or more . The only evidence for the potential of chemoprevention for RCC are studies which show diets rich in fruit and vegetables as well as high vitamin D levels to be preventive . Candidates for a future chemopreventive strategy would be inherited RCC, ESRD patients and also RCC patients at high risk of recurrence.
Molecular early detection strategies must be designed with careful regard to the abundance of tumor cells in the clinical specimen as well as the frequency and timing of the alteration to be detected . LOH of 3p and point mutation of VHL are frequent and early in clear cell RCC but urine or blood contain a low ratio of DNA from renal tumor cells to DNA from normal cells that is insufficient for the robust detection of these alterations by polymorphic marker and sequencing analysis respectively. Because point mutations occur throughout the VHL gene, rather than at hotspots of particular codons like RAS, the design of more sensitive oligonucleotide molecular tests is very complicated. However, if a tumor cell-rich biopsy specimen is available, LOH and point mutation can be assessed as prognostic markers.
Read Also: Ductal Carcinoma Breast Cancer Survival Rates
How Kidney Cancer Stages Are Determined
Kidney cancer stage is determined through diagnostic testing. Usually, imaging tests will be done to analyze the tumor or tumors within the kidney.
Imaging tests will also be done to identify metastasis in other areas of the body, including the lungs, brain, and bones. These tests may include CT scans, MRIs, a bone scan, and a chest CT or X-ray.
Incidence Risk Factors And Clinical Features
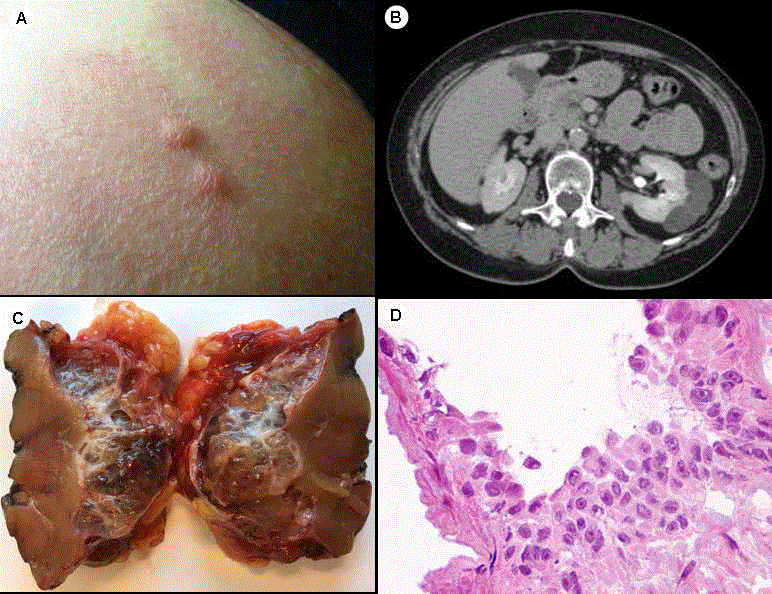
In recent decades, the incidence of RCC has been steadily rising by 24% each year and RCC is now the 7th leading cancer type in men in the US. In 2010, it is projected that in the US there will be approximately 58,000 new cases of, and 13,000 deaths from, kidney cancer, the vast majority being RCC . Compared to 1971, there has been a 5-fold increase in the incidence of, and a two-fold increase in mortality from, RCC . Increasing use of imaging for other medical indications has resulted in more RCCs found by incidental detection but this does not entirely explain the rise in incidence. The gender ratio is approximately male 2:1 female. African Americans have both a higher incidence and mortality rates for kidney cancer . Cigarette smoking, obesity, hypertension and/or related medications have been implicated as risk factors although the increase in risk is relatively modest . The etiology of most RCCs remain unclear. Approximately 24% of RCC is hereditary and since the predisposition genes have been identified, genetic screening can identify carriers who represent a group at high risk of RCC. Another population at high risk for RCC is individuals at an advanced stage of chronic kidney disease on long-term dialysis. More than 100,000 people will begin treatment for end stage renal disease this year among the almost 20 million with CKD in the US.
Recommended Reading: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Grade 1 Survival Rate
Aggressive Kidney Cancer Prognosis
Aggressive cancer means the cancer grows and develops more quickly, which also means that there is greater chance for the cancer cells to spread to other parts of the body. Kidney cancer can become aggressive, too. For such case, immediate treatment is required. How about the prognosis?
Differential Clinical Outcomes Observed In Molecular Subsets
Despite the relatively small patient sample size of our high-grade uRCC cohort, differential cancer-specific outcomes were observed among the above-defined molecular subgroups . NF2 loss and FH-deficient uRCC appeared to have worse clinical outcome than mTORC1 hyperactive and thus far unspecified uRCC, whereas uRCC with mutations mainly in chromatin modulation or DNA damage response genes fared intermediately .
SETD2 or BAP1 mutation alone did not discern tumour subsets with significantly different clinical outcomes in this uRCC cohort .
Read Also: Stage 2 Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Survival Rate
Coping With Kidney Cancer
Coping with kidney cancer isnt easy. Its important to remember that not every person with renal cell carcinoma has the same esponse to treatment.
Living with a diagnosis of kidney cancer can be highly stressful. Taking care of yourself can help you feel better physically and mentally. Theres even some evidence that proactive behaviors can support longevity, such as exercising and eating healthy foods.
Quitting smoking also can help. Smoking cigarettes is a leading risk factor for kidney cancer. Of course, it can be stressful trying to quit, especially if you feel that the damage has been done.
However, data indicates that stopping smoking improves survival rates in people with clear cell renal cell carcinoma. It also lowers your risk of getting and dying from another disease.
Try to get enough sleep. Adequate rest can help you maintain your strength. You may need more sleep during cancer treatment while your body works to repair itself.
In your quest to support health, you may find yourself drawn to the supplements aisle of your drugstore. Talk to your doctor before taking supplements, even if they seem to be a health booster. Many supplements, just like analgesic pain medications, may harm your kidneys and shouldnt be used.
When To Get Medical Advice
See a GP if you have symptoms of kidney cancer.
Although its unlikely you have cancer, its important to get your symptoms checked out.
The GP will ask about your symptoms and may test a sample of your urine to see if it contains blood or an infection.
If necessary, they may refer you to a hospital specialist for further tests to find out what the problem is.
Metastatic renal cell carcinoma
Renal cell carcinoma, also called kidney cancer, occurs when cancer cells form in the tubules of the kidney. Tubules are tiny tubes in your kidney that help filter waste products from your blood in order to make urine.
Smoking, hypertension, obesity, and hepatitis C all increase the risk of renal cell carcinoma. Renal cell carcinoma becomes metastatic renal cell carcinoma when it spreads beyond your kidney to your lymph system, bones, or other organs.
Renal cell carcinoma can spread from a mass of cancer cells or tumor to other parts of your body. This process is called metastasis. It occurs in one of three ways:
- Cancer cells spread into the tissue around the tumor in your kidney.
- The cancer moves from your kidney into your lymph system, which has vessels throughout the body.
- Kidney cancer cells enter the bloodstream and are carried and deposited to another organ or location in your body.
When renal cell carcinoma is in its early stages, its unlikely that youll experience obvious symptoms. Noticeable symptoms are often a sign that the disease has metastasized.
Also Check: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Stage 2 Survival Rate
How Is Papillary Renal Cell Carcinoma Treated
Treatment for papillary renal cell carcinoma usually starts with surgery to remove part or all of the kidney. This procedure is known as a nephrectomy. 1 Surgery is the most common treatment option for early-stage kidney cancers. Radiation therapy may then be recommended to kill cancer cells in the area of the tumor.
Treatments For Renal Cell Carcinoma
There are five kinds of standard treatments for RCC. One or more may be used to treat your cancer.
Read Also: What Is The Most Aggressive Skin Cancer
You May Like: Skin Cancer Spread To Lymph Nodes