What Does Bcc Look Like
BCCs can look like open sores, red patches, pink growths, shiny bumps, scars or growths with slightly elevated, rolled edges and/or a central indentation. At times, BCCs may ooze, crust, itch or bleed. The lesions commonly arise in sun-exposed areas of the body. In patients with darker skin, about half of BCCs are pigmented .
Its important to note that BCCs can look quite different from one person to another. For more images and information on BCC signs, symptoms and early detection strategies, visit our BCC Warning Signs page.
Please note: Since not all BCCs have the same appearance, these photos serve as a general reference to what they can look like. If you see something new, changing or unusual on your skin, schedule an appointment with your dermatologist.
An open sore that does not heal
A shiny bump or nodule
A reddish patch or irritated area
A scar-like area that is flat white, yellow or waxy in color
A small pink growth with a slightly raised, rolled edge and a crusted indentation in the center
Effective Options For Early And Advanced Bcc
When detected early, most basal cell carcinomas can be treated and cured. Prompt treatment is vital, because as the tumor grows, it becomes more dangerous and potentially disfiguring, requiring more extensive treatment. Certain rare, aggressive forms can be fatal if not treated promptly.
If youve been diagnosed with a small or early BCC, a number of effective treatments can usually be performed on an outpatient basis, using a local anesthetic with minimal pain. Afterwards, most wounds can heal naturally, leaving minimal scarring.
Options include:
Infiltrated Basal Cell Carcinoma
This version of basal cell carcinoma is presented as thin bundles of basaloid cells with nest-like configuration located between the collagenous fibers on the dermis and infiltrating in the depth. Clinically, it is a whitish, compact, not-well defined plaque . The most common localization is in the upper part of the trunk or the face. Seldom had the paresthesia or hyperesthesia as a symbol of perineural infiltration appeared, especially when the tumor is localized on face. This clinical version is often underestimated when the borders of surgical excision are estimated. Histologically this variant is presented as thin, nest-like bundles of basaloid cells infiltrating in the dermal collagenous fibers .
Infiltrated basal cell carcinoma. Thin bundles of basaloid cells invade the dermis
You May Like: Merkel Cancer Prognosis
Additional And Relevant Useful Information For Micronodular Basal Cell Carcinoma Of Skin:
There are multiple types of Basal Cell Carcinoma of Skin:
- Superficial Basal Cell Carcinoma of Skin
- Nodular Basal Cell Carcinoma of Skin
- Infiltrating Basal Cell Carcinoma of Skin
- Micronodular Basal Cell Carcinoma of Skin
- Fibroepithelial Basal Cell Carcinoma of Skin
- Basal Cell Carcinoma of Skin with Adnexal Differentiation
- Basosquamous Carcinoma
- Keratotic Basal Cell Carcinoma of Skin
What Is A Basal Cell
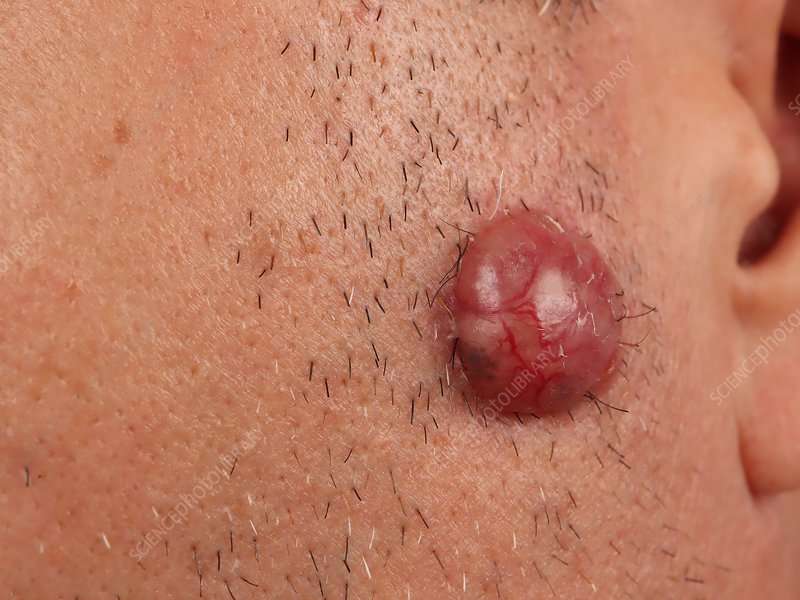
One of three main types of cells in the top layer of the skin, basal cells shed as new ones form. BCC most often occurs when DNA damage from exposure to ultraviolet radiation from the sun or indoor tanning triggers changes in basal cells in the outermost layer of skin , resulting in uncontrolled growth.
Read Also: Stage 5 Cancer Symptoms
Symptoms Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
There are several types of basal cell carcinomas.
The nodular type of basal cell carcinoma usually begins as small, shiny, firm, almost clear to pink in color, raised growth. After a few months or years, visible dilated blood vessels may appear on the surface, and the center may break open and form a scab. The border of the cancer is sometimes thickened and pearly white. The cancer may alternately bleed and form a scab and heal, leading a person to falsely think that it is a sore rather than a cancer.
Other types of basal cell carcinomas vary greatly in appearance. For example, the superficial type appears as flat thin red or pink patches, and the morpheaform type appears as thicker flesh-colored or light red patches that look somewhat like scars.
Basal Cell Carcinoma Stages Stanford Health Car
Melanoma, the most fatal skin cancer, is the second most common cancer in young women. Rates of other skin cancers, such basal cell and squamous cell carcinomas, have also skyrocketed, by 145% and. Basal cell carcinoma sub-types2.1.1. Nodular basal cell carcinoma. Is the most common clinical sub-type of BCC. It occurs most commonly on the sun-exposed areas of the head and neck and appears as a translucent papule or nodule depending on duration Basal cell carcinoma may resemble a slowly growing pink, skin-colored or light brown nodule on the skin, which gradually increases in size. Often a dark crust develops in the middle, which could bleed with a light touch. The tissue of the nodule can also look somewhat glassy, shiny and sometimes shows small blood vessels
Also Check: Basal Cell Carcinoma Late Stages
Is It Time For Your Annual Skin Check
One of the best ways to prevent basal cell carcinoma is to take steps to protect your skin from the sun, including daily sunscreen, protective clothing, and seeking shade whenever possible. If you have a high risk of developing skin cancer, then make sure that you dont miss your yearly skin check-up with your dermatologist.
Are you experiencing any symptoms that concern you? Schedule an appointment with the dermatologists at the Center for Surgical Dermatology. Were now accepting patients for telemedical appointments!
More Information About Basal Cell Carcinoma
The following are some English-language resources that may be useful. Please note that THE MANUAL is not responsible for the content of these resources.
See the following sites for comprehensive information about basal cell carcinoma, including detection, prevention, treatment options, and other resources:
Recommended Reading: Non Invasive Breast Cancer Survival Rate
What Are The Subtypes Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
General Principles In Outer Nose Repair
Most of nasal skin is of the sebaceous type. Whenever possible, scar lines should be placed along relaxed skin tension lines. Aesthetic units of the nose need consideration although tumours do not respect their borders. Aging affects the nose anatomy. Characteristic symptoms are frown lines , transverse crease on the nasal root, drooping of tip of nose, and deepened nasolabial folds. Skin diseases of elderly, like rosacea and rhinophyma can interfere with surgical techniques.
The skin covering the bony parts is highly movable, while the skin over cartilage parts is thicker, tighter and bound to the cartilage. Healing by second ary intention of convex surfaces like the nose tip should be avoided since healing often is delayed and may lead to uneven scars.
Don’t Miss: Ductal Carcinoma Survival Rate
What Is Basal Cell Carcinoma
Basal cell carcinoma is the most common form of skin cancer, with approximately 80% of skin cancers developing from basal cells. The epidermis has three types of cells. The cells in the bottom layer of the epidermis are the basal cells.
Basal cells consistently divide to form new cells. These replace squamous cells, pushing old cells towards the skin’s surface, where they die and slough off. Cancers that start in this bottom/basal layer of skin cells are called basal cell carcinoma.
Basal cell carcinoma is usually triggered by damage from ultraviolet radiation. This is most commonly from either exposure to the sun or tanning beds. UV radiation can damage basal cells, causing them to change and grow uncontrollably.
Basal cell carcinoma can look different from person to person. It may present as an open sore, scaly patch, shiny bump, a red irritated patch, pink growth, waxy scar-like growth, or a growth that dips in the center. They can sometimes ooze, crust, or bleed
As it can vary in how it looks, it is essential to get any new growths, lesions, lumps, bumps, or changes of your skin checked by your healthcare provider.
Prevention Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
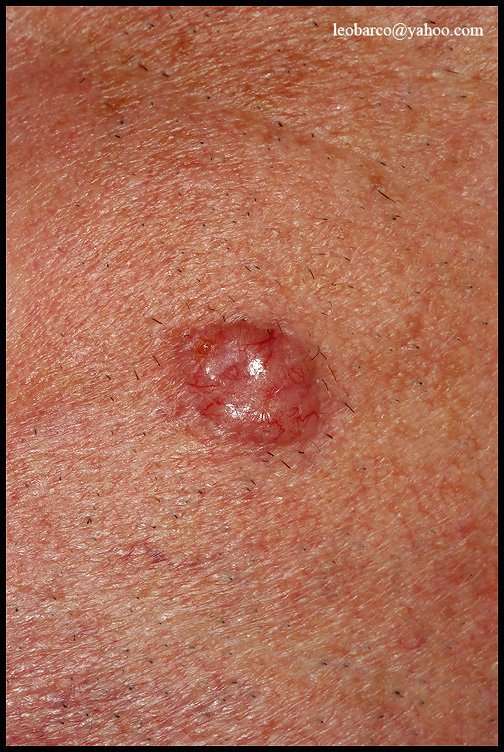
Because basal cell carcinoma is often caused by sun exposure, people can help prevent this cancer by doing the following:
-
Avoiding the sun: For example, seeking shade, minimizing outdoor activities between 10 AM and 4 PM , and avoiding sunbathing and the use of tanning beds
-
Wearing protective clothing: For example, long-sleeved shirts, pants, and broad-brimmed hats
-
Using sunscreen: At least sun protection factor 30 with UVA and UVB protection used as directed and reapplied every 2 hours and after swimming or sweating but not used to prolong sun exposure
In addition, any skin change that lasts for more than a few weeks should be evaluated by a doctor.
Read Also: In Situ Cancer Melanoma
How Is Basal Cell Carcinoma Treated
BCCs can almost always be successfully treated. Treatment will depend on the type, size and location of the BCC, and on your age and health.
If the BCC was removed during the biopsy, you may not need any further treatment. Surgery is the most common treatment for a BCC. It involves cutting out the skin spot and nearby normal-looking tissue. A pathologist will check the tissue around the skin spot to make sure the cancer has been removed. If cancer cells remain, you may need more surgery.
Other treatment options include:
- freezing the spot with liquid nitrogen to kill the cancer cells
- scraping off the spot, then using low-level electric current to seal the wound and kill cancer cells
- immunotherapy creams, liquids and lotions, to treat superficial BCCs
Superficial Basal Cell Carcinoma
This version occurs as erythematous plaque with different sizes . It is about 10-30% of basal cell carcinoma and occurs on the body skin. There is an erythematous squamous plaque with clear borders, pearl-shape edge, superficial erosion, without tendencies for invasive growth . The regression areas are presented as pale sections with fibrosis. The differential diagnosis includes Bowen disease, psoriasis, or eczema. The numerous superficial BCC are met often in case of arsenic exposure. Histology showed nests of basaloid cells located subepidermally, with clear connection with the basal layer of the epidermis and no infiltration of tumor cells in the reticular dermis .
Superficial basal cell carcinoma. Several nests of basaloid cells are located subepidermally with clear connection with the basal layer of the epidermis
You May Like: Can You Die From Squamous Cell Carcinoma
What You Should Know About Basal Cell Carcinoma Symptoms
When it comes to BCC symptoms, they can vary significantly from one person to the next, according to physicians and other practitioners. For example, skin anomalies tend to appear darker in dark-skinned individuals compared to those who are fair-skinned. Additionally, some people with BCC will experience oozing, bleeding, or crusting of the skin while others will not. That said, it is best to avoid self-diagnosis and seek medical treatment if you notice any changes in the appearance of your skin. This is true even if they are small changes.
What Is The Prognosis Of Micronodular Basal Cell Carcinoma Of Skin
- In general, the prognosis of Micronodular Basal Cell Carcinoma of Skin is excellent, if it is detected and treated early. However, if it metastasizes to the local lymph nodes, the prognosis is guarded or unpredictable
- In such cases of metastatic BCC, its prognosis depends upon a set of several factors that include:
- Stage of tumor: With lower-stage tumors, when the tumor is confined to site of origin, the prognosis is usually excellent with appropriate therapy. In higher-stage tumors, such as tumors with metastasis, the prognosis is poor
- The surgical resectability of the tumor
- Overall health of the individual: Individuals with overall excellent health have better prognosis compared to those with poor health
- Age of the individual: Older individuals generally have poorer prognosis than younger individuals
- Whether the tumor is occurring for the first time, or is a recurrent tumor. Recurring tumors have a poorer prognosis compared to tumors that do not recur
- Response to treatment: Tumors that respond to treatment have better prognosis compared to tumors that do not respond so well to treatment
You May Like: Is Melanoma In Situ Malignant
What Is A Melanocyte
Melanocytes are skin cells found in the upper layer of skin. They produce a pigment known as melanin, which gives skin its color. There are two types of melanin: eumelanin and pheomelanin. When skin is exposed to ultraviolet radiation from the sun or tanning beds, it causes skin damage that triggers the melanocytes to produce more melanin, but only the eumelanin pigment attempts to protect the skin by causing the skin to darken or tan. Melanoma occurs when DNA damage from burning or tanning due to UV radiation triggers changes in the melanocytes, resulting in uncontrolled cellular growth.
About Melanin
Naturally darker-skinned people have more eumelanin and naturally fair-skinned people have more pheomelanin. While eumelanin has the ability to protect the skin from sun damage, pheomelanin does not. Thats why people with darker skin are at lower risk for developing melanoma than fair-skinned people who, due to lack of eumelanin, are more susceptible to sun damage, burning and skin cancer.
What About Other Treatments That I Hear About
When you have cancer you might hear about other ways to treat the cancer or treat your symptoms. These may not always be standard medical treatments. These treatments may be vitamins, herbs, special diets, and other things. You may wonder about these treatments.
Some of these are known to help, but many have not been tested. Some have been shown not to help. A few have even been found to be harmful. Talk to your doctor about anything youre thinking about using, whether its a vitamin, a diet, or anything else.
You May Like: What Is The Survival Rate For Invasive Lobular Carcinoma
Get To Know Your Skin And Check It Regularly
Look out for changes such as:
- A mole that changes shape, color, size, bleeds, or develops an irregular border
- A new spot on the skin that changes in size, shape, or color
- Sores that don’t heal
- New bumps, lumps, or spots that don’t go away
- Shiny, waxy, or scar type lesions
- New dark patches of skin that have appeared
- Rough, red, scaly, skin patches
If you notice any changes to your skin, seek advice from a medical professional. Basal cell carcinoma is very treatable when caught early.
What Does Most Dangerous Skin Cancer Look Like
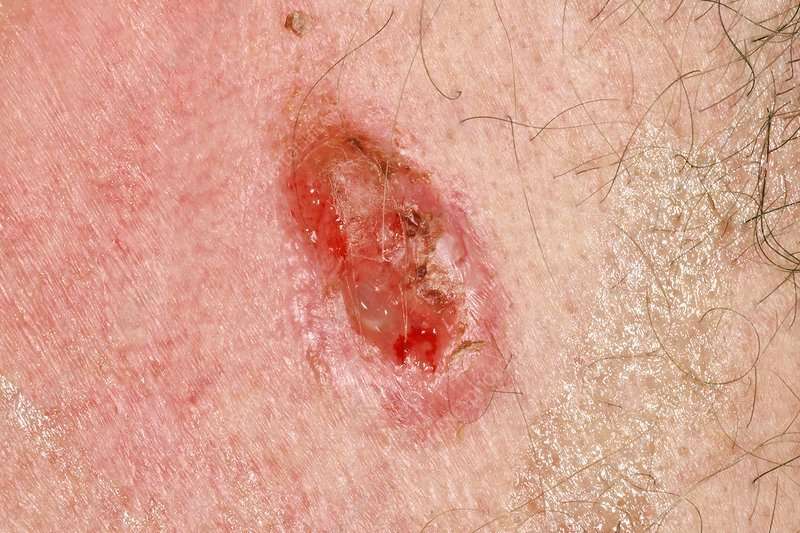
Skin cancer typically stands out as being different to surrounding skin. If a spot strikes you as being a bit odd, take it seriously it is worth getting it had a look at.
Skin cancer mainly looks like a new and uncommon looking spot. It may likewise look like an existing spot that has actually altered in color, size or shape.
Here are some different types of skin cancers :
You May Like: Nodulo Infiltrative Basal Cell Carcinoma
Basal Cell Carcinoma: What You Need To Know
Basal cell carcinoma is the most common cancer in the world. One out of two people will have a BCC growth before age 65. Although BCC is rarely life threatening, it should be taken seriously. If left untreated, this cancer can be disfiguring, especially on the face.
The information in these pages will help you understand more about BCC: what it is, what causes it, how it is diagnosed and treated, and how you can prevent it.
What is basal cell carcinoma?
Basal cell carcinoma is a type of skin cancer. It begins in the basal cells, the deepest part of the skins outermost layer. Basal cell carcinomas almost never spread beyond their original site to other parts of the body, especially when treated early.
What do basal cell carcinomas look and feel like?
As shown below, basal cell carcinomas vary widely, with a number of different appearances:
-
Open sores that dont heal
-
A round ulcer that looks as though a bite has been taken out of the middle
-
Red patches that have a sandpapery feel
-
Shiny bumps that are raised, hard, pearly pink or gray
-
An area of thickened skin
-
A bump with a rolled edge
-
A lesion with blood vessels that look like the spokes of a wheel
Basal cell carcinomas can occur anywhere on the body they may appear to sit on top of the skin, or burrow into it. Most lesions are painless. Sometimes they can feel itchy. They may bleed easily if caught on clothing or nicked during shaving.
What causes basal cell carcinoma?
How is basal cell carcinoma diagnosed?
Surgery
How Is Micronodular Basal Cell Carcinoma Of Skin Diagnosed
Some of the tests that may help in diagnosing Micronodular Basal Cell Carcinoma of Skin include:
- Complete physical examination with detailed medical history evaluation
- Examination by a dermatologist using a dermoscopy, a special device to examine the skin
- Woodâs lamp examination: In this procedure, the healthcare provider examines the skin using ultraviolet light. It is performed to examine the change in skin pigmentation
- Skin or tissue biopsy: A skin or tissue biopsy is performed and sent to a laboratory for a pathological examination, who examines the biopsy under a microscope. After putting together clinical findings, special studies on tissues and with microscope findings, the pathologist arrives at a definitive diagnosis
- Differential diagnosis of other tumors should be ruled out hence, biopsy is an important diagnostic tool
Many clinical conditions may have similar signs and symptoms. Your healthcare provider may perform additional tests to rule out other clinical conditions to arrive at a definitive diagnosis.
Read Also: What Does Well Differentiated Mean