Dermatologists Are Not Happy With Us
Not surprisingly, some dermatologists were dismayed by this message. One wrote:
After spending over 40 years treating skin cancer and counseling patients on sunscreen use, I feel that the data you reported needs interpretation in real life terms.
Sunscreen use in many studies does not necessarily mean adequate use. A good British study done years ago showed that the average person applies only about 25 percent of the recommended amount of sunscreen. I suspect that the subjects in the studies you cited did not apply sunscreen half an hour before going outside, reapply it every two hours, or put it on more often if they were swimming or perspiring.
My favorite advice to patients is if you can see without a flashlight, you should have sunscreen on.
The Importance Of Protecting Against Uv Light
Dr. Julie Sharp, head of health information at Cancer Research UK, notes that although sunscreen when applied properly can protect against UV radiation, people tend to think theyre invincible once they have put it on and spend longer in the sun. As a result, overall exposure to UV light is increased.
This research adds important evidence showing that sunscreen has a role, but that you shouldnt just rely on this to protect your skin, she adds. Its essential to get into good sun safety habits, whether at home or abroad, and take care not to burn sunburn is a clear sign that the DNA in your skin cells has been damaged and, over time, this can lead to skin cancer.
As well as applying generous amounts of sunscreen SPF 30 or higher when in the sun, the National Council on Skin Cancer Prevention recommend seeking shade when the sun is at its strongest and wearing sun-protective clothing, such as a wide-brimmed hat, wrap-on sunglasses and a T-shirt.
Medical News Today recently reported on a study published in the journal Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention, which suggests that five or more blistering sunburns experienced before the age of 20 could increase the risk of melanoma by 80%.
Sure Sunscreen Protects Me From The Sun But What About The Chemicals In It Are They Safe For My Health
The evidence we do have suggests sunscreen is generally safe, but theres still a lot we dont know about the long-term effects of sunscreen use.
There have been some concerns about the toxicity of products that contain titanium dioxide and zinc oxide nanoparticles, though little clarity on the precise dangers to human health.
Para-aminobenzoic acid -based sunscreens and products containing benzophenones can cause skin irritation including rashes and pimples in some people.
Chemicals like octinoxate and oxybenzone have been found to have estrogenic effects in cell and animal studies, as have some parabens. Again, what this means for humans is still unclear.
Most recently, a small 2019 study, published in JAMA, showed chemicals in sunscreen avobenzone, oxybenzone, octocrylene, and ecamsule absorb into the bloodstream when people lathered up four times per day for four days. And they did so at levels the Food and Drug Administration suggests require further safety testing. Again, that doesnt mean the chemicals are unsafe. But, according to an accompanying editorial co-authored by the former head of the FDA, we urgently need studies to understand whether it matters.
Recommended Reading: Basal Cell Melanoma Prognosis
How Well Do Sunscreens Work To Prevent Skin Cancer
We have all been told countless times to smear on the sunscreen! The Australians even had a slogan: Slip! Slop! Slap! It was part of a 1981 health campaign to: Slip on a shirt, slop on sunscreen and slap on a hat to stop skin cancer. There is little doubt that sun exposure, especially in Australia, contributes to a lot of skin cancer. But do sunscreens prevent skin cancer? Its more complicated that you might think, as this reader suggests:
Carcinogen Detected In Sun Care Products

Valisure, an online pharmacy known for testing every batch of medication they sell, announced this week that they petitioned the FDA to recall 40 batches of sunscreens and after-sun products they say tested for high levels of the chemical benzene. The company tested 294 batches from 69 companies and found benzene in 27% — many in major national brands like Neutrogena and Banana Boat. Some batches contained as much as three times the emergency FDA limit of 2 parts per million .
Long-term exposure to benzene is known to cause cancer in humans.
âThis is especially concerning with sunscreen because multiple FDA studies have shown that sunscreen ingredients absorb through the skin and end up in the blood at high levels,â says David Light, CEO of Valisure.
See a list of products Valisure says contacts benzene here, starting on page 12. And here is a list of sunscreens the company says did not show unsafe levels of the chemical.
The FDA is seeking more information about the potential risks from common sunscreen ingredients.
âThere is not a safe level of benzene that can exist in sunscreen products,â Christopher Bunick, MD, PhD, associate professor of dermatology at Yale University, said in Valisureâs FDA petition. âThe total mass of sunscreen required to cover and protect the human body, in single daily application or repeated applications daily, means that even benzene at 0.1 ppm in a sunscreen could expose people to excessively high nanogram amounts of benzene.â
Don’t Miss: Large Cell Cancer Of The Lung
Ways To Choose And Use Sunscreen Wisely So That Your Sunscreen Prevent Skin Cancer:
A. Read the label and choose your own sunscreen:
- While buying sunscreen, watch the label. If broad-spectrum is mentioned, it protects against both UVA and UVB rays. If SPF is mentioned only, it protects against UVB rays. Choose to use a broad-spectrum sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher if you have high exposure to sun.
- You can prefer sunscreen with SPF 15 for occasional exposure and everyday activities such as driving to work, walking, etc. If you work outdoors and activities like hiking, running, swimming need SPF 30 or higher.
- Intense physical activity and swimming need water-resistant labelled sunscreens. They are effective for up to forty minutes in water. Sunscreen labelled as Very water-resistant are effective up to eighty minutes in water.
- Sunscreens are available as creams, gels, sticks, and sprays. Creams are suitable for dry skin, and Gels are suitable for hairy or scalp areas. Sticks can be used around the eyes. You can pick your sunscreen based on your activities, the area to be protected, and how comfortable you are with a particular product. People who have sensitive skin can go for physical sunscreens, and there are also special sunscreens available for sensitive skin and babies.
B. Things to remember while applying sunscreen:
Where Should I Apply Sunscreen
Experts recommend applying sunscreen to your entire body before you dress for the day. That way your skin will be protected if your clothing shifts or you remove layers. At the very least, you should use sunscreen on every part of your body that is exposed to the sun, including those easy-to-miss spots: the tops of your ears, back of your neck, your scalp , tops of your feet and behind your knees.
Recommended Reading: Lobular Carcinoma Survival Rate
Why You Need It How It Works For You
The big picture: Sunscreen is an important part of a complete sun protection strategy. But sunscreen alone isnt enough to keep you safe in the sun.
When used as directed, sunscreen is proven to:
Regular daily use of SPF 15 sunscreen can reduce your risk of developing squamous cell carcinoma by about 40 percent, and lower your melanoma risk by 50 percent.
Help prevent premature skin aging caused by the sun, including wrinkles, sagging and age spots.
KNOW THE 5 WS OF SUNSCREEN
WHO: Everyone under the sunWHAT: Broad spectrum SPF 15 or higher SPF 30 or higher for a day outdoorsWHEN: Every day 30 minutes prior to going outdoors. Reapply every two hoursWHERE: All exposed skinHOW: One ounce to entire body for each applicationWHY: Reduce your risk of skin damage and skin cancer!
How Much Sunscreen Should I Use
To get the full broad-spectrum protection out of your sunscreen, apply one ounce about a shot glass full to your entire body. Most people apply less than half of that amount, translating into reduced protection. Learn more.
With reapplication, a family of four should use one four-ounce bottle of sunscreen per person during a long day outdoors.
Read Also: If You Have Skin Cancer How Do You Feel
Which Sunscreen Should I Use
Choose a sunscreen that best suits your skin type and activity and that you find easy to reapply. If you have sensitive skin and have had a reaction to sunscreen in the past, look for fragrance-free products. If you dont want sunscreen residue left on your hands, look for a gel.
Not all sunscreens contain the same ingredients. If your skin reacts to one sunscreen, talk to a chemist or doctor about choosing one with different ingredients.
Make sure the sunscreen is at least 30SPF, broad-spectrum and water resistant. Also check the expiry date of the sunscreen and the storage conditions recommended on the label. Most sunscreens last about two to three years and should be stored at a temperature below 30ºC.
Should I Use Sunscreen On My Baby Or Child
Sunscreen is not recommended for use on babies under 6 months old. The main forms of sun protection for babies should always be protective clothing, hats and shade. Sunscreen on children should be used in conjunction with, protective clothing and hats, and shade. Always test a new sunscreen on a small area of your childs skin first for any negative reactions. If irritation occurs discontinue use and seek advice from a Doctor.
You May Like: Well Differentiated
Potential New Sunscreen Technologies
Topical photolyases and antioxidants are emerging as potential agents of topical and nontopical photoprotection. Antioxidants cannot yet be stabilized within sunscreen formulations to remain biologically active. Studies have established that sunscreens that claim antioxidant activity have little to no actual antioxidant activity.
Photoprotective agents taken orally, such as niacinamide and Polypodium leucotomos extract, which is derived from a fern native to Central and South America, are used as agents for prevention of photodamage. There is evidence from small RCTs that P. leucotomos extract increases the minimal erythema dose of sun exposure without significant adverse effects, and is helpful for dermatologic diseases induced by ultraviolet radiation, such as polymorphous light eruption and solar urticaria.
Nicotinamide, also known as niacinamide, is the active amide form of niacin . However, unlike niacin, it does not cause cutaneous flushing. Nicotinamide has been shown in early studies to enhance DNA repair and decrease the formation of cyclobutene pyrimidine dimers in human keratocytes. In one phase III RCT, which has not been replicated, nicotinamide 500 mg twice daily was associated with a decreased rate of development of both actinic keratoses and nonmelanoma skin cancers over a 12-month period. However, the skin cancers that did occur tended to be high-grade malignancies.
And You Still Need Sunscreen
Since we have yet to find a magic pill that completely prevents sunburns and eliminates skin cancer risk, this is my plug for good old-fashioned sunscreen. Sunscreen has been shown to reduce both melanoma and squamous cell carcinoma. Randomized prospective studies in Australia showed that individuals who used daily sunscreen had a 50% reduction in melanoma and a 40% reduction in squamous cell carcinoma, compared to individuals who used sunscreen intermittently. So when the sun and warm weather beckon, remember to apply a broad-spectrum sunscreen with at least SPF 30 prior to going out in the sun, reapply every two hours, and apply liberally: 1 teaspoon to each arm, head and neck, front torso, and back and 2 teaspoons to each leg.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Survival Rate Of Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
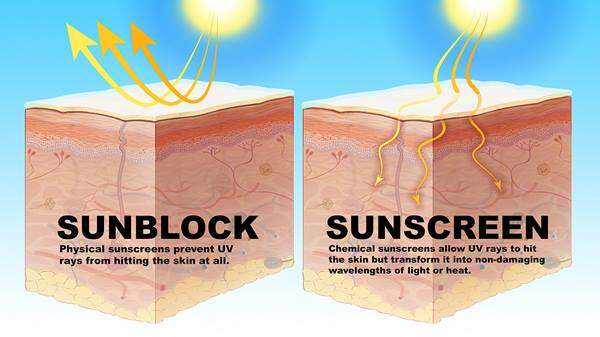
How Do Sunscreens Work
Sunscreens contain chemical or physical compounds that act to block ultraviolet radiation, which is light with wavelengths shorter than visible light , as shown in . Generally, the shorter the wavelength, the greater the potential for light radiation to cause biological damage. Sunscreen filters are active against UVA1, UVA2 and UVB radiation. Chemical filters, such as oxybenzone, avobenzone, octocrylene and ecamsule, are aromatic compounds that absorb high-intensity ultraviolet radiation, resulting in excitation to higher energy states. When these molecules return to their ground states, the result is conversion of the absorbed energy into lower-energy wavelengths, such as infrared radiation .
Schematic representation of the electromagnetic spectrum of light, emphasizing ultraviolet radiation frequencies and their effect on human skin. Generally, the shorter the wavelength of radiation, the greater the potential for biological damage. Note: UVA = ultraviolet A, UVB = ultraviolet B, UVC = ultraviolet C. Sunscreen filters are active against UVA1, UVA2 and UVB radiation.
How About The Environmental Effects: Is Sunscreen Killing Off Coral Reefs
Between 2015 and 2018, one-fifth of the coral reefs in the world have died off and there is a growing awareness that sunscreen is playing a role in this mass extinction.
In May 2018, Hawaii lawmakers passed a bill banning the sale of over-the-counter sunscreens that contain oxybenzone and octinoxate, which are harming the islands coral reefs. If its signed into law, Hawaii would be the first jurisdiction in the US to pass such a measure, NPR reported.
So some sunscreens can certainly be toxic to these underwater ecosystems. But as Brad Plumer reported for Vox, sunscreen certainly isnt the only threat to them. Instead, increased ocean temperature as a result of global warming is the major reason coral reefs are dying around the world.
According to the Environmental Protection Agency, coral reefs are incredibly vulnerable to human activities overfishing, coral harvesting, as well as coastal development and boats have also played a role in jeopardizing their health. The chemicals in sunscreen are just some of the many pollutants that are threatening coral reefs.
Don’t Miss: Melanoma Stage 3 Life Expectancy
Better Results Lie In Better Use
Most of us use only twenty-five to fifty percent of the recommended amounts of sunscreen, and adults need almost one ounce of sunscreen to fully cover the body. According to the skin cancer foundation, proper sunscreen usage can decrease the chance of developing squamous cell carcinoma by 40% and melanoma by 50%. Say no to the sun without sunscreen and lower your skin cancer risk.
How Many Sunburns Can Lead To Skin Cancer
Theres a dose-response relationship here: The more sunburns you have in your life, the higher the risk of skin cancers. Those blistering sunburns are the ones that are very strongly linked with skin cancer, Linos added.
And in childhood, you dont even want one. Thats because younger skin is more vulnerable to cancer-causing UV damage.
But how much burning any one individual can handle varies hugely and depends on a mixture of genetic factors and environmental factors .
Not everybodys skin is equally able to withstand UV light. In general, the darker your skin, the less likely to burn and the lower the skin cancer risk. And if you burn in the sun more easily, you are at a higher risk of skin cancer.
Somebody who comes from Sudan and has dark skin is at a very low risk of skin cancers, even if they get exposed to the sun, said Sekulic. Somebody from Iceland who is very fair, or somebody who is a redhead and who cannot tan these people are at very, very high risk.
Read Also: Skin Cancer Mayo
So Lets Separate The Facts From The Fiction
Lets be straight: melanoma can be deadly if it isnt caught quickly enough. It is the leading kind of skin cancer in the United States.
But using sunscreen is not an effective way to prevent it. In fact, using sunscreen can put you more at risk for developing melanoma cancer. Heres why.
First, its important to understand the difference between the long and short rays that reach us from the sun. Long rays are called UVA rays, and the short ones are called UVB rays.
The short UVB rays have a more immediate surface effect on your skin and can cause sunburn pretty quickly. They also help facilitate the production of skin-cancer preventing vitamin D in the skin. The long UVA rays penetrate more deeply into your skin and can cause melanoma cancer lesions to form.
Most sunscreen works to prevent sunburn, which means that it is formulated to block out UVB rays, the shorter rays. But it doesnt protect as well, and in many cases it doesnt protect at all against the longer UVA rays.
So if you put some sunscreen on and go lay outside in order to get a tan, you stay out longer because you have protected yourself against the risk of getting sunburn. However, unfortunately, the longer you stay out in the sun without the protective effects of the UVB rays, the more you increase the risk of getting cancer, due to exposure to UVA rays.
Where Are The Modern Rcts That Answer: Does Sunscreen Prevent Skin Cancer
One of the authors of the original Australian study admits that randomized controlled trials are essential to answer the question whether sunscreens prevent skin cancer . Thats because observational evidence is intractably confounded. In other words, it is not trustworthy. The only meaningful RCT remains the Australian study that was conducted between 1992 and 1996.
We are not suggesting that people should avoid sunscreen. Quite the contrary. But if we believe in evidence-based medicine, we really do need large, well-controlled clinical trials using modern sunscreens for the 21st century. Why hasnt the very lucrative sunscreen industry sponsored such studies?
Don’t Miss: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Breast Cancer Survival Rates