Get To Know Your Skin
The sooner a skin cancer is identified and treated, the better your chance of avoiding surgery or, in the case of a serious melanoma or other skin cancer, potential disfigurement or even death.
It is also a good idea to talk to your doctor about your level of risk and for advice on early detection.
It’s important to get to know your skin and what is normal for you, so that you notice any changes. Skin cancers rarely hurt and are much more frequently seen than felt.
Develop a regular habit of checking your skin for new spots and changes to existing freckles or moles.
What Happens When Skin Cancer Goes Untreated
If you notice an abnormality on your skin you may be tempted to ignore it. However, if it is skin cancer you could be putting your health at risk by waiting to get a skin and mole check. There are three main types of skin cancer in Australia with melanoma, basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma, and they each have their own set of unique characteristics. The most important thing to remember is that if you delay treatment of skin cancer it could have life threatening consequences:
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Warning Signs
Squamous cell carcinoma can take on many different appearances. The warning signs can include:
- a rough and red scaly patch
- an open sore that often has raised borders
- a firm, dome-shaped growth
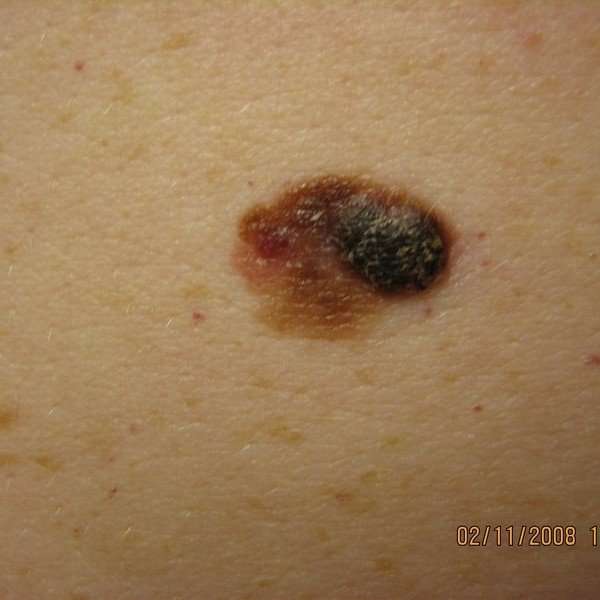
of skin cancer deaths. It often first appears as changes to a preexisting mole. Experts recommend looking for the ABCDE signs to identify moles that could be melanoma:
- Asymmetry: one half of a mole or lesion does not match the other
- Border: the edges are irregularly shaped or poorly defined
- Color: the mole contains different colors, such as red, blue, black, pink, or white
- Diameter: the mole measures more than 1/4 inch across about the size of a pencil eraser
- Evolving: the mole is changing in size, shape, or color
Another warning sign for melanoma is the Ugly Duckling rule. Most normal moles look similar to each other. A mole that stands out from others should raise suspicion and be examined by a medical professional.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Survival Rate For Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Surgical Procedures For Basal & Squamous Cell Skin Cancers
Basal or squamous cell skin cancers may need to be removed with procedures such as electrodessication and curettage, surgical excision, or Mohs surgery, with possible reconstruction of the skin and surrounding tissue.
Squamous cell cancer can be aggressive, and our surgeons may need to remove more tissue. They may also recommend additional treatments for advanced squamous cell cancer, such as medications or radiation therapyenergy beams that penetrate the skin, killing cancer cells in the body.
Basal cell cancer is less likely to become aggressive, but if it does, our doctors may use surgery and other therapies to treat it.
What Is My Skin Type
Skin types that are more sensitive to ultraviolet radiation burn more quickly and are at a greater risk of skin cancer.
All skin types can be damaged by too much UV radiation. Skin types that are more sensitive to UV radiation burn more quickly and are at a greater risk of skin cancer.
People with naturally very dark skin still need to take care in the sun even though they may rarely, if ever, get sunburnt. The larger amount of melanin in very dark skin provides natural protection from UV radiation. This means the risk of skin cancer is lower.
Eye damage can occur regardless of skin type. High levels of UV radiation have also been linked to harmful effects on the immune system.
Vitamin D deficiency may be a greater health concern for people with naturally very dark skin, as it is more difficult for people with this skin type to make vitamin D.
Also Check: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Grade 2 Survival Rate
What Are The 4 Signs Of Skin Cancer
How to Spot Skin Cancer
- Asymmetry. One part of a mole or birthmark doesnt match the other.
- Border. The edges are irregular, ragged, notched, or blurred.
- Color. The color is not the same all over and may include shades of brown or black, sometimes with patches of pink, red, white, or blue.
- Diameter.
Types Of Skin Malignancies:
- Melanoma the least common form of skin cancer, but responsible for more deaths per year than squamous cell and basal cell skin cancers combined. Melanoma is also more likely to spread and may be harder to control.
- Nonmelanoma malignancies:
- Squamous cell cancer the second-most common skin cancer. It’s more aggressive and may require extensive surgery, depending on location and nerve involvement.
- Basal cell cancer the most common form of skin cancer. It is rarely fatal but can be locally aggressive.
These skin malignancies are typically caused by ultraviolet radiation from exposure to the sun and tanning beds.
Recommended Reading: Prognosis Of Skin Cancer
Basal Cell Carcinoma Warning Signs
Basal cell carcinoma typically develops on parts of your body exposed to sunlight, but it does occasionally occur in other places. often include:
- an open sore that doesnt heal or heals and returns it may ooze or crust over
- a pink growth with raised edges and a depressed center, sometimes with abnormal blood vessels that resemble the spokes of a wheel
- a small pink or red bump thats shiny, pearly, or translucent it may have areas that are black, blue, or brown
- a raised red patch that itches
- a flat and firm area that resemble a pale or yellow scar
E: Evolving And/or Elevated
E stands for two different features of melanoma:
- Elevation: Moles are often elevated above the skin, often unevenly so with some parts raised and others flat.
- Evolving: A mole that is evolving is also concerning and, in retrospect, many people with melanomas note that a mole had been changing in terms of size, shape, color, or general appearance before they were diagnosed.
When a melanoma develops in an existing mole, the texture may change and become hard, lumpy, or scaly. Although the skin may feel different and itch, ooze, or bleed, a melanoma does not usually cause pain.
Also Check: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Survival
Waited For My Scheduled Skin Check
I already had a regular skin check scheduled with my dermatologist in a few weeks, so I decided to wait until that appointment to have it looked at. And honestly, within a week I was ready to call her to have her look at it sooner because it was that painful. Every time it rubbed against my clothing, it hurt. When I turned over at night while I was sleeping, it hurt and the pain woke me up.
During the appointment, when I told my doctor it appeared out of nowhere and it hurt, she told me she thought it was squamous cell skin cancer because they tend to appear suddenly. She biopsied it, and when the results came back as squamous cell, we scheduled surgery. During the surgery, I asked her why it had hurt so much, and she said that was typical of squamous cell areasâ they grow rather suddenly and become a placeholder of space in a place they dont belong.
Recommended Reading: How Can You Get Skin Cancer
Why Does It Happen
Non-melanoma skin cancer is mainly caused by overexposure to ultraviolet light. UV light comes from the sun, as well as artificial sunbeds and sunlamps.
In addition to UV light overexposure, there are certain things that can increase your chances of developing non-melanoma skin cancer, such as:
- a family history of the condition
- pale skin that burns easily
- a large number of moles or freckles
Read more about the causes of non-melanoma skin cancer
Don’t Miss: Stage 3 Cancer Symptoms
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Risk Factors
Certain things make you more likely to develop SCC:
Your doctor may refer you to a dermatologist who specializes in skin conditions. They will:
- Ask about your medical history
- Ask about your history of severe sunburns or indoor tanning
- Ask if you have any pain or other symptoms
- Ask when the spot first appeared
- Give you a physical exam to check the size, shape, color, and texture of the spot
- Look for other spots on your body
- Feel your lymph nodes to make sure they arent bigger or harder than normal
If your doctor thinks a bump looks questionable, theyll remove a sample of the spot to send to a lab for testing.
Continued
What Skin Cancer Looks Like
Skin cancer appears on the body in many different ways. It can look like a:
-
Changing mole or mole that looks different from your others
-
Dome-shaped growth
-
Non-healing sore or sore that heals and returns
-
Brown or black streak under a nail
It can also show up in other ways.
To find skin cancer on your body, you dont have to remember a long list. Dermatologists sum it up this way. Its time to see a dermatologist if you notice a spot on your skin that:
-
Differs from the others
-
Itches
-
Bleeds
To make it easy for you to check your skin, the AAD created the Body Mole Map. Youll find everything you need to know on a single page. Illustrations show you how to examine your skin and what to look for. Theres even place to record what your spots look like. Youll find this page, which you can print, at Body Mole Map.
Also Check: Melanoma Stage 3 Life Expectancy
Treatment For Skin Cancer
If you are diagnosed with skin cancer, you may have multiple options for treatment. Based on the specifics of your case, your doctor will recommend your best course of action. The suggested methods for fighting the cancer may include:
-
Cryotherapy. In cryotherapy, a doctor freezes and kills precancerous or cancerous skin cells using liquid nitrogen. This technique is most often used to treat minor basal or squamous carcinomas or precancerous skin conditions.
-
Surgery. Different types of skin cancer may be removed by surgery. Surgery can be excisional – simply cutting out a cancerous area and the skin surrounding it – or may involve meticulous removal of layers of skin.
-
Radiation therapy. In radiation therapy, energy beams are used to kill cancerous cells. Radiation therapy may help finish off a cancer that was not fully removed by surgery, and can also be instrumental in cases that dont allow for surgery.
-
Chemotherapy. This type of therapy uses drugs to kill cancer cells. To treat some cases of skin cancer, chemotherapy may be applied locally through topical creams or lotions. It may also be administered by IV to target multiple body parts at once.
-
Immunotherapy. Immunotherapy, also called biological therapy, involves boosting the immune system to fight cancer cells. With the help of strengthening medicines, the immune system may be better prepared to kill cancerous cells.
What Is Skin Cancer And Melanoma
Skin cancer is a disease that occurs when your skin cells grow abnormally, usually from too much exposure to ultraviolet radiation from the sun.
This uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells forms a tumour in the skin. Tumours are either benign , or malignant .
Skin cancer is the most common type of cancer: each year, more than 13,000 Australians are diagnosed with a melanoma and almost 980,000 new cases of non-melanoma skin cancers are treated. Skin cancer is mostly preventable, and there are effective treatment options available.
Skin cancers are named according to the cells in which they form. There are 3 main types:
- Basal cell carcinoma begins in the lower segment of cells of the epidermis your outer layer of skin. These tend to grow slowly, and rarely spread to other parts of the body.
- Squamous cell carcinoma grows from the flat cells found in the top layer of your epidermis. SCC can grow quickly on the skin over several weeks or months. Bowens disease is an early form of SCC that hasnt grown beyond the top layer of skin.
- Melanoma grows from cells called melanocytes cells that give your skin its colour. Melanoma is the rarest type of skin cancer but is considered the most serious because it can spread quickly throughout the body.
BCC and SCC are also called non-melanoma skin cancers. BCC represents more than 2 in 3 non-melanoma skin cancers, and around 1 in 3 are SCC. There are other types of non-melanoma skin cancers, but they are rare.
Don’t Miss: Lobular Breast Cancer Survival Rate
Skin Cancer Of The Head And Neck Treatment
Many early-stage small basal cell cancers or squamous cell cancers can be removed by Mohs surgery, a technique that spares normal tissue through repeated intraoperative margin testing, removing only the cancer and leaving adjacent normal tissue. Tumors with nerve involvement, lymph node involvement or of a large size are not suitable for Mohs surgery. They require a multimodality approach to treatment, with formal surgical resection and adjuvant radiation or chemotherapy.
Melanoma is more likely to spread, and aggressive surgical resection with wide margins is required, in addition to radiation and/or chemotherapy.
Johns Hopkins Head and Neck Cancer Surgery
Johns Hopkins Head and Neck Cancer Surgery provides comprehensive surgical care and treatment for head and neck cancers. Our surgeons are at the leading edge of head and neck cancer treatment. You will benefit from the skilled care of head and neck surgeons, guiding clinical advancements in the field of head and neck cancer care.
Skin Painful To Touch But Nothing Visible
Suki_girl
My teenage daughter has an area of skin on her upper back that is painful to touch, even lightly , but the skin there looks completely normal – no sign of redness or a rash. What could cause this? I thought it might be shingles , but that usually causes a rash.
0 likes, 25 replies
-
Posted 3 years ago
I can tell you its not psoriasis .. get to a dermatologist After 30 years of going to doctors for this you should always go to a dermatologist affiliated with a teaching hospital to get the best care not some guy who works alone in his own practice
-
Posted 3 years ago
I assure you, if it continues I will book her an appointment with a dermatologist- we have private health cover, so no problems there. Also we live near Oxford, so tend to use the Oxford teaching hospitals.
Posted 3 years ago
Sounds like Allodynia. Has she had a an injury to the area? Its a heightened awareness of skin pain in patches. Sometimes this can subside quite naturally,especially if she can ignore it, but if it continues she may need some help in desensitization. You could try giving her Ibuprofen twice a day for 3 days….
Has it become sensitive due to a label in her clothes rubbing or scratching?
Posted 3 years ago
oh, yes, she hasnt had any injury or trauma to that area. However, when it started there appeared to be two tiny puncture wounds on her back in that area, just tiny blood spots but no swelling or redness. Those have gone now.
Don’t Miss: Skin Cancer Mayo
Melanomas That Could Be Mistaken For A Common Skin Problem
Melanoma that looks like a bruise
Melanoma can develop anywhere on the skin, including the bottom of the foot, where it can look like a bruise as shown here.
Melanoma that looks like a cyst
This reddish nodule looks a lot like a cyst, but testing proved that it was a melanoma.
Dark spot
In people of African descent, melanoma tends to develop on the palm, bottom of the foot, or under or around a nail.
Did you spot the asymmetry, uneven border, varied color, and diameter larger than that of a pencil eraser?
Dark line beneath a nail
Melanoma can develop under a fingernail or toenail, looking like a brown line as shown here.
While this line is thin, some are much thicker. The lines can also be much darker.
A Primer On Skin Cancer
Malignant melanoma, especially in the later stages, is serious and treatment is difficult. Early diagnosis and treatment can increase the survival rate. Nonmelanoma skin cancers include basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma. Both are common and are almost always cured when found early and treated. People whove had skin cancer once are at risk for getting it again they should get a checkup at least once a year.
Don’t Miss: Does Melanoma Blanch When Pressed
Basal Cell And Squamous Cell Carcinomasigns And Symptoms
The most common warning sign of skin cancer is a change on the skin, especially a new growth or a sore that doesn’t heal. The cancer may start as a small, smooth, shiny, pale or waxy lump. It also may appear as a firm red lump. Sometimes, the lump bleeds or develops a crust.
Both basal and squamous cell cancers are found mainly on areas of the skin that are exposed to the sun the head, face, neck, hands and arms. But skin cancer can occur anywhere.
An early warning sign of skin cancer is the development of an actinic keratosis, a precancerous skin lesion caused by chronic sun exposure. These lesions are typically pink or red in color and rough or scaly to the touch. They occur on sun-exposed areas of the skin such as the face, scalp, ears, backs of hands or forearms.
Actinic keratoses may start as small, red, flat spots but grow larger and become scaly or thick, if untreated. Sometimes they’re easier to feel than to see. There may be multiple lesions next to each other.
Early treatment of actinic keratoses may prevent them from developing into cancer. These precancerous lesions affect more than 10 million Americans. People with one actinic keratosis usually develop more. Up to 1 percent of these lesions can develop into a squamous cell cancer.
Basal cell carcinoma is the most commonly diagnosed skin cancer. In recent years, there has been an upturn in the diagnoses among young women and the rise is blamed on sunbathing and tanning salons.
- Raised, dull-red skin lesion