Preventing Basal Cell Carcinoma
Basal cell carcinoma prevention is the same as prevention methods for all skin cancers, with the goal of protecting skin from harmful UV rays.
The number one thing people can do is to practice good sun protection and sun avoidance, meaning wear sunscreen and protect the skin from getting sun damage, says Stevenson. Its also important to get skin checks regularly for early detection.
Stevenson says if someone is prone to skin cancers for example, has very fair skin, sunburns as a child, or a history of skin cancer in the family its better to go out in the late afternoon or early morning when the sun isnt as strong, or stay primarily in the shade.
Anyone spending time in the sun, regardless of complexion, should practice sun protective behaviors, including wearing sunscreen.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends a sunscreen with a minimum sun protection factor of 15, and UVA and UVB broad spectrum protection. It also advises people to stay in the shade as much as possible and wear protective clothing including brimmed hats and sunglasses. Stevenson suggests looking for a SPF over 30.
Lebwohl says the SPF number directly correlates with the amount of protection it gives you. He says to divide the amount of time in the sun by the SPF number. For example, if someone is in the sun for 60 minutes, and wearing SPF 30, its as if they were exposed to two minutes of damaging rays rather than the full 60 minutes.
Where Do Skin Cancers Start
Most skin cancers start in the top layer of skin, called the epidermis. There are 3 main types of cells in this layer:
- Squamous cells: These are flat cells in the upper part of the epidermis, which are constantly shed as new ones form. When these cells grow out of control, they can develop into squamous cell skin cancer .
- Basal cells: These cells are in the lower part of the epidermis, called the basal cell layer. These cells constantly divide to form new cells to replace the squamous cells that wear off the skins surface. As these cells move up in the epidermis, they get flatter, eventually becoming squamous cells. Skin cancers that start in the basal cell layer are called basal cell skin cancers or basal cell carcinomas.
- Melanocytes: These cells make the brown pigment called melanin, which gives the skin its tan or brown color. Melanin acts as the bodys natural sunscreen, protecting the deeper layers of the skin from some of the harmful effects of the sun. Melanoma skin cancer starts in these cells.
The epidermis is separated from the deeper layers of skin by the basement membrane. When a skin cancer becomes more advanced, it generally grows through this barrier and into the deeper layers.
Recommended Reading: Do You Need Chemo For Melanoma
How Is Basal Cell Skin Cancer Treated When It Grows Deep Or Spreads
While this skin cancer tends to grow slowly, early treatment is recommended. Without treatment, BCC can grow deep, destroying what lies in its way. This can be disfiguring. The medical term for this is advanced basal cell carcinoma.
Its also possible for BCC to spread to other parts of your body, but this is rare. When the cancer spreads, it typically travels first to the lymph nodes closest to the tumor. From there, it tends to spread through the blood to bones, the lungs, and other parts of the skin. When this skin cancer spreads, it is called metastatic basal cell carcinoma.
For cancer that has grown deep or spread to the closest lymph nodes, treatment may involve:
-
Surgery to remove the tumor
-
Follow-up treatment with radiation to kill any remaining cancer cells
For some patients, medication that works throughout the body may be an option. Medication may also be used to treat cancer that:
-
Returns after surgery or radiation treatments
-
Has spread to another part of the body
Two such medications have been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration . Both come in pill form and are taken every day. A patient only stops taking the medication if the cancer starts to grow, or the side effects become too severe.
The two medications are:
-
Sonidegib
-
Vismodegib
In clinical trials, these medications have been shown to stop or slow down the spread of the cancer and shrink the cancerous tumors in some patients.
Cemplimab may be an option if sonidegib or vismodegib:
Also Check: Is Melanoma Cancer Curable
Who Is At The Greatest Risk
Anyone can develop this type of cancer but it is more common in light-skinned individuals with blonde or red hair and light green or blue eyes. It most frequently occurs in elderly males, but it can also occur in younger males and females. If a family has a history of basal cell naevus syndrome, Bazex-Dupré-Christol syndrome, Rombo syndrome, Oley syndrome or xeroderma pigmentosum they are at greater risk for developing basal cell carcinoma.
Recommended Reading: What Does Different Types Of Skin Cancer Look Like
What Is The Prognosis Of Superficial Basal Cell Carcinoma Of Skin
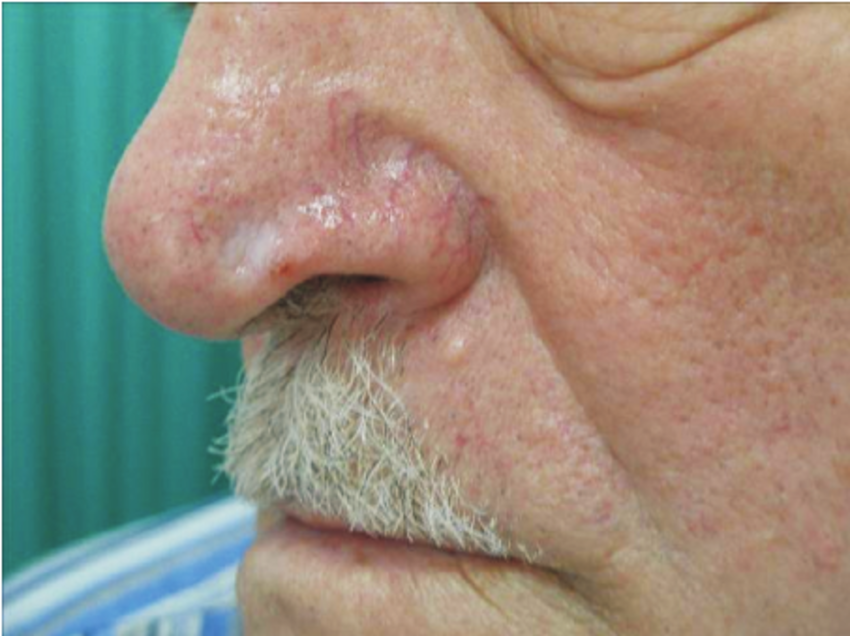
- In general, the prognosis of Superficial Basal Cell Carcinoma of Skin is excellent, if it is detected and treated early.
- Stage of tumor: With this lower-stage tumor, the prognosis is usually excellent with appropriate therapy
- The surgical resectability of the tumor
- Overall health of the individual: Individuals with overall excellent health have better prognosis compared to those with poor health
- Age of the individual: Older individuals generally have poorer prognosis than younger individuals
- Whether the tumor is occurring for the first time, or is a recurrent tumor. Recurring tumors have a poorer prognosis compared to tumors that do not recur
Also Check: Is An Itchy Neck A Sign Of Cancer
Different Kinds Of Skin Cancer
There are many types of skin cancer. Some are very rare. Your doctor can tell you more about the type you have.
The two most common kinds of skin cancers are:
- Basal cell cancer, which starts in the lowest layer of the skin
- Squamous cell cancer, which starts in the top layer of the skin
Another kind of skin cancer is called melanoma. These cancers start from the color-making cells of the skin . You can read about melanoma in If You Have Melanoma Skin Cancer.
How Does The Doctor Know I Have Skin Cancer
Basal and squamous skin cancer may look like:
- Flat, firm, pale or yellow areas that look a lot like a scar
- Raised reddish patches that might itch
- Rough or scaly red patches, which might crust or bleed
- Small, pink or red, shiny, pearly bumps, which might have blue, brown, or black areas
- Pink growths or lumps with raised edges and a lower center
- Open sores that dont heal, or that heal and then come back
- Wart-like growths
Don’t Miss: What Type Of Skin Cancer Spreads The Fastest
Four Reasons To Treat Basal Cell Carcinoma
Even when lesions from basal cell carcinoma on your skins surface dont appear to be changing, the cancer might still be growing. Some BCCs grow in irregular patterns under the skin, making the cancer seem smaller than it is. The cancer can affect tissue and bones. While major organs are rarely affected, muscle and nerve damage can occur, according to the Skin Cancer Foundation.
When not treated, the growth of the cancer can cause disfigurement because of internal damage. Treatment, which usually includes excision of the tumor, can be quite extensive when the cancer continues to grow unchecked. The longer you wait, the more damage and disfigurement the tumor can do and the more difficult it is to treat without causing cosmetic issues, according to Rex Amonette, M.D., the co-founder of The Skin Cancer Foundation.
When treated early, BCC is highly curable. Mohs surgery, a common treatment for BCC, has a cure rate of 99 percent. Excision, where the physician cuts out the growth, has a cure rate above 95 percent.
Most treatments for BCC are done as outpatient and often can be performed in your doctors office. Treatment does not usually involve extended time away from work or family.
Skin: Condition: Infomation Superficial Bccs
- Curettage and cautery the skin is numbed with local anaesthetic and the BCC is scraped away and then the skin surface is sealed by heat .
- Cryotherapy freezing the BCC with liquid nitrogen.
- Creams these can be applied to the skin. The two most commonly used are 5-fluorouracil and imiquimod.
- a special cream is applied to the BCC which is taken up by the cells that are then destroyed by exposure to a specific wavelength of light. This treatment is only available in certain dermatology departments .
Surgical excision is the preferred treatment, but the choice of other treatments depends on the site and size of the BCC, the condition of the surrounding skin and number of BCC to be treated as well as the overall state of health of each person to be treated.
You May Like: Stage 5 Cancer Symptoms
What Does A Basal Cell Carcinoma Look Like
BCCs can vary greatly in their appearance, but people often first become aware of them as a scab that bleeds and does not heal completely or a new lump on the skin. Some BCCs are superficial and look like a scaly red flat mark on the skin. Others form a lump and have a pearl-like rim surrounding a central crater and there may be small red blood vessels present across the surface. If left untreated, BCCs can eventually cause an ulcer hence the name rodent ulcer. Most BCCs are painless, although sometimes they can be itchy or bleed if caught.
What Causes Intraepidermal Scc
Ultraviolet radiation is the main cause of intraepidermal SCC. It damages the skin cell nucleic acids , resulting in a mutantclone of the genep53, setting off uncontrolled growth of the skin cells. UV also suppresses the immune response, preventing recovery from damage.
Human papillomavirus is another major cause of intraepidermal SCC. Oncogenic strains of HPV are the main cause of squamous intraepithelial lesions , that is, squamous cell carcinoma in situ in mucosal tissue.
Thomas Urban Marron, MD, PhDAlamy
Mark Lebwohl, MD, a professor and the chairman at the Kimberly and Eric J. Waldman Department of Dermatology at Mount Sinai and a spokesperson for the Skin Cancer Foundation, recalls once running into a doctor colleague at work with a scab on his lip.
Crossing paths again weeks later, his colleague had the same scab.
I looked at him and said, You really should have that looked at, and he said, Oh, its just a scab, I keep hitting it when I shave, says Dr. Lebwohl. Ultimately, his colleague did get it looked at by a dermatologist. It was skin cancer, more specifically basal cell carcinoma .
Also Check: What Type Of Skin Cancer Spreads The Fastest
Don’t Miss: Can You Get Cancer In The Back Of Your Neck
Melanoma Signs And Symptoms
Melanoma skin cancer is much more serious than basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma. It can spread quickly to other organs and causes the vast majority of skin cancer deaths in the United States. Usually melanomas develop in or around an existing mole.
Appearance
Signs and symptoms of melanoma vary depending on the exact type and may include:
- A flat or slightly raised, discolored patch with irregular borders and possible areas of tan, brown, black, red, blue or white
- A firm bump, often black but occasionally blue, gray, white, brown, tan, red or your usual skin tone
- A flat or slightly raised mottled tan, brown or dark brown discoloration
- A black or brown discoloration, usually under the nails, on the palms or on the soles of the feet
See more pictures and get details about different types of melanoma in our dedicated melanoma section.
Recommended Reading: What Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of The Head And Neck
What Is Basal Cell Carcinoma
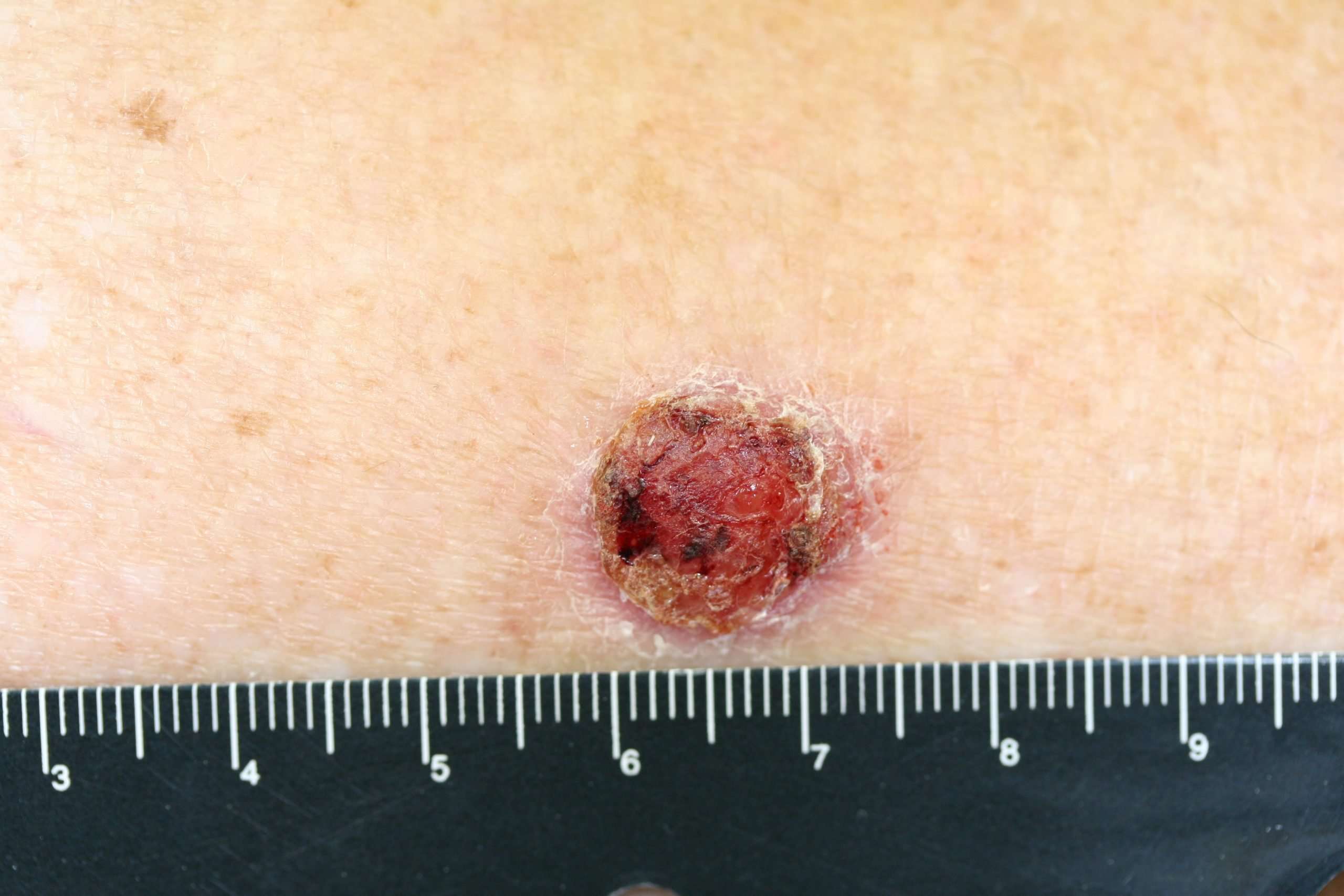
Basal cell carcinoma is the most common form of skin cancer, with approximately 80% of skin cancers developing from basal cells. The epidermis has three types of cells. The cells in the bottom layer of the epidermis are the basal cells.
Basal cells consistently divide to form new cells. These replace squamous cells, pushing old cells towards the skin’s surface, where they die and slough off. Cancers that start in this bottom/basal layer of skin cells are called basal cell carcinoma.
Basal cell carcinoma is usually triggered by damage from ultraviolet radiation. This is most commonly from either exposure to the sun or tanning beds. UV radiation can damage basal cells, causing them to change and grow uncontrollably.
Basal cell carcinoma can look different from person to person. It may present as an open sore, scaly patch, shiny bump, a red irritated patch, pink growth, waxy scar-like growth, or a growth that dips in the center. They can sometimes ooze, crust, or bleed
As it can vary in how it looks, it is essential to get any new growths, lesions, lumps, bumps, or changes of your skin checked by your healthcare provider.
Don’t Miss: Invasive Lobular Carcinoma Grade 2 Survival Rates
Prevention Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
Because basal cell carcinoma is often caused by sun exposure, people can help prevent this cancer by doing the following:
-
Avoiding the sun: For example, seeking shade, minimizing outdoor activities between 10 AM and 4 PM , and avoiding sunbathing and the use of tanning beds
-
Wearing protective clothing: For example, long-sleeved shirts, pants, and broad-brimmed hats
-
Using sunscreen: At least sun protection factor 30 with UVA and UVB protection used as directed and reapplied every 2 hours and after swimming or sweating but not used to prolong sun exposure
In addition, any skin change that lasts for more than a few weeks should be evaluated by a doctor.
Skin Cancer Support Groups And Counseling
Living with skin cancer presents many new challenges for you and for your family and friends. You will probably have many worries about how the cancer will affect you and your ability to live a normal life, that is, to care for your family and home, to hold your job, and to continue the friendships and activities you enjoy.
Many people with a skin cancer diagnosis feel anxious and depressed. Some people feel angry and resentful others feel helpless and defeated. For most people with skin cancer, talking about their feelings and concerns helps. Your friends and family members can be very supportive. They may be hesitant to offer support until they see how you are coping. Dont wait for them to bring it up. If you want to talk about your concerns, let them know.
Continued
Some people dont want to burden their loved ones, or prefer talking about their concerns with a more neutral professional. A social worker, counselor, or member of the clergy can be helpful. Your dermatologist or oncologist should be able to recommend someone.
Many people with cancer are profoundly helped by talking to other people who have cancer. Sharing your concerns with others who have been through the same thing can be remarkably reassuring. Support groups for people with cancer may be available through the medical center where you are receiving your treatment. The American Cancer Society also has information about support groups throughout the U.S.
Don’t Miss: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Stage 3 Survival Rate
Basal Cell Skin Cancer
BCC is the most common type of skin cancer. About 75 out of every 100 non melanoma skin cancers are BCCs. They develop from basal cells and these are found in the deepest part of the outer layer of the skin .
They develop mostly in areas of skin exposed to the sun, including parts of the face such as the nose, forehead and cheeks. Also, on your back or lower legs.
They are most often diagnosed in people who are middle aged or older.
Doctors might also call a basal cell cancer a rodent ulcer.
There are a number of different types of BCC. Each type can look and behave differently. They include:
- nodular basal cell skin cancer
- superficial basal cell skin cancer
- morphoeic basal cell skin cancer also known as sclerosing or infiltrating basal cell skin cancer
- pigmented basal cell skin cancer
Nodular basal cell cancer is the most common subtype.
Its very rare for basal cell skin cancer to spread to another part of the body to form a secondary cancer. Its possible to have more than one basal cell cancer at any one time and having had one does increase your risk of getting another.
How Dangerous Is A Basal Cell Carcinoma
While melanoma rightly deserves the attention it receives as the most dangerous form of skin cancer, basal cell carcinoma isnt something to brush off as harmless. Yes, this most common form of skin cancer rarely causes fatalities, but it can become quite disfiguring.
While basal cell carcinoma lesions rarely spread beyond the original tumor site, they should not be allowed to grow freely. These lesions can grow widely, penetrating deeply into the skin destroying skin, tissue, and bone. Plus, the longer you leave a basal cell carcinoma untreated, the more likely it is to come back. And because it will usually return in the same area, this can create problems removing the lesions without overly disfiguring the patient.
Read Also: Should I Be Worried About Basal Cell Carcinoma
Recommended Reading: Invasive Ductal Breast Cancer Prognosis
Three Most Common Skin Cancers
It is estimated that one in seven people in the United States will develop some form of skin cancer during their lifetime. Although anyone can get skin cancer, people who burn easily and are fair-skinned are at higher risk. Researchers believe that one serious sunburn can increase the risk of skin cancer by as much as 50%. A yearly skin exam by a doctor is the best way to detect skin cancer early, when it is most treatable. If you have a new growth or any change in your skin, be sure to see your doctor to have it examined. Remember, protecting yourself from the sun is the best way to prevent all forms of skin cancer.
Read Also: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Grade 2 Survival Rate