How Fast Does Squamous Cell Cancer Spread To Lymph Nodes
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
HealthTap doctors are based in the U.S., board certified, and available by text or video.
Tests That Examine The Tissues Of The Neck Respiratory Tract And Upper Part Of The Digestive Tract Are Used To Detect And Diagnose Metastatic Squamous Neck Cancer And The Primary Tumor
Tests will include checking for a primary tumor in the organs and tissues of the respiratory tract , the upper part of the digestive tract , and the genitourinary system.
The following procedures may be used:
- Physical exam and health history: An exam of the body, especially the head and neck, to check general signs of health. This includes checking for signs of disease, such as lumps or anything else that seems unusual. A history of the patients health habits and past illnesses and treatments will also be taken.
- Biopsy: The removal of cells or tissues so they can be viewed under a microscope by a pathologist or tested in the laboratory to check for signs of cancer.
Three types of biopsy may be done:
- Fine-needle aspiration biopsy: The removal of tissue or fluid using a thin needle.
- Core needle biopsy: The removal of tissue using a wide needle.
- Excisional biopsy: The removal of an entire lump of tissue.
The following procedures are used to remove samples of cells or tissue:
One or more of the following laboratory tests may be done to study the tissue samples:
When Was My Husband Diagnosed With Squamous Cell Lung Cancer
My husband was also a Vietnam Vet his last tour of duty in Vietnam ended in 1969. In June 2001 he was diagnosed with Squamous Cell Lung Cancer. The doctors at the VA in Tampa Florida made the diagnosis. They asked him if he was a Vietnam Vet and he said yes he was and that he did 2 tours of duty in Vietnam.
Don’t Miss: Melanoma Bone Cancer Life Expectancy
What Is Squamous Cell Skin Cancer Of The Head And Neck
Skin malignancies are the most common cancer in the United States, responsible for more than half of all new cancer cases. These can be broken down into melanoma and non-melanoma malignancies, which are squamous cell cancer and basal cell cancer. These skin malignancies are caused by ultraviolet radiation from exposure to the sun and tanning beds.
Squamous cell cancer is the second most common form of skin cancer. It is more aggressive and may require extensive surgery depending on location and nerve involvement. Radiation, chemotherapy and immunotherapy are used in advanced cases.
You May Like: How To Treat Melanoma In Nails
Who Gets Metastatic Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of Skin
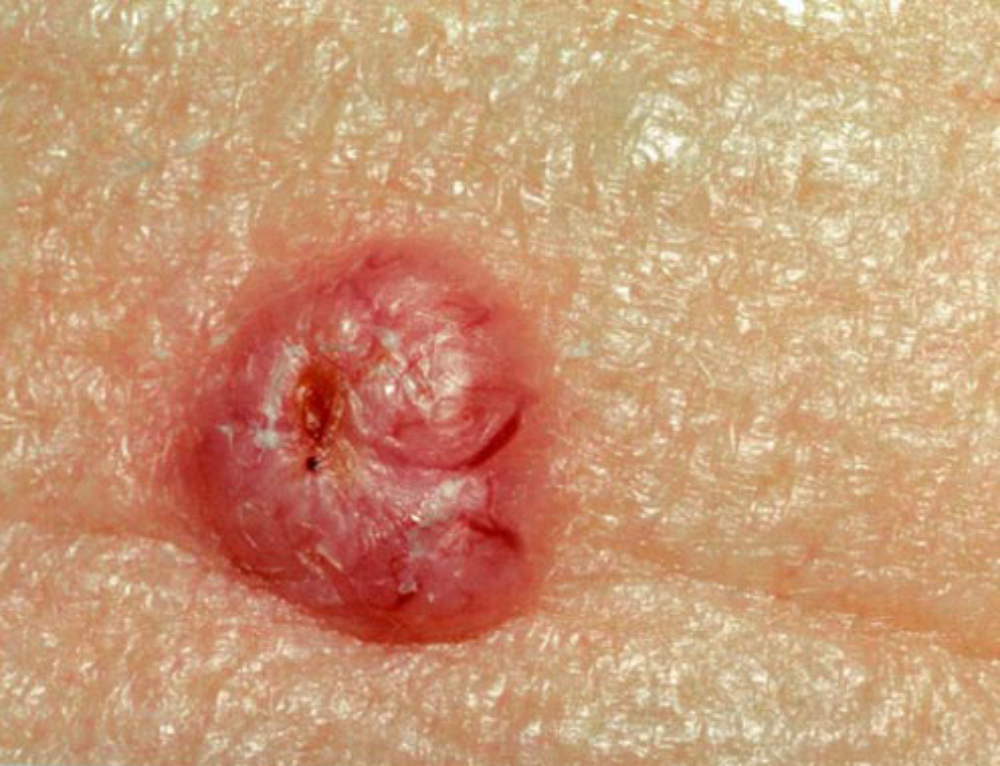
- Metastatic Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Skin is generally uncommon and it affects elderly or older adults some cases rarely develop in children too
- It can occur in both males and females
- The condition is prevalent worldwide, though dark-skinned individuals are affected less than lighter-skinned individuals
Recommended Reading: Treatment For Stage 4 Melanoma
What Are The Risk Factors For Squamous Cell Skin Cancer
Squamous cell skin cancer is mainly caused by cumulative ultraviolet exposure from the sun, according to Dr. Leffell.
Daily year-round exposure to the suns UV light and intense exposure in the summer months add to the damage that causes this type of cancer, he says. People at the highest risk for squamous cell skin cancer tend to have light or fair-colored skin blue, green or gray eyes a history of sun exposure and a tendency to sunburn quickly. Squamous cell cancers occur four times more frequently in men than in women.
Although squamous cell cancer can be more aggressive than basal cell cancer, the risk of this type of cancer spreading is lowas long as the cancer is treated early, Dr. Leffell says. He notes that the lesions must be treated with respect because they may grow rapidly and invade deeply. While it is more difficult to treat squamous cell cancer that has metastasized, up to half of cases can be cured.
In a small percentage of cases, squamous cell skin cancer can grow along the tiny nerves in the skin. In this very serious condition, the squamous cell cancer of the face or scalp can travel along the nerves and spread to the brain.
Also Check: What Can Happen If Skin Cancer Is Left Untreated
How To Improve Your Odds
Even if youve exhausted all of your treatment options, you dont have to give up. Researchers are always testing new SCC treatments in clinical trials. Getting into one of these studies could give you access to a drug or therapy that might slow or stop your cancer.
To avoid the worsening of your skin cancer or a new cancer in a different area, protect yourself from the suns damaging UV rays. Wear sun-protective clothing and a wide-brimmed hat whenever you go outdoors. Apply a layer of broad-spectrum sunscreen that protects against both UVA and UVB rays.
Also check your own skin for any new growths on a regular basis. Report any skin changes to your doctor right away.
Also Check: What Is The Survival Rate For Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
How Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of The Skin Treated When It Spreads
When this cancer spreads beyond the skin, it travels to the lymph nodes or other organs. Once it spreads, a patient has advanced cancer.
If youve been diagnosed with advanced SCC, you will be cared for by a team of medical professionals. This team will include oncologists . Your treatment plan may include one or more of the following:
Surgery: When surgery can remove the cancer and youre healthy enough to have surgery, this is often the preferred treatment. After surgery, another treatment, such as radiation therapy or chemotherapy, is often given. Adding another treatment helps to kill cancer cells.
Radiation therapy: Radiation can target cancer cells in the skin, lymph nodes, or other areas of the body. When a patient has advanced SCC, radiation therapy is often used along with another treatment.
Immunotherapy: This type of treatment helps strengthen your immune system so that it can fight the cancer. Drugs called immunotherapy medications are given for this purpose.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has approved one immunotherapy medication for the treatment of advanced SCC of the skin. Its called cemiplimab-rwlc.
In the clinical trials that led the FDA to approve cemiplimab-rwlc, about half the patients who had advanced SCC of the skin had their tumors shrink. In many patients who had tumor shrinkage, the shrinking lasted 6 months or longer. A few patients had their tumors disappear completely.
Immunotherapy
Pembrolizumab is also given by IV infusion.
Answer: Squamous Cell Carcinoma Growth
While it is said that most skin cancers grow slowly, the true answer is it depends. It depends on location of the skin cancer, your general health, the health of your skin and the cause of the skin cancer. Most squamous cell carcinomas arise in skin damaged by ultra violet light and, often, grow slowly. However, if the UV damage is severe or if the SCC arose from a burn or infection site, the cancer can grow rapidly and spread to other organs. Additionally, SCC, which grows contiguously will sometimes send seeds beyond the tissue containing the roots. These factors all have to be considered in determining how to deal with SCC. The best advice I can give you is to not delay and have this evaluated by a fellowship-trained Mohs surgeon. I hope I have answered your question. Best. jlr
Don’t Miss: Lobular Breast Cancer Stage 3
What Are The 5 Stages Of Skin Cancer
Staging is an important tool used to treat skin cancer. Your stage helps the medical team determine where the tumor is, how large it is, where it has spread, your prognosis, and the most effective treatment plan.
The five stages of squamous cell carcinoma include:
- Stage 0: Also known as carcinoma in situ, in this stage cancer is present in the epidermis. It has not spread to deeper layers.
- Stage 1: The tumor is smaller than 2 centimeters and has not spread to nearby lymph nodes or other organs. The individual has one or fewer risk factors for spread.
- Stage 2: The tumor is wider than 2 centimeters and has not spread to nearby lymph nodes or other organs. This stage also applies to any sized tumor when the individual has two or more risk factors.
- Stage 3: The tumor has spread into nearby facial bones or one lymph node. It has not spread to other organs.
- Stage 4: The tumor is of any size and has metastasized to one or more of the lymph nodes. It may have spread to the bones and other distant organs.
Symptoms Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
There are several types of basal cell carcinomas.
The nodular type of basal cell carcinoma usually begins as small, shiny, firm, almost clear to pink in color, raised growth. After a few months or years, visible dilated blood vessels may appear on the surface, and the center may break open and form a scab. The border of the cancer is sometimes thickened and pearly white. The cancer may alternately bleed and form a scab and heal, leading a person to falsely think that it is a sore rather than a cancer.
Other types of basal cell carcinomas vary greatly in appearance. For example, the superficial type appears as flat thin red or pink patches, and the morpheaform type appears as thicker flesh-colored or light red patches that look somewhat like scars.
Recommended Reading: Can Skin Cancer Cause Pain
Also Check: What Is The Survival Rate For Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
When Skin Cancer Spreads
If squamous cell carcinoma spreads it first moves to nearby lymph nodes. From the lymph nodes it can metastasize to other organs. In most cases the cancer spreads to the lungs, although it can travel elsewhere.
The risk of metastasis is low. It is estimated that from two to six percent of cases metastasize. Generally, it is the high-risk cases of the disease that have this problem, when they are left untreated. Factors such as age, sun exposure, and fair skin increase risk. Once the cancer has reached the lymph nodes the morbidity rate is significant. If squamous cell carcinoma reaches the lungs it cannot be cured.
What Are The Possible Complications Of Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of Vagina
The complications of Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Vagina could include:
- Ulceration of large tumor masses may get secondarily infected with bacteria or fungus
- The malignant lesion can invade into the adjacent tissues and structures or metastasize :
- Tumors nearer to the cervix may cause lymph node of the pelvis to be affected more often, and also spread to the cervix, causing cervical cancer
- Lower vaginal tract SCCs can cause vulvar cancers and also affect the inguino-femoral lymph nodes
Don’t Miss: Carcinoma Cancer Symptoms
How Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma Diagnosed
Diagnosis of cutaneous SCC is based on clinical features. The diagnosis and histological subtype are confirmed pathologically by diagnostic biopsy or following excision. See squamous cell carcinoma pathology.
Patients with high-risk SCC may also undergo staging investigations to determine whether it has spread to lymph nodes or elsewhere. These may include:
- Imaging using ultrasound scan, X-rays, CT scans, MRI scans
- Lymph node or other tissue biopsies
Mohs Micrographic Surgery For Squamous Cell Carcinoma
It is often used on tumours that have recurred, are poorly demarcated, or are in hard-to-treat, critical areas around the eyes, nose, lips, ears, neck, hands and feet.
Mohs Micrographic Surgery Treatment Process Using a scalpel or curette , a Mohs Surgeon removes the visible Squamous Cell Carcinoma with a very thin layer of tissue around it. While the patient waits, this layer is sectioned, frozen, stained and mapped in detail, then checked thoroughly under a microscope.
If cancer is still present in the depths or peripheries of this excised surrounding tissue, the procedure is repeated on the adjacent area of the body which still contains tumour cells until the last layer viewed under the microscope is cancer-free.
Mohs Micrographic Surgery Treatment Recovery After tumour removal, the wound may be allowed to heal naturally or may be reconstructed immediately.
Mohs Micrographic Surgery Prognosis The cosmetic outcome is often excellent.
Also Check: What Is The Prognosis For Skin Cancer
Growth Rate Varies At Different Stages
Tumor growth also may change during different stages in the life of the developing cancer cells. Tumors are not just copies of the exact same abnormal cells involved in out-of-control growth. The cells experience new mutations that change the tumor. Many people see this when new mutations make their cancers resist treatment that worked in the past. Some of the new mutations in a tumor may cause cancer cells to grow and divide more rapidly than when it first began.
Symptoms And Signs Of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Oral lesions are asymptomatic initially, highlighting the need for oral screening. Most dental professionals carefully examine the oral cavity and oropharynx during routine care and may do a brush biopsy of abnormal areas. The lesions may appear as areas of erythroplakia or leukoplakia and may be exophytic or ulcerated. Cancers are often indurated and firm with a rolled border. As the lesions increase in size, pain, dysarthria, and dysphagia may result.
This photo shows a close-up of the inside of the mouth in a patient with squamous cell carcinoma of the oral mucosa.
Erythroplakia is a general term for red, flat, or eroded velvety lesions that develop in the mouth. In this image, an exophytic squamous cell carcinoma on the tongue is surrounded by a margin of erythroplakia.
Leukoplakia is a general term for white hyperkeratotic plaques that develop in the mouth. About 80% are benign. However, in this image, squamous cell carcinoma is present in one of the leukoplakic lesions on the ventral surface of the tongue .
You May Like: What Is Large Cell Carcinoma
Factors That Could Affect Your Prognosis
Certain aspects of your health or cancer could affect your outlook. For example, people who have a weakened immune system from a disease like HIV or a medication they take tend to have a less positive outlook.
The location of the tumor also matters. Cancers on the face, scalp, fingers, and toes are more likely to spread and return than those on other parts of the body. SCC that starts in an open wound is also more likely to spread.
Larger tumors or ones that have grown deep in the skin have a higher risk of growing or returning. If a cancer does recur after treatment, the prognosis is less positive than it was the first time around.
Ask your doctor if you have any risk factors that can be managed or controlled. You may need more aggressive treatment, or to be monitored more closely for recurrence.
How Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of Oral Cavity Treated
Early diagnosis and treatment of Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Oral Cavity is important to avoid complications such as metastasis to other regions. The treatment measures may include:
- In most cases, a wide surgical excision and removal of the entire tumor is the preferred treatment option. This may be followed by radiation therapy and/or chemotherapy
- If the tumor has metastasized , then a combination of chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and invasive procedures may be used to treat the tumor
- Targeted therapy medications are generally used for locally infiltrated or metastatic SCCs. This therapy destroys the tumor cells by acting against the proteins that are responsible for tumor growth
- Reconstructive surgery may be necessary after cancer therapy
- Post-operative care is important: One must maintain minimum activity levels, until the surgical wound heals
- Follow-up care with regular screening and check-ups are important and encouraged
Also Check: What Is The Survival Rate For Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
General Prognosis After Treatment
An individuals prognosis depends on the type and stage of cancer, as well as their age and general health at the time of diagnosis. The majority of Squamous Cell Carcinoma cancers are successfully treated.
When small Squamous Cell Carcinomas are removed, the scars are usually cosmetically quite acceptable. If the tumours are very large, a skin graft or flap may be used to repair the wound in order to achieve the best cosmetic result and facilitate healing.
How Can Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of Vagina Be Prevented
Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Vagina may be prevented through the timely and adequate treatment of in situ Vaginal SCC. Some steps for the prevention of SCC of Vagina may include:
- Use of measures to prevent sexually-transmitted infections, such as usage of condoms, avoiding multiple sexual partners, and circumcision in men
- Avoidance of smoking
- Regular screening to detect pre-cancers:
- The American Cancer Society recommends screening of women from age 21 years
- A Pap smear is recommended every 3 years, from ages 21-29 years
- From age 30-65 years, a Pap smear and HPV testing is recommended, once every 5 years
- More frequent screenings are advised for women having a high-risk for cervical cancer
Note: Per se, Pap smears can only help in detecting cervical cancers. They are not helpful in screening for vaginal cancers. However, since cervical cancers are much more frequently noted, early screening to detect precancers is important.
- Vaccination against human papilloma virus :
- Two vaccines have been studied and approved for use in the United States – Gardasil and Cervarix
- Cervarix has been approved for use in females aged 10-25 years, while Gardasil may be used in the 9-26 years age group
- The American Cancer Society recommends routine vaccination of girls at 11-12 years of age
- HPV vaccines are not successful against women who are already infected though
Recommended Reading: Stage Iii Melanoma Treatment