Recovery And Management Of Pyoderma In Dogs
Re-check appointments with your veterinarian will ensure that your dogs infection has completely cleared before its antibiotic treatment has ended. Treatment may need to be continued for 7 to 14 days past when their skin appears normal, so please do not stop the antibiotics before a full course of treatment has been completed. Ending antibiotic treatment too early can contribute to the development of antibiotic resistance.
Infection often needs to be cleared before your veterinarian can begin investigating the underlying cause of the pyoderma. It is important to determine the underlying cause, whether it be allergies, Cushings disease, hypothyroidism, or another illness, so your dog doesnt experience frequent relapses of pyoderma.
Bacterial Skin Infection In Dogs
As the skin is the largest organ of the body, it harbours many bacteria that benefit the body to synthesize different metabolites. But due to some abnormal conditions like skin allergy or autoimmune skin disorder, these bacteria can start damaging the skin. Thats the way they cause dog skin infection.
Pyoderma In Dogs & Cats
Content Reviewed by an Essentials PetCare Veterinarian
Pyoderma in Dogs & Cats
The Basics
What Is a Skin Infection?
Pyoderma, or skin infection, commonly results from bacterial and/or yeast organisms causing an opportunistic infection due to the skins defense mechanisms being compromised.
How Pets Develop Skin Infection
Moreover, any condition that causes itching can lead to self-trauma, which may generate a secondary pyoderma. Areas of the skin that hold moisture, like the ear canals and folds around the mouth, genitals, and toes, are prone to infection.
Types of Pyoderma
Deep Pyoderma
Also Check: How Long Can You Live With Squamous Cell Carcinoma
What Causes Pyoderma In Dogs
Bacterial skin infection occurs when the skin’s surface has been broken, the skin has become injured due to chronic exposure to moisture, the normal skin bacteria have been altered or changed, the blood flow to the skin has become impaired, or the immune system has been suppressed.
A specific type of pyoderma is skin fold pyoderma that develops in skin folds, such as facial folds, lip folds, tail folds, and in the groin or armpits. It may develop between the mammary glands in females that have had multiple litters of pups. It may also occur secondary to obesity when adjacent skin folds upon itself. The skin folds allow the surface of the two adjacent areas to lie in close contact, creating a warm, humid environment. In the presence of moisture, the normal skin bacteria then multiply, creating an infection in the fold.
Certain breeds appear to be predisposed to the condition. These include:
Spaniels with lip fold pyoderma Pekingese, Pugs, Boxer Dogs, and Bulldogs with facial fold pyoderma affecting the wrinkles on the face and nose Shar-Pei and other breeds with loose skin and skin folds.
“Pyoderma is often secondary to allergic dermatitis and develops in the abrasions on the skin’s surface that occur as a result of scratching.”
Causes Of Bacterial Infection Of The Skin In Dogs
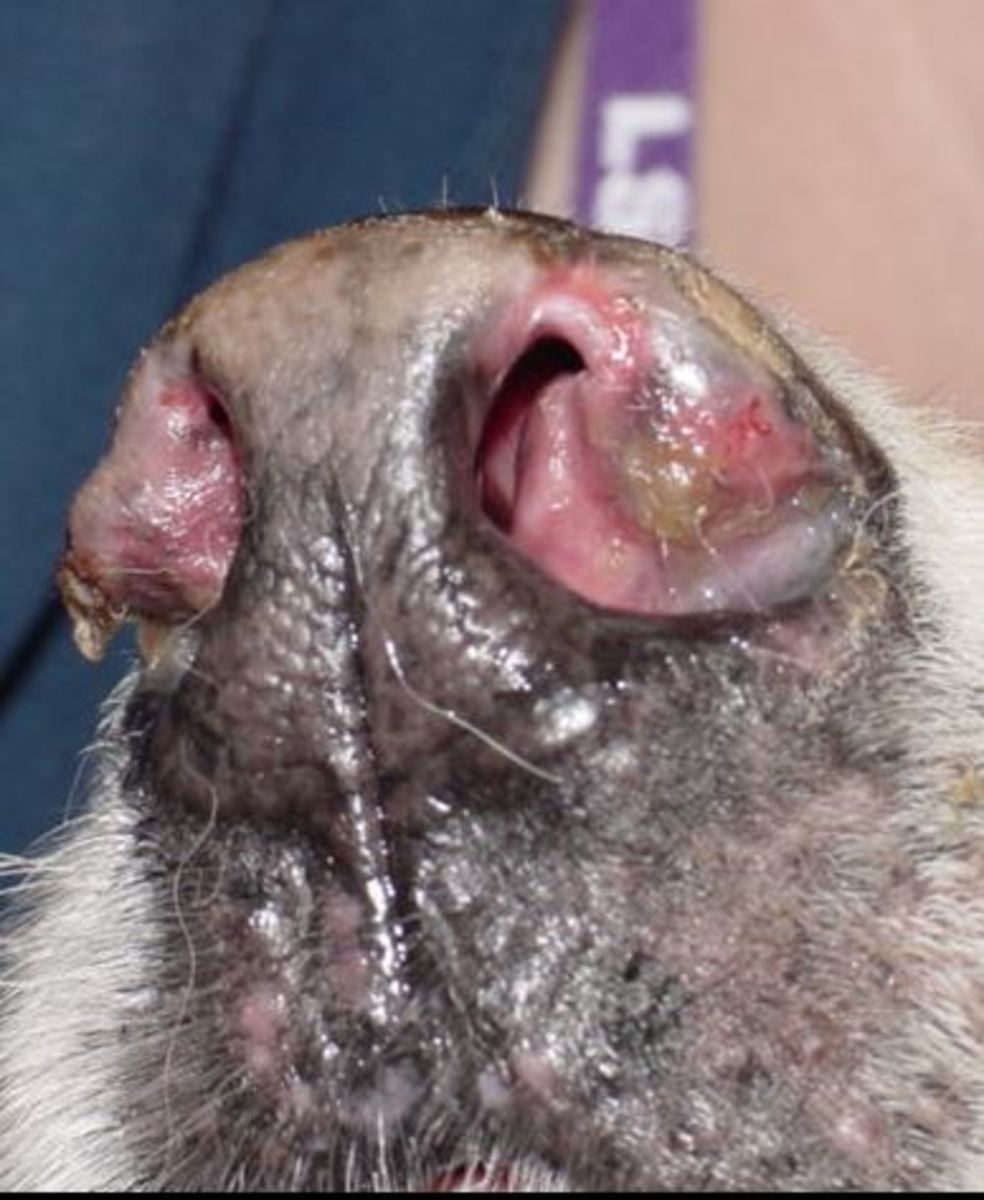
Pyoderma can be associated with many different conditions and veterinarians often struggle to find the exact cause. The following conditions are often related.
- Any chronic form of dermatitis
- Fungal or yeast infection
- Endocrine imbalance that reduces lymphocyte counts like Cushings disease , and hypothyroidism
Read Also: How To Spot Skin Cancer On Face
Bacterial Skin Infections In Dogs
Bacterial skin infections can have many causes, including allergies. Regardless of the reason, skin infections require swift action by pet owners as they cause itching and pain. Some dogs are more vulnerable to develop bacterial skin infections than others.
Its important to check common areas like the paws, groins and armpits. Skinfolds are particularly prone to skin infections, and dogs with heavy pendulous ears are very susceptible to infections. These infections happen because long, heavy ears can promote bacterial growth. However, any dog can develop a skin infection, so you should be on the lookout for warning signs.
Symptoms of skin infections include redness, itching, hair loss, bumps, pustules, and spots. Your vet may be able to diagnose by looking however, a conclusive diagnosis requires the examination of hair, discharge, and skin cultures. Some of the tests and procedures your vet may conduct include:
- Skin scrapes and hair plucks.
- Swab of the skin or pus to look under the microscope and culture for bacterial growth.
- Looking down the ear with an otoscope to evaluate the ear canal.
If your dog is diagnosed with a bacterial skin infection, your vet will direct you to keep the affected areas as clean as feasible. In certain dog breeds, it may be necessary to have their hair clipped to allow air to areas to assist in the healing process. In many cases, prescription antibiotics will aid in recovery. Your vet may also suggest topical creams or shampoos.
Common Skin Infections In Dogs
Bacterial and fungal infections can cause your pup’s skin to become flaky, crusty or moist, leading to itchiness and discomfort. Inflammation, redness and smell can also be a problem, not to mention recurring yeast dermatitis or staph infection. Although skin problems are fairly common in dogs they can indicate underlying health issues that require veterinary care.
Yeast Dermatitis
Yeast dermatitis is an extremely common cause of skin disease in dogs. While the fungus Malassezia pachydermatis is naturally found on the skin of healthy dogs, if it grows excessively, it can lead to skin inflammation .
Staphylococcal Infection
The most common bacterial skin infection seen in dogs is a staph infection . This skin infection is caused by the bacterium Staphylococcus sp which can be transmitted between dogs and humans, making good hygiene and early treatment a high priority for this skin infection.
A staph infection can impact your dogs skin or upper respiratory tract and is typically treated using oral antibiotics such as cephalexin, erythromycin or clindamycin. Antibiotic ointments and shampoos may also be prescribed to help your dog’s skin feel more comfortable.
Recommended Reading: Does Skin Cancer Burn Or Itch
Diagnosis Of Fungal Dermatitis & Bacterial Skin Infections In Dogs
Our Mooresville vets at Lake Norman at Mooresville Animal Hospitaltreat a wide range of skin, eye, ear, and nail conditions in pets. We use several techniques to collect samples and diagnose skin infections in dogs.
Yeast infections can be diagnosed through impression smears, skin biopsy, skin scraping, acetate tape preparations or cotton swab samples.
To diagnose a staph infection, your dog will need a complete physical examination, and your vet may perform a complete blood count, biochemistry profile, and urinalysis, in addition to thoroughly reviewing your pets medical history and asking questions such as when you began to notice symptoms.
Skin tests may also be required to find out whether the inflammation is caused by immune-related issues or an allergic reaction to something. A skin biopsy may be necessary, during which your veterinarian will swab the skin to determine which antibiotic should be used to treat the condition.
At our in-house lab, we can perform tests and get results quickly with our advanced imaging and testing equipment.
Montgomery Pet Skin And Ear Clinicdr Louis N Gotthelf
Canine Pyoderma or Bacterial Skin Infection
Bacterial folliculitis is the most common type of bacterial skin infection in the dog. The Staphylococcus pseudintermedius bacteria, which is a normal resident bacteria of canine skin, can cause infection of the skin in some dogs. Current theories indicate that most dogs who develop theinfection, particularly recurrent infections, have an underlying abnormality of their metabolic or immune systems. This form of pyoderma is a frequent complication of environmental allergies, food hypersensitivities, skin parasites and endocrine diseases, like hypothyroidism. An idiopathic primary bacterial folliculitis is also seen in short-haired dogs.
Pus Filling the Hair Follicle Spotty Infected Follicles Wide Ruptured PustulesLocated within the hair follicle, this bacterial infection causes
- Inflammation in and around the hair follicle
- Itching in some cases
- Hair loss in many cases
The clinical signs of bacterial folliculitis can be quite variable and may include
Acute moist pyoderma
Chin Acne is often a bacterialinfection
SKIN BACTERIAL CULTURING can be done in our office. Dogs that have had long standing pyodermas are the best candidates for antibiotic sensitivity testing. We can get culture and antibiotic sensitivity results in 24 hours in our own bacteriology mini lab. We also can test for MRSP, a methcillin resistant form of antibiotic resistant bacterial skin infections, similar to MRSA in people.
- Surface pyodermas
Shampoos:
Read Also: Dog Food Allergy Symptoms Skin
Symptoms Of Bacterial Infection In Dogs
Although there are many symptoms of a bacterial infection from Streptococcus canis bacteria, these are the most common ones:
- High body temperature
- Sores and abscesses on the dogs skin
- Obviously infected areas of skin, ears, and eyes.
- Urinary tract or respiratory system infection
- Inflammation and redness
- Refusal to play or exercise
- Excessive sleepiness
- Skin Infection Lesions and abscesses on skin anywhere on the body
- Throat Infection Pain when eating and drinking, refusing food and water
- Urinary Tract Infection Pain with urination, frequent urination, blood in urine
- Respiratory Infection Coughing, vomiting, high fever, breathing difficulty
- Sinus Infection Runny nose and watery eyes
Bacterial Eye Infections In Dogs
The most well-known bacterial eye infection in dogs is bacterial conjunctivitis, but there are dozens of bacterial eye infections that can affect your pet pooch.
Symptoms of bacterial eye infections usually include watery, red, sticky, itchy eyes, squinting and light sensitivity, and excess blinking.
Read Also: Where Can Skin Cancer Be Found
How To Reduce Bacterial Infections
One of the best ways to reduce bacterial infections is bathing. For some dogs whose bacteria have become resistant to all antibiotics, bathing is the only option we have. Sometimes, daily bathing with a chlorhexidine shampoo or a dilute bleach formula can resolve a superficial infection without antibiotics.
: Dogs commonly develop bacterial skin infections by the isolate Staphylococcuspseudintermedius which is different from the human strain Staphylococcusaureus. The dog Staph has developed changes in its genetics where not all antibiotics will work to resolve a given skin infection. So, a skin culture and/or frequent baths are often needed if prescribed antibiotics do not resolve the skin infection.
References:
Best Dog Antibiotics For Skin Infection With Prevention Tips
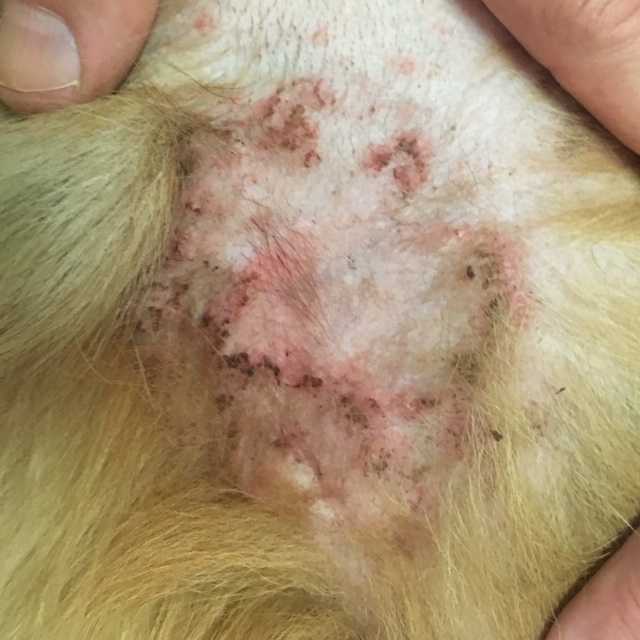
Skin infections are common in dogs. Several different things can cause them. As a result, doctors often use antibiotics to treat these infections. So today, I will share the five best dog antibiotics for skin infection.
However, you should know a few things before giving your dog antibiotics for a skin infection.
Its crucial to ensure that bacteria cause the infection in canines. Perhaps its a viral illness or an allergic response.
Then antibiotics wont help.
Many common oral antibiotics are used to treat dog skin infections. It includes amoxicillin, cephalexin, and clindamycin.
Mupirocin is the most common topical antibiotic used to treat skin infections in dogs.
Recommended Reading: Why Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma Fatal
Diagnosing A Bacterial Skin Infection
When a veterinarian examines a dog with a bacterial skin infection,he first completes a physical exam and asks the pet owner about thedogs history of symptoms. To get a good idea about what type ofbacteria a dog is fighting, a veterinarian will remove pus from insidea pustule or bump thats developed from the infection. The sample willbe examined under a microscope and a vet will find an elevated numberof white blood cells, neutrophils, if an infection is present.
A vet may also look for parasites by taking a small sample of adogs skin. This is done by gently scraping off some of a dogs dry,flaky skin or by placing a piece of adhesive tape on the skin andpeeling it off. Skin samples will show the presence of parasites, likemites. Ringworm, which causes a fungal infection, can lead to asecondary infection in a dogs skin.
A veterinarian will also perform blood tests to see if allergies oran imbalance of hormones are the cause of a dogs discomfort. In moreextreme cases, cancer can cause a dogs immune system to become weaker,making him more vulnerable to a bacterial skin infection.
Once a veterinarian has determined the cause behind a dogsbacterial skin infection, he can begin treatment to eliminate theantigens from the dogs body. Bacterial infections of the skin aretreatable and the earlier they are taken care of, the sooner the pup inpain will feel better.
How Successful Is This
Desensitization therapy or ‘allergy shots’ are not successful 100% of the time – in dogs or in people. Research has demonstrated that up to 77% of dogs to respond well to this treatment. Most dogs will remain on routine injections for the first one to two years and then less frequent injections may be attempted.
Also Check: What Are The 3 Most Common Types Of Skin Cancer
Identifying And Treating Fungal Infections In Dogs
Bacteria and viruses are what typically spring to mind hen pet parents think infection, but fungi can also be to blame. While not as common as bacterial or viral infections, fungal infections can be just as serious. Dogs can contract fungal infections from other animals, from the environment, or as a result of the overgrowth of fungi that are naturally present on their own bodies. Every pet is potentially at risk for contracting a fungal infection, and an accurate diagnosis is necessary before appropriate treatment can begin. Read on to learn more about fungal infections in dogs.
Diagnosis Of Bacterial Infection Of The Skin In Dogs
The veterinarian will perform a complete physical examination. Signs of skin infection will suggest pyoderma. Blood and urine tests will help to determine the underlying cause. Cell cultures may be taken of the infected area and examined microscopically to determine what organisms are present. Malassezia fungal infections are commonly found concurrent with bacterial pyoderma. The veterinarian will also check for the presence other parasites. In some cases, the culture may be sent to a lab to analyze the bacterias resistance to antibiotics and determine the best treatment.
The veterinarian will need to know your dogs medical history and current medications. If your dog is taking a steroid, or another medication that suppresses the immune system this is important since it will limit the effectiveness of an antibiotic. Any prior skin infections or treatment with antibiotics is also relevant.
Recommended Reading: Rough Skin Texture Large Pores
The Natural Bacteria On Dogs Skin Skin Dysbiosis And Skin Infections
A wide range of bacterial species are naturally present on the dogs skin. However, if the skin health is compromised in any way, some opportunistic bacteria can overgrow and cause secondary infections.
This overgrowth is sometimes called Skin Dysbiosis, and this imbalance between bacteria is the real cause of Staph infection in dogs. The bacteria were there before the infection and will still be there after its treated: but if theyre kept in check by other more friendly species, they dont cause a problem.
The most clinically important Staphylococcus in dogs is Staphylococcus pseudintermedius, a species which seems to be particularly prone to overgrowth if the skin flora is disrupted, and is responsible for around 75% of pyodermas. Whatever the cause of this disruption, it tends to result in clinical disease more commonly than other bacterial species. In comparison, Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa account for around 10-20% of cases each. Infection with Staph in dogs, however, can also involve a wider range of species, including Staphylococcus aureus, even if it is quite uncommon. Sadly, many strains are resistant to many of our antibiotics – due to selection and dissemination of resistant bacteria linked to massive use of antibiotics in human and veterinary medicine.
Ways To Prevent Dog Skin Infection
You can easily prevent skin infections in dogs by adopting simple skincare techniques.
- During the summer season, your dogs skin can become dry due to heat. To avoid dry skin, you can use moisturizers and prevent your dog from going out in direct sunlight.
- You can prevent parasitic dog skin infections by controlling parasites. Keeping your dog in a neat and clean environment and controlling fleas will be helpful.
- You should bath your dog regularly with best dog shampoos to avoid dog skin problems.
Read Also: How To Treat Basal Cell Carcinoma
Diagnosing & Treating Bacterial Skin Infections In Dogs
As mentioned, treatment for skin infections in dogs will ultimately depend on proper identification and diagnosis. The best way to diagnose skin infection in canines is through skin cytology, bacterial and/or fungal culture, and identification. Several methods like skin scraping, smear biopsy, and acetate cytology have proven effective in determining whether a skin infection is bacterial or fungal in nature. Identification of specific bacterial or fungal causes will involve culturing and isolating the bacteria taken from skin samples.
Most bacterial skin infections respond well to antibacterial medications. Localized and solitary bacterial infections can easily be treated with topical medications such as antibacterial creams and ointments. A more generalized infection will often need systemic antibacterial therapy for treatment.
Similarly, fungal infections are mostly treated with topical medications such as ointments or medicated shampoos, depending on how widespread the lesions are. Systemic antifungal medications are usually only prescribed in severe cases of fungal skin infections because of their potential liver and kidney side effects.