Are There Complications Of Skin Cancer Treatment
Most skin cancer treatments involve some localised damage to surrounding healthy skin such as swelling, reddening or blistering of the skin where the cancer is removed. Your doctor will explain any specific risks, which may include:
- pain or itching where the skin has been treated, or if lymph nodes have been removed
- scarring or changes to skin colour, after a skin cancer has been removed
- bleeding during or after surgery for more complicated skin cancers
- reactions sometimes your body may react to medicines used in treatment or surgery
- lymphoedema if your lymph nodes have been removed your neck, arm or leg may swell with fluid.
Its best to manage complications as early as possible, so ask your doctor for advice.
When Should You Call Your Doctor
The most important warning sign for melanoma is a change in size, shape, or colour of a mole or other skin growth . Call your doctor if you have:
- Any change in a mole, including size, shape, colour, soreness, or pain.
- A bleeding mole.
- A discoloured area under a fingernail or toenail not caused by an injury.
- A general darkening of the skin unrelated to sun exposure.
if you have been diagnosed with melanoma and:
- You have trouble breathing or swallowing.
- You cough up or spit up blood.
- You have blood in your vomit or bowel movement.
- Your urine or bowel movement is black, and the blackness isn’t caused by taking iron or Pepto-Bismol.
Biological Therapies And Melanoma
Biological therapies are treatments using substances made naturally by the body. Some of these treatments are called immunotherapy because they help the immune system fight the cancer, or they occur naturally as part of the immune system.
There are many biological therapies being researched and trialled, which in the future may help treat people with melanoma. They include monoclonal antibodies and vaccine therapy.
Read Also: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Stage 3 Survival Rate
How Can I Tell If I Have Skin Cancer
¿Cómo se ve el cáncer de la piel? ¿Cómo puedo prevenir el cáncer de piel?¿Estoy en riesgo de desarrollar melanoma?Cáncer de piel en personas de colorCómo examinar sus manchasNoe Rozas comparte su
Skin cancer is actually one of the easiest cancers to find. Thats because skin cancer usually begins where you can see it.
You can get skin cancer anywhere on your skin from your scalp to the bottoms of your feet. Even if the area gets little sun, its possible for skin cancer to develop there.
You can also get skin cancer in places that may surprise you. Skin cancer can begin under a toenail or fingernail, on your genitals, inside your mouth, or on a lip.
Where Do Skin Cancers Start
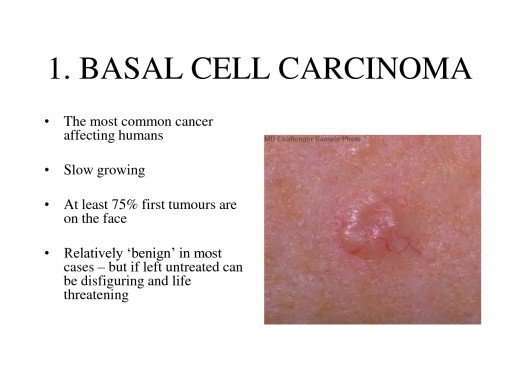
Most skin cancers start in the top layer of skin, called the epidermis. There are 3 main types of cells in this layer:
- Squamous cells: These are flat cells in the upper part of the epidermis, which are constantly shed as new ones form. When these cells grow out of control, they can develop into squamous cell skin cancer .
- Basal cells: These cells are in the lower part of the epidermis, called the basal cell layer. These cells constantly divide to form new cells to replace the squamous cells that wear off the skins surface. As these cells move up in the epidermis, they get flatter, eventually becoming squamous cells. Skin cancers that start in the basal cell layer are called basal cell skin cancers or basal cell carcinomas.
- Melanocytes: These cells make the brown pigment called melanin, which gives the skin its tan or brown color. Melanin acts as the bodys natural sunscreen, protecting the deeper layers of the skin from some of the harmful effects of the sun. Melanoma skin cancer starts in these cells.
The epidermis is separated from the deeper layers of skin by the basement membrane. When a skin cancer becomes more advanced, it generally grows through this barrier and into the deeper layers.
You May Like: Signs Of Stage 4 Cancer
Where Melanoma Usually Occurs
Melanoma can occur anywhere on the body, including areas not exposed to the sun, like inside the mouth or the palms of the hands. Men are more likely to get melanomas on their back and trunk or on their head and neck while women are more likely to get them on their arms and legs.
A study in the Journal of American Academy of Dermatology found that melanomas in blacks, Asians, Filipinos, Indonesians, and native Hawaiians most often occur on non-exposed skin with less pigment, with up to 60-75 percent of tumors arising on the palms, soles, mucous membranes and nail regions.
Squamous Cell Skin Cancer
SCC is generally faster growing than basal cell cancers. About 20 out of every 100 skin cancers are SCCs. They begin in cells called keratinocytes, which are found in the epidermis.
Most SCCs develop on areas of skin exposed to the sun. These areas include parts of the head, neck, and on the back of your hands and forearms. They can also develop on scars, areas of skin that have been burnt in the past, or that have been ulcerated for a long time.
SCCs don’t often spread. If they do, it’s most often to the deeper layers of the skin. They can spread to nearby lymph nodes and other parts of the body, but this is unusual.
Recommended Reading: Melanoma 3b
Who Gets Skin Cancer And Why
Sun exposure is the biggest cause of skin cancer. But it doesn’t explain skin cancers that develop on skin not ordinarily exposed to sunlight. Exposure to environmental hazards, radiation treatment, and even heredity may play a role. Although anyone can get skin cancer, the risk is greatest for people who have:
- Fair skin or light-colored eyes
- An abundance of large and irregularly-shaped moles
- A family history of skin cancer
- A history of excessive sun exposure or blistering sunburns
- Lived at high altitudes or with year-round sunshine
- Received radiation treatments
Where Within The Skin Layers Does Skin Cancer Develop
Where skin cancer develops specifically, in which skin cells is tied to the types and names of skin cancers.
Most skin cancers begin in the epidermis, your skins top layer. The epidermis contains three main cell types:
- Squamous cells: These are flat cells in the outer part of the epidermis. They constantly shed as new cells form. The skin cancer that can form in these cells is called squamous cell carcinoma.
- Basal cells: These cells lie beneath the squamous cells. They divide, multiply and eventually get flatter and move up in the epidermis to become new squamous cells, replacing the dead squamous cells that have sloughed off. Skin cancer that begins in basal cells is called basal cell carcinoma.
- Melanocytes: These cells make melanin, the brown pigment that gives skin its color and protects your skin against some of the suns damaging UV rays. Skin cancer that begins in melanocytes is called melanoma.
Also Check: Lobular Breast Cancer Survival Rate
Radiation And Immunologic Origins
Radiation has proven to be tumorigenic by two mechanisms. The first entails the initiations of prolonged cellular proliferation, thereby increasing the likelihood of transcription errors that can lead to cellular transformation. The second mechanism is direct damage of DNA replication, leading to cellular mutation that may activate proto-oncogenes or deactivate tumor suppressor genes.
Immunologically, the mechanism by which prolonged ultraviolet radiation exposure leads to the development of BCC includes suppression of the cutaneous immune system and immunologic unresponsiveness to cutaneous tumors. This local effect includes a decrease in Langerhans cells, dendritic epidermal T cells, and Thy1+ cells. Furthermore, systemic proliferation of suppressor T cells and the release of immunosuppressive factors are believed to be pathogenic to the development of BCC.
What Increases Your Risk
A risk factor for melanoma is something that increases your chance of getting this cancer. Having one or more of these risk factors can make it more likely that you will get melanoma. But it doesn’t mean that you will definitely get it. And many people who get melanoma don’t have any of these risk factors.
Risk factors for melanoma include:footnote 1
- Too much exposure to the sun’s UV rays. This includes:
- Having had blistering sunburns at any time of life.
- Getting intense sun exposure every now and then.
Also Check: Well Differentiated Carcinoma
Why Does Skin Cancer Occur In More Non
Scientists dont fully know why people of skin with color develop cancer in non-sun-exposed areas, such as their hands and feet. They think that the sun is less of a factor though. However, dermatologists still see plenty of UV sunlight-induced melanomas and squamous cell skin cancer in people of color, in skin tones ranging from fair to very dark.
Where Melanoma Is Found
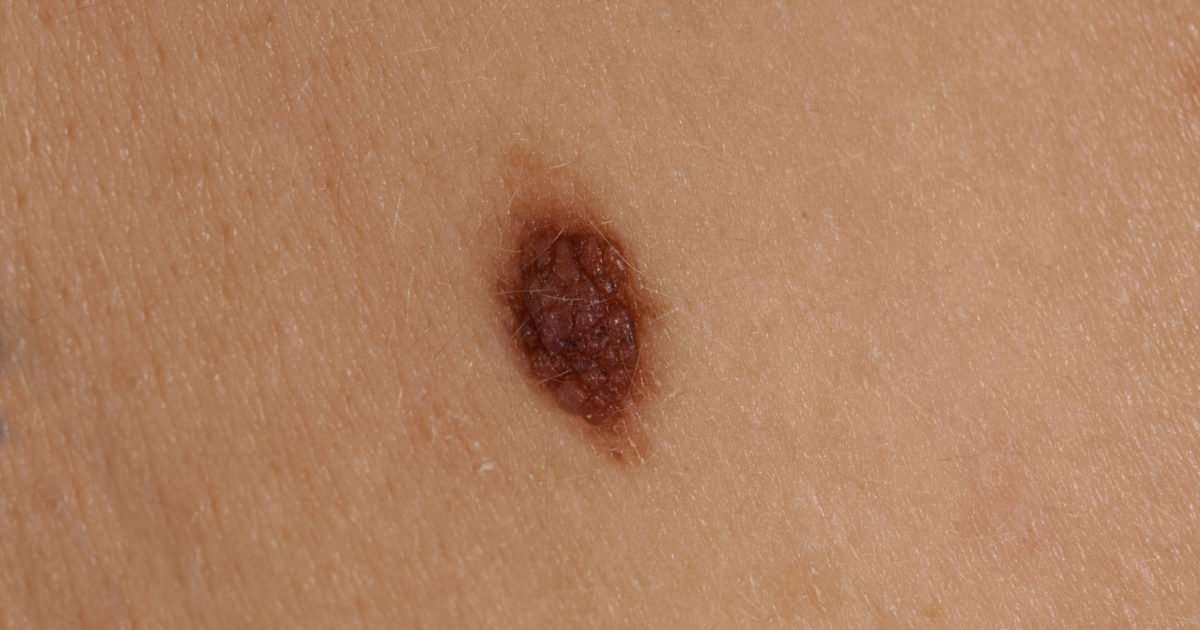
Melanoma is the least common but deadliest type of skin cancer. Melanoma begins in melanocyte cells found in the innermost layer of the epidermis. It occurs when those cells behave abnormally, growing excessively and taking over surrounding tissues. Melanomas can develop from existing moles or skin growths, but, more commonly, they will start as a new growth.
Most common sites: Melanoma can occur anywhere on the body, including areas not exposed to the sun, like inside the mouth or the palms of the hands. Men are more likely to get melanomas on their back and trunk or on their heads and neck while women are more likely to get them on their arms and legs.
A study in the Journal of American Academy of Dermatology found that melanomas in blacks, Asians, Filipinos, Indonesians, and native Hawaiians most often occur on non-exposed skin with less pigment, with up to 60-75 percent of tumors arising on the palms, soles, mucous membranes and nail regions. > Learn more about these rarer symptoms of melanoma.
Also Check: Stage 2 Carcinoma
What Is Skin Cancer And Melanoma
Skin cancer is a disease that occurs when your skin cells grow abnormally, usually from too much exposure to ultraviolet radiation from the sun.
This uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells forms a tumour in the skin. Tumours are either benign , or malignant .
Skin cancer is the most common type of cancer: each year, more than 13,000 Australians are diagnosed with a melanoma and almost 980,000 new cases of non-melanoma skin cancers are treated. Skin cancer is mostly preventable, and there are effective treatment options available.
Skin cancers are named according to the cells in which they form. There are 3 main types:
- Basal cell carcinoma begins in the lower segment of cells of the epidermis your outer layer of skin. These tend to grow slowly, and rarely spread to other parts of the body.
- Squamous cell carcinoma grows from the flat cells found in the top layer of your epidermis. SCC can grow quickly on the skin over several weeks or months. Bowens disease is an early form of SCC that hasnt grown beyond the top layer of skin.
- Melanoma grows from cells called melanocytes cells that give your skin its colour. Melanoma is the rarest type of skin cancer but is considered the most serious because it can spread quickly throughout the body.
BCC and SCC are also called non-melanoma skin cancers. BCC represents more than 2 in 3 non-melanoma skin cancers, and around 1 in 3 are SCC. There are other types of non-melanoma skin cancers, but they are rare.
Tips For Screening Moles For Cancer
Examine your skin on a regular basis. A common location for melanoma in men is on the back, and in women, the lower leg. But check your entire body for moles or suspicious spots once a month. Start at your head and work your way down. Check the “hidden” areas: between fingers and toes, the groin, soles of the feet, the backs of the knees. Check your scalp and neck for moles. Use a handheld mirror or ask a family member to help you look at these areas. Be especially suspicious of a new mole. Take a photo of moles and date it to help you monitor them for change. Pay special attention to moles if you’re a teen, pregnant, or going through menopause, times when your hormones may be surging.
Recommended Reading: Large Cell Cancer Of The Lung
Causes Of Skin Cancer
Both types of skin cancer occur when mutations develop in the DNA of your skin cells. These mutations cause skin cells to grow uncontrollably and form a mass of cancer cells.
Basal cell skin cancer is caused by ultraviolet rays from the sun or tanning beds. UV rays can damage the DNA inside your skin cells, causing the unusual cell growth. Squamous cell skin cancer is also caused by UV exposure.
Squamous cell skin cancer can also develop after long-term exposure to cancer-causing chemicals. It can develop within a burn scar or ulcer, and may also be caused by some types of human papillomavirus .
The cause of melanoma is unclear. Most moles dont turn into melanomas, and researchers arent sure why some do. Like basal and squamous cell skin cancers, melanoma can be caused by UV rays. But melanomas can develop in parts of your body that arent typically exposed to sunlight.
Your recommended treatment plan will depend on different factors, like the size, location, type, and stage of your skin cancer. After considering these factors, your healthcare team may recommend one or more of the following treatments:
You Can Find Skin Cancer On Your Body
The best way to find skin cancer is to examine yourself. When checking, you want to look at the spots on your skin. And you want to check everywhere from your scalp to the spaces between your toes and the bottoms of your feet.
If possible, having a partner can be helpful. Your partner can examine hard-to-see areas like your scalp and back.
Getting in the habit of checking your skin will help you notice changes. Checking monthly can be beneficial. If you have had skin cancer, your dermatologist can tell you how often you should check your skin.
People of all ages get skin cancer
Checking your skin can help you find skin cancer early when its highly treatable.
You May Like: Skin Cancer 1st Stage
What Are The Signs Of Skin Cancer
The most common warning sign of skin cancer is a change on your skin, typically a new growth, or a change in an existing growth or mole. The signs and symptoms of common and less common types of skin cancers are described below.
Basal cell carcinoma
Basal cell cancer is most commonly seen on sun-exposed areas of skin including your hands, face, arms, legs, ears, mouths, and even bald spots on the top of your head. Basal cell cancer is the most common type of skin cancer in the world. In most people, its slow growing, usually doesnt spread to other parts of the body and is not life-threatening.
Signs and symptoms of basal cell carcinoma include:
- A small, smooth, pearly or waxy bump on the face, ears, and neck.
- A flat, pink/red- or brown-colored lesion on the trunk or arms and legs.
- Areas on the skin that look like scars.
- Sores that look crusty, have a depression in the middle or bleed often.
Squamous cell carcinoma
Squamous cell cancer is most commonly seen on sun-exposed areas of skin including your hands, face, arms, legs, ears, mouths, and even bald spots on the top of your head. This skin cancer can also form in areas such as mucus membranes and genitals.
Signs and symptoms of squamous cell carcinoma include:
- A firm pink or red nodule.
- A rough, scaly lesion that might itch, bleed and become crusty.
Melanoma
Signs and symptoms of melanoma include:
- A brown-pigmented patch or bump.
- A mole that changes in color, size or that bleeds.
Where Does Skin Cancer Develop
Skin cancer is most commonly seen in sun-exposed areas of your skin your face , ears, neck, arms, chest, upper back, hands and legs. However, it can also develop in less sun-exposed and more hidden areas of skin, including between your toes, under your fingernails, on the palms of your hands, soles of your feet and in your genital area.
Also Check: Stage 3b Melanoma Survival Rate
Basal Cell And Squamous Cell Survival Rates
Because basal cell and squamous cell carcinomas are lower-risk skin cancers, theres little information on survival rates based on stage.
Both types of cancer have a very high cure rate. According to the Canadian Cancer Society, the five-year survival rate for basal cell carcinoma is 100 percent. The five-year survival rate for squamous cell carcinoma is 95 percent.
What Are The Symptoms Of Skin Cancer
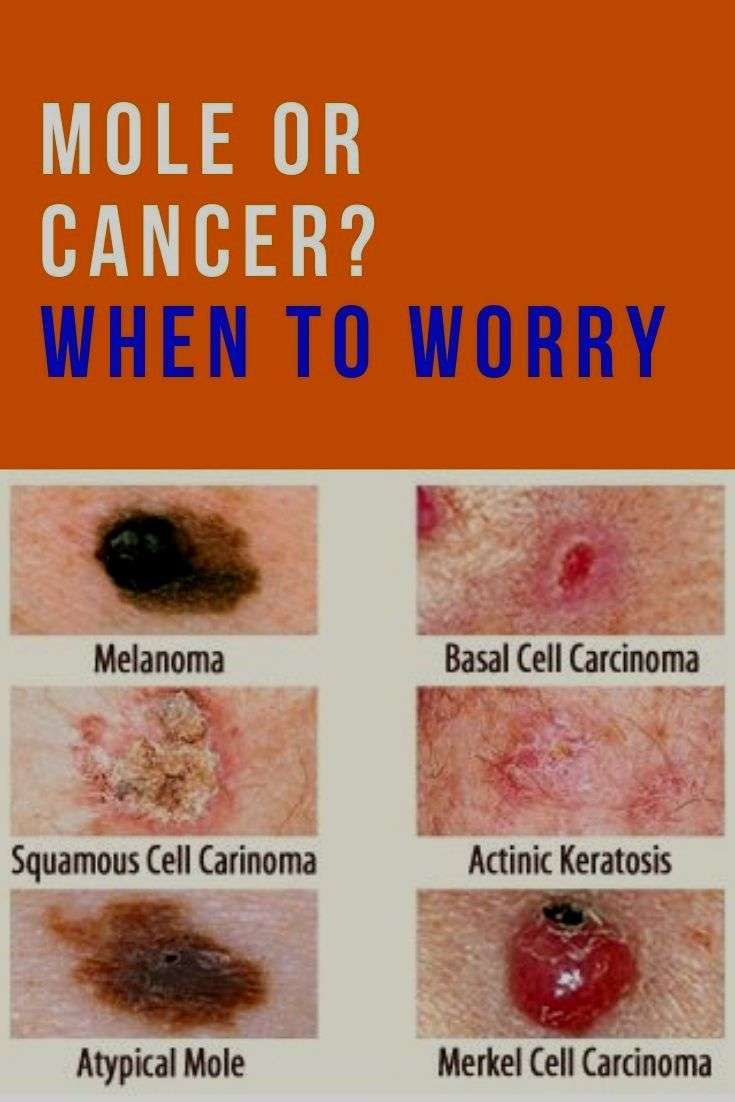
Skin cancers first appear as a spot, lump or scaly area on the skin, or a mole that changes colour, size or shape over several weeks or months. These changes can appear anywhere on the body, particularly areas frequently exposed to the sun. Skin cancers may bleed and become inflamed, and can be tender to the touch.
There are certain characteristics to look for in spots and moles. Remember the ‘ABCDE’ of skin cancer when checking your skin:
- Asymmetry does each side of the spot or mole look different to the other?
- Border is it irregular, jagged or spreading?
- Colours are there several, or is the colour uneven or blotchy?
- Diameter look for spots that are getting bigger
- Evolution is the spot or mole changing or growing over time?
Changes may include an area that is scaly, shiny, pale or bright pink in colour, or a spot or lump that grows quickly and is thick, red, scaly or crusted.
See your doctor if you notice any new spots or an existing spot that changes size, shape or colour over several weeks or months. Your doctor can help you distinguish between a harmless spot such as a mole, and a sunspot or irregular mole that could develop later into skin cancer.
Don’t Miss: Stage 3 Melanoma Life Expectancy