How Is Skin Cancer Treated
Treatment depends upon the stage of cancer. Stages of skin cancer range from stage 0 to stage IV. The higher the number, the more cancer has spread.
Sometimes a biopsy alone can remove all the cancer tissue if the cancer is small and limited to your skins surface only. Other common skin cancer treatments, used alone or in combination, include:
Cryotherapy uses liquid nitrogen to freeze skin cancer. The dead cells slough off after treatment. Precancerous skin lesions, called actinic keratosis, and other small, early cancers limited to the skins top layer can be treated with this method.
Excisional surgery
This surgery involves removing the tumor and some surrounding healthy skin to be sure all cancer has been removed.
Mohs surgery
With this procedure, the visible, raised area of the tumor is removed first. Then your surgeon uses a scalpel to remove a thin layer of skin cancer cells. The layer is examined under a microscope immediately after removal. Additional layers of tissue continue to be removed, one layer at a time, until no more cancer cells are seen under the microscope.
Mohs surgery removes only diseased tissue, saving as much surrounding normal tissue as possible. Its most often used to treat basal cell and squamous cell cancers and near sensitive or cosmetically important areas, such as eyelids, ears, lips, forehead, scalp, fingers or genital area.
Curettage and electrodesiccation
Chemotherapy and immunotherapy
What Is Nonmelanoma Skin Cancer
Skin cancer is a disease that begins in the cells of the skin. The area of skin with the cancer is often called a lesion. There are several types of skin cancer . Melanoma is the most serious. But there are others that are known as nonmelanoma skin cancer. These include:
-
Basal cell carcinoma
Basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma are by far the most common.
What Is The Treatment Of Merkel Cell Carcinoma
Once a Merkel cell carcinoma is diagnosed, and studies are performed to determine if the tumor has spread treatment options might include:
- Surgery is the most common treatment for Merkel Cell Carcinoma. The tumor is removed in addition to a margin of normal skin surrounding the tumor to assure the complete removal of the cancer. Often times, regional lymph nodes in the area of the tumor are removed at the same time to assess whether the tumor has spread. Spread to lymph nodes is found in approximately one-half of patients.
- Radiation Therapy. Following surgery, localized radiation therapy at the tumor site is commonly used to destroy the remaining cancer cells. Radiation therapy is also used in patients when surgery is not an option due to ill health, certain tumor locations or if the tumor has reoccurred after initial treatment.
- Chemotherapy. Following surgery, chemotherapy may be initiated especially when Merkel cell carcinoma has spread to lymph nodes, distant parts of the body, or has reoccurred after initial therapy.
When diagnosed and treated early, Merkel cell carcinoma can be controlled and even cured.
You May Like: Can Merkel Cell Carcinoma Be Cured
Don’t Miss: Grade 3 Cancer Treatment
After Skin Cancer Treatment
Most skin cancer is cured surgically in the dermatologist’s office. Of skin cancers that do recur, most do so within three years. Therefore, follow up with your dermatologist as recommended. Make an appointment immediately if you suspect a problem.
If you have advanced malignant melanoma, your oncologist may want to see you every few months. These visits may include total body skin exams, regional lymph node checks, and periodic chest X-rays and body scans. Over time, the intervals between follow-up appointments will increase. Eventually these checks may be done only once a year.
What Happens If Precancers Go Untreated
As the name suggests, precancers are damaged skin cells that arent considered cancerous, but if they are left untreated, these lesions are at high risk to become skin cancer. There are two main types of precancerous skin conditions: actinic keratosis and dysplastic nevi. Actinic keratosis looks like a rough, scaly patch of the skin that is usually red or brown. This condition may develop into squamous cell carcinoma if left untreated.
Nevi are moles, and dysplastic nevi is a term that means a mole is abnormal. Dysplastic nevi may develop into melanoma without proper treatment. While precancerous skin cancers are not malignant on their own, the potential to develop into life-threatening forms of this condition means they need to be evaluated regularly.
Also Check: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Grade 2 Survival Rate
Who Is Most At Risk For Skin Cancer
Although anyone can develop skin cancer, youre at increased risk if you:
- Spend a considerable amount of time working or playing in the sun.
- Get easily sunburned have a history of sunburns.
- Live in a sunny or high-altitude climate.
- Tan or use tanning beds.
- Have light-colored eyes, blond or red hair and fair or freckled skin.
- Have many moles or irregular-shaped moles.
- Have actinic keratosis .
- Have a family history of skin cancer.
- Have had an organ transplant.
- Take medications that suppress or weaken your immune system.
- Have been exposed to ultraviolet light therapy for treating skin conditions such as eczema or psoriasis.
What Are The Risk Factors For Merkel Cell Carcinoma
Recommended Reading: What Type Of Skin Cancer Spreads The Fastest
It Affects People Of All Races Genders And Ages Which Is Why Its Absolutely Critical For Americans To Learn About
Here are the top 10 cancer hospitals in the usa. As the saying goes, eyes are the window to the soul, so it is important to keep them as sharp and clear as possible. Cancer is a common cause of death, but treatment has improved vastly over the past decade. Unfortunately, accidents, age or genes can lead to a loss of full or partial vision, leaving us with a foggy or blurred vie. Some hospitals are more renowned than others, of course. It can often cure early stage melanomas. Learn about melanoma surgery options here. Although it is the most commonly diagnosed cancer in american women, breast cancer can impact people of all genders. The strongest risk factor for developing skin cancer is ultraviolet ray exposure, typically from the sun. As with any ranking of cancer hospitals, this list provides a few prestigious names but doesnt. There are a number of different treatments doctors recommend. Surgery is the main treatment for most melanomas. Some types of skin cancer are more dangerous than others, but if you have a spot.
Squamous Cell Skin Cancer
SCC is generally faster growing than basal cell cancers. About 20 out of every 100 skin cancers are SCCs. They begin in cells called keratinocytes, which are found in the epidermis.
Most SCCs develop on areas of skin exposed to the sun. These areas include parts of the head, neck, and on the back of your hands and forearms. They can also develop on scars, areas of skin that have been burnt in the past, or that have been ulcerated for a long time.
SCCs don’t often spread. If they do, it’s most often to the deeper layers of the skin. They can spread to nearby lymph nodes and other parts of the body, but this is unusual.
You May Like: Stage 3 Melanoma Life Expectancy
Causes Of Bowen’s Disease
Bowen’s disease usually affects older people in their 60s and 70s.
The exact cause is unclear, but it’s been closely linked with:
- long-term exposure to the sun or use of sunbeds especially in people with fair skin
- having a weak immune system for example, it’s more common in people taking medicine to suppress their immune system after an organ transplant, or those with AIDS
- previously having radiotherapy treatment
- the human papillomavirus a common virus that often affects the genital area and can cause genital warts
Bowen’s disease does not run in families and it’s not infectious.
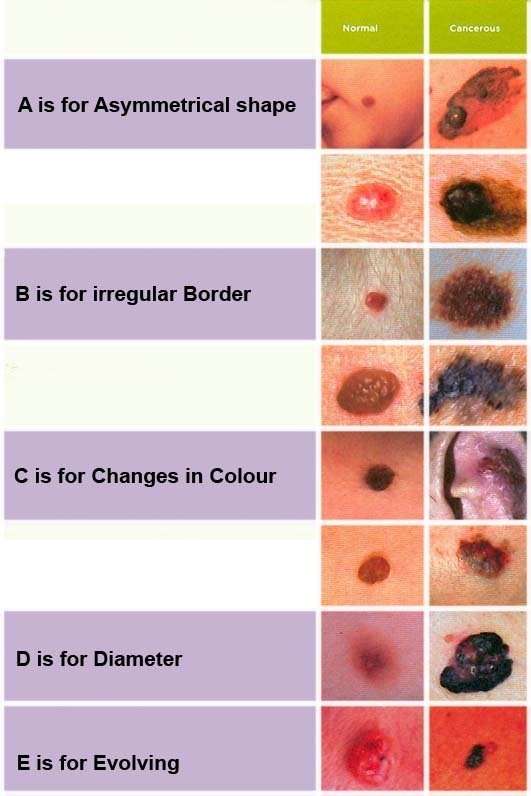
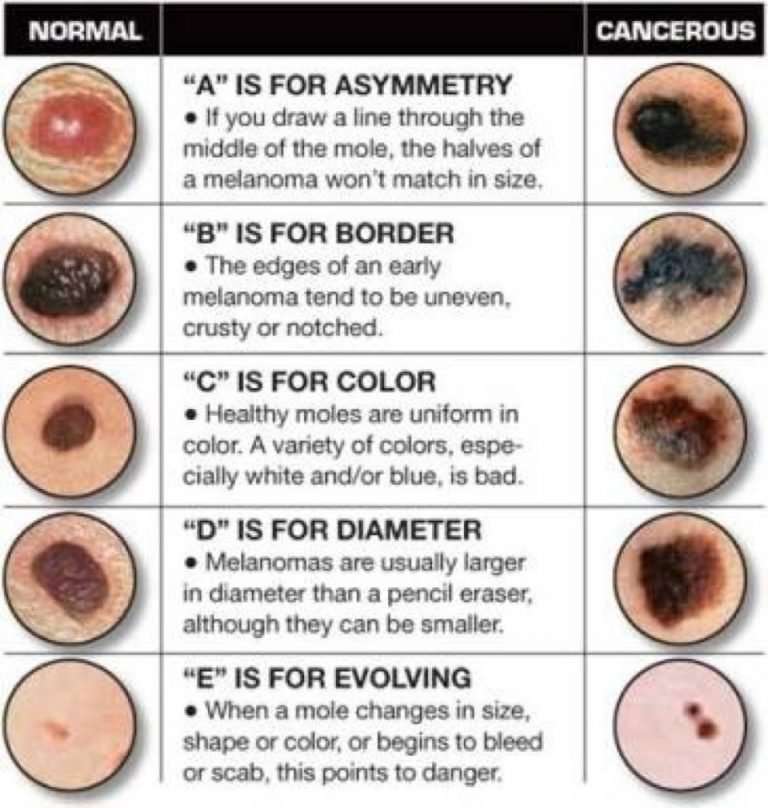
What Are The Symptoms Of Skin Cancer
Diagnosing skin cancer early saves lives, so its really important to know what to look for.
Melanoma usually causes changes to moles.
You should contact your GP if you have a mole that:
- gets bigger
- has a blurred, rough or jagged outline
- gets darker or red
- has more than one colour in it
- gets itchy or painful
- gets crusty or bleeds.
Non-melanoma skin cancer is very rare in young people. The signs are usually easy to recognise. Look out for:
- spots or sores that dont heal, even after a few weeks
- spots or sores that are itchy, sore, scabbed or bloody for a few weeks
- ulcers that last for a few weeks without any obvious cause.
You May Like: Skin Cancer Perineural Invasion
Symptoms Of Bowen’s Disease
Bowen’s disease usually appears as a patch on the skin that has clear edges and does not heal.
Some people have more than 1 patch.
- up to a few centimetres across
- itchy
The patch can appear anywhere on the skin, but is especially common on exposed areas like the lower legs, neck and head.
Sometimes they can affect the groin area and, in men, the penis.
If the patch bleeds, starts to turn into an open sore or develops a lump, it could be a sign it’s turned into squamous cell skin cancer.
Why Does Skin Cancer Occur In More Non
Scientists dont fully know why people of skin with color develop cancer in non-sun-exposed areas, such as their hands and feet. They think that the sun is less of a factor though. However, dermatologists still see plenty of UV sunlight-induced melanomas and squamous cell skin cancer in people of color, in skin tones ranging from fair to very dark.
Read Also: Prognosis Of Skin Cancer
Is Bowen’s Disease Serious
Bowen’s disease itself is not usually serious. It tends to grow very slowly over months or years, and there are several very effective treatments for it.
The concern is that Bowen’s disease can eventually develop into a different type of skin cancer called squamous cell skin cancer if it’s left undiagnosed or neglected.
It’s estimated this happens in up to 1 in 20 to 1 in 30 people with untreated Bowen’s disease.
Squamous cell skin cancer is often treatable, but it can spread deeper into the body and is sometimes very serious.
What Is Skin Cancer
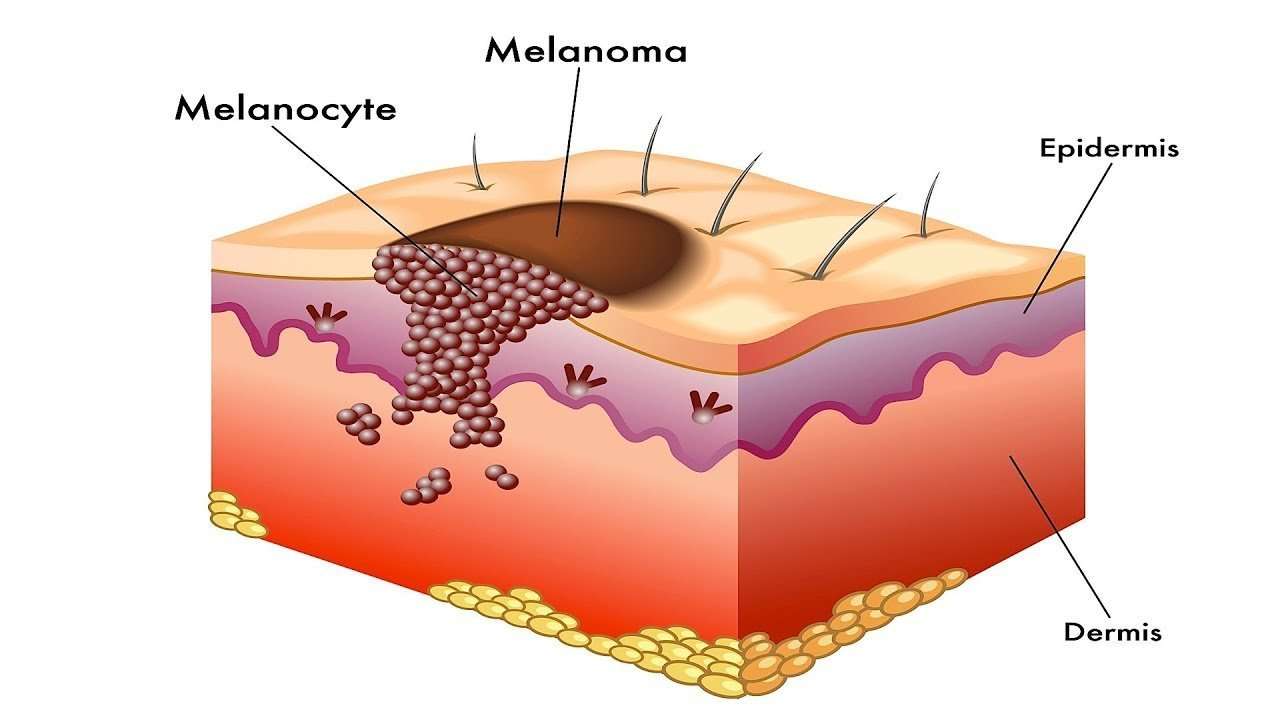
Basal cell carcinoma begins in the basal cell layer of the skin. Squamous cell carcinoma begins in the squamous layer of the skin. Melanoma begins in the melanocytes, which are the cells that make melanin, the pigment that gives skin its color.
Basal cell carcinoma begins in the basal cell layer of the skin. Squamous cell carcinoma begins in the squamous layer of the skin. Melanoma begins in the melanocytes, which are the cells that make melanin, the pigment that gives skin its color.
The skin is the bodys largest organ. Skin has several layers, but the two main layers are the epidermis and the dermis . Skin cancer begins in the epidermis, which is made up of three kinds of cells
- Squamous cells: Thin, flat cells that form the top layer of the epidermis.
- Basal cells: Round cells under the squamous cells.
- Melanocytes: Cells that make melanin and are found in the lower part of the epidermis. Melanin is the pigment that gives skin its color. When skin is exposed to the sun, melanocytes make more pigment and cause the skin to darken.
Basal and squamous cell carcinomas are the two most common types of skin cancer. They begin in the basal and squamous layers of the skin, respectively. Both can usually be cured, but they can be disfiguring and expensive to treat.
Don’t Miss: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Grade 1 Survival Rate
What Is A Merkel Cell
Merkel cells are located deep in the top layer of skin. Merkel cells are connected to nerves, signaling touch sensation as touch receptors. MCC was named after Merkel cells due to the similar microscopic features however, recent research suggests that it is unlikely that MCC originates directly from normal Merkel cells.
Normal Merkel cells in the skin: In this illustration of a cross-section of the skin, normal Merkel cells are shown in red and connect to nerves shown in yellow. The structures drawn include the epidermis , dermis , and deeper adipose layer containing the fatty tissue. Arteries are depicted in red and veins are blue. Figure copyright by Paul Nghiem & Quade Medical Group.
Recommended Reading: Does Basal Cell Carcinoma Hurt
What It Looks Like
Squamous cell cancer involves the runaway growth of keratinocytes, cells in the outermost layer of skin, which produce the protein keratin. Squamous means scaly in 60%80% of cases, the lesions emerge on or near scaly patches called actinic keratoses that develop from sun-damaged skin.
To continue reading this article, you must log in.
- Research health conditions
- Prepare for a doctors visit or test
- Find the best treatments and procedures for you
- Explore options for better nutrition and exercise
You May Like: What Does Stage 3 Melanoma Mean
Don’t Miss: How Long Until Melanoma Spreads
Skin Cancer Of The Head And Neck Treatment
Many early-stage small basal cell cancers or squamous cell cancers can be removed by Mohs surgery, a technique that spares normal tissue through repeated intraoperative margin testing, removing only the cancer and leaving adjacent normal tissue. Tumors with nerve involvement, lymph node involvement or of a large size are not suitable for Mohs surgery. They require a multimodality approach to treatment, with formal surgical resection and adjuvant radiation or chemotherapy.
Melanoma is more likely to spread, and aggressive surgical resection with wide margins is required, in addition to radiation and/or chemotherapy.
Johns Hopkins Head and Neck Cancer Surgery
Johns Hopkins Head and Neck Cancer Surgery provides comprehensive surgical care and treatment for head and neck cancers. Our surgeons are at the leading edge of head and neck cancer treatment. You will benefit from the skilled care of head and neck surgeons, guiding clinical advancements in the field of head and neck cancer care.
What Are Some Of The Lesser
Some of the less common skin cancers include the following:
Kaposi sarcoma is a rare cancer most commonly seen in people who have weakened immune systems, those who have human immunodeficiency virus /AIDS and people who are taking immunosuppressant medications who have undergone organ or bone marrow transplant.
Signs and symptoms of Kaposi sarcoma are:
- Blue, black, pink, red or purple flat or bumpy blotches or patches on your arms, legs and face. Lesions might also appear in your mouth, nose and throat.
Merkel cell carcinoma
Merkel cell carcinoma is a rare cancer that begins at the base of the epidermis, the top layer of your skin. This cancer starts in Merkel cells, which share of the features of nerve cells and hormone-making cells and are very close to the nerve ending in your skin. Merkel cell cancer is more likely to spread to other parts of the body than squamous or basal cell skin cancer.
Signs and symptoms of Merkel cell carcinoma are:
- A small reddish or purplish bump or lump on sun-exposed areas of skin.
- Lumps are fast-growing and sometimes open up as ulcers or sores.
Sebaceous gland carcinoma
Sebaceous gland carcinoma is a rare, aggressive cancer that usually appears on your eyelid. This cancer tends to develop around your eyes because theres a large number of sebaceous glands in that area.
Signs and symptoms of sebaceous gland carcinoma are:
- A painless, round, firm, bump or lump on or slightly inside your upper or lower eyelid.
Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans
Don’t Miss: Stage Iiia Melanoma Prognosis
Basal Cell And Squamous Cell Carcinoma
The two most common kinds of skin cancer are basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma, which are sometimes called nonmelanoma skin cancer. These cancers are carcinomas that begin in the cells that cover or line an organ.
Basal cell carcinoma accounts for more than 90 percent of all skin cancers in the United States and is the most common of all cancers. Typically, it is a slow-growing cancer that seldom spreads to other parts of the body.
Squamous cell carcinoma also rarely spreads, but does so more often than basal cell carcinoma. It is important that skin cancers are found and treated early because they can invade and destroy nearby tissue. Organ transplant recipients have a 65-fold higher risk of developing squamous cell carcinoma than others. UCSF Medical Center offers a High Risk Skin Cancer Clinic for those at high risk for non-melanoma skin cancers, such as transplant recipients.
What Are The Risk Factors For Basal Cell Carcinoma
Basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma and melanoma are all skin cancers caused by exposure to damaging ultraviolet raysfrom natural and artificial sunlight. Theres also a genetic condition called basal cell nevus or Gorlin syndrome, which can cause people to develop hundreds of basal cell skin cancers, but its extremely rare, says Dr. Christensen.
People at the highest risk for basal cell carcinoma tend to have fair or light-colored skin, a history of sun exposure and a tendency to sunburn quickly. Fair-skinned people have a 50 percent risk of developing basal skin cancer at some point in their lives, Dr. Christensen says. The cancer is the result of cumulative damage of years spent in the sun, and may take 20 years to manifest.
Although its often more common in older people, it can occur in younger adults, too.
Basal cell carcinoma spreads very slowly and very rarely will metastasize, Dr. Christensen says. But if its not treated, basal cell carcinoma can continue to grow deeper under the skin and cause significant destruction to surrounding tissues. It can even become fatal. For example, an untreated basal cell carcinoma on the face can grow into the bones and, over time, directly into the brain, Dr. Christensen says.
Recommended Reading: How Long Does It Take For Melanoma To Metastasize