Diagnosis And Staging What It Means For You
How is melanoma diagnosed?
To diagnose melanoma, a dermatologist biopsies the suspicious tissue and sends it to a lab, where a dermatopathologist determines whether cancer cells are present.
After the disease is diagnosed and the type of melanoma is identified, the next step is for your medical team to identify the stage of the disease. This may require additional tests including imaging such as PET scans, CT scans, MRIs and blood tests.
The stage of melanoma is determined by several factors, including how much the cancer has grown, whether the disease has spread and other considerations. Melanoma staging is complex, but crucial. Knowing the stage helps doctors decide how to best treat your disease and predict your chances of recovery.
Early Signs Of Skin Cancer To Look Out For
Detecting skin cancer early is the best way to ensure it is treated successfully. But how can skin cancer be detected early? The good thing about skin cancer is that it leaves easily identifiable marks on our bodies long before it becomes a serious problem. During skin cancer screenings your dermatologist will look for these telltale signs. Well help you identify them so that you can be on the lookout when youre at home and, therefore, spot skin cancer early.
There are three common types of skin cancer basal cell carcinoma , squamous cell carcinoma , and melanoma. BCC and SCC are far more common than melanoma and are both non-life threatening. Melanoma, on the other hand, is the more aggressive of the three and typically causes serious complications, including death.
What Does Melanoma Look Like
Melanoma is a type of cancer that begins in melanocytes . Below are photos of melanoma that formed on the skin. Melanoma can also start in the eye, the intestines, or other areas of the body with pigmented tissues.
Often the first sign of melanoma is a change in the shape, color, size, or feel of an existing mole. However, melanoma may also appear as a new mole. People should tell their doctor if they notice any changes on the skin. The only way to diagnose melanoma is to remove tissue and check it for cancer cells.
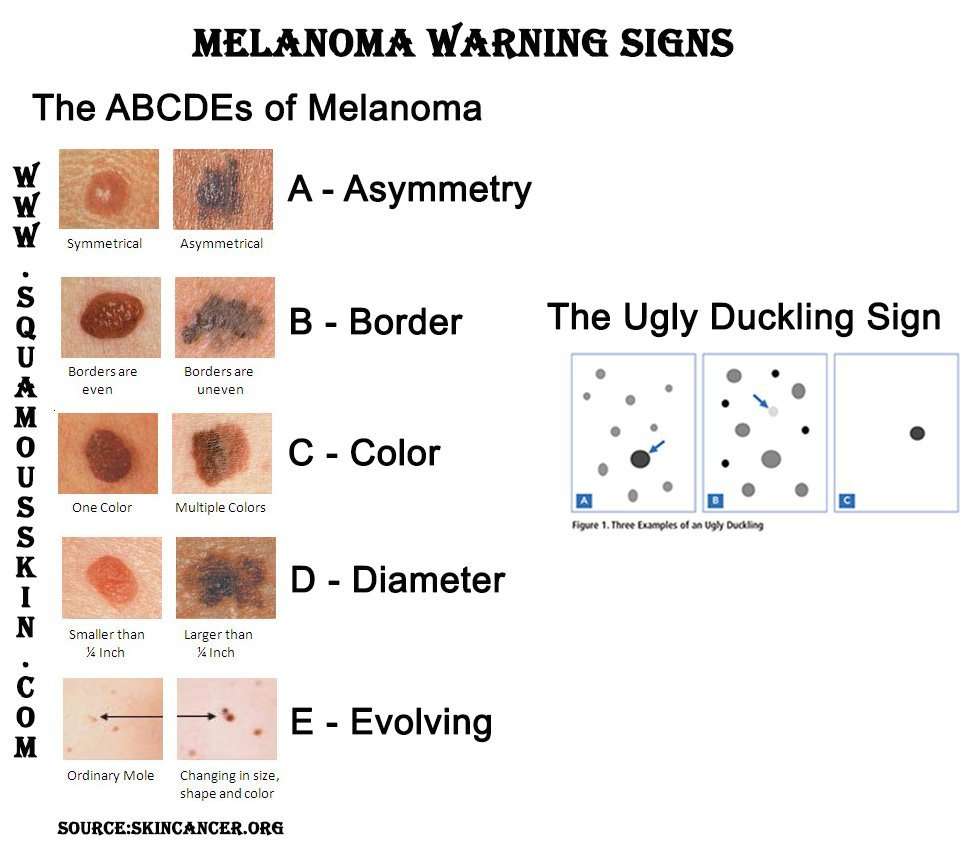
Thinking of “ABCDE” can help you remember what to look for:
- Asymmetry: The shape of one half does not match the other half.
- Border that is irregular: The edges are often ragged, notched, or blurred in outline. The pigment may spread into the surrounding skin.
- Color that is uneven: Shades of black, brown, and tan may be present. Areas of white, gray, red, pink, or blue may also be seen.
- Diameter: There is a change in size, usually an increase. Melanomas can be tiny, but most are larger than the size of a pea .
- Evolving: The mole has changed over the past few weeks or months.
Melanomas can vary greatly in how they look. Many show all of the ABCDE features. However, some may show changes or abnormal areas in only one or two of the ABCDE features.
You May Like: Can You Die From Basal Cell Skin Cancer
Skin Cancer Pictures: What Does Skin Cancer Look Like
Skin cancer images by skin cancer type. Skin cancer can look different than the photos below.
Basal Cell Carcinoma | Squamous Cell Carcinoma | Bowens Disease | Keratoacanthoma | Actinic Keratosis | Melanoma
Skin cancer often presents itself as a change in the skins appearance. This could be the appearance of a new mole or other mark on the skin or a change in an existing mole.
Please remember that you should always seek advice from your doctor if you have any concern about your skin. Skin cancers often look different from skin cancer images found online.
How Are Moles Evaluated
If you find a mole or spot that has any ABCDE’s of melanoma — or one that’s tender, itching, oozing, scaly, doesn’t heal or has redness or swelling beyond the mole — see a doctor. Your doctor may want to remove a tissue sample from the mole and biopsy it. If found to be cancerous, the entire mole and a rim of normal skin around it will be removed and the wound stitched closed. Additional treatment may be needed.
Recommended Reading: Prognosis Of Skin Cancer
The Ugly Duckling Sign
The “ugly duckling sign” is another warning method to help identify melanomas. Usually, moles on your body look quite similar to each other. However, compared to other moles, melanomas tend to stand out like an ugly duckling. The more you check your skin and become familiar with it, the easier it becomes to spot an ugly duckling early.
What You Need To Know About Early Detection
Finding melanoma at an early stage is crucial early detection can vastly increase your chances for cure.
Look for anything new,changing or unusual on both sun-exposed and sun-protected areas of the body. Melanomas commonly appear on the legs of women, and the number one place they develop on men is the trunk. Keep in mind, though, that melanomas can arise anywhere on the skin, even in areas where the sun doesnt shine.
Most moles, brown spots and growths on the skin are harmless but not always. The ABCDEs and the Ugly Duckling sign can help you detect melanoma.
Early detection makes a difference
99%5-year survival rate for patients in the U.S. whose melanoma is detected early. The survival rate drops to 66% if the disease reaches the lymph nodes and27% if it spreads to distant organs.
Also Check: Cancer Spread All Over Body
What You Can Do
Check yourself: No matter your risk, examine your skin head-to-toe once a month to identify potential skin cancers early. Take note of existing moles or lesions that grow or change. Learn how to check your skin here.
When in doubt, check it out. Because melanoma can be so dangerous once it advances, follow your instincts and visit your doctor if you see a spot that just doesnt seem right.
Keep in mind that while important, monthly self-exams are not enough. See your dermatologist at least once a year for a professional skin exam.
If youve had a melanoma, follow up regularly with your doctor once treatment is complete. Stick to the schedule your doctor recommends so that you will find any recurrence as early as possible.
Reviewed by:
When Is A Mole A Problem
A mole is a benign growth of melanocytes, cells that gives skin its color. Although very few moles become cancer, abnormal or atypical moles can develop into melanoma over time. “Normal” moles can appear flat or raised or may begin flat and become raised over time. The surface is typically smooth. Moles that may have changed into skin cancer are often irregularly shaped, contain many colors, and are larger than the size of a pencil eraser. Most moles develop in youth or young adulthood. It’s unusual to acquire a mole in the adult years.
Also Check: What Stage Is Invasive Lobular Carcinoma
What Does Skin Cancer Look Like
Basal cell carcinoma
-
BCC frequently develops in people who have fair skin. People who have skin of color also get this skin cancer.
-
BCCs often look like a flesh-colored round growth, pearl-like bump, or a pinkish patch of skin.
-
BCCs usually develop after years of frequent sun exposure or indoor tanning.
-
BCCs are common on the head, neck, and arms however, they can form anywhere on the body, including the chest, abdomen, and legs.
-
Early diagnosis and treatment for BCC are important. BCC can grow deep. Allowed to grow, it can penetrate the nerves and bones, causing damage and disfigurement.
Squamous cell carcinoma of the skin
-
People who have light skin are most likely to develop SCC. This skin cancer also develops in people who have darker skin.
-
SCC often looks like a red firm bump, scaly patch, or a sore that heals and then re-opens.
-
SCC tends to form on skin that gets frequent sun exposure, such as the rim of the ear, face, neck, arms, chest, and back.
-
SCC can grow deep into the skin, causing damage and disfigurement.
-
Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent SCC from growing deep and spreading to other areas of the body.
SCC can develop from a precancerous skin growth
-
People who get AKs usually have fair skin.
-
AKs usually form on the skin that gets lots of sun exposure, such as the head, neck, hands, and forearms.
-
Because an AK can turn into a type of skin cancer, treatment is important.
Melanoma
What Is A Biopsy
A proper diagnosis of cancer in the skin is made possible through biopsy. We will remove a skin tissue sample and send it to a laboratory. A pathologist will then examine your samples and look for abnormal cells that could be cancerous. Through a biopsy, you can also get accurate information about the stage of skin cancer you might have.
For advanced melanoma, we request imaging tests and lymph node biopsy to see whether cancer has affected other parts of the body. Additional evaluation is made possible using any or a combination of the following methods:
- Computed tomography
- Measurement of lactate dehydrogenase levels
Don’t Miss: What Is Braf Testing In Melanoma
Basal And Squamous Cell Skin Cancer Stages
After someone is diagnosed with cancer, doctors will try to figure out if it has spread, and if so, how far. This process is called staging. The stage of a cancer describes how much cancer is in the body. It helps determine how serious the cancer is and how best to treat it.
The stage is based on the results of the physical exam, the skin biopsy , and the results of imaging tests if they are done. These exams and tests are described in Tests for Basal and Squamous Cell Skin Cancers.
Determining the stage of basal cell skin cancers is rarely needed, because these cancers are almost always cured before they spread to other parts of the body.
Squamous cell skin cancers are more likely to spread , so determining the stage can be more important, particularly in people who are at higher risk. This includes people with weakened immune systems, such as those who have had organ transplants and people infected with HIV, the virus that causes AIDS. Most squamous cell skin cancers occur in the head and neck region and tend to have a higher risk of recurring or spreading compared to those in other locations.
Basal Cell Carcinoma Early Stages
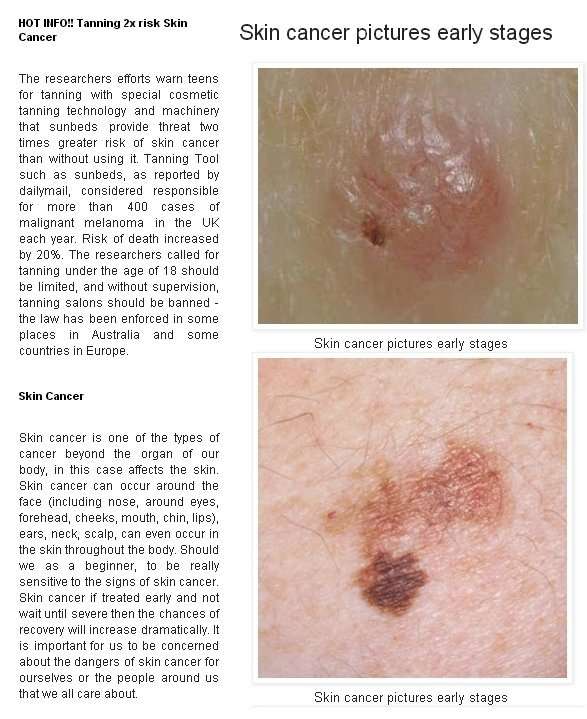
Basal cells are found within the skin and are responsible for producing new skin cells as old ones degenerate. Basal cell carcinoma starts with the appearance of slightly transparent bumps, but they may also show through other symptoms.
In the beginning, a basal cell carcinoma resembles a small bump, similar to a flesh-colored mole or a pimple. The abnormal growths can also look dark, shiny pink, or scaly red in some cases.
Also Check: Can Squamous Cell Carcinoma Metastasis
How To Diagnose Skin Cancer
First, a doctor will examine a personâs skin and take their medical history. They will usually ask the person when the mark first appeared, if its appearance has changed, if it is ever painful or itchy, and if it bleeds.
The doctor will also ask about the personâs family history and any other risk factors, such as lifetime sun exposure.
They may also check the rest of the body for other atypical moles and spots. Finally, they may feel the lymph nodes to determine whether or not they are enlarged.
The doctor may then refer a person to a skin doctor, or dermatologist. They may examine the mark with a dermatoscope, which is a handheld magnifying device, and take a small sample of skin, or a biopsy, and send it to a laboratory to check for signs of cancer.
How Does The Penile Cancer Look Like
Commonly penile cancers appear as a lump, mass or ulcer on the penis. The lesions can be raised and wart-like or simply flat. The penile lesions are sore and inflamed, and there is itching and burning in the region as well. Mostly, penile cancers affect the head or foreskin of the penis rather than the shaft of the penis. The appearance of penile cancers varies significantly from a small bump to very large, infected, and aggressive lesions. The cause for such a wide range of presentations delays the diagnosis.
Some men with penile cancer have swollen groin lymph nodes at the time of diagnosis but only a half of these swollen nodes are due to cancer. The swelling in lymph nodes caused by penile cancer lesions is mostly due to infections. With the progression of the disease, the cancer cells form a raised lesion that can sometimes cause parts of the tissue of the penis to die and erode away. Spread of the disease is very uncommon and symptoms in other parts of the body are generally not found.
You May Like: Ductal Carcinoma Survival Rate
Most Common Types Of Skin Cancer
- Basal Cell Carcinoma: This is the first most common type of skin cancer, appearing on the skin as a pinkish patch or a flesh-colored, pearly bump.
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma: This is the second most common type of skin cancer. It may present with a recurring sore that heals and reopens, a scaly patch, or a red bump that is firm to the touch.
- Melanoma: Because of its ability to spread to local lymph nodes, melanoma can be deadly, making early detection and treatment crucial. Melanoma may develop in a pre-existing mole, but it commonly develops as a new dark spot on the skin.
- Merkel Cell Carcinoma: This type of skin cancer is very rare, but individuals with fair skin who are at a higher risk should know that it most often appears on the head or neck as a painless, firm, shiny nodule.
What Does Early Skin Cancer Look Like
It can be challenging to tell if a skin change is unimportant or, in fact, is a sign of developing skin cancer. Skin cancer is not uncommon, as one in five Americans will develop skin cancer before age 70. Learning to spot the warning signs is vital. When identified early, skin cancer is highly curable. Do you know what to look for or when to seek medical advice?
Also Check: Melanoma Stage 4 Treatments
When To See A Dermatologist
Plan an appointment with a dermatologist as soon as possible if you notice any changes to your skin that worry you. Not all skin changes are evidence of cancer. Your dermatologist will evaluate your skin changes to identify the cause and prepare a plan of treatment. Remember, early detection of skin cancer is the key to proper treatment and survival. Almost all skin cancers respond favorably to treatment when detected early enough.
Who Gets Skin Cancer And Why
Sun exposure is the biggest cause of skin cancer. But it doesn’t explain skin cancers that develop on skin not ordinarily exposed to sunlight. Exposure to environmental hazards, radiation treatment, and even heredity may play a role. Although anyone can get skin cancer, the risk is greatest for people who have:
- Fair skin or light-colored eyes
- An abundance of large and irregularly-shaped moles
- A family history of skin cancer
- A history of excessive sun exposure or blistering sunburns
- Lived at high altitudes or with year-round sunshine
- Received radiation treatments
You May Like: What Is Braf Testing In Melanoma
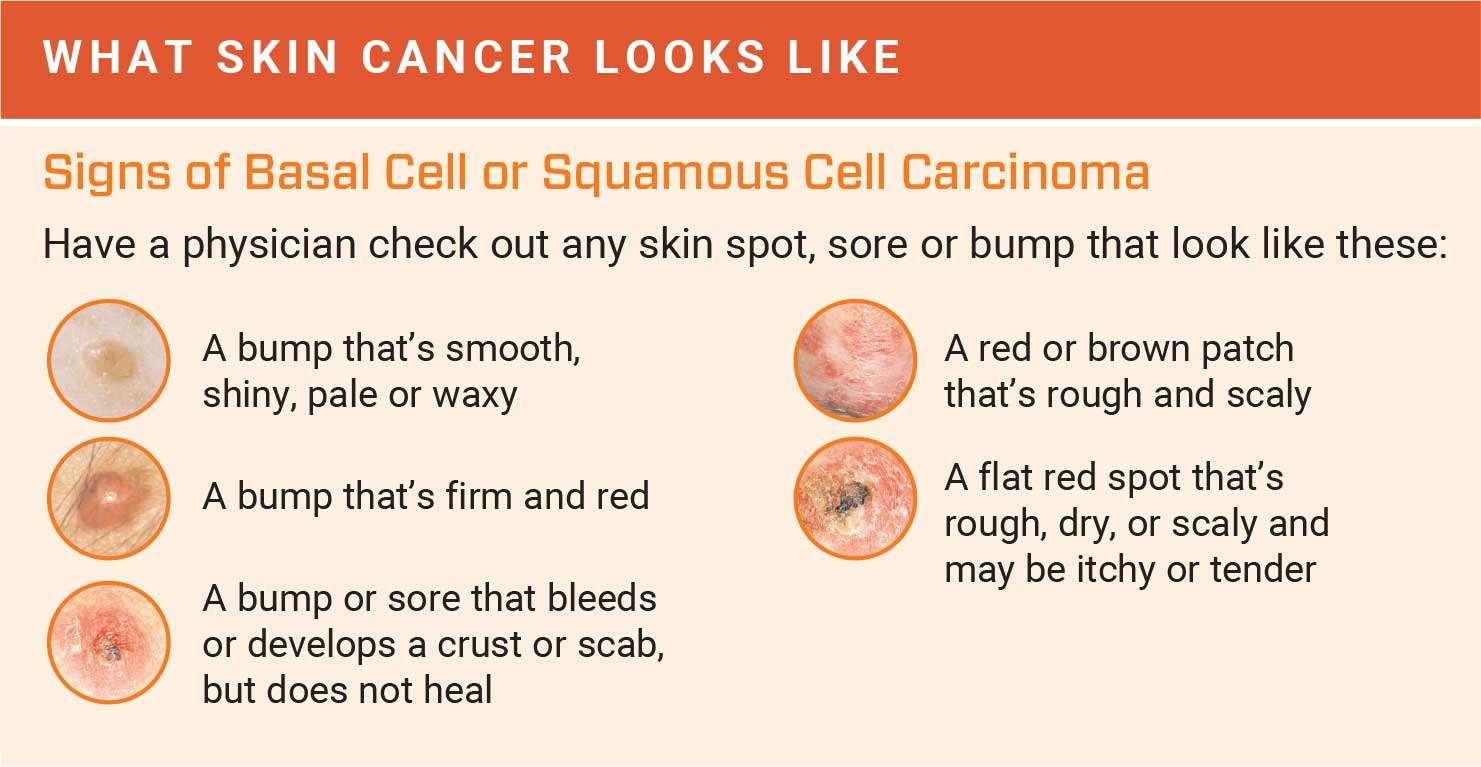
Squamous Cell And Basal Cell Warning Signs
The two most common skin cancers are squamous cell carcinoma and basal cell carcinoma . They both tend to appear on areas of your body that experience a lot of sun exposure. These are the warning signs for a BCC: a pearly or waxy bump flat, flesh-colored or brown scar-like lesion bleeding, oozing or scabbing sore wont go away or heals and returns a small, pink bump with a crusted indentation in the middle a scar-like area that is shiny, white or yellow or waxy and taut. If you have an SCC, you might see these on your skin: a firm, red nodule a raised area with an indentation in the middle a spot that regularly bleeds or crusts and wont heal . SCCs are often surrounded by sun damaged skin that is wrinkled, has loss of elasticity, or has pigment changes.
How To Prevent Melanoma
Most skin cancers, including melanoma are preventable. The following protective measures can help prevent skin cancer:
- Avoiding the sun during the hottest part of the day, which is typically 11 AM to 4 PM.
- Applying sunscreen throughout the year. Sunscreens don’t usually filter out all harmful UV radiation, especially radiation that can lead to melanoma but they are essential in providing overall protection from the sun. A broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30 should be used all year around and reapplied as required. Sunscreen is to be applied on all days including winter and cloudy days. It is advised to apply sunscreen over all exposed skin of the body and face, including the lips and ears. Special sunscreen is needed while swimming in the pools and beaches.
- Wearing protective clothing can provide protection against the sun and harmful UV radiation. Sunglasses are essential to protect the eyes and skin around the eyes, such as the eyelids, against UVB radiation.
- Avoid tanning beds because they emit UV rays that cause skin cancer.
- Consuming sun-sensitizing medications such as certain antibiotics or isotretinoin for acne can increase skin sensitivity to sun.
- Self examination of the skin regularly is important for diagnosis and treatment. Any new skin changes or changes in existing skin growths, patches or moles should be reported to a physician as soon as possible
Read Also: What Happens If You Pick At A Basal Cell Carcinoma