What Does It Mean If My Doctor Asks For A Special Molecular Test To Be Performed On My Specimen
Molecular tests such as Oncotype DX® and MammaPrint® may help predict the prognosis of certain breast cancers, but not all cases need these tests. If one of these tests is done, the results should be discussed with your treating doctor. The results will not affect your diagnosis, but they might affect your treatment.
What If My Report Mentions Margins Or Ink
When an entire tumor is removed, the outside edges of the specimen are coated with ink, sometimes even with different colors of ink on different sides of the specimen. The pathologist looks at slides of the tumor under the microscope to see how close the cancer cells get to the ink . If cancer cells are touching the ink , it can mean that some cancer was left behind, and more surgery or other treatments may be needed. Sometimes, though, the surgeon has already removed more tissue to help make sure that this isnt needed.
Sometimes, all of the invasive cancer is removed, but there may be pre-cancer or another serious condition at or near the margin, such as ductal carcinoma in situ or lobular carcinoma in situ .
If your pathology report shows positive margins, your doctor will talk to you about what treatment is best.
Central Necrosis On Breast Cancer Screening
When a suspicious lesion appears on breast cancer screening then a biopsy may well follow. At this point, the pathologist may well encounter a characteristic central necrosis pattern in the lesion.
The danger however, is that doctors and specialists may underestimate the suspicious lesion and diagnose Ductal Carcinoma In-Situ . However, the lesion may in fact be evidence of a larger, invasive ductal carcinoma with central necrosis.
Infiltrating ductal carcinoma with central necrosis is an uncommon but readily identifiable sub type of breast carcinoma. Furthermore, Invasive Ductal Cancer with Central Necrosis is a highly aggressive breast cancer. Sadly it often has early systemic metastasis and an accelerated clinical course.
Don’t Miss: How Long Does It Take Melanoma To Metastasize
How Is Lobular Breast Cancer Diagnosed
Your doctor will likely order a mammogram and ultrasound to look for abnormal breast tissue. A breast MRI scan is a more sensitive test for detecting breast cancer. Your doctor may order this test if you are at higher risk of breast cancer or if mammogram or ultrasound findings raise concerns that should be investigated further.
If abnormal breast tissue is seen on breast imaging, a small sample of tissue is taken from the area of concern using a needle and examined under a microscope. The results of the biopsy either confirm or rule out a diagnosis of breast cancer.
Breast Cancer Survival Rates Are Affected By Tumor Grade
Breast cancer grade refers to the size and shape of the malignant breast cancer cells. If the breast cancer cells look very different than normal breast tissue cells, and somewhat random in appearance, they are called poorly differentiated and described as high grade.
There are three main breast cancer grades and these are as follows:-
- Grade 1: The cancer cells are well differentiated and look the most like normal cells. These type of cancers tend to be slow-growing.
- Grade 2: These cancer cells are moderately differentiated. This means that the cells look less like normal cells and tend to grow faster.
- Grade 3: Poorly differentiated cells do not appear like normal cells at all and tend to be very fast growing. Hence, the affect on prognosis.
Microscopic Images of Ductal cell carcinoma in Situ Grades 1, 2 and 3
Higher grade breast cancers tend to have a poorer prognosis.
You will be able to find the Grade of your tumor on your pathology report.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Survival Rate For Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
How Does Staging Relate To Types Of Breast Cancer
In addition to cancer stage, doctors will determine the tumor grade and subtype.
Tumors are graded on a scale of 1 to 3, based on how abnormal the cells appear compared to normal cells. The higher the grade, the more aggressive the cancer, meaning that it tends to be growing quickly.
The subtype is important because treatment and outlook will vary depending on which subtype of breast cancer that you have. Subtypes include:
These are different types of invasive ductal carcinoma that can be identified under the microscope.
- Tubular, mucinous, and cribriform carcinomas are âspecial typesâ of well-differentiated cancers that often have a better prognosis than the more common type of invasive ductal carcinoma .
- Micropapillary carcinoma is a type of invasive breast carcinoma that often has a worse prognosis.
If your doctor knows that your tumor is made up of one of these special types of breast cancer, he or she may recommend different treatment.
Since some tumors are made up of more than one type, the entire tumor must be removed in order to know what types your tumor contains. A needle biopsy doesnt give enough information to guide treatment.
Hormonal Therapy For Idc
If the cancer tested positive for hormone receptors, your doctor likely will recommend some form of hormonal therapy. Hormonal therapy, also called anti-estrogen therapy or endocrine therapy, works by lowering the amount of estrogen in the body or blocking the estrogen from signaling breast cancer cells to grow. Because hormonal therapy affects your whole body, its sometimes called a systemic treatment.
In some cases of advanced-stage IDC, hormonal therapy can be given before surgery to help shrink the cancer . Still, it’s more common for hormonal therapy to start after other treatments, such as chemotherapy or radiation therapy, unless these treatments arent needed.
Hormone receptors are special proteins found on the surface of certain cells throughout the body, including breast cells. These receptor proteins are the eyes and ears of the cells, receiving messages from the hormones in the bloodstream and then telling the cells what to do. In other words, the receptors act like an on-off switch for a particular activity in the cell. If the right substance comes along that fits into the receptor like a key fitting into a lock the switch is turned on and a particular activity in the cell begins.
You and your doctor will work together to decide which form of hormonal therapy is best in your situation. Two types of hormonal therapy are most frequently used:
Also Check: Stage 4 Carcinoma
What Are The Treatments For Stage 1 Ductal Breast Cancer
Treatments for Stage 1 Invasive Ductal Breast Cancer. For Stage I cancer patients, radiation is generally not needed if the entire breast is removed. Reconstruction techniques vary and can include implants or using a womans own tissues. The plastic and reconstructive surgeon will help a woman make the most appropriate choice for her.
What If My Report Mentions Her2/neu Or Her2
Some breast cancers have too much of a growth-promoting protein called HER2/neu . The HER2/neu gene instructs the cells to make this protein. Tumors with increased levels of HER2/neu are referred to as HER2-positive.
The cells in HER2-positive breast cancers have too many copies of the HER2/neu gene, resulting in greater than normal amounts of the HER2 protein. These cancers tend to grow and spread more quickly than other breast cancers.
All newly diagnosed breast cancers should be tested for HER2, because women with HER2-positive cancers are much more likely to benefit from treatment with drugs that target the HER2 protein, such as trastuzumab , lapatinib , pertuzumab , and T-DM1 .
Testing of the biopsy or surgery sample is usually done in 1 of 2 ways:
- Immunohistochemistry : In this test, special antibodies that will stick to the HER2 protein are applied to the sample, which cause cells to change color if many copies are present. This color change can be seen under a microscope. The test results are reported as 0, 1+, 2+, or 3+.
- Fluorescent in situ hybridization : This test uses fluorescent pieces of DNA that specifically stick to copies of the HER2/neu gene in cells, which can then be counted under a special microscope.
Many breast cancer specialists think that the FISH test is more accurate than IHC. However, it is more expensive and takes longer to get the results. Often the IHC test is used first:
Read Also: Etiology Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
Concluding Remarks And Future Directions
In this review, we have cited evidence that myoepithelial cells in both mice and human mammary glands originate from a suprabasal cell type within the luminal epithelial compartment within the adult breast. Furthermore, we discuss observations that normal myoepithelial cells are critical for correct polarity of luminal epithelial cells, most likely via production of laminin-1. On the other hand, the myoepithelial cells present in tumors have many traits in common with normal myoepithelial cells, but show either complete absence or reduced expression of laminin-1 and are thus unable to induce the polarization of luminal epithelial cells.
In summary, although much remains to be learned, the role of myoepithelial cells as possible tumor suppressors may include their function as a guardian of ânormalcy,â being a paracrine inhibitor of invasion in early breast cancer as well as a target for differentiation therapy by inducing malignant cancer cells to differentiate along the myoepithelial pathway to a less devastating cell type.
Ductal Carcinoma In Situ
DCIS is the most common type of noninvasive breast cancer, with about 60,000 new cases diagnosed in the United States each year. About one in every five new breast cancer cases is ductal carcinoma in situ.
Also called intraductal carcinoma or stage 0 breast cancer, its considered a noninvasive breast cancer. With DCIS, abnormal and cancerous cells havent spread from the ducts into nearby breast tissue nor anywhere else, such as the lymph nodes.
DCIS is divided into several subtypes, mainly according to the appearance of the tumor. These subtypes include micropapillary, papillary, solid, cribriform and comedo.
Patients with ductal carcinoma in situ are typically at higher risk for seeing their cancer return after treatment, although the chance of a recurrence is less than 30 percent. Most recurrences occur within five to 10 years after the initial diagnosis and may be invasive or noninvasive. DCIS also carries a heightened risk for developing a new breast cancer in the other breast. A recurrence of ductal carcinoma in situ would require additional treatment.
The type of therapy selected may affect the likelihood of recurrence. Treating DCIS with a lumpectomy , and without radiation therapy, carries a 25 percent to 35 percent chance of recurrence. Adding radiation therapy to the treatment decreases this risk to about 15 percent. Currently, the long-term survival rate for women with ductal carcinoma in situ is nearly 100 percent.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Most Aggressive Skin Cancer
What Is The Cause Of Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
The primary cause for a condition like Invasive or Infiltrating Ductal Carcinoma is still not completely clear, but researchers are of the opinion that when the cells present in the milk ducts tend to grow rapidly and uncontrollably, this results in Invasive Ductal Carcinoma. These cells tend to survive longer than their actual span, which results in accumulation of excess cells taking the shape of a tumor of Invasive Ductal Carcinoma.
As the cells continue to grow rapidly, this mass or tumor then spreads to the adjoining structures resulting in malignancy. Why do the cells start growing rapidly is something, which is still a mystery.
However, researchers have been able to identify certain environmental, lifestyle and hormonal factors that makes an individual vulnerable to Invasive or Infiltrating Ductal Carcinoma. These include nicotine abuse, nutritional deficiencies, radiation to treat other forms of cancer around the region of the chest, which can increase the persons risk for Invasive Ductal Carcinoma.
Certain genetic factors have also been identified as a potential cause for Invasive or Infiltrating Ductal Carcinoma like BRCA-1, BRCA-2, and erb-B2 gene, which have shown to increase the risk of Infiltrating Ductal Carcinoma.
Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Treatment
What is invasive ductal carcinoma?
About 268,600 women in the United States will be diagnosed with breast cancer in 2019. The most common form of breast cancer is called invasive ductal carcinoma . Its responsible for about 80 percent of all breast cancer diagnoses.
Carcinoma refers to a type of cancer that begins in the skin cells or the tissues lining your internal organs. Adenocarcinomas are more specific types of carcinomas that originate in the glandular tissue of the body.
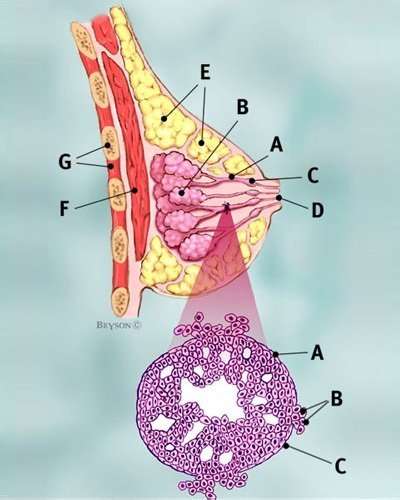
Invasive ductal carcinoma, also known as infiltrating ductal carcinoma, gets its name because it begins in the milk-carrying ducts of the breast, and spreads to surrounding breast tissues. The two most common forms of invasive breast cancer are:
- Invasive ductal carcinoma. Accounts for 80 percent of breast cancer diagnoses. This type begins in and spreads from the milk ducts.
- Invasive lobular carcinoma. Accounts for 10 percent of breast cancer diagnoses. This type begins in the milk-producing lobules.
While IDC can affect women at any age, its most frequently diagnosed in
If you or someone you know has been diagnosed with IDC, rest assured that there are many different forms of treatment available.
The treatments for IDC fall into two main types:
Donât Miss: Does Melanoma Metastasize To The Brain
Recommended Reading: What Does Stage 3b Melanoma Mean
Special Types Of Invasive Breast Cancer
These are less common forms of invasive ductal breast cancer, and all have particular distinguishing features, which are seen under a microscope.
Pagets Disease of the Breast This rare type of breast cancer accounts for approximately 2% of all breast cancers and usually presents with a red, scaly or ulcerated nipple, sometimes accompanied by a burning sensation or discharge. The cancer cells accumulate in the ducts of the nipple but may extend out to the nipple surface. The skin changes sometimes extend to the areola but they first arise on the nipple. Pagets Disease is often initially confused with eczema or other skin conditions. A full-thickness skin biopsy taken from the nipple/areola is usually required for diagnosis.Occasionally the disease is confined solely to the nipple, but the majority of people with Pagets Disease will also have underlying DCIS or, in some cases, an invasive tumour in the breast.
Mucinous carcinoma This is a rare form of invasive ductal cancer in which cancer cells are surrounded by mucin, a principal component of mucous. It accounts for 2-3% of all breast cancers, and tends to occur in women over 60. It is extremely rare in men. It is generally less aggressive and less likely to spread to the lymph nodes than other types.
Micropapillary carcinoma This is an aggressive form of breast cancer with a high rate of lymph node involvement. The cells form in clusters with distinct clear spaces between them.
Mixed tumours
Grading Breast Cancer Cells
Three cancer cell features are studied and each is assigned a score. The scores are then added to get a number between 3 and 9 that is used to get a grade of 1, 2, or 3, which is noted on your pathology report. Sometimes the terms well differentiated, moderately differentiated, and poorly differentiated are used to describe the grade instead of numbers:
- Grade 1or well differentiated . The cells are slower-growing, and look more like normal breast tissue.
- Grade 2 or moderately differentiated . The cells are growing at a speed of and look like cells somewhere between grades 1 and 3.
- Grade 3or poorly differentiated . The cancer cells look very different from normal cells and will probably grow and spread faster.
Our information about pathology reports can help you understand details about your breast cancer.
Also Check: What Is The Latest Treatment For Melanoma
Also Check: Is Melanoma Cancer Curable
Grade 2 Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
HealthTap doctors are based in the U.S., board certified, and available by text or video.
Receptor Status And Triple Negative Breast Cancer
Your pathology report and your healthcare providers may describe your breast cancer as estrogen receptor , progesterone receptor or human epidermal growth factor receptor-2 positive or negative. Or, they may say that your breast cancer is triple negative or triple positive.
Estrogen and progesterone receptors are proteins found in some cancer cells that allow a hormone to attach and feed the cancer cells. Hormone receptor status is reported as positive or negative and sometimes a percent is also provided. For example, 90% estrogen receptor positive. ER/PR+ breast cancers will, at a minimum, receive some form of hormone therapy such as Tamoxifen.
HER2 is a protein involved in normal cell growth, which may also be present on breast cancer cells. If too much of the HER2 protein is produced, the tumor is considered HER2+ . Breast cancers that are HER2+ will receive HER2 directed therapy such as Herceptin.
Triple positive breast cancer is positive for HER2, ER and PR. You will receive HER2 directed therapies as well as hormone therapy.
Triple negative breast cancer is negative for HER2, ER and PR. Therefore, HER2 directed therapy and hormone therapy are not utilized. Typical treatment is chemotherapy.
Related Topics
Read Also: What Are The Early Warning Signs Of Breast Cancer
You May Like: Can You Cure Stage 4 Melanoma
What Is The Staging For Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Staging refers to the extent of a cancer. A cancer is always referred to by the stage it was determined to be at diagnosis, even if it spreads.
Stages of invasive ductal carcinoma include:
- Stage I: Breast tumor is smaller than 2 centimeters in diameter and the cancer has not spread beyond the breast
- Stage II: Breast tumor measures 2 to 4 centimeters in diameter or cancerous cells have spread to the lymph nodes in the underarm area
- Stage III: Cancer is more extensive but it is confined to the breast, surrounding tissues, and lymph nodes
- Stage IV: Breast cancer has spread to lymph nodes beyond the underarm area or to distant sites, such as the lungs, liver, bones, or brain