What Are The Treatment Options For Basaloid Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Treatment options for basaloid squamous cell carcinoma may include a combination of surgical and non-surgical procedures. In most cases, treatment will begin with surgery to remove the tumor. This can sometimes be quite difficult, depending on the location of the tumor. After surgery, doctors usually recommend another type of treatment to kill any remaining cancerous cells. This treatment may include radiation therapy or, in some cases, chemotherapy. Talk to your doctor to determine the best treatment method for you.
How Fast Does Squamous Cell Carcinoma Spread
Squamous cell carcinoma rarely metastasizes , and when spreading does occur, it typically happens slowly. Indeed, most squamous cell carcinoma cases are diagnosed before the cancer has progressed beyond the upper layer of skin. There are various types of squamous cell carcinoma and some tend to spread more quickly than others.
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Basaloid Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of Cervix
Usually, there are no symptoms, during the pre-cancer and early cancer stages . Once, Basaloid Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Cervix has sufficiently progressed and the presence of large-sized tumors is seen, the following set of signs and symptoms may be observed:
- Abnormal vaginal bleeding
- Anemia
- Loss of weight, loss of appetite
During the advanced stages of Basaloid Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Cervix, the following signs and symptoms may be observed:
- Lower back pain
- Frequent urination
- Urinary bladder pain and blood in urine
- The tumor may spread from the cervix to the ureters leading to decreased urine production by the kidneys and increased blood urea levels
- Involvement of the pelvic muscles by tumor cells can cause pain radiating along the leg
- Occasionally, swollen lymph nodes in the groin and lower extremities, may be noted due to tumor metastasis
- If the urinary bladder is involved, then it may obstruct the bladder and lead to retention of urine
- Urinary retention can cause the abnormal formation of a fistula in the urogenital area
- Rectal tenesmus or the urge to keep emptying the bowel, even after it is emptied
Don’t Miss: What Is The Survival Rate For Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
What Are The Symptoms Of Stage 4 Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Symptoms of stage 4 squamous cell carcinoma usually begin with some kind of skin lesion or growth. Often, the tumors of squamous cell carcinoma look like a scaly red patch of skin that wont heal. These tumors are often crusty and raised, and they may cause sores or ulcers that last for several weeks.
What Are The Causes Of Basaloid Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of Cervix
The human papilloma virus infection is a major cause behind the development of Basaloid Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Cervix.
- Under normal circumstances, certain genes called tumor suppressor genes, keep a check on the growth and division of cervical cells
- HPV infection has been found to disrupt some tumor suppressor genes, thus allowing cervical cells to grow and multiply uncontrollably
Almost all cervical cancer types are attributed to human papilloma virus infections around 15 different HPV types have been implicated.
Research has shown that the human papilloma virus causes the development of cervical cancer in the following manner:
- The first step is an individual acquiring HPV infection: High-risk individuals are those with multiple sexual partners, or sex with high-risk or highly promiscuous men
- The next step is the persistence of HPV infection and formation of premalignant lesions. This may take a long period of time
- The final step is the development of cancer from the premalignant stage: The time period of development from premalignancy to malignancy is variable, but can be very slow and may take many decades
Recommended Reading: Merkel Cell Carcinoma Immunotherapy
What Is Basosquamous Carcinoma
4.5/5Basosquamous carcinomacell carcinomacell carcinoma
Then, what is Basaloid squamous cell carcinoma?
Oncology. Basaloid squamous cell carcinoma is an uncommon histological variant of lung cancer composed of cells exhibiting cytological and tissue architectural features of both squamous cell lung carcinoma and basal cell carcinoma.
Additionally, what is Merkel cell carcinoma? Merkel cell carcinoma is a rare type of skin cancer that usually appears as a flesh-colored or bluish-red nodule, often on your face, head or neck. Merkel cell carcinoma is also called neuroendocrine carcinoma of the skin. Merkel cell carcinoma most often develops in older people.
Then, what is Metatypical basal cell carcinoma?
Basosquamous carcinoma, also known as metatypical carcinoma , is a non-melanoma skin cancer that shares the features of both the squamous and basal cell carcinomas. This high incidence of positive-surgical margins for excised BCC may be caused by the irregular infiltration of these tumours.
What is Mohs surgery for skin cancer?
Doctors use Mohs surgery to treat skin cancer. The goal is to remove as much of it as possible while saving the healthy tissue around it. Layers of skin are removed one at a time and examined under a microscope until all the cancer is gone.
What Are The Risk Factors For Keratinizing Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of Lung
The following factors have been identified as increasing the risk for Keratinizing Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Lung:
- Smoking: Smoking cigarettes, cigars, or pipes, increase the risk due to damaging chemicals being inhaled into the lungs. Prolonged smoking damages the lung, resulting in reduced clearance of the chemical carcinogens that accumulate in the lungs. The factors related to smoking that impact the development of squamous cell carcinoma include:
- Duration of smoking
- Quality of cigarette
- Even, fraction of the cigarette that is smoked
In general, physicians believe that certain factors may increase an individuals risk for lung cancers and these include:
It is important to note that having a risk factor does not mean that one will get the condition. A risk factor increases ones chances of getting a condition compared to an individual without the risk factors. Some risk factors are more important than others.
Also, not having a risk factor does not mean that an individual will not get the condition. It is always important to discuss the effect of risk factors with your healthcare provider.
Recommended Reading: Skin Cancer Pictures Mayo Clinic
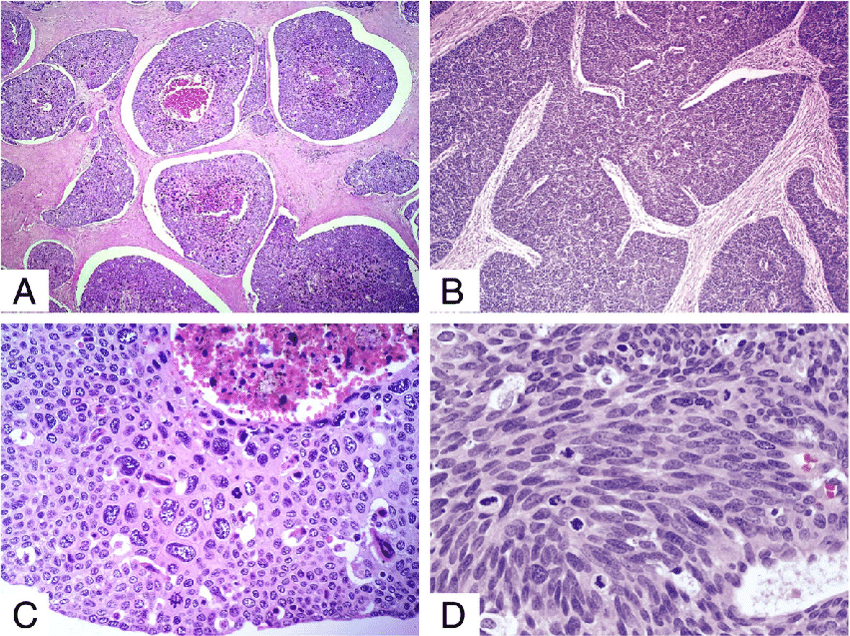
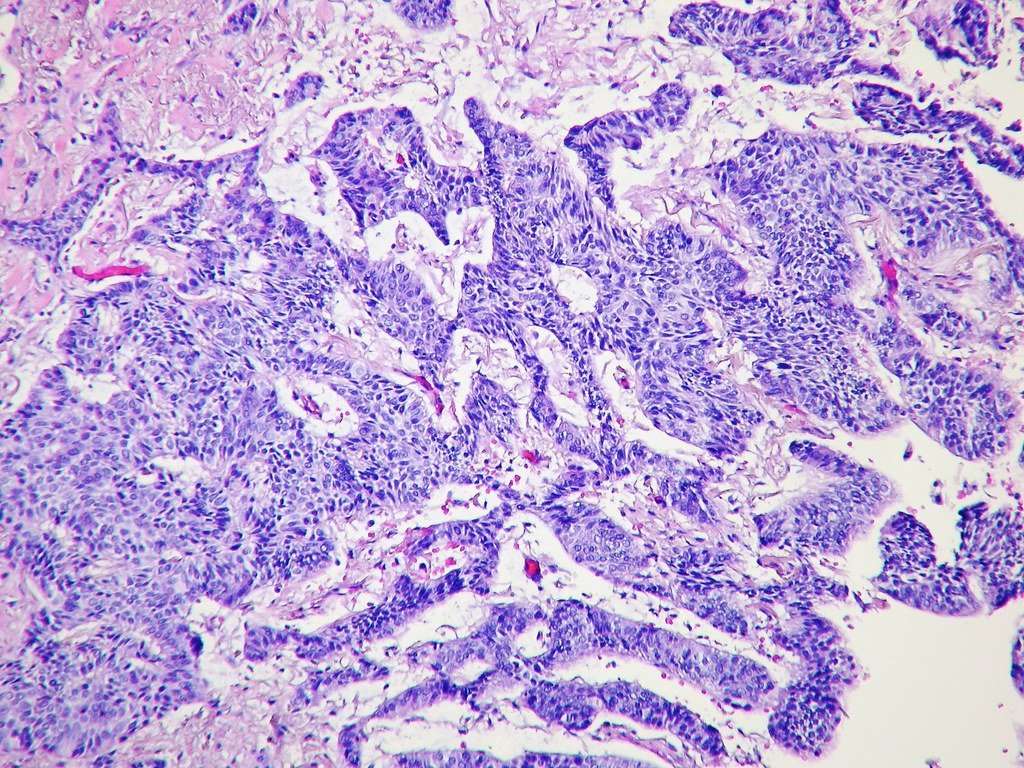
What Is Basaloid Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Basaloid squamous cell carcinoma, or BSCC, is a rare cancer most often found in the upper digestive and respiratory tracts. These types of carcinomas may develop in either gender at any age, but the condition seems more predominant in males around the age of 60. Once properly diagnosed, oncologists generally prefer aggressive forms of carcinoma treatment, as basaloid squamous cell carcinoma produces rapid abnormal cell growth.
The tongue is frequently the site where basaloid squamous cell carcinoma develops, but tumors can form anywhere within the mouth and esophagus. Oncologists have also noted BSCC formation on the nose and in the sinus passages. The cancer quickly spreads to the cervical lymph nodes in 64 percent of cases, and almost half of diagnosed patients experience metastasis to other body locations including the lungs, liver, and genitourinary system. Individuals usually do not notice the growing mass until it reaches an advanced size, measuring anywhere from one to six centimeters, and causes discomfort or obstruction.
What Is The Prognosis Of Basaloid Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of Vulva
Recommended Reading: How Long Does It Take For Melanoma To Spread To Organs
Treating Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Most of squamous cell carcinomas can be cured if they are treated early. Once squamous cell carcinoma has spread beyond the skin, though, less than half of people live five years, even with aggressive treatment.
There are many ways to treat squamous cell carcinoma that has not spread. These include:
- cutting away the cancer and a small amount of healthy tissue around it. If a large area of skin is removed, a skin graft may be necessary.
- scraping away the cancer with a surgical tool. An electric probe is used to kill any cancerous cells left behind.
- freezing cancer cells with liquid nitrogen. This treatment is usually used only for very small tumors or for a patch of skin that looks abnormal but isnât yet cancerous.
- destroying the tumor with radiation.
- shaving away the cancer, one thin layer at a time. Each layer is examined under the microscope as it is removed. This technique helps the doctor preserve as much healthy skin as possible.
- applying drugs directly to the skin or injecting them into the tumor
- using a narrow laser beam to destroy the cancer.
The treatment that is best for you depends on the size and location of the cancer, whether it has returned after previous treatment, your age, and your general health.
Once your treatment is finished, itâs important to have regular follow-up skin exams. Your doctor may want to see you every three months for the first year, for example, and then less often after that.
How Can Basaloid Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of Cervix Be Prevented
Some steps for the prevention of Basaloid Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Cervix include:
- Use of measures to prevent sexually-transmitted infections, such as usage of condoms, avoiding multiple sexual partners, and circumcision in men
- Avoidance of smoking
- Regular screening to detect pre-cancers:
- The American Cancer Society recommends screening of women from age 21 years
- A Pap smear is recommended every 3 years, from ages 21-29 years
- From age 30-65 years, a Pap smear and HPV testing is recommended, once every 5 years
- More frequent screenings are advised for women having a high-risk for cervical cancer
Recommended Reading: Invasive Breast Cancer Prognosis
How Is Basaloid Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of Cervix Diagnosed
- In order to make a diagnosis of Basaloid Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Cervix, a detailed history followed by a physical and pelvic exam is undertaken
- Pelvic examination:
- During a pelvic examination, the healthcare provider will exam the uterus, cervix, vagina, ovaries, fallopian tubes, bladder, and rectum to check for any abnormal changes in these organs
- Also, during the exam, the tumor may appear as a polyp , or it may appear as a firm, non-polyp area
- Small tumors that may arise in the cervical canal area may be difficult to visualize. Hence, a careful exam in a high-risk individual is recommended
Blood tests to aid in the diagnostic process may include:
- Complete blood count with differential of white blood cells
- Liver function test and kidney function test
- Blood tests called serum tumor markers that include:
- CA-125 test
Some of the definitive tests that help in diagnosing the cancer include:
Colposcopy:
Cervical biopsy: Biopsy is the process of removing tissue for examination. A pathologist looks at the tissue sample under a microscope, to detect any evidence of cancer. Types of cervical biopsies include:
Two methods can be used to obtain a cone biopsy specimen:
Electronic Skin Surface Brachytherapy
Some skin cancers that do not require very deep radiation may be treated with a new form of radiation therapy applied directly to the skin, called electronic skin surface brachytherapy .
In ESSB, we apply smooth, round disks to the skin these disks are attached to a radiation therapy machine. They are left in place for just a few minutes while the radiation is delivered, allowing the tumor to be treated. The approach spares underlying healthy skin from the effects of the radiation.
Also Check: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Breast Cancer Survival Rates
Basaloid Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of The Ethmoid Sinus With Invasion Into The Skull Base Treated With Craniofacial Resection And Adjuvant Intensity
December 21, 2015
DOI:10.7759/cureus.421
Cite this article as:Al Feghali K A, Traboulsi H, Youssef B Basaloid Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Ethmoid Sinus with Invasion into the Skull Base Treated with Craniofacial Resection and Adjuvant Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy: A Case Report. Cureus 7: e421. doi:10.7759/cureus.421
What Are The Risk Factors For Basaloid Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of Cervix
The following factors increase the risk of Basaloid Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Cervix:
- Infection with human papilloma virus types: It is considered to be a significant risk factor for this tumor type
- Lack of periodic/regular Pap smear tests
- Sexual promiscuity and high-risk sexual behavior
- Poor immune system: HIV infection or AIDS, organ transplantation, immunosuppressant medications, greatly increase risk for chronic infection
- Smoking
- Use of oral contraceptives for long time duration
- Having the first child at a young age and having had multiple pregnancies
- Presence of other sexually transmitted infections
- Chronic inflammation, in some cases
- Family history of cervical cancer: This is a relatively low strength risk factor
- A diet lacking fruits and vegetables
- Poverty or poor socio-economic status
It is important to note that having a risk factor does not mean that one will get the condition. A risk factor increases ones chances of getting a condition compared to an individual without the risk factors. Some risk factors are more important than others.
Also, not having a risk factor does not mean that an individual will not get the condition. It is always important to discuss the effect of risk factors with your healthcare provider.
Also Check: Stage 3 Melanoma Survival Rate
How Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of Tongue Diagnosed
A diagnosis of Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Tongue is made by:
- Complete physical examination with detailed medical history evaluation
- Examination by a dermatologist using a dermoscopy, a special device to examine the skin
- Woodâs lamp examination: In this procedure, the healthcare provider examines the skin using ultraviolet light. It is performed to examine the change in skin pigmentation
Although the above modalities can be used to make an initial diagnosis, a tissue biopsy of the tumor is necessary to make a definitive diagnosis to begin treatment.
Tissue biopsy: A portion of the tongue tumor is removed for biopsy.
- A tissue biopsy of the tumor is performed and sent to a laboratory for a pathological examination. A pathologist examines the biopsy under a microscope. After putting together clinical findings, special studies on tissues and with microscope findings, the pathologist arrives at a definitive diagnosis. Examination of the biopsy under a microscope by a pathologist is considered to be gold standard in arriving at a conclusive diagnosis
- Biopsy specimens are studied initially using Hematoxylin and Eosin staining. The pathologist then decides on additional studies depending on the clinical situation
- Sometimes, the pathologist may perform special studies, which may include immunohistochemical stains, molecular testing, and very rarely, electron microscopic studies to assist in the diagnosis
The Risks The Causes What You Can Do
Squamous cell carcinoma of the skin is caused by DNA damage that leads to abnormal changes in the squamous cells in the outermost layer of skin.
Understanding what causes this damage and the factors that increase your risk of developing SCC can help you detect the disease early or prevent it from happening in the first place.
These factors increase your SCC risk:
- Unprotected exposure to ultraviolet radiation from the sun or tanning beds.
- Weakened immune system due to illness or certain immunosuppressive medications.
Recommended Reading: Treatment For Stage 3 Melanoma
Don’t Miss: Large Cell Carcinoma Definition
Continue Learning About Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Important: This content reflects information from various individuals and organizations and may offer alternative or opposing points of view. It should not be used for medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. As always, you should consult with your healthcare provider about your specific health needs.
Aggressiveness Pattern And Second Primary Tumor Risk Associated With Basaloid Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of The Larynx
Metrics: PDF 938 views | HTML 2056 views | ?
Filippo Ricciardiello, Michele Caraglia , Brigida Iorio, Teresa Abate, Mariarosaria Boccellino, Giuseppe Colella, Flavia Oliva, Pierpaolo Ferrise, Silvia Zappavigna, Mario Faenza, Giuseppe A. Ferraro, Giulio Sequino, Giovanni Francesco Nicoletti and Massimo Mesolella
Recommended Reading: Malignant Breast Cancer Survival Rate
How Is Basaloid Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of Vulva Treated
Once a diagnosis of vulvar cancer has been made, the extent to which the tumor has spread is assessed, known as staging. The staging for vulvar cancer is based upon the FIGO and the AJCC TNM staging systems.
The TNM classification for vulvar cancer is given below:
Tumor extent :
- Tis: The cancer is not growing into the underlying tissues. This stage, also known as carcinoma in situ, is not included in the FIGO system
- T1: The cancer is growing only in the vulva or perineum
- T1a: The cancer has grown no more than 1 mm into underlying tissue and is 2 cm or smaller in size
- T1b: The cancer is either more than 2 cm or it has grown more than 1 mm into underlying tissue
Lymph node spread of cancer :
- N0: No lymph node spread
- N1: The cancer has spread to 1 or 2 lymph nodes in the groin with the following features:
- N1a: The cancer has spread to 1 or 2 lymph nodes and the areas of cancer spread are both less than 5 mm in size
- N1b: The cancer has spread to one lymph node and the area of cancer spread is 5 mm or greater
Distant spread of cancer
Stage 0 :
Stage I :
Stage II :
Stage IIIA :