The Differences Between Basal Cell And Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Although basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinomas are the two most common types of skin cancer in the United States, theyre also highly treatable.
BCC and SCC are part of the carcinomas group, which are cancerous tumors characterized by a slower development in the upper layers of the skin. These cancers are also known as non-melanoma, meaning they occur in the epithelial tissue, and theyre far less aggressive than melanoma, a rare yet very aggressive form of skin cancer.
As advocates of prevention, we want you to be informed about the most common types of skin cancer. To help you out, we asked our expert, Dr. Gail Zimmerman, all about them. Read on to learn how BCC is different from SCC, and find out how these skin cancers are diagnosed.
What Is A Squamous Cell
One of three main types of cells in the top layer of the skin , squamous cells are flat cells located near the surface of the skin that shed continuously as new ones form.
SCC occurs when DNA damage from exposure to ultraviolet radiation or other damaging agents trigger abnormal changes in the squamous cells.
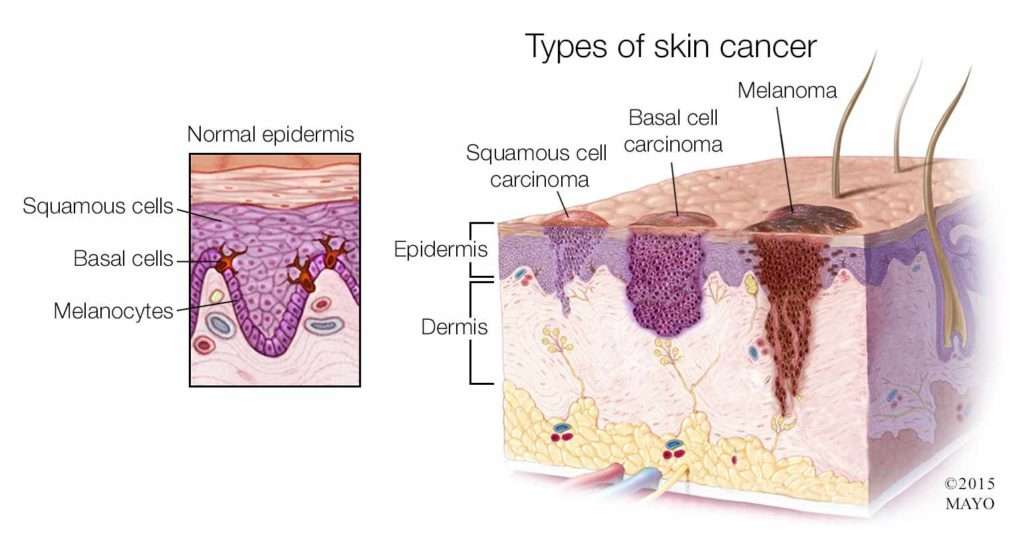
Basal Cell And Squamous Cell Carcinoma
The two most common kinds of skin cancer are basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma, which are sometimes called nonmelanoma skin cancer. These cancers are carcinomas that begin in the cells that cover or line an organ.
Basal cell carcinoma accounts for more than 90 percent of all skin cancers in the United States and is the most common of all cancers. Typically, it is a slow-growing cancer that seldom spreads to other parts of the body.
Squamous cell carcinoma also rarely spreads, but does so more often than basal cell carcinoma. It is important that skin cancers are found and treated early because they can invade and destroy nearby tissue. Organ transplant recipients have a 65-fold higher risk of developing squamous cell carcinoma than others. UCSF Medical Center offers a High Risk Skin Cancer Clinic for those at high risk for non-melanoma skin cancers, such as transplant recipients.
You May Like: Stage 3 Melanoma Life Expectancy
From The Harvard Health Letter May 2006
Summers the season for fun in the sunbut also for skin cancer. Of the three main types of skin cancer, melanoma is most deadly, and basal cell, most common. Squamous cell cancer falls in between. Its three times as common as melanoma . Though not as common as basal cell , squamous cell is more serious because it is likely to spread . Treated early, the cure rate is over 90%, but metastases occur in 1%5% of cases. After it has metastasized, its very difficult to treat.
Read Also: Stage 3 Lobular Breast Cancer
Melanoma: The Deadliest Skin Cancer
Melanoma is the most serious type of skin cancer, because it tends to spread if its not treated early.
This cancer starts in the melanocytes cells in the epidermis that make pigment.
About 100,350 new melanomas are diagnosed each year.
Risk factors for melanoma include:
- Having fair skin, light eyes, freckles, or red or blond hair
- Having a history of blistering sunburns
- Being exposed to sunlight or tanning beds
- Living closer to the equator or at a higher elevation
- Having a family history of melanoma
- Having many moles or unusual-looking moles
- Having a weakened immune system
Melanoma can develop within a mole that you already have, or it can pop up as a new dark spot on your skin.
This cancer can form anywhere on your body, but it most often affects areas that have had sun exposure, such as the back, legs, arms, and face. Melanomas can also develop on the soles of your feet, palms of your hands, or fingernail beds.
Signs to watch out for include:
- A mole that changes in color, size, or how it feels
- A mole that bleeds
Dont Miss: Infiltrating Ductal Carcinoma Survival Rate
You May Like: How Long Does It Take For Melanoma To Spread To Organs
Basal Cell Skin Cancer
BCC is the most common type of skin cancer. About 75 out of every 100 non melanoma skin cancers are BCCs. They develop from basal cells and these are found in the deepest part of the outer layer of the skin .
They develop mostly in areas of skin exposed to the sun, including parts of the face such as the nose, forehead and cheeks. Also, on your back or lower legs.
They are most often diagnosed in people who are middle aged or older.
Doctors might also call a basal cell cancer a rodent ulcer.
There are a number of different types of BCC. Each type can look and behave differently. They include:
- nodular basal cell skin cancer
- superficial basal cell skin cancer
- morphoeic basal cell skin cancer – also known as sclerosing or infiltrating basal cell skin cancer
- pigmented basal cell skin cancer
Nodular basal cell cancer is the most common subtype.
It’s very rare for basal cell skin cancer to spread to another part of the body to form a secondary cancer. It’s possible to have more than one basal cell cancer at any one time and having had one does increase your risk of getting another.
The Difference Between Basal Cell Carcinoma And Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma are the two most common types of skin cancers. According to the American Cancer Society, over 5 million cases of basal cell and squamous cell cancers are diagnosed every year. Though, basal cell carcinoma occurs more often, taking credit for about 80% of these cases. Other than the disparities in occurrence, what is the difference between basal cell and squamous cell carcinomas? You may also be wondering is squamous cell worse than basal cell, or vice versa. Here is some insight.
You May Like: Malignant Breast Cancer Survival Rate
Symptoms Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
A change in the skin might be the first sign of the presence of basal cancer cells. The changes may include a bump or sore that wont heal. The following can be a few symptoms of the disease:
- A translucent skin-colored bump: The bump can be either white or pink on fair skin, while the bump generally looks brown or shiny black on dark skin. You also might be able to see blood vessels. Sometimes, the bump may bleed.
- Lesions: A brown, black, or blue lesion can appear with a slightly raised translucent border.
- Flat and scaly spots: Such patches can be seen with raised edges. Also, they can grow quite large over a period of time.
- Scar-like lesion: A whitish scar-like lesion without any proper border can also be an essential sign of basal cell carcinoma.
Where Do Skin Cancers Start
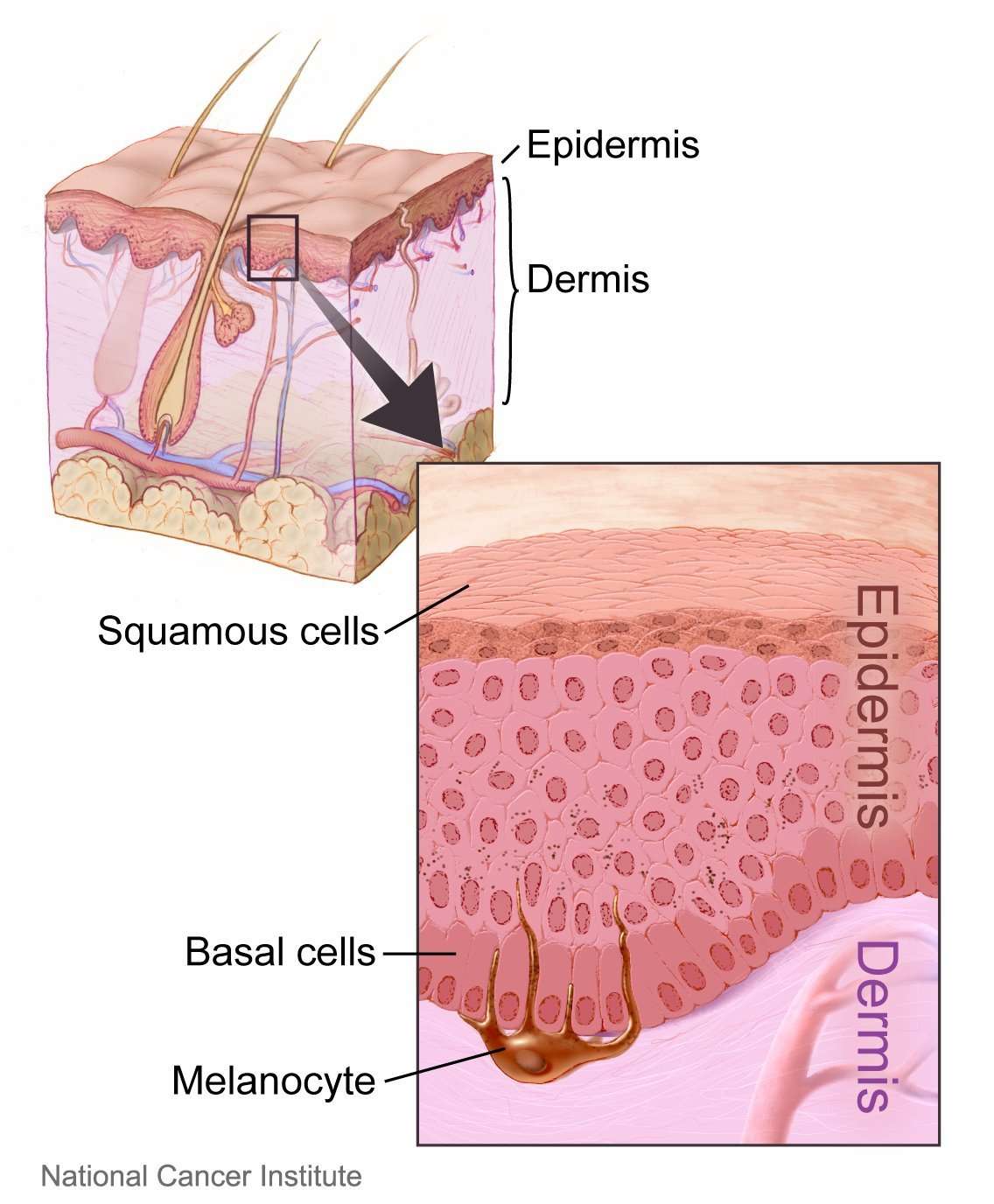
Most skin cancers start in the top layer of skin, called the epidermis. There are 3 main types of cells in this layer:
- Squamous cells: These are flat cells in the upper part of the epidermis, which are constantly shed as new ones form. When these cells grow out of control, they can develop into squamous cell skin cancer .
- Basal cells: These cells are in the lower part of the epidermis, called the basal cell layer. These cells constantly divide to form new cells to replace the squamous cells that wear off the skins surface. As these cells move up in the epidermis, they get flatter, eventually becoming squamous cells. Skin cancers that start in the basal cell layer are called basal cell skin cancers or basal cell carcinomas.
- Melanocytes: These cells make the brown pigment called melanin, which gives the skin its tan or brown color. Melanin acts as the bodys natural sunscreen, protecting the deeper layers of the skin from some of the harmful effects of the sun. Melanoma skin cancer starts in these cells.
The epidermis is separated from the deeper layers of skin by the basement membrane. When a skin cancer becomes more advanced, it generally grows through this barrier and into the deeper layers.
Read Also: Stage 3 Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Survival Rate
What Is The Difference Between Basal Cell And Squamous Cell Carcinoma And Melanoma
Melanoma typically begins as a mole and can occur anywhere on the body. Squamous cell carcinoma may appear as a firm red bump, a scaly patch, or open sore, or a wart that may crust or bleed easily. Basal cell carcinoma may appear as a small white or flesh-colored bump that grows slowly and may bleed.
Can squamous turn into melanoma? Squamous cell cancer falls in between. Its three times as common as melanoma . Though not as common as basal cell , squamous cell is more serious because it is likely to spread .
Different Kinds Of Skin Cancer
There are many types of skin cancer. Some are very rare. Your doctor can tell you more about the type you have.
The two most common kinds of skin cancers are:
- Basal cell cancer, which starts in the lowest layer of the skin
- Squamous cell cancer, which starts in the top layer of the skin
Another kind of skin cancer is called melanoma. These cancers start from the color-making cells of the skin . You can read about melanoma in If You Have Melanoma Skin Cancer.
Read Also: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Stage 3 Survival Rate
What Is Skin Cancer
Cancer can start any place in the body. Skin cancer starts when cells in the skin grow out of control.
Skin cancer cells can sometimes spread to other parts of the body, but this is not common. When cancer cells do this, its called metastasis. To doctors, the cancer cells in the new place look just like the ones from the skin.
Cancer is always named based on the place where it starts. So if skin cancer spreads to another part of the body, its still called skin cancer.
The skin
You May Like: Well Differentiated
Actinic Keratoses And Squamous Cell Carcinoma Can Look Similar In Fact An Actinic Keratosis Can Turn Into A Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Some doctors even believe they are one and the same, just at different points along the continuum.
Squamous cell carcinoma is the second-most common skin cancer. About 3,500 people in the U.S. die from it every year.
This skin malignancy grows slowly, but the deadliness lies in the delayed diagnosis.
The delay means that five percent of squamous cell carcinoma spreads, and this is what makes it lethal. As it grows locally, the destruction can become quite gruesome.
Don’t Miss: Skin Cancer 1st Stage
Radiation And Immunologic Origins
Radiation has proven to be tumorigenic by two mechanisms. The first entails the initiations of prolonged cellular proliferation, thereby increasing the likelihood of transcription errors that can lead to cellular transformation. The second mechanism is direct damage of DNA replication, leading to cellular mutation that may activate proto-oncogenes or deactivate tumor suppressor genes.
Immunologically, the mechanism by which prolonged ultraviolet radiation exposure leads to the development of BCC includes suppression of the cutaneous immune system and immunologic unresponsiveness to cutaneous tumors. This local effect includes a decrease in Langerhans cells, dendritic epidermal T cells, and Thy1+ cells. Furthermore, systemic proliferation of suppressor T cells and the release of immunosuppressive factors are believed to be pathogenic to the development of BCC.
Knowing Signs Of Basal Cell And Squamous Cell Cancer
Most people have been warned about the dangers of another form of skin cancer called melanoma. This type of cancer is caused by another skin cell in the epidermis, the melanocyte. They know to check themselves for the unusual moles that are its telltale sign.
Basal cell cancers and squamous cell cancers can be more difficult to spot. The signs may just seem like irritated skin or a dry patch. However, the best results for treatment happen when skin cancers are caught before they break through the basement membrane and into lower levels of the skin and bone, so it is important to catch them early. These are two things to look out for.
Also Check: Invasive Breast Cancer Survival Rate
Knowing The Difference Between Squamous Cell Skin Cancer And Basal Cell Skin Cancer
Understanding the type of skin cancer you have been diagnosed with will help you to ask the right questions to understand your treatment options. The difference between two of the most common types of skin cancerbasal cell and squamous cellwill be described here. We will not cover melanoma, which is another type of skin cancer.
The skin is divided into three layers, with many cells and tissues in each layer. The outermost layer is called the epidermis. The epidermis works hard to protect the body against things found in our environment, like chemicals and UV rays.
Basal and squamous cells are found within the epidermis. Cancer happens when those healthy cells grow out of control. To know if there are cancer cells, a small piece of the skin will be removed and looked at under a microscope. This is called a biopsy. The type of cancer the person has is named after the cells where the cancer is found.
Basal Cell Vs Squamous Cell Carcinoma
The difference between Basal Cell and Squamous Cell Carcinoma is that Basal Cell is more dangerous than squamous cell carcinoma. The basal cell carcinoma is found in the epidermis layer of the lower part of the skin, while the squamous cell carcinoma is found in the upper part of the uppermost layer.
Basal cell carcinoma is one type of dermis cancer that can affect the body when it meets harmful sun rays. This cell does not affect the internal organs but can target bones if not diagnosed and treated on time. Otherwise, it poses the least amount of risk to the human body.
Squamous cell carcinoma is also a dermis cancer that develops when ultraviolet rays fall on the human skin. This aberrant cell can affect the lips, back, and ear, despite its modest growth rate. It can target human lymph nodes and bones, and tumors of this cell begin as a harmless lump on the body.
You May Like: Large Cell Cancer Of The Lung
Can Squamous Cell Carcinoma Be Prevented
The best way to prevent SCC is to avoid sunburn. Avoid going outin the sun when the UV Index is higher than 3, such as in the middle of theday. Seek shade, wear a hat, sunglasses and clothing that protects you from thesun, and always use an SPF30+ sunscreen. Do not go to tanningsalons.
If you are at very high risk of developing another skin cancer, yourdoctor may prescribe you specific vitamins.
You May Like: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Survival
Early Detection Is The Key
The sooner skin cancer is detected, the better the chance for successful treatment. The goal of any skin cancer treatment is to remove the cancerous area before it can spread deeper into the body. If you see any unusual patches on your skin, be sure to call Dr. Bairds office for an appointment right away. You can schedule a skin cancer screening in Farmington by calling or filling out our online form.
Read Also: Skin Cancer Pictures Mayo Clinic
Incidence Of Melanoma Of The Ear
Squamous cell carcinoma and basal cell carcinomas of the pinna of the ear are more common than melanomas, but this patient had a melanoma. The patient showed classic nodal drainage for ear cancers into the parotid lymph nodes . The median age at diagnosis of pinna cancer is in the 70s. Recurrences are more common with squamous cell carcinomas than with basal cell carcinomas. Of the cancers treated with radiation therapy, those in which tumor size exceeded 2cm, those with higher T stage, those with cartilage necrosis, recurrent lesions, those with a field size exceeding 6cm2, and those for which treatment time was longer had an increased rate of local treatment failure.
Yaohui G. Xu, Gary S. Wood, in, 2020
Choosing To Stop Treatment Or Choosing No Treatment At All
For some people, when treatments have been tried and are no longer controlling the cancer, it could be time to weigh the benefits and risks of continuing to try new treatments. Whether or not you continue treatment, there are still things you can do to help maintain or improve your quality of life.
Some people, especially if the cancer is advanced, might not want to be treated at all. There are many reasons you might decide not to get cancer treatment, but its important to talk to your doctors and you make that decision. Remember that even if you choose not to treat the cancer, you can still get supportive care to help with pain or other symptoms.
You May Like: Chances Of Squamous Cell Carcinoma Spreading
Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Common In Sun
Squamous cell carcinoma, also called squamous cell cancer, is the second most common type of skin cancer. It accounts for about 20 percent of cases.
This type of cancer starts in flat cells in the outer part of the epidermis. It commonly crops up on sun-exposed areas, such as the face, ears, neck, lips, and hands. It can also develop on scars or chronic sores.
Squamous cell carcinomas may develop from precancerous skin spots, known as actinic keratosis .
These cancers might look like:
- A firm, red bump
- A flat lesion with a scaly, crusted surface
- A sore that heals and then reopens
People with lighter skin are more at risk for developing squamous cell carcinoma, but the skin cancer can also affect those with darker skin.
Other risk factors include:
- Having light eyes, blond or red hair, or freckles
- Being exposed to the sun or tanning beds
- Having a history of skin cancer
- Having a history of sunburns
- Having a weakened immune system
- Having the genetic disorder xeroderma pigmentosum
RELATED: 10 Things You May Know Cause Skin Cancer