Treatment Options Skin Cancer Surgery & Other Options
Mole removal is an important part of early skin cancer treatment and there are several methods for removing moles. The less invasive ones are radiofrequency mole removal and cryotherapy mole removal. In the former, concentrated radiofrequencies are used to shave off raised unharmful moles. Cryotherapy involves freezing off moles. There are also forms of skin cancer surgery such as excision, punch excision and shaving.
The Most Common Form Of Cancer
One in five people over the course of a lifetime and over one million people each year are diagnosed with skin cancer, making it the most common form of cancer in the United States.
Skin cancer refers to the abnormal, uncontrolled growth of skin cells. The most common skin cancers are basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma. A rarer but more dangerous skin cancer is melanoma, the leading cause of death from skin disease.
What Does Skin Cancer Look Like
Basal cell carcinoma
-
BCC frequently develops in people who have fair skin. People who have skin of color also get this skin cancer.
-
BCCs often look like a flesh-colored round growth, pearl-like bump, or a pinkish patch of skin.
-
BCCs usually develop after years of frequent sun exposure or indoor tanning.
-
BCCs are common on the head, neck, and arms however, they can form anywhere on the body, including the chest, abdomen, and legs.
-
Early diagnosis and treatment for BCC are important. BCC can grow deep. Allowed to grow, it can penetrate the nerves and bones, causing damage and disfigurement.
Squamous cell carcinoma of the skin
-
People who have light skin are most likely to develop SCC. This skin cancer also develops in people who have darker skin.
-
SCC often looks like a red firm bump, scaly patch, or a sore that heals and then re-opens.
-
SCC tends to form on skin that gets frequent sun exposure, such as the rim of the ear, face, neck, arms, chest, and back.
-
SCC can grow deep into the skin, causing damage and disfigurement.
-
Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent SCC from growing deep and spreading to other areas of the body.
SCC can develop from a precancerous skin growth
-
People who get AKs usually have fair skin.
-
AKs usually form on the skin that gets lots of sun exposure, such as the head, neck, hands, and forearms.
-
Because an AK can turn into a type of skin cancer, treatment is important.
Melanoma
You May Like: Clear Cell Carcinoma Symptoms
The Incidence Of Melanoma Among Canadians Has Been On The Rise Heres What You Need To Know
When Karen Jokinen of Peterborough, ON, first noticed a small black spot like a smudge from a marker on the back of her heel, she was only mildly curious. After all, the mark was tiny, and when youre over 50, age spots and skin tags do start to appear.
Since the mark wasnt visible unless she looked for it and didnt hurt or itch, Jokinen mostly forgot about it. It wasnt until about five months had passed that she turned to the Internet to help her decide whether to see her doctor about the spotand a small blemish on her nose that stubbornly refused to heal.
I dont usually google anything medical, but I searched black spot on heel of foot or something similar, Jokinen says, and the results told me it was either nothing or melanoma.
Although rates have risen more quickly in younger women, about half of melanomas are diagnosed in people over 50, and the incidence increases with age, especially in men past the half-century mark. While more women than men are diagnosed with melanoma before age 50, by 65, rates are twice as high in men, and at 80 and up, three times higher.
Before we cover what to look for, however, well explore how melanoma arises and the factors that are linked with increased risk.
Risk Factors
Like other cancers, melanoma is caused by mutations, or misprints, in the DNA of cellsin this case, the skins pigment cells, or melanocytes.
The Signs
The ABCs of Melanoma
A: Asymmetry: one side may be different from the other.
Which Type Of Skin Cancer Is The Most Serious
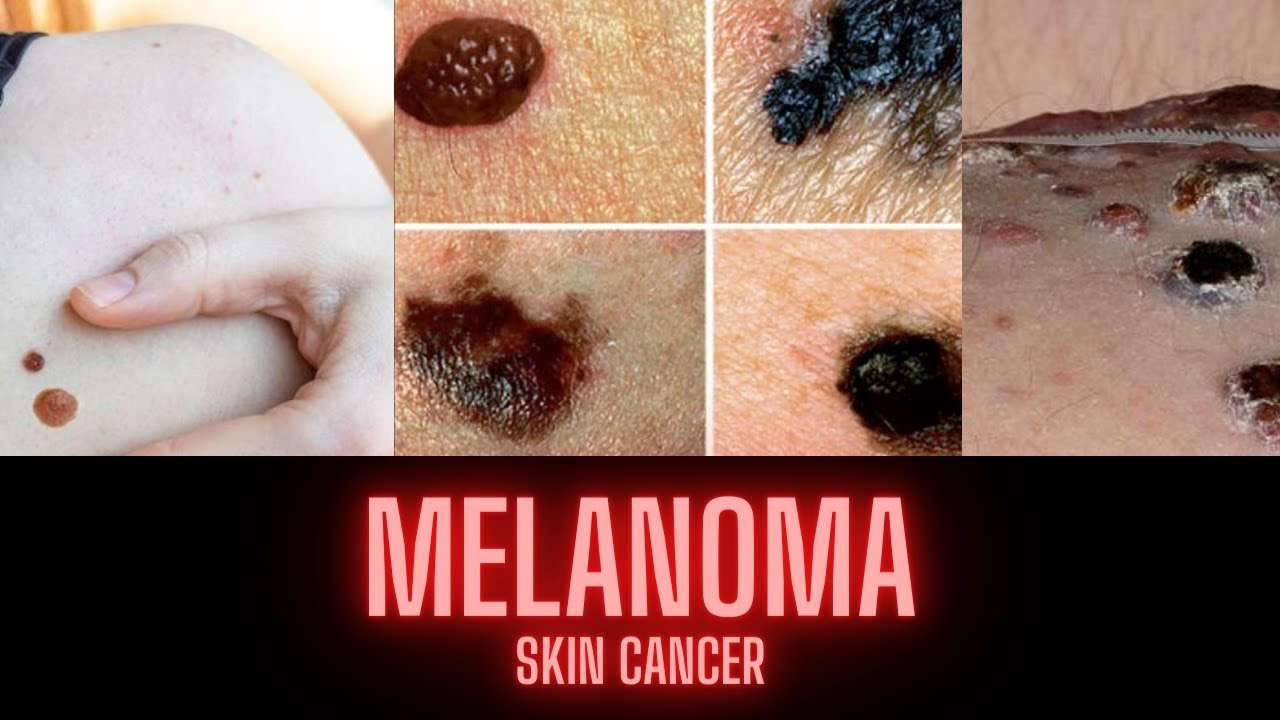
Spring is finally here, and that means people will be enjoying more of their time outdoors in the sun. While its always great to enjoy time outside, its important to remember the harmful effects the sun can have on your skin. In this blog post, I answer a frequently asked question: Which type of skin cancer is the most serious?
Skin cancer is the most common type of cancer in the world for humans. One in five Americans will develop skin cancer over the course of their lifetime, and the risk for skin cancer significantly increases with exposure to the UV rays from the sun or tanning beds. There are three major types of skin cancers: basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and melanoma.
All three types of skin cancer are extremely important to treat however, which skin cancer is the most dangerous? The answer is melanoma. Melanoma is the most serious type of skin cancer, and will typically spread to other organs or parts of the body if left untreated. In almost all cases, melanoma is likely caused by UV rays from the sun or tanning beds, but it can also be developed out of coincidence or genetic predisposition.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Most Aggressive Skin Cancer
Read Also: Stage 5 Cancer Symptoms
Merkel Cell Carcinoma: A Rare Skin Cancer On The Rise
Merkel cell carcinoma is a rare type of skin cancer that affects about 2,000 people in the United States each year.
Though its an uncommon skin cancer, cases of Merkel cell carcinoma have increased rapidly in the last couple of decades.
This type of cancer starts when cells in the skin, called Merkel cells, start to grow out of control.
Merkel cell carcinomas typically grow quickly and can be difficult to treat if they spread.
They can start anywhere on the body, but Merkel cell carcinomas commonly affect areas exposed to the sun, such as the face, neck, and arms.
They may look like pink, red, or purple lumps that are firm when you touch them. Sometimes, they can open up as ulcers or sores.
Risk factors include:
Where Within The Skin Layers Does Skin Cancer Develop
Where skin cancer develops specifically, in which skin cells is tied to the types and names of skin cancers.
Most skin cancers begin in the epidermis, your skins top layer. The epidermis contains three main cell types:
- Squamous cells: These are flat cells in the outer part of the epidermis. They constantly shed as new cells form. The skin cancer that can form in these cells is called squamous cell carcinoma.
- Basal cells: These cells lie beneath the squamous cells. They divide, multiply and eventually get flatter and move up in the epidermis to become new squamous cells, replacing the dead squamous cells that have sloughed off. Skin cancer that begins in basal cells is called basal cell carcinoma.
- Melanocytes: These cells make melanin, the brown pigment that gives skin its color and protects your skin against some of the suns damaging UV rays. Skin cancer that begins in melanocytes is called melanoma.
Read Also: Stage 2 Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Survival Rate
Risk Factor Pigment Marks
Congenital moles have a certain risk of degenerating into malignant melanoma.
This risk seems to depend, among other things, on the size of the pigment mark. In the case of very large marks, some of which cover entire parts of the body, there is a need for action in the first few weeks of a childs life, as large proportions of these pigment marks can be removed by grinding the skin at this age. Smaller congenital pigment marks should also be removed. The timing of surgical removal depends primarily on the type of mole.
Three Most Common Skin Cancers
It is estimated that one in seven people in the United States will develop some form of skin cancer during their lifetime. Although anyone can get skin cancer, people who burn easily and are fair-skinned are at higher risk. Researchers believe that one serious sunburn can increase the risk of skin cancer by as much as 50%. A yearly skin exam by a doctor is the best way to detect skin cancer early, when it is most treatable. If you have a new growth or any change in your skin, be sure to see your doctor to have it examined. Remember, protecting yourself from the sun is the best way to prevent all forms of skin cancer.
Don’t Miss: Merkel Cell Carcinoma Immunotherapy
Types Of Skin Malignancies:
- Melanoma the least common form of skin cancer, but responsible for more deaths per year than squamous cell and basal cell skin cancers combined. Melanoma is also more likely to spread and may be harder to control.
- Nonmelanoma malignancies:
- Squamous cell cancer the second-most common skin cancer. It’s more aggressive and may require extensive surgery, depending on location and nerve involvement.
- Basal cell cancer the most common form of skin cancer. It is rarely fatal but can be locally aggressive.
These skin malignancies are typically caused by ultraviolet radiation from exposure to the sun and tanning beds.
The More Times The Greater The Risk
In almost every person, a more or less large number of benign pigment marks develop, especially in the first half of life. So this is not in itself a cause for concern. However, it is now known that people with a large number of birthmarks in particular have a significantly increased risk of developing black skin cancer.
So if you have more than 40 or 50 pigment marks, then you should definitely be examined regularly, even if there are no specific suspicions. From the age of 35, take advantage of the chance of skin cancer screening, especially every two years.
You May Like: Cancer All Over Body Symptoms
What Are The Symptoms Of Skin Cancer
Skin cancers first appear as a spot, lump or scaly area on the skin, or a mole that changes colour, size or shape over several weeks or months. These changes can appear anywhere on the body, particularly areas frequently exposed to the sun. Skin cancers may bleed and become inflamed, and can be tender to the touch.
There are certain characteristics to look for in spots and moles. Remember the ‘ABCDE’ of skin cancer when checking your skin:
- Asymmetry does each side of the spot or mole look different to the other?
- Border is it irregular, jagged or spreading?
- Colours are there several, or is the colour uneven or blotchy?
- Diameter look for spots that are getting bigger
- Evolution is the spot or mole changing or growing over time?
Changes may include an area that is scaly, shiny, pale or bright pink in colour, or a spot or lump that grows quickly and is thick, red, scaly or crusted.
See your doctor if you notice any new spots or an existing spot that changes size, shape or colour over several weeks or months. Your doctor can help you distinguish between a harmless spot such as a mole, and a sunspot or irregular mole that could develop later into skin cancer.
What Causes Skin Cancer
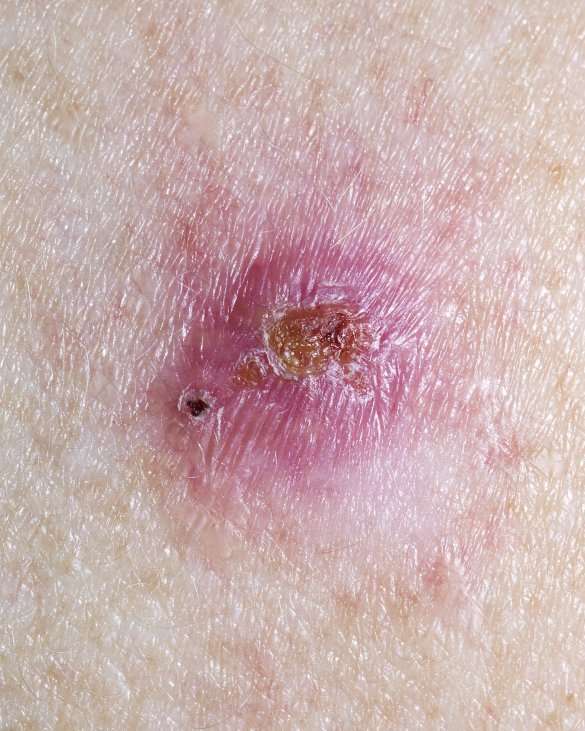
The main cause of skin cancer is overexposure to sunlight, especially when it results in sunburn and blistering. Ultraviolet rays from the sun damage DNA in your skin, causing abnormal cells to form. These abnormal cells rapidly divide in a disorganized manner, forming a mass of cancer cells.
Another cause of skin cancer is frequent skin contact with certain chemicals, such as tar and coal.
Many other factors can increase your risk of developing skin cancer. See question, Who is most at risk for skin cancer?
Don’t Miss: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Survival
How Is Skin Cancer Treated
Treatment depends upon the stage of cancer. Stages of skin cancer range from stage 0 to stage IV. The higher the number, the more cancer has spread.
Sometimes a biopsy alone can remove all the cancer tissue if the cancer is small and limited to your skins surface only. Other common skin cancer treatments, used alone or in combination, include:
Cryotherapy uses liquid nitrogen to freeze skin cancer. The dead cells slough off after treatment. Precancerous skin lesions, called actinic keratosis, and other small, early cancers limited to the skins top layer can be treated with this method.
Excisional surgery
This surgery involves removing the tumor and some surrounding healthy skin to be sure all cancer has been removed.
Mohs surgery
With this procedure, the visible, raised area of the tumor is removed first. Then your surgeon uses a scalpel to remove a thin layer of skin cancer cells. The layer is examined under a microscope immediately after removal. Additional layers of tissue continue to be removed, one layer at a time, until no more cancer cells are seen under the microscope.
Mohs surgery removes only diseased tissue, saving as much surrounding normal tissue as possible. Its most often used to treat basal cell and squamous cell cancers and near sensitive or cosmetically important areas, such as eyelids, ears, lips, forehead, scalp, fingers or genital area.
Curettage and electrodesiccation
Chemotherapy and immunotherapy
Dermatology Care At Florida Medical Clinic
Florida Medical Clinics Dermatology Department offers full diagnostic and treatment options for skin cancer. We offer Mohs Surgery as an outpatient procedure, which is an effective way of treating most kinds of skin cancer. Whether youre unsure if the mole on your leg is benign or cancerous, or if youre needing treatment for diagnosed cancers, weve got you covered.
Contact us today! You can also Request an Appointment online for non-urgent medical problems.
Recommended Reading: Is Stage 3 Melanoma Curable
How Common Is Melanoma
Melanoma accounts for only about 1% of all skin cancers, but causes the great majority of skin cancer-related deaths. Its one of the most common cancers in young people under 30, especially in young women.
Melanoma incidence has dramatically increased over the past 30 years. Its widely accepted that increasing levels of ultraviolet exposure are one of the main reasons for this rapid rise in the number of melanoma cases.
If You Suspect See A Doctor
In the appearance of a pigment mark, there may be various indications of suspicious changes . Even if a mole itches, bleeds or burns, it is better to have it examined by a dermatologist
Every mole deserves special attention in an unusual place.
Frequent injuries to a pigment spot, for example from rubbing the clothing on the chest, waist and / or the collar line or from shaving, do not necessarily increase the risk of degeneration. However, such pigment marks should be removed.
Read Also: Invasive Breast Cancer Survival Rate
What Is The Deadliest Form Of Skin Cancer
Melanoma is the most deadly skin cancer, affecting over 100,000 people in the United States each year and killing over 7,000. When diagnosed in the early stages, melanoma has a five-year survival rate of 83%. But, if the cancer spreads to regional lymph nodes or distant organs, the five-year survival drops to 68% and 30% respectively.
Exams And Tests For Skin Cancer
If you think a mole or other skin lesion has turned into skin cancer, your primary care provider will probably refer you to a dermatologist. The dermatologist will examine any moles in question and, in many cases, the entire skin surface. Any lesions that are difficult to identify, or are thought to be skin cancer, may then be checked. Tests for skin cancer may include:
- The doctor may use a handheld device called a dermatoscope to scan the lesion. Another handheld device, MelaFind, scans the lesion then a computer program evaluates images of the lesion to indicate if its cancerous.
- A sample of skin will be taken so that the suspicious area of skin can be examined under a microscope.
- A biopsy is done in the dermatologists office.
If a biopsy shows that you have malignant melanoma, you may undergo further testing to determine the extent of spread of the disease, if any. This may involve blood tests, a chest X-ray, and other tests as needed. This is only needed if the melanoma is of a certain size.
Continued
You May Like: How Does Immunotherapy Work For Melanoma
Read Also: Signs Of Stage 4 Cancer
What Is Melanoma Skin Cancer
Melanoma is a type of skin cancer that develops when melanocytes start to grow out of control.
Cancer starts when cells in the body begin to grow out of control. Cells in nearly any part of the body can become cancer, and can then spread to other areas of the body. To learn more about cancer and how it starts and spreads, see What Is Cancer?
Melanoma is much less common than some other types of skin cancers. But melanoma is more dangerous because its much more likely to spread to other parts of the body if not caught and treated early.
Recurrent Basal Cell Carcinoma
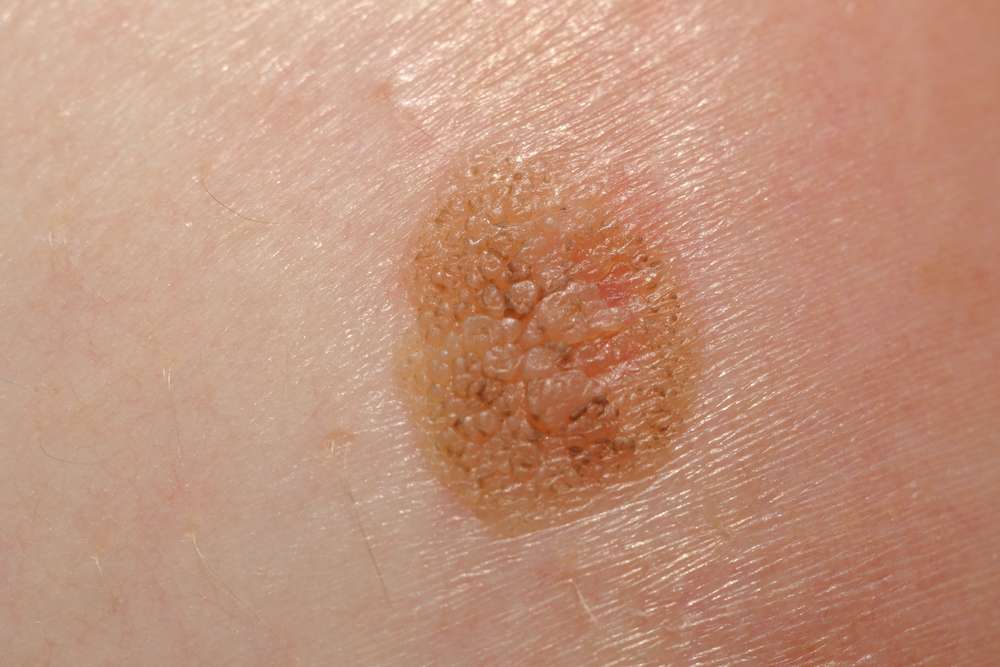
Basal cell carcinomas are the most common type of skin cancer, according to the American Cancer Society. These cancers develop within the basal cell layer of the skin, in the lowest part of the epidermis.
Patients who have had basal cell carcinoma once have an increased risk of developing a recurrent basal cell cancer. Basal cell cancers may recur in the same location that the original cancer was found or elsewhere in the body. As many as 50 percent of cancer patients are estimated to experience basal cell carcinoma recurrence within five years of the first diagnosis.
Basal cell carcinomas typically grow slowly, and it is rare for them to metastasize or spread to nearby lymph nodes or other parts of the body. But early detection and treatment are important.
After completing treatment for basal cell carcinoma, it is important to perform regular self-examinations of the skin to look for new symptoms, such as unusual growths or changes in the size, shape or color of an existing spot. Skin cancers typically develop in areas of the body that are exposed to the sun, but they may also develop in areas with no sun exposure. Tell your oncologist or dermatologist about any new symptoms or suspicious changes you may have noticed.
- Have a history of eczema or dry skin
- Have been exposed to high doses of UV light
- Had original carcinomas several layers deep in the skin
- Had original carcinomas larger than 2 centimeters
Also Check: Invasive Ductal Cancer Prognosis