Do Basal Cell Carcinoma And Melanoma Look Different
The first sign of basal cell carcinoma is usually a small white or flesh-colored skin bump that grows slowly and may bleed. On the other hand, the first sign of melanoma is often a noticeable change in a mole, such as:
- Asymmetry. The shape of one half of the mole does not mirror the other half.
- An irregular border. The edges of the mole may be ragged, notched or blurred, with the pigment appearing to spread into the surrounding skin.
- Uneven coloring. The mole may display shades of black, brown, tan, white, gray, red, pink or blue.
- An increase in diameter. There is a change in size, usually an increase. Melanomas can be tiny, but most are larger than the size of a pea .
- Evolution. The mole has changed over the past few weeks or months.
A skin biopsy is the only way to diagnose basal cell carcinoma or melanoma. A physician can remove a small portion of suspicious tissue, then send it to a lab to be analyzed under a microscope for evidence of cancer. Therefore, it is important to promptly discuss any unusual skin changes with a physician.
If you have been diagnosed with basal cell carcinoma or melanoma, a skin cancer specialist at Moffitt Cancer Center can offer a second opinion after reviewing your lab work, biopsies and images. Or, if you have a suspicious skin lesion, you can have it checked at Moffitt with or without a referral. To request an appointment, call or submit a new patient registration form online.
Does Fluorouracil Work On Squamous Cell Carcinoma
4.6/5fluorouracilsquamous cellcancersisdoes
Likewise, people ask, what is the best treatment for squamous cell carcinoma?
Squamous Cell Skin Cancer Treatment
- Mohs Surgery. Mohs surgery has the highest cure rate of all therapies for squamous cell carcinomas.
- Curettage and Electrodessication. This very common treatment for squamous cell carcinoma is most effective for low-risk tumors.
- Cryosurgery.
- Laser Surgery.
Secondly, is Squamous Cell Carcinoma an aggressive cancer? Squamous cell carcinoma of the skin is usually not life-threatening, though it can be aggressive. Untreated, squamous cell carcinoma of the skin can grow large or spread to other parts of your body, causing serious complications.
In this regard, what type of chemo is used for squamous cell carcinoma?
One drug that is commonly used for topical chemotherapy to treat squamous cell carcinoma is fluorouracil .
What is the survival rate for squamous cell carcinoma?
The 5-year survival rates were 62% for patients with stage I disease, 80% for patients with stage II disease, 42% for patients with stage III, and 19% for patients with stage IV disease.
What Is Squamous Cell Vs Basal Cell Skin Cancer
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
HealthTap doctors are based in the U.S., board certified, and available by text or video.
Recommended Reading: Scalp Melanoma Stages
Merkel Cell Carcinoma: A Rare Skin Cancer On The Rise
Merkel cell carcinoma is a rare type of skin cancer that affects about 2,000 people in the United States each year.
Though its an uncommon skin cancer, cases of Merkel cell carcinoma have increased rapidly in the last couple of decades.
This type of cancer starts when cells in the skin, called Merkel cells, start to grow out of control.
Merkel cell carcinomas typically grow quickly and can be difficult to treat if they spread.
They can start anywhere on the body, but Merkel cell carcinomas commonly affect areas exposed to the sun, such as the face, neck, and arms.
They may look like pink, red, or purple lumps that are firm when you touch them. Sometimes, they can open up as ulcers or sores.
Risk factors include:
How Do You Know If A Spot Is Skin Cancer
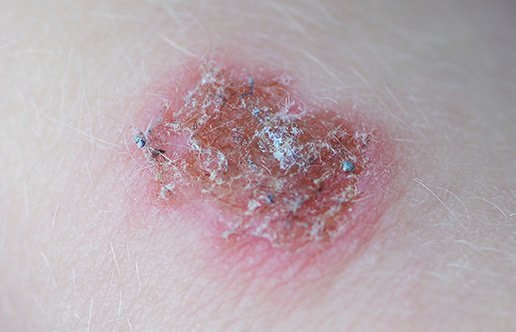
Redness or new swelling beyond the border of a mole. Color that spreads from the border of a spot into surrounding skin. Itching, pain, or tenderness in an area that doesnt go away or goes away then comes back. Changes in the surface of a mole: oozing, scaliness, bleeding, or the appearance of a lump or bump.
Don’t Miss: Can You Have Cancer Without A Tumor
Can Skin Cancer Pop Up Overnight
Melanoma is a very serious skin cancer characterized by the uncontrolled growth of cells that produce pigment, the substance in skin that produces color. Melanomas may appear suddenly and without warning. They are found most frequently on the face and neck, upper back and legs, but can occur anywhere on the body.
Squamous Cell Skin Cancer
SCC is generally faster growing than basal cell cancers. About 20 out of every 100 skin cancers are SCCs. They begin in cells called keratinocytes, which are found in the epidermis.
Most SCCs develop on areas of skin exposed to the sun. These areas include parts of the head, neck, and on the back of your hands and forearms. They can also develop on scars, areas of skin that have been burnt in the past, or that have been ulcerated for a long time.
SCCs don’t often spread. If they do, it’s most often to the deeper layers of the skin. They can spread to nearby lymph nodes and other parts of the body, but this is unusual.
Read Also: How Fast Does Squamous Cell Carcinoma Spread
The Difference Between Basal Cell Carcinoma And Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma are the two most common types of skin cancers. According to the American Cancer Society, over 5 million cases of basal cell and squamous cell cancers are diagnosed every year. Though, basal cell carcinoma occurs more often, taking credit for about 80% of these cases. Other than the disparities in occurrence, what is the difference between basal cell and squamous cell carcinomas? You may also be wondering is squamous cell worse than basal cell, or vice versa. Here is some insight.
The Differences Between Basal Cell And Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Although basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinomas are the two most common types of skin cancer in the United States, theyre also highly treatable.
BCC and SCC are part of the carcinomas group, which are cancerous tumors characterized by a slower development in the upper layers of the skin. These cancers are also known as non-melanoma, meaning they occur in the epithelial tissue, and theyre far less aggressive than melanoma, a rare yet very aggressive form of skin cancer.
As advocates of prevention, we want you to be informed about the most common types of skin cancer. To help you out, we asked our expert, Dr. Gail Zimmerman, all about them. Read on to learn how BCC is different from SCC, and find out how these skin cancers are diagnosed.
Read Also: How Long Does It Take For Melanoma To Spread
How Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma Treated
Although squamous cell carcinomas usually grow slowly, it is important to see a dermatologist quickly. “The sooner you see your doctor and the cancer is diagnosed and treated, the less complicated the surgery to remove it will be, and the faster you will make a complete recovery, Dr. Leffell explains. The treatment for squamous cell cancer varies according to the size and location of the lesion. The surgical options are the same as those for basal cell cancer:
- Surgical excision: Removing a squamous cell lesion is a simple procedure that typically takes place in the dermatologist’s office. After numbing the cancer and the area around it with a local anesthetic, the doctor uses a scalpel to remove the tumor and some of the surrounding skin to make sure all cancer is eliminated. Estimating how much to take requires skill and expertise, Dr. Leffell notes. The risk of taking too little tissue is that some cancer remains taking too much leaves a larger scar than is necessary. Shaped like a football, the wound is stitched together, using plastic surgery techniques. If dissolvable stitches are used, they will disappear on their own as the area heals. Though the procedure leaves some redness and a small scar, it tends to become less noticeable over time. “The cure rate for this type of excision is typically about 90 to 93 percent,” says Dr. Leffell. But, of course, this is dependent on the skill and experience of the doctor.”
How Is Skin Cancer Of The Head And Neck Diagnosed
Diagnosis is made by clinical exam and a biopsy. Basal cell and squamous cell cancers are staged by size and extent of growth. Basal cell cancers rarely metastasize to lymph nodes, but they can grow quite large and invade local structures. Squamous cell cancers have a much higher incidence of lymph node involvement in the neck and parotid gland and can spread along nerves.
Melanoma is staged, based not on size but on how deeply it invades the skin layers. Therefore, a superficial or shave biopsy will not provide accurate staging information used to guide treatment. Melanomas can have a very unpredictable course and may spread to distant organs. Melanomas with intermediate thickness often require sentinel node biopsy, a surgical procedure performed by a head and neck surgeon, to determine if microscopic spreading to lymph nodes has occurred.
Recommended Reading: Non Invasive Breast Cancer Survival Rate
Surgery For Skin Cancer
Small skin cancer lesions may be removed through a variety of techniques, including simple excision , electrodesiccation and curettage , and cryosurgery .
Larger tumors, lesions in high-risk locations, recurrent tumors, and lesions in cosmetically sensitive areas are removed by a technique called Mohs micrographic surgery. For this technique, the surgeon carefully removes tissue, layer by layer, until cancer-free tissue is reached.
Malignant melanoma is treated more aggressively than just surgical removal. To ensure the complete removal of this dangerous malignancy, 1-2 cm of normal-appearing skin surrounding the tumor is also removed. Depending on the thickness of the melanoma, neighboring lymph nodes may also be removed and tested for cancer. The sentinel lymph node biopsy method uses a mildly radioactive substance to identify which lymph nodes are most likely to be affected.
Continued
How The Stage Is Determined
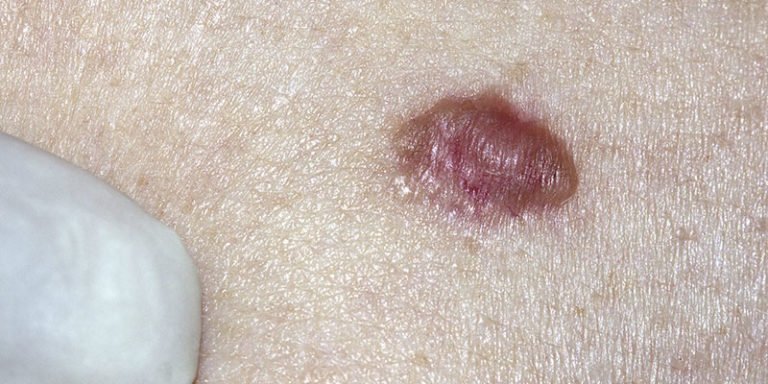
Once you have been diagnosed with squamous cell carcinoma, your doctor will want to determine its stage. While the risk of this type of cancer spreading is low, determining the stage will help your doctor develop the best treatment plan.
The TNM system is a uniform system for staging many types of cancer. TNM stands for:
- T is for tumor: How far has the primary tumor grown through the layers of skin or to nearby tissues?
- N is for nodes: Have cancer cells spread to the lymph nodes near the tumor?
- M is for metastasis: Has the cancer metastasized to distant sites in the body such as the lungs or liver?
Skin Cancer Doctor Discussion Guide
Also Check: Does Amelanotic Melanoma Blanch When Pressed
What Are Symptoms Of Squamous Cell Cancer
Squamous cell cancer can occur anywhere on the skin, but it tends to develop on sun-exposed areas of the body such as the face, ear, scalp, shoulders, neck, lips, backs of the hands, and forearms.
Squamous cell cancers may look like:
- Rough or scaly red patches, which might crust or bleed
- Raised growths or lumps, sometimes with a depressed area in the center
- Open sores that dont completely heal, or that heal and return
- A flat area that is only slightly different from normal skin
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Stages
There are certain features that are considered to make the cancer at higher risk for spreading or recurrence, and these may also be used to stage squamous cell carcinomas. These include:
- Greater than 2 mm in thickness
- Invasion into the lower dermis or subcutis layers of the skin
- Invasion into the tiny nerves in the skin
- Location on the ear or on a hair-bearing lip
After the TNM components and risk factors have been established, the cancer is assigned to one of the five squamous cell carcinoma stages, which are labeled 0 to 4. The characteristics and stages of squamous cell cancer are:
Stage 0: Also called carcinoma in situ, cancer discovered in this stage is only present in the epidermis and has not spread deeper to the dermis.
Stage 1 squamous cell carcinoma: The cancer is less than 2 centimeters, about 4/5 of an inch across, has not spread to nearby lymph nodes or organs, and has one or fewer high-risk features.
Stage 2 squamous cell carcinoma: The cancer is larger than 2 centimeters across, and has not spread to nearby organs or lymph nodes, or a tumor of any size with 2 or more high risk features.
Stage 3 squamous cell carcinoma: The cancer has spread into facial bones or 1 nearby lymph node, but not to other organs.
Stage 4 squamous cell carcinoma: The cancer can be any size and has spread to 1 or more lymph nodes which are larger than 3 cm and may have spread to bones or other organs in the body.
Don’t Miss: Melanoma Cancer Prognosis
Basal Cell And Squamous Cell Carcinoma
The two most common kinds of skin cancer are basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma, which are sometimes called nonmelanoma skin cancer. These cancers are carcinomas that begin in the cells that cover or line an organ.
Basal cell carcinoma accounts for more than 90 percent of all skin cancers in the United States and is the most common of all cancers. Typically, it is a slow-growing cancer that seldom spreads to other parts of the body.
Squamous cell carcinoma also rarely spreads, but does so more often than basal cell carcinoma. It is important that skin cancers are found and treated early because they can invade and destroy nearby tissue. Organ transplant recipients have a 65-fold higher risk of developing squamous cell carcinoma than others. UCSF Medical Center offers a High Risk Skin Cancer Clinic for those at high risk for non-melanoma skin cancers, such as transplant recipients.
Widely Used Kidney Cancer Diagnosis And Treatment Methods
The kidneys primary job is to filter out the impurities from our blood. At times, we grow chunks inside our kidneys. A few of these masses are cancerous, but several are not. You must have your growths checked out to know if it is malignant or not.
There are a lot of different methods for kidney cancer treatment. Generally, there are even more treatment methods if your cancer is detected early. Your healthcare team is there to assist you. They can assist you in learning more about the advantages and disadvantages of treatments. Today, we will mention more information about kidney cancer and the diagnosis and treatment methods.
Don’t Miss: Does Melanoma Blanch When Pressed
Which Is More Dangerous A Melanoma Or A Carcinoma
Melanomas are generally much more dangerous than carcinomas. Early detection helps with treatment in both cases and can be a key to dealing with the problem. A visual inspection can sometimes be enough to tell the difference between carcinoma and melanoma. Both cancers generally manifest as small bumps or growths on the skin.
What About Other Treatments That I Hear About
When you have cancer you might hear about other ways to treat the cancer or treat your symptoms. These may not always be standard medical treatments. These treatments may be vitamins, herbs, special diets, and other things. You may wonder about these treatments.
Some of these are known to help, but many have not been tested. Some have been shown not to help. A few have even been found to be harmful. Talk to your doctor about anything youre thinking about using, whether its a vitamin, a diet, or anything else.
Recommended Reading: Small Blue Cell Tumor Prognosis
How Can You Prevent Basal Cell Carcinoma
Being safe in the sun is the best way to prevent BCC and other skin cancers. Here are some tips:
- Avoid being in the sun from 10 am to 4 pm.
- Avoid tanning beds.
- Use a broad spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 15 or higher each day. If you will be outside for longer periods of time, use a broad spectrum sunscreen that is water-resistant and has an SPF of 30 or higher. Put the sunscreen on 30 minutes before going outside. Put sunscreen on again every two hours, or more frequently if you have been swimming or sweating a lot.
- Use protective clothing that has built-in sun protection, which is measured in UPF. Also, use broad-brimmed hats and sunglasses.
- Do your own skin self-exam about once per month and see a dermatologist about one time per year for a professional skin exam.
- Have any skin changes examined as soon as possible by a healthcare provider.
Skin Cancer Support Groups And Counseling
Living with skin cancer presents many new challenges for you and for your family and friends. You will probably have many worries about how the cancer will affect you and your ability to “live a normal life,” that is, to care for your family and home, to hold your job, and to continue the friendships and activities you enjoy.
Many people with a skin cancer diagnosis feel anxious and depressed. Some people feel angry and resentful others feel helpless and defeated. For most people with skin cancer, talking about their feelings and concerns helps. Your friends and family members can be very supportive. They may be hesitant to offer support until they see how you are coping. Don’t wait for them to bring it up. If you want to talk about your concerns, let them know.
Continued
Some people don’t want to “burden” their loved ones, or prefer talking about their concerns with a more neutral professional. A social worker, counselor, or member of the clergy can be helpful. Your dermatologist or oncologist should be able to recommend someone.
Many people with cancer are profoundly helped by talking to other people who have cancer. Sharing your concerns with others who have been through the same thing can be remarkably reassuring. Support groups for people with cancer may be available through the medical center where you are receiving your treatment. The American Cancer Society also has information about support groups throughout the U.S.
You May Like: Survival Rates For Invasive Ductal Carcinoma