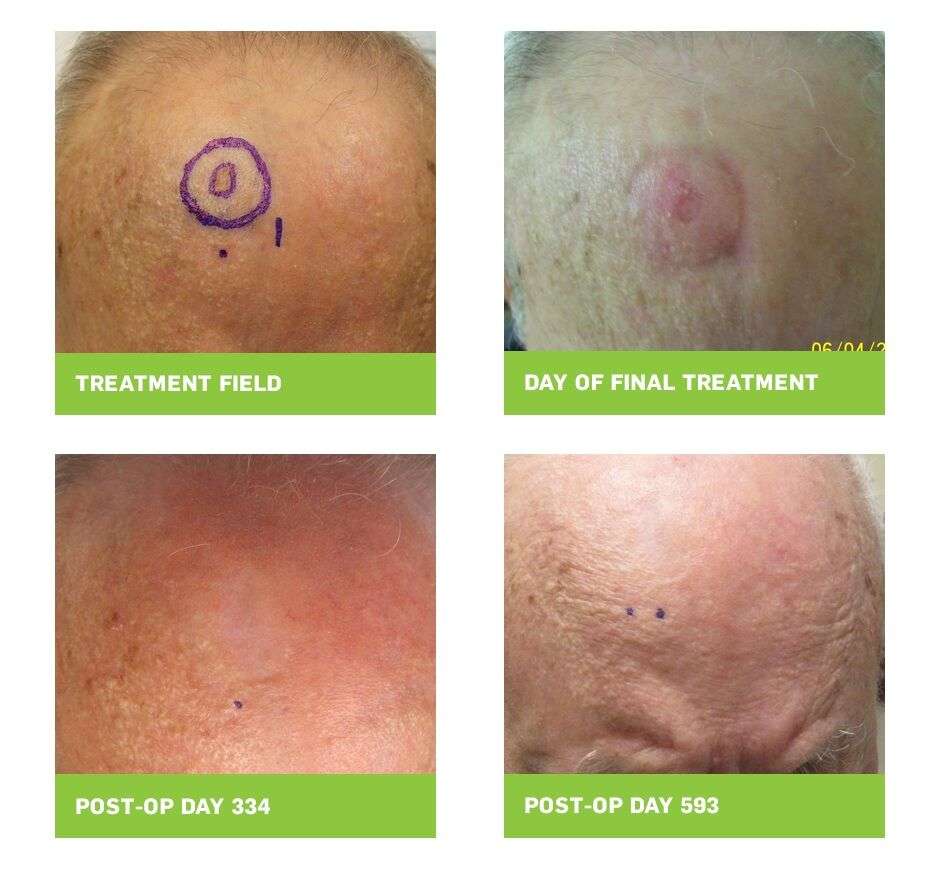
Merkel Cell Carcinoma Vs Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Merkel cells are receptors formed of neuroendocrine cells which are connected by nerve endings and these take the sensation of touch and vibration to the brain and are located in the epidermis.
Squamous cells are flat cells of epithelial origin forming the outermost and uppermost layer of skin and even epidermis. These are keratin containing cells which perform the function of protecting the body against traumas and abrasions by maintaining its continuity.
The unrestricted overgrowth of both the cells due to various factors leads to their respective cancers. Squamous cell cancers are much more common than Merkel cell cancer. Squamous cell carcinoma makes 20% of the total skin cancers of non-melanomatous origin whereas, on the other hand, the Merkel cell cancer is quite rare cancer to be found alone. It is associated with other skin cancers and found in multiple cancer syndromes of skin.
These cancers differ very much in their presentation and signs. Merkel cell carcinoma usually presents as nodule of small size on the skin especially of head and neck regions with a property of changing colors like blue, purple, red, etc. whereas squamous cell carcinoma presents as a shallow ulcerative lesion with elevated margins and presence of plaques marks its configuration.
New Approach To Studying Molecular Abnormalities In Scc
In a separate study, we have focused on characterizing targeted-therapy related molecular bio-markers from NSCLC ever-smokers versus never-smokers, using microdissected paired tumor/normal cells and a novel qRT-PCR with pre-amplification method developed by our group . The data provided potentially useful information in guiding an individual treatment approach for lung cancer.
Although these strategies have been developed in ESCC, these novel methodologies can be applied to other SCCs to identify potential therapeutic targets directly related to tumorigenesis. We hope that these new approaches to studying SCC will also elucidate markers for prognosis and lead to effective therapies for SCCs of all anatomical sites.
From The Harvard Health Letter May 2006
Summers the season for fun in the sunbut also for skin cancer. Of the three main types of skin cancer, melanoma is most deadly, and basal cell, most common. Squamous cell cancer falls in between. Its three times as common as melanoma . Though not as common as basal cell , squamous cell is more serious because it is likely to spread . Treated early, the cure rate is over 90%, but metastases occur in 1%5% of cases. After it has metastasized, its very difficult to treat.
You May Like: Etiology Of Skin Cancer
What Makes Yale Medicines Approach To Squamous Cell Carcinoma Unique
Simple, small cancers can often be treated very well by a local dermatologist, according to Dr. Leffell. We rarely see the small cancers. We get referred to the cases that need special attention.
Dr. Leffell emphasizes that at Yale Medicine, the patient always comes first. We like to have a discussion with the patient about what happens after the skin cancer is removed, he says. We talk about what’s involved with plastic surgery and what’s involved with letting the area heal naturally. We prefer to take a minimalist approach and let the patient decide what they want us to do and how they want to let their skin heal.
If the decision is made to repair the wound using plastic surgery, we do that immediately in the office setting, Dr. Leffell says. Alternatively, allowing the wound to heal naturally is often a great option, and does not rule out doing plastic surgery down the road if needed, though that is very rarely the case.
What Will Happen After Treatment
Youll be glad when treatment is over. Your doctor will want you to check your skin at least once a month. It will be very important to protect yourself from getting too much sun.
For years after treatment ends, you will see your skin cancer doctor. At first, your visits may be every few months. Then, the longer youre cancer-free, the less often the visits are needed. Be sure to go to all of these follow-up visits. Your doctor will ask about symptoms and check you for signs of the cancer coming back or a new skin cancer. Other exams and tests may also be done.
Having cancer and dealing with treatment can be hard, but it can also be a time to look at your life in new ways. You might be thinking about how to improve your health. Call us at 1-800-227-2345 or talk to your cancer care team to find out what you can do to feel better.
You cant change the fact that you have cancer. What you can change is how you live the rest of your life making healthy choices and feeling as good as you can.
Also Check: What Is Melanoma In The Brain
Sarcoma Vs Carcinoma: Differences And Similarities
There are a number of differences between sarcomas and carcinomas, though individual cancers within each category can vary tremendously. Carcinomas account for the majority of cancers with only 1% of cancers in adults being sarcomas. In children, however, sarcomas account for over 15% of cancers, making research critical. Carcinomas arise out of epithelial cells that line the surface and organs of the body, whereas sarcomas arise from connective tissues such as bone, cartilage, fibrous tissue, blood vessels, and nerves. Learn about the similarities and differences with regard to subtypes, symptoms, causes, diagnosis, treatments, and prognosis.
Which Is Worse Basal Cell Or Squamous Cell Cancer
basal cellsquamous cell
Melanoma typically begins as a mole and can occur anywhere on the body. Squamous cell carcinoma may appear as a firm red bump, a scaly patch, or open sore, or a wart that may crust or bleed easily. Basal cell carcinoma may appear as a small white or flesh-colored bump that grows slowly and may bleed.
Subsequently, question is, how long can you live with squamous cell carcinoma? Most of squamous cell carcinomas can be cured if they are treated early. Once squamous cell carcinoma has spread beyond the skin, though, less than half of people live five years, even with aggressive treatment.
In this way, how serious is a squamous cell carcinoma?
Squamous cell carcinoma of the skin is usually not life-threatening, though it can be aggressive. Untreated, squamous cell carcinoma of the skin can grow large or spread to other parts of your body, causing serious complications.
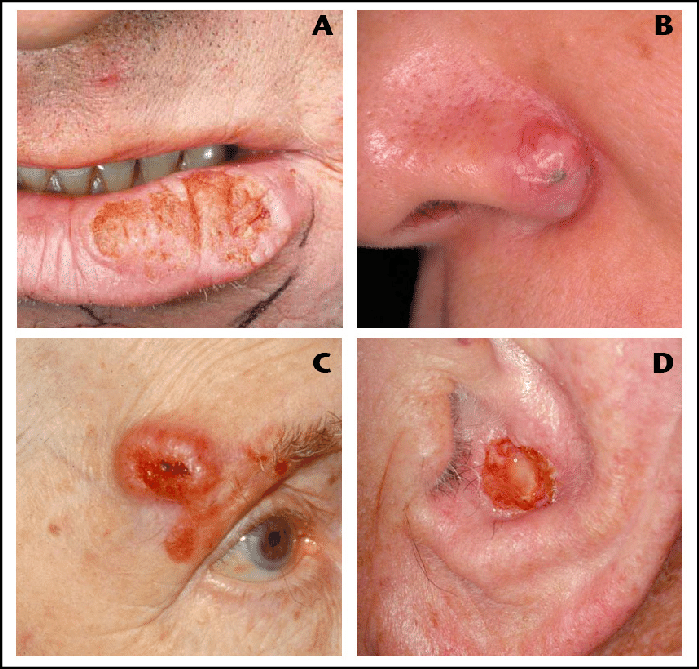
What does squamous cell cancer look like?
Squamous cell carcinomas may appear as flat reddish or brownish patches in the skin, often with a rough, scaly, or crusted surface. They tend to grow slowly and usually occur on sun-exposed areas of the body, such as the face, ears, neck, lips, and backs of the hands. Normal moles also develop from these skin cells.
Recommended Reading: Metastatic Basal Cell Carcinoma Survival Rate
Surgery For Skin Cancer
Small skin cancer lesions may be removed through a variety of techniques, including simple excision , electrodesiccation and curettage , and cryosurgery .
Larger tumors, lesions in high-risk locations, recurrent tumors, and lesions in cosmetically sensitive areas are removed by a technique called Mohs micrographic surgery. For this technique, the surgeon carefully removes tissue, layer by layer, until cancer-free tissue is reached.
Malignant melanoma is treated more aggressively than just surgical removal. To ensure the complete removal of this dangerous malignancy, 1-2 cm of normal-appearing skin surrounding the tumor is also removed. Depending on the thickness of the melanoma, neighboring lymph nodes may also be removed and tested for cancer. The sentinel lymph node biopsy method uses a mildly radioactive substance to identify which lymph nodes are most likely to be affected.
Continued
Molecular Characteristics And Prognostic Markers
The development of clinically evident SCC is a multistep process involving the accumulation of multiple genetic alterations modulated by genetic predisposition, known risk factors, and other unknown environmental influences. The alterations are typically oncogene activation, including recessive oncogenes and tumor suppressor gene inactivation via mutations, loss of heterozygosity, deletions, or other mechanisms . Molecular profiling studies that began with single or relatively small groups of genes or proteins have now progressed to large-scale and high-throughput methods using DNA-, RNA-, and protein-based approaches. These large-scale methods analyze thousands of genes at one time and have led to a better understanding of the complexity of gene abnormality patterns of SCC and have accelerated the discovery of novel genes involved in SCC pathogenesis. In addition to conventional prognostic factors , these molecular characteristics are becoming increasingly valuable as biomarkers in adjunct prognostic tools. There are numerous molecular markers that have been identified in SCC, and in this section we compare and contrast the major molecular abnormalities and their prognostic value among the four major SCCs.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Survival Rate For Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Head And Neck Squamous Cell Carcinomas
Head and neck squamous cell carcinomas make up the vast majority of head and neck cancers and rank as the sixth most common cancer worldwide , with 45,660 new cases of HNSCC diagnosed in 2007 and 35,720 new cases reported in the US during 2009 . They are a group of tumor entities that arise from squamous mucosal surfaces, including nasal cavities, paranasal sinuses, oral cavity, nasopharynx, oropharynx, hypopharynx, and larynx. In contrast to the declining overall incidence of HNSCC, which is mainly due to smoking prevention and cessation , oropharynx carcinoma shows a rising incidence, particularly among individuals less than 45 years of age, suggesting some nontraditional behavioral and environmental factors play a key role in its epidemiology. HNSCC has a 75% overall 5-year survival rate if detected early . Despite advances in detection and treatments over recent decades, most patients present with metastatic disease at the time of diagnosis, reducing the overall 5-year survival rate to 35% . Late diagnosis, formation of additional primary tumors, and metastases largely contribute to this poor survival rate .
What About Other Treatments That I Hear About
When you have cancer you might hear about other ways to treat the cancer or treat your symptoms. These may not always be standard medical treatments. These treatments may be vitamins, herbs, special diets, and other things. You may wonder about these treatments.
Some of these are known to help, but many have not been tested. Some have been shown not to help. A few have even been found to be harmful. Talk to your doctor about anything youre thinking about using, whether its a vitamin, a diet, or anything else.
Recommended Reading: Tumor Calcification
Patient Health And Supportive Care
Given the complex nature of everyday functions within the head and neck area, the inherent consequences of HNSCC and its treatment and the increasing choices of treatments have a large effect on the health-related QOL of patients with HNSCC.
The wide array and combinations of treatments all have their specific sequelae, including physical, emotional, functional, social, and occupational dysfunction, as well as a profound effect on the families of patients with HNSCC. Furthermore, HRQOL is significantly associated with survival,. For example, a clinically meaningful association exists between HRQOL scores measured at diagnosis and overall survival of patients after treatment . Depending on the primary tumour site, patients with HNSCC might be confronted with specific symptoms, such as oral dysfunction and swallowing and speech problems, during treatment, which often improve 6 months after treatment. However, long-term reduction in QOL in HNSCC survivors is common. On average, overall HRQOL deteriorated by 11% when compared with pre-treatment, and by 15% when compared with years 1 and 2 post-treatment.
Squamous Or Basal Cell Cancer: Which One Is Worse
Skin, the largest organ of the human body, protects us from infections, injuries and helps to modulate the body temperature. Also, the organ stores water and fat and is responsible for producing vitamin D. You might have studied in your school that skin is made up of three layers, i.e., the epidermis, dermis, and hypodermis. As we know, the epidermis is the outermost layer of the skin, while the dermis and hypodermis are the inner layer of the skin and the deep layer of the fat, respectively.
The abnormal growth of skin cells is known as skin cancer. It generally develops on skin exposed to the ultraviolet rays of the sun. You would be surprised to learn that more than 3 million people in the United States are diagnosed with skin cancer, making it the countrys most common type of cancer. If found at an early stage, the disease can be treated with medication, procedures provided by a dermatologist , or a surgeon.
Primarily, there are four types of skin cancer: basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, Merkel cell cancer, and melanoma, but basal and squamous cell cancer are the most common types. Lets find out more about these diseases.
Recommended Reading: What Does Stage 3b Melanoma Mean
Initiating And Early Events
HPV-negative HNSCC.
Tobacco consumption is the primary risk factor for development of HPV-negative HNSCC. Tobacco consists of over 5,000 different chemicals, of which dozens have been shown to have carcinogenic activity. The chemicals thought to be most responsible for the cancer-causing effects of tobacco are polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons , including benzopyrene, and nitrosamines, including 4–1–1-butanone and N-nitrosonornicotine ,. In smokeless tobacco, nitrosamines are the dominant carcinogen, whereas the carcinogens in areca nut and betel quid are poorly defined. Tobacco-derived carcinogens, including PAHs and nitrosamines, undergo metabolic activation, with detoxication enzymes and pathways promoting excretion . However, many of the reactive metabolites of these carcinogens can also form covalent DNA adducts, which, if not properly repaired, lead to mutations and other genetic abnormalities. The propensity for tobacco carcinogens to promote genetic changes and neoplastic transformation likely depends on the balance between metabolic activation versus detoxification and DNA repair . The use of tobacco products is also associated with inflammation in the exposed tissues. Coincident with inflammation is the local production of cytokines, chemokines and growth factors that can have an important role in promoting proliferation, angiogenesis and, ultimately, carcinogenesis.
Development of carcinogen-associated, HPV-negative HNSCC.
HPV-positive HNSCC.
Keyword Research: People Who Searched Basaloid Cells Definition Skin Also Searched
| Keyword |
|---|
What does basaloid cell mean?
Basaloid Cell. A cell usually of the epidermis that resembles a basal cell.
Which is worse basal cell or squamous cell cancer?
Basal cell skin cancers often grow deeper and more destructive when left untreated causing large ulcerated areas. Squamous carcinomas more often spread radially and have a higher risk of spread to other organs if left untreated. Different cell types. Squamous cell carcinomasare worse than basal cell carcinomas.
How serious is basal cell skin cancer?
Basal cell carcinoma is a cancer that grows on parts of your skin that get a lot of sun. It’s natural to feel worried when your doctor tells you that you have it,but keep in mind that it’s the least riskytype of skin cancer. As long as you catch it early,you can be cured.
What is basaloid squamous cell carcinoma ?
Basaloid squamous cell carcinoma is a rare variant of SCC having a marked predilection for the upper aerodigestive tract. It is regarded as a high-grade tumourwith increased propensity for metastasis to distant sites.
Recommended Reading: Show Me What Skin Cancer Looks Like
Genomic Alterations And Key Pathways
There is a tremendous need to identify molecular biomarkers that can be used to predict progression of premalignant HNSCC lesions, prognosticate survival, reveal new targets for intervention and predict response to therapeutic agents. The search for biomarkers has focused on defining the molecular abnormalities that characterize HNSCC. In this section, we highlight findings regarding genetic and epigenetic alterations, as well as dysregulation of cellular signalling pathways, which occur during HNSCC development.
Two additional members of the TP53 gene family, TP63 and TP73, are frequently altered in HNSCC. TP63 encodes two major isoforms, Np63 and TAp63 domain, respectively), and is overexpressed in a majority of HNSCC tumours. Np63 promotes HNSCC tumour growth by multiple mechanisms, including suppression of apoptosis and p16INK4A expression and induction of mitogenic signalling. By contrast, TAp73, a major isoform encoded by TP73, exhibits tumour suppressor activity and the function of TAp73 is commonly abrogated in HNSCC. For example, stimulation of HNSCC cells with TNF results in the induction of c-REL oncoprotein that binds to Np63, displacing TAp73 from Np63TAp73 complexes and inactivating TAp73,. Phosphorylation of Tap73 by casein kinase 2 or Polo-like kinase 2 also leads to TAp73 inactivation and results in induction of NANOG, SOX2 and OCT4, promoting the stem cell-like properties of HNSCC tumour cells,.
Symptoms Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
A change in the skin might be the first sign of the presence of basal cancer cells. The changes may include a bump or sore that wont heal. The following can be a few symptoms of the disease:
- A translucent skin-colored bump: The bump can be either white or pink on fair skin, while the bump generally looks brown or shiny black on dark skin. You also might be able to see blood vessels. Sometimes, the bump may bleed.
- Lesions: A brown, black, or blue lesion can appear with a slightly raised translucent border.
- Flat and scaly spots: Such patches can be seen with raised edges. Also, they can grow quite large over a period of time.
- Scar-like lesion: A whitish scar-like lesion without any proper border can also be an essential sign of basal cell carcinoma.
Read Also: Prognosis Of Skin Cancer
Other Types Of Skin Cancer
Unusual types of skin cancer include Merkel cell tumors. Merkel cell carcinoma starts when cells in the skin, also called Merkel cells, start to grow uncontrollably. This type of cancer can grow quickly and can be hard to treat if it spreads beyond the skin.
Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans is another rare skin cancer that begins in the middle layer of skin, known as the dermis. This type of cancer tends to grow slowly and seldom spreads to other parts of the body.