What Can Be Done At Home
- Avoid excessive exposure to the sun, especially the midday sun .
- Move into the shade and have a ‘siesta’ instead.
- Clothing and sun hats can protect the skin from the sun’s harmful rays.
- Children must be protected from getting sunburn. Although the sunburn clears up nicely, the skin may have suffered damage that will become apparent later in life. Sunburn increases the risk of developing skin cancer.
- Consult your doctor if you have sores that will not heal.
If You Have Basal Or Squamous Cell Skin Cancer Non
Basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma are the two most common types of skin cancers. According to the American Cancer Society, over 5 million cases of basal cell and squamous cell cancers are diagnosed every year.Though, basal cell carcinoma occurs more often, taking credit for about 80% of these cases Basal cell carcinoma is most commonly caused by exposure of the skin to ultraviolet light, either from the sun or a tanning bed. Gradually, the effects of exposure damage the DNA, resulting in the development of cancer. The process can take anywhere from weeks to months to several years before it becomes noticeable Basal cell carcinoma is the most common type of skin cancer. It accounts for more than 80 percent of skin cancer diagnoses. It forms in the basal cells and is found on parts of the body heavily. Basal cell carcinoma is the most common skin cancer in humans. It is responsible for around 75% of nonmelanoma skin cancers and almost 25% of all cancers in the United States. 1 Studies have shown that the incidence of basal cell carcinoma is increasing from 3% to 10% annually. 2 This is commonly seen in elderly patients in sun-exposed areas, and affects men more than women.
What Should I Do If I Have Skin Cancer On My Face
Treatment options include surgery, specifically curettage and electrodesiccation, Mohs surgery, cryosurgery, laser surgery. Your doctor might also recommend destroying the tumor by using photodynamic therapy or radiation treatment. Medications, including topical medications Aldara or Adrucil, can be used to treat BCCs.
Recommended Reading: What Are The Causes Of Carcinoma Cancer
What Is Intraepidermalsquamous Cell Carcinoma
Intraepidermal squamous cell carcinoma is a common superficial form of keratinocytecancer. It is also known as Bowen disease, intraepidermal carcinoma and carcinoma in situ .
Intraepidermal SCC is derived from squamous cells, the flat epidermal cells that make keratin, the horny protein that makes up skin, hair and nails. Intraepidermal and in situ mean the malignant cells are confined to the tissue of origin, in this case, the epidermis.
Recommended Reading: What Causes Small Cell Carcinoma
Melanoma Signs And Symptoms
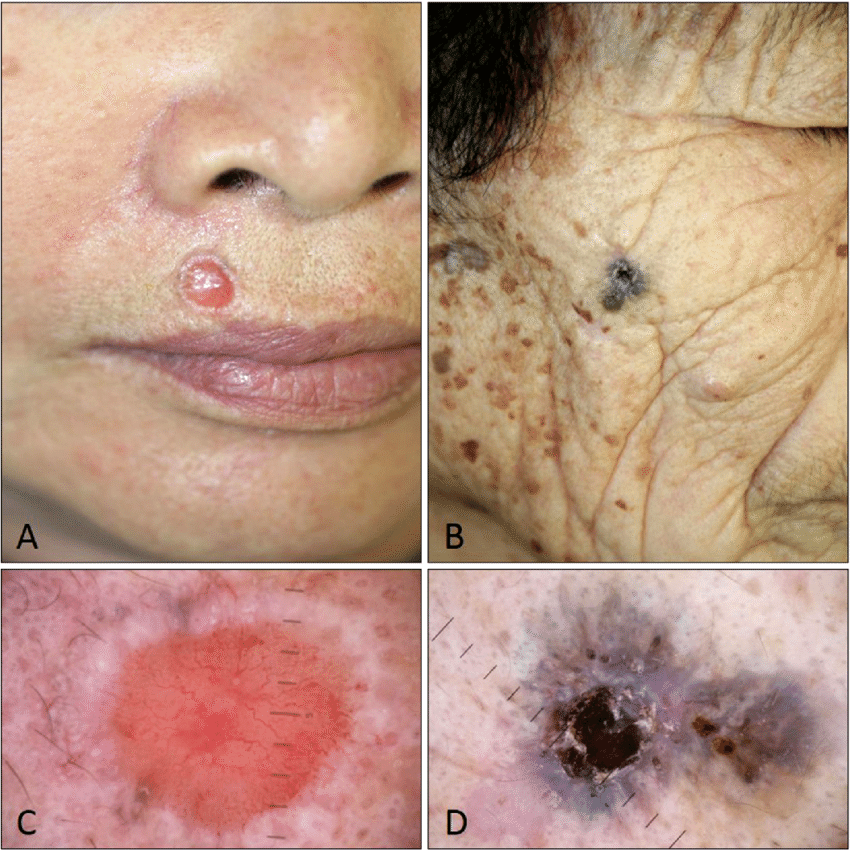
Melanoma skin cancer is much more serious than basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma. It can spread quickly to other organs and causes the vast majority of skin cancer deaths in the United States. Usually melanomas develop in or around an existing mole.
Appearance
Signs and symptoms of melanoma vary depending on the exact type and may include:
- A flat or slightly raised, discolored patch with irregular borders and possible areas of tan, brown, black, red, blue or white
- A firm bump, often black but occasionally blue, gray, white, brown, tan, red or your usual skin tone
- A flat or slightly raised mottled tan, brown or dark brown discoloration
- A black or brown discoloration, usually under the nails, on the palms or on the soles of the feet
See more pictures and get details about different types of melanoma in our dedicated melanoma section.
Recommended Reading: What Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of The Head And Neck
What Are The Similarities In Basal Cell Carcinoma Vs Squamous Cell Carcinoma
The majority of people who are diagnosed with basal cell carcinoma or squamous cell carcinoma are fair skinned and have signs of sun damage. These signs include deep wrinkles, age spots, and patches of discolored skin. However, people of all skin tones can be diagnosed with skin cancer.
You are at a higher risk of being diagnosed with skin cancer if you:
- Regularly use a tanning bed
- Spend time in the sun without protecting your skin using sunscreen or clothing
- Are fair skinned, have light colored eyes, or are a natural red head or blonde
- A history of skin cancer
- Experienced blistering sunburns
Is Basal Cell Carcinoma The Same As Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Basal cell carcinoma accounts for more than 90 percent of all skin cancers in the United States and is the most common of all cancers. Typically, it is a slow-growing cancer that seldom spreads to other parts of the body. Squamous cell carcinoma also rarely spreads, but does so more often than basal cell carcinoma.
Also Check: Melanoma Bone Cancer Life Expectancy
Less Common Types Of Skin Cancer
Nearly all skin cancers diagnosed in the U.S. are nonmelanomas or melanoma. But there are a few other very rare types of skin cancer that can develop. Combined, these types of skin cancer make up less than 1 percent of all skin cancers diagnosed in the U.S. today.
Preventing Basal Cell Carcinoma
Basal cell carcinoma prevention is the same as prevention methods for all skin cancers, with the goal of protecting skin from harmful UV rays.
The number one thing people can do is to practice good sun protection and sun avoidance, meaning wear sunscreen and protect the skin from getting sun damage, says Stevenson. Its also important to get skin checks regularly for early detection.
Stevenson says if someone is prone to skin cancers for example, has very fair skin, sunburns as a child, or a history of skin cancer in the family its better to go out in the late afternoon or early morning when the sun isnt as strong, or stay primarily in the shade.
Anyone spending time in the sun, regardless of complexion, should practice sun protective behaviors, including wearing sunscreen.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends a sunscreen with a minimum sun protection factor of 15, and UVA and UVB broad spectrum protection. It also advises people to stay in the shade as much as possible and wear protective clothing including brimmed hats and sunglasses. Stevenson suggests looking for a SPF over 30.
Lebwohl says the SPF number directly correlates with the amount of protection it gives you. He says to divide the amount of time in the sun by the SPF number. For example, if someone is in the sun for 60 minutes, and wearing SPF 30, its as if they were exposed to two minutes of damaging rays rather than the full 60 minutes.
Recommended Reading: Invasive Lobular Breast Cancer Survival Rate
Does Fluorouracil Work On Squamous Cell Carcinoma
4.6/5fluorouracilsquamous cellcancersisdoes
Squamous Cell Skin Cancer Treatment
- Mohs Surgery. Mohs surgery has the highest cure rate of all therapies for squamous cell carcinomas.
- Curettage and Electrodessication. This very common treatment for squamous cell carcinoma is most effective for low-risk tumors.
- Cryosurgery.
- Laser Surgery.
Beside above, is Squamous Cell Carcinoma an aggressive cancer? Squamous cell carcinoma of the skin is usually not life-threatening, though it can be aggressive. Untreated, squamous cell carcinoma of the skin can grow large or spread to other parts of your body, causing serious complications.
Furthermore, what type of chemo is used for squamous cell carcinoma?
One drug that is commonly used for topical chemotherapy to treat squamous cell carcinoma is fluorouracil .
What is the survival rate for squamous cell carcinoma?
The 5-year survival rates were 62% for patients with stage I disease, 80% for patients with stage II disease, 42% for patients with stage III, and 19% for patients with stage IV disease.
Three Most Common Skin Cancers
It is estimated that one in seven people in the United States will develop some form of skin cancer during their lifetime. Although anyone can get skin cancer, people who burn easily and are fair-skinned are at higher risk. Researchers believe that one serious sunburn can increase the risk of skin cancer by as much as 50%. A yearly skin exam by a doctor is the best way to detect skin cancer early, when it is most treatable. If you have a new growth or any change in your skin, be sure to see your doctor to have it examined. Remember, protecting yourself from the sun is the best way to prevent all forms of skin cancer.
Read Also: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Grade 2 Survival Rate
What Causes Intraepidermal Scc
Ultraviolet radiation is the main cause of intraepidermal SCC. It damages the skin cell nucleic acids , resulting in a mutantclone of the genep53, setting off uncontrolled growth of the skin cells. UV also suppresses the immune response, preventing recovery from damage.
Human papillomavirus is another major cause of intraepidermal SCC. Oncogenic strains of HPV are the main cause of squamous intraepithelial lesions , that is, squamous cell carcinoma in situ in mucosal tissue.
Donât Miss: How Do You Know If Squamous Cell Carcinoma Has Spread
What Is Basal Cell Carcinoma Skin Cancer
Thomas Urban Marron, MD, PhDAlamy
Mark Lebwohl, MD, a professor and the chairman at the Kimberly and Eric J. Waldman Department of Dermatology at Mount Sinai and a spokesperson for the Skin Cancer Foundation, recalls once running into a doctor colleague at work with a scab on his lip.
Crossing paths again weeks later, his colleague had the same scab.
I looked at him and said, You really should have that looked at, and he said, Oh, its just a scab, I keep hitting it when I shave, says Dr. Lebwohl. Ultimately, his colleague did get it looked at by a dermatologist. It was skin cancer, more specifically basal cell carcinoma .
Skin cancer is the most common type of cancer in the United states, and BCC is the most frequently occurring of all forms of cancer, according to the Skin Cancer Foundation. Basal cell carcinoma, which can appear, as in the case of Lebwohls colleague, as a minor irritation, has more than 4 million cases diagnosed annually. And like Lewohl’s colleague, a wound that wont heal is just one possible manifestation of basal cell carcinoma.
RELATED:What Doctors and Specialists Treat Skin Cancer?
Also Check: What Type Of Skin Cancer Spreads The Fastest
What Is Nodular Basal Cell Carcinoma With Pictures
- Micronodular basal cell carcinoma may be more difficult to eradicate and prone to recurrence than nodular subtype. Micronodular basal cell carcinoma is thought to have a greater potential for clinically surreptitious tumor spread compared with the majority of basal cell carcinomas that are nodular
- The nodular type of basal cell carcinoma usually begins as small, shiny, firm, almost clear to pink in color, raised growth. After a few months or years, visible dilated blood vessels may appear on the surface, and the center may break open and form a scab. The border of the cancer is sometimes thickened and pearly white
- superficial basal cell skin cancer Nodular basal cell cancer. Nodular basal cell cancers can look see through and shiny. You can often also see their blood vessels. Sometimes they have a sore area and it may also have fluid filled sacs . Pigmented basal cell cancer. Pigmented basal cell cancers have dark areas.
- Nodular Basal Cell Carcinoma Nodular BCC is the most common clinical subtype of BCC . 47 , 48 It occurs most commonly on the sun-exposed areas of the head and neck and appears as a translucent papule or nodule depending on duration
- Basal cell carcinoma is the most common form of skin cancer, with an estimated 4.3 million cases diagnosed in the United States each year .Although it rarely metastasizes, BCC can cause significant local tissue destruction, resulting in disfigurement and infiltration into vital underlying structures if left untreated
What Does Scc Look Like
SCCs can appear as scaly red patches, open sores, rough, thickened or wart-like skin, or raised growths with a central depression. At times, SCCs may crust over, itch or bleed. The lesions most commonly arise in sun-exposed areas of the body.
SCCs can also occur in other areas of the body, including the genitals.
SCCs look different on everyone. You can find more images, as well as signs, symptoms and early detection strategies on our SCC Warning Signs page.
Please note: Since not all SCCs have the same appearance, these photos serve as general reference for what they can look like. If you see something new, changing or unusual on your skin, schedule an appointment with your dermatologist.
A persistent, scaly red patch with irregular borders that sometimes crusts or bleeds.
An open sore that bleeds or crusts and persists for weeks.
An elevated growth with a central depression that occasionally bleeds. It may rapidly increase in size.
A wart-like growth that crusts and occasionally bleeds.
Read Also: How Fast Does Cancer Spread Without Treatment
From The Harvard Health Letter May 2006
Summers the season for fun in the sunbut also for skin cancer. Of the three main types of skin cancer, melanoma is most deadly, and basal cell, most common. Squamous cell cancer falls in between. Its three times as common as melanoma . Though not as common as basal cell , squamous cell is more serious because it is likely to spread . Treated early, the cure rate is over 90%, but metastases occur in 1%5% of cases. After it has metastasized, its very difficult to treat.
Our Approach To Basal Cell And Squamous Cell Carcinoma
UCSF provides superior, proven care to prevent, detect and manage basal cell and squamous cell carcinomas, and will tailor cutting-edge treatment plans to the individual patient. Our dermatologists, medical and surgical oncologists, radiation oncologists and dermatopathologists are known for providing the best treatment options and cure rates for skin cancer, while giving outstanding cosmetic results.
Some of our new diagnostic and treatment techniques include lymph node mapping to detect early occurrences of cancer, electron beam radiation and Mohs micrographic surgery, which removes the smallest amount of healthy tissue in order to minimize scarring and preserve skin function. We also offer our patients access to educational programs, resources for emotional support and opportunities to participate in experimental treatments.
You May Like: Non Invasive Breast Cancer Survival Rate
What About Other Treatments That I Hear About
When you have cancer you might hear about other ways to treat the cancer or treat your symptoms. These may not always be standard medical treatments. These treatments may be vitamins, herbs, special diets, and other things. You may wonder about these treatments.
Some of these are known to help, but many have not been tested. Some have been shown not to help. A few have even been found to be harmful. Talk to your doctor about anything youre thinking about using, whether its a vitamin, a diet, or anything else.
Is Basal Cell Carcinoma Dangerous Answer: Yes
Read Also: Carcinoma Cancer Symptoms
Do You Need Chemo For Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Larger squamous cell cancers are harder to treat, and fast-growing cancers have a higher risk of coming back. In rare cases, squamous cell cancers can spread to lymph nodes or distant parts of the body. If this happens, treatments such as radiation therapy, immunotherapy, and/or chemotherapy may be needed.
Understanding Nonmelanoma Skin Cancer
What is nonmelanoma skin cancer?
Skin cancer is a disease that starts in the cells of the skin. The area of skin with the cancer is often called a lesion. There are several types of skin cancer . Melanoma is the most serious. But there are others that are known as nonmelanoma skin cancer. These include:
-
Basal cell carcinoma.
Basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma are by far the most common.
Understanding the skin
The skin is the largest organ of the body. Skin protects us from heat, sunlight, injury, and infection. It also stores water and fat, and makes vitamin D. The skin has 3 layers:
-
Epidermis. This is the outer layer.
-
Dermis. This is the middle layer.
-
Hypodermis. This is the inner, deep layer, also called subcutaneous tissue.
The epidermis is made of flat cells called squamous cells. Round basal cells are under the squamous cells. The lower part of the epidermis has pigment-producing cells called melanocytes. These cells darken the skin when exposed to the sun.
The dermis has blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, hair follicles, and glands. Some of these glands make sweat, which helps keep the body cool. Other glands make an oily substance called sebum. Sebum helps keep the skin from getting dry. Sweat and sebum reach the skin’s surface through tiny openings called pores.
The hypodermis and the lowest part of the dermis form a network of collagen and fat cells. This layer conserves heat and helps protect the body’s organs from injury.
Basal cell carcinoma
Recommended Reading: Malignant Breast Cancer Survival Rate