Whats The Prognosis For Advanced Kidney Cancer
Overall, about 13% of patients with metastatic kidney disease survive for five years after their diagnosis, according to the most recent figures. Researchers have also found a number of risk factors that can help predict your chance of survival with advanced kidney disease, including how quickly you require systemic treatment after your diagnosis, as well as certain markers in your blood for:
-
Calcium
-
Platelet counts
-
Neutrophils
Keep in mind that although 13% is a low number, many treatments are so new that their success is not yet captured in the data. Also, survival rates refer to an average outcome of a large groupit cant tell you about your disease and response to treatment.
While its not the norm, some metastatic patients remain disease-free after treatment with certain medications, though doctors still dont fully understand why these drugs beat off cancer in some people and not others.
The bottom line: Statistics are just thataverages of many people, none of whom have your unique situation . While statistics can help guide your doctors in what treatments to try, it cant tell themor anyonehow your story will unfold. You can still play a role in shaping your future by making healthy choices and thinking positive thoughts. Go ahead, were right here with you.
Metastatic Disease To The Adrenal Gland
Certain cancers can spread from other parts of the body to the adrenal gland, including kidney cancer , melanoma , lung cancer, colon cancer, and lymphoma. The best treatment for metastatic cancer is usually systemic therapy like chemotherapy, however doctors will sometimes recommend removing the adrenal gland. Adrenalectomy may be recommended when the primary disease is well controlled and the adrenal is the only site of metastatic disease, if the patient is having significant symptoms from a large adrenal tumor, or if a diagnosis needs to be made and the adrenal is the easiest site to perform a biopsy. It is uncommon for metastatic cancer to appear in the adrenal gland before the primary site is known.
The Role Of Akt/integrin
In previous evidence, the phosphoinositide 3-kinase /protein kinase B signaling pathway, which is engaged in the development and progression of many malignancies, may be disrupted by varying integrin signaling . Primary RCC cells can recognize increased levels of pro-migratory and pro-adhesive factors, like fibronectin and collagen I. These are highly concentrated in bone tissue and can promote RCC bone metastasis. Aside from adherence to ECM compounds, increased integrin 5 levels and downstream signaling via AKT can help tumor cells and facilitate their migration to bone , suggesting that integrin 5 may be a prognostic marker of RCC bone metastasis. In other tumors, an integrin 5 inhibitor being tested as cancer therapy in a phase II trial prevented tumor cell invasion and metastasis .
Also Check: Squamous Cell Carcinoma Scalp Prognosis
You May Like: Does Amelanotic Melanoma Blanch When Pressed
What Gets Stored In A Cookie
This site stores nothing other than an automatically generated session ID in the cookie no other information is captured.
In general, only the information that you provide, or the choices you make while visiting a web site, can be stored in a cookie. For example, the site cannot determine your email name unless you choose to type it. Allowing a website to create a cookie does not give that or any other site access to the rest of your computer, and only the site that created the cookie can read it.
How Does Ccrcc Form
Scientists are always working to understand how cancer forms, but it can be hard to prove. Because ccRCC can run in families, we know that changes in the VHL gene are important in causing ccRCC. The VHL gene is also changed in ccRCC from people without a family history of Von Hippel-Lindau syndrome. Scientists have learned a lot about what the VHL gene does in the body. This has given scientists clues about treatments to try for ccRCC.
Don’t Miss: Invasive Lobular Breast Cancer Survival Rate
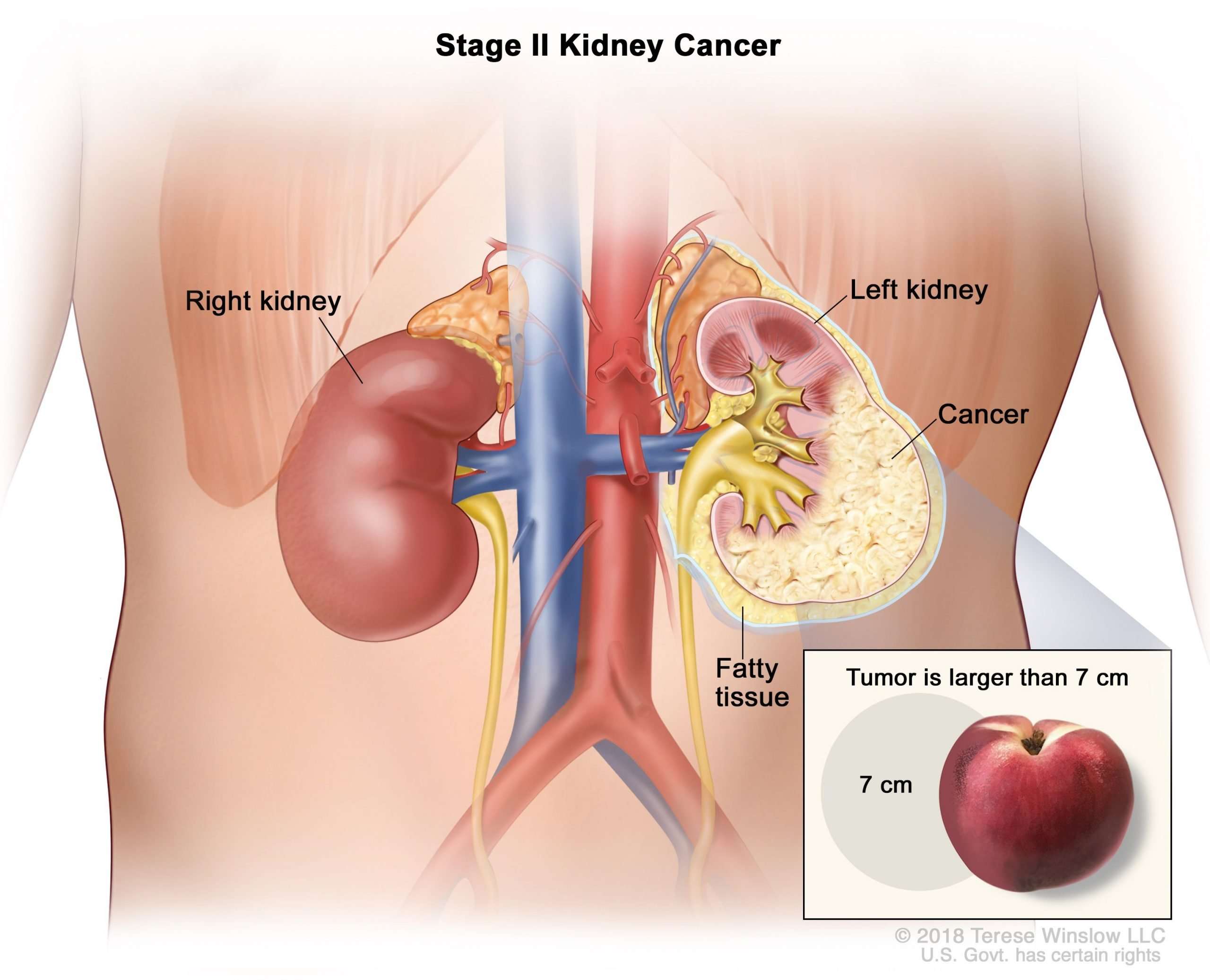
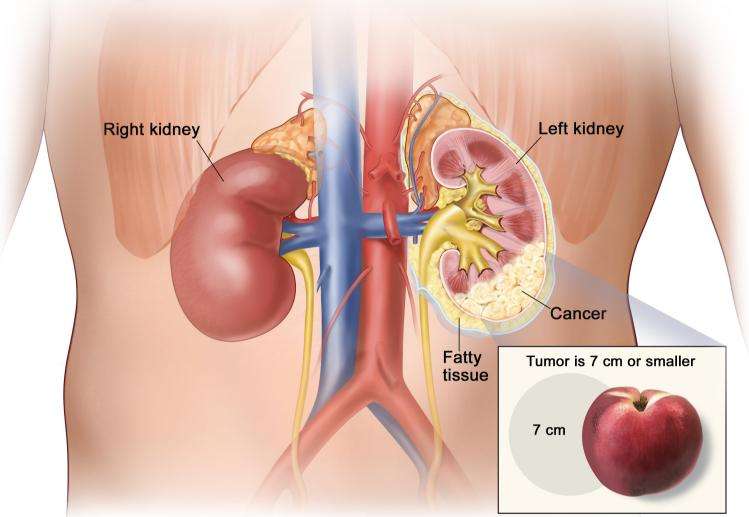
Renal Cell Carcinoma Tumor Stages
- Stage 1: The tumor is only in the kidney and it is smaller than 7 centimeters in size.
- Stage 2: The tumor is only in the kidney and it is larger than 7 cm in size.
- Stage 3: The tumor has spread beyond the kidney to adjacent areas, such as the adrenal gland.
- Stage 4: the tumor has spread beyond the kidney and adjacent structures to at least one other area of the body.
Cancer May Spread From Where It Began To Other Parts Of The Body
When cancer spreads to another part of the body, it is called metastasis. Cancer cells break away from where they began and travel through the lymph system or blood.
- Lymph system. The cancer gets into the lymph system, travels through the lymph vessels, and forms a tumor in another part of the body.
- Blood. The cancer gets into the blood, travels through the blood vessels, and forms a tumor in another part of the body.
The metastatic tumor is the same type of cancer as the primary tumor. For example, if renal cell cancer spreads to the bone, the cancer cells in the bone are actually cancerous renal cells. The disease is metastatic renal cell cancer, not bone cancer.
Read Also: What Does Skin Cancer Do To You
Read Also: Body Cancer Symptoms
What Are Causes And Risk Factors Of Renal Cell Carcinoma
The exact cause of renal cell cancer has not been determined. A number of different factors seem to contribute to renal cell cancer. These risk factors include the following:
- Cigarettesmoking doubles the risk of renal cell cancer and contributes to as many as one-third of all cases. The more someone smokes, the greater the risk is of that person developing renal cell cancer.
- Obesity is a risk factor. As body weight increases, so does the risk of developing renal cell cancer. This is especially true in women.
- Occupational exposure to petroleum products, heavy metals, solvents, coke-oven emissions, or asbestos
- Cystic kidney disease associated with chronic renal insufficiency
- Cystic changes in the kidney and renal dialysis
- Tuberous sclerosis
In its early stages, renal cell cancer usually causes no noticeable symptoms. Symptoms may occur only when cancer grows and begins to press on surrounding tissues or spread to other parts of the body. The symptoms vary considerably from person to person. Some people never develop any symptoms before the disease is discovered the cancer is found when they undergo imaging tests, such as a CT scan, for another reason. In a study in the Journal of Urology, approximately 53% of people with localized renal cell carcinoma had no symptoms.
Signs and symptoms of renal cell cancer may include the following:
- Malaise
- Anemia
- Weight loss
- Night sweats
Axillary Skin Metastasis Of Renal Cell Carcinomacase Report
Metastatic renal cell carcinoma is encountered in about 25% of cases.
-
Metastases are usually found in lymph nodes, lungs, liver, bones and brain.
-
Sometimes the metastasis can have unusual sites.
-
We present a 35 year old patient with a painful left axillary mass, appeared 2 years after nephrectomy for a left renal cell carcinoma.
-
Although the patient received tyrosin kinase inhibitors the metastasis appeared two years after treatment in an unusual site axilla.
Don’t Miss: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Grade 3 Life Expectancy
What Are The Types Of Kidney Cancer
The information in this document refers to renal cell carcinoma the most common form of kidney cancer. However, there are different types of kidney cancer, including:
- Renal cell carcinoma : This is the most common form of kidney cancer in adults and accounts for 85% of all kidney cancers. Renal cell carcinoma usually develops as a single tumor in one kidney, but it can affect both kidneys. Renal cell carcinoma begins in the cells that line the small tubes that are part of the nephrons within the kidneys. .
- Transitional cell carcinoma: Transitional cell carcinoma accounts for 6% to 7% of all kidney cancers. This cancer usually begins in the area where the ureter connects to the main part of the kidney. This area is called the renal pelvis. Transitional cell carcinoma also can occur in the ureters or bladder.
- Renal sarcoma: This is the least common form of kidney cancer, accounting for only 1% of kidney cancer cases. It begins in the connective tissues of the kidneys and, if not treated, can spread to nearby organs and bones.
- Wilms’ tumor: This is the most common type of kidney cancer in children. It accounts for about 5% of kidney cancers.
What Will Happen After Treatment
Youll be glad when treatment is over. But its hard not to worry about cancer coming back. Even when cancer never comes back, people still worry about it. For years after treatment ends, you will see your cancer doctor. Be sure to go to all of these follow-up visits. You will have exams, blood tests, and maybe other tests to see if the cancer has come back.
At first, your visits may be every 3 to 6 months. Then, the longer youre cancer-free, the less you will need to go. After 5 years, they may be done once a year.
Having cancer and dealing with treatment can be hard, but it can also be a time to look at your life in new ways. You might be thinking about how to improve your health. Call us at 1-800-227-2345 or talk to your cancer care team to find out what you can do to feel better.
You cant change the fact that you have cancer. What you can change is how you live the rest of your life making healthy choices and feeling as good as you can.
Don’t Miss: How Long Does It Take Melanoma To Metastasize
Recurrent Renal Cell Carcinoma
Renal cell cancers typically develop resistance to treatment. Resistant cancer may return locally in the area of the kidney, or in other parts of the body such as the lungs or bones. Its important to understand that not all sites of recurrence are the same. Different cancer causing mutations may lead to resistance in different locations of the body and some of these resistant cancers can be effectively treated by surgical removal while areas continue to respond to systemic treatment.
Standard treatment for recurrent cancer is with the checkpoint inhibitor combinations if not already used, otherwise combinations of other precision cancer medicines, immunotherapy, or participation in a clinical trial utilizing new, innovative therapies may provide the most promising treatment. There are several medications approved for the treatment of advanced or recurrent RCC.
Doctors can perform NGS â biomarker testing on a biopsy sample to help determine whether surgery may be beneficial and to identify cancer driving mutations that could be treated with newer precision cancer medicines available through clinical trials.
- Systemic therapy is cornerstone of treatment with checkpoint inhibitor immunotherapy.
- TKI therapy is preferred if checkpoint inhibitor has already been used.
- NGS â biomarker testing to determine if isolated metastases can be surgically removed and to determine clinical trial participation.
Questions To Ask The Doctor
-
What treatment do you think is best for me?
-
Whats the goal of this treatment? Do you think it could cure the cancer?
- Will treatment include surgery? If so, who will do the surgery?
- What will the surgery be like?
- Will I need other types of treatment, too?
- Whats the goal of these treatments?
- What side effects could I have from these treatments?
- What can I do about side effects that I might have?
- Is there a clinical trial that might be right for me?
- What about special vitamins or diets that friends tell me about? How will I know if they are safe?
- How soon do I need to start treatment?
- What should I do to be ready for treatment?
- Is there anything I can do to help the treatment work better?
- Whats the next step?
Read Also: How Long Until Melanoma Spreads
If Kidney Cancer Spreads
Cancer cells can spread from the kidney to other parts of the body. This spread is called metastasis.
Understanding how a type of cancer usually grows and spreads helps your healthcare team plan your treatment and future care. If kidney cancer spreads, it can spread to the following:
- lymph nodes around the kidney
- the main vein in the kidney
- the large vein in the abdomen leading to the heart
- the other kidney
- American Cancer Society. Kidney Cancer Stages. 2017: .
- Lane BR, Canter DJ, Rin BL, et al. Cancer of the kidney. DeVita VT Jr, Lawrence TS, Rosenberg SA. Cancer: Principles and Practice of Oncology. 10th ed. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins 2015: 63:865-884.
- National Cancer Institute. Renal Cell Cancer Treatment Health Professional Version. 2018: .
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology: Kidney Cancer . .
There Are Three Ways That Cancer Spreads In The Body
Cancer can spread through tissue, the lymph system, and the blood:
- Tissue. The cancer spreads from where it began by growing into nearby areas.
- Lymph system. The cancer spreads from where it began by getting into the lymph system. The cancer travels through the lymph vessels to other parts of the body.
- Blood. The cancer spreads from where it began by getting into the blood. The cancer travels through the blood vessels to other parts of the body.
Read Also: Melanoma On Face Prognosis
How To Manage Your Symptoms
Palliative care can relieve symptoms like pain, fatigue, and nausea. This treatment won’t cure your cancer, but it can help you feel better. You can still get your other cancer treatments while you’re getting palliative care.
Palliative care can include:
- Pain relievers and other medicines
- Relaxation techniques
Ask your doctor if your hospital or cancer center offers palliative care services.
How Cancer Stage Affects Prognosis
The stage of cancer not only helps your care team determine a treatment planit also helps predict a potential prognosis. This is done by calculating the percentage of people with kidney cancer who survive five years after diagnosis. Its important to remember that this is only a statistic based on all people with kidney cancer several years in the past, so individual statistics may vary.
The ACS estimates that about 76,080 new cases of kidney cancer may be diagnosed in 2021 in the United States. Survival numbers predict that 75 percent of these people will survive at least five years. However, the stage of cancer makes a difference. If the cancer hasnt grown outside the kidney, the five-year survival is 93 percent. For stage 4 kidney cancer, the five-year survival rate is much lower.
Its important to know that even with more advanced cancer, the five-year survival rate is based on the past five years and doesnt include new advances in clinical trials.
Don’t Miss: Basal Cell Melanoma Prognosis
How Cancer Spreads
Cancer can spread throughout the body via the lymphatic system, the blood, or grow into other tissues.
Lymphatic system: The lymphatic system contains a network of lymph vessels that carry fluid from the tissues back to the blood circulation, plus white blood cells such as lymphocytes that are active in the immune system and cells that clean up debris.
When cancer cells break off from a tumor, they can travel through the lymph system and settle into lymph nodes. The lymph nodes closest to the primary location are usually the first sites where the cancer cells form new tumors.
Blood: When cancer cells break off from a tumor, they can get into small blood vessels near the primary source. The cancer cells can then enter the bloodstream and circulate throughout the body.
Cancer cells that travel this way are called circulating tumor cells. When circulating tumor cells break through the wall of a blood vessel, they can penetrate the tissues of other organs.
Tissues: Cancer cells can spread from the primary tumor site into other tissues of the same organ or the tissues of other organs. There they can continue to grow and form a new tumor.
How Will I Feel
The symptoms of kidney cancer are different for each person. In most cases, youâll see blood in your pee. You may feel generally sick, tired, and like you donât want to eat much. And you may have:
- A fever that comes and goes
- A lump in your belly
- Night sweats, so much that you need to change your clothes or sheets
- Pain in your back or side that wonât go away
- Weight loss for no reason
You might also get symptoms where the cancer spreads. If itâs in one of your bones, you might feel pain there. In your lungs, it can give you a cough or trouble breathing.
You May Like: Survival Rate Of Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
The Effects Of Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma On The Body
Your kidneys are two bean-shaped organs located near your back. Each day, they filter wastes and extra water from your blood to produce urine. The kidneys also release hormones that regulate blood pressure and other body functions. Renal cell carcinoma can start in the filtering tubes of your kidneys. From there, it can grow and spread to other parts of your body.
Renal cell carcinoma is a type of cancer that starts in the tiny filtering tubes of the kidneys. Metastatic means the cancer has spread outside of the kidneys. It may have reached lymph nodes or organs like the brain and lungs. When cancer spreads, it can affect many different parts of your body.