How Is Melanoma Of The Head And Neck Diagnosed
Diagnosis is made by clinical exam and a biopsy. Melanoma is diagnosed by the presence of abnormal melanocytes.
Melanoma of the skin is staged based on how deeply it invades the skin layers and whether or not it has spread. A superficial or shave biopsy will not provide the accurate staging information used to guide treatment. The depth of invasion determines the risk of spread to lymph nodes or other organs. Ulceration and microsatellitosis are additional diagnostic features that, when present, are associated with a higher risk of spread. In patients without clinically enlarged lymph nodes, sentinel lymph node biopsy is used to determine if microscopic spread to lymph nodes in the neck has occurred, and is used for all but very thin melanomas unless other high-risk features are present.
This information is used for staging, to guide prognosis and further treatment. Thick melanomas are associated with a higher risk of spread to other organs, which is evaluated by pretreatment imaging. When enlarged lymph nodes are detected on clinical exam, a fine needle aspiration biopsy is performed to determine whether melanoma is present in nodes.
Some subtypes of melanoma may be less likely to spread: lentigo maligna and desmoplastic melanoma. The role of sentinel node biopsy is controversial in these cases, and will be discussed with you by your treatment team.
What Is Metastatic Melanoma
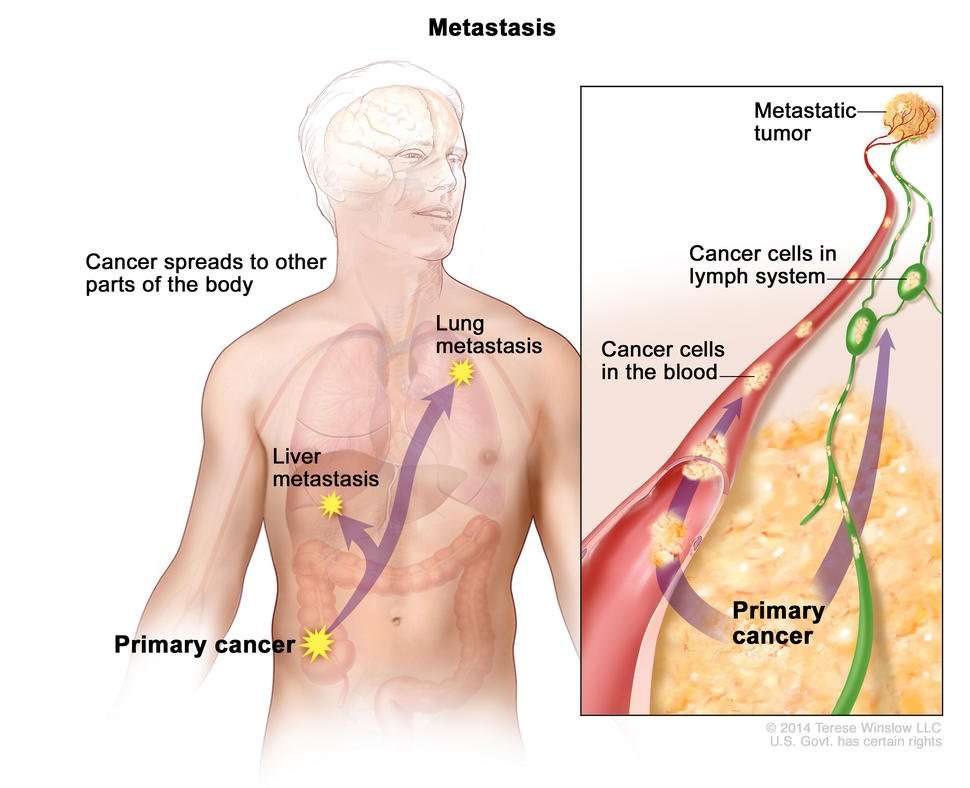
Metastatic melanoma occurs when the cancerous cells from the original tumor get loose, travel through the lymph or blood circulation, and start a new tumor somewhere else. Once it spreads, or metastasizes, the disease is known as metastatic melanoma. This type of melanoma may typically occur during stage III or stage IV. Common sites for metastases include the lymph nodes, lungs, liver, bones and brain.
About 106,110 adults in the United States will be diagnosed with melanoma in 2021, according to the American Society of Clinical Oncology . Approximately 4 percent of people are diagnosed with melanomas that have spread to distant parts of the body, according to the ASCO. This is the most advanced stage of metastatic melanoma.
The percentage of people diagnosed with melanoma that has spread to nearby lymph nodes is 8.5 percent, according to the National Cancer Institute . These cases have a slightly better prognosis.
From 2014 to 2018, the incidence rate of melanoma that had spread to distant parts of the body was 0.9 per 100,000 people, according to the NCI.
Melanoma tumors that have metastasized to other parts of the body are still considered melanoma. For example, melanoma found in the lungs is called metastatic melanoma of the lung or melanoma with lung metastases.
Topical Diphencyprone For Melanoma
Topical diphenylcyclopropenone or diphencyprone in various concentrations in solution or cream may be useful for small cutaneous melanoma metastases. The first application sensitises the patient to the chemical over about 10 days. Further applications applied to the lesions at weekly intervals cause allergic contact dermatitis, which can be very itchy and uncomfortable and may generalise. When effective, existing treated lesions stop enlarging and may shrink or disappear. Dramatic responses have been reported including regression of involved lymph nodes.
Intralesional immunotherapy for melanoma metastases using T-VEC, Allovectin-7® and Rose Bengal is under investigation.
Also Check: Well-differentiated Meaning
What Do Cutaneous Melanoma Metastases Look Like
Cutaneous melanoma metastases usually grow rapidly within the skin or under the skin surface dermal metastases are more common than subcutaneous. They are usually firm or hard in consistency. Cutaneous metastases may be any colour but are often black or red. They may also ulcerate and bleed.
Cutaneous metastatic melanoma
Epidermotropic metastatic melanoma is rare. In this case, the metastases develop more superficially than usual, within the epidermis. Epidermotropic metastatic melanoma is often initially misdiagnosed as the primary melanoma. The diagnosis of epidermotropic metastatic melanoma should be considered if multiple lesions arise with similar pathology.
Subcutaneous metastases are skin coloured or bluish lumps. They are usually painless.
Subcutaneous metastatic melanoma
Obstruction of lymphatic vessels due to melanoma in the lymph nodes or surgical removal of the lymph glands can result in swelling of the associated limb .
Metastatic melanoma
Where Else Does Melanoma Spread To
When melanoma advances to stage 3, it means the tumor has spread to the lymph nodes or the skin around the primary tumor and lymph nodes. In stage 4, the cancer has moved to other areas far beyond the lymph nodes, like your internal organs. The most common places melanoma spreads to are the:
- lungs
- brain
- stomach, or abdomen
These growths will cause different symptoms, depending on which areas it has spread to. For example, you may feel breathless or constantly cough if the cancer has spread to your lungs. Or you may have a long-term headache that wont go away if it has spread to your brain. Sometimes the symptoms for stage 4 melanoma may not appear for many years after the original tumor was removed.
Talk to your doctor if youre feeling new pains and aches or symptoms. Theyll be able to help diagnose the cause and recommend treatment options.
Also Check: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Stage 3 Survival Rate
Who Gets Metastatic Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of Skin
- Metastatic Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Skin is generally uncommon and it affects elderly or older adults some cases rarely develop in children too
- It can occur in both males and females
- The condition is prevalent worldwide, though dark-skinned individuals are affected less than lighter-skinned individuals
Box 1detection Of Melanoma: Summary Of Different Aspects Of Occult Melanoma Detection
Before melanoma cells metastasize they extend into the adjacent epidermis. Field cells were characterized by Bastian et al. . Epidermis adjacent to the acral lentiginous melanoma can harbor cells with a high level of DNA amplifications that can be detected by fluorescent in situ hybridization. Genetic analysis of these cells suggests that they precede melanoma in situ. They also extend significantly into normal skin without a correlation to tumor thickness or size .
Another potential step in the evolution of a primary tumor into its metastasis to lymph nodes is local lymphatic invasion. This is usually only assessed in the excisions of the primary tumor on hematoxylin and eosin slides. In a recent study, immunohistochemical stains with antibodies against podoplanin and S-100 were combined with multispectral imaging analysis. This increased the sensitivity of detection of lymphatic invasion sevenfold. Dadras et al. used the antibody against lymphatic endothelial hyaluronan receptor -1 to decorate lymphatic vessels in the tumor and its close proximity to its border . Additionally, they assessed expression of VEGF-C and VEGF-D in melanomas. As it turned out, VEGF-C and not VEGF-D correlated with a higher frequency of melanoma metastases to sentinel lymph nodes. The relative area of vascular invasion of primary melanomas correlated with metastasis to sentinel lymph nodes to a greater extent than did tumor thickness , as determined by the Wilcoxon rank test.
Read Also: Well Differentiated Meaning
This Is Why A New Though Tiny Spot Or Speck Should Not Be Ignored Even If It Looks Normal
Melanoma
Ultimately I believe genetics will help determine the behavior of these, but until we have that data we have to look at patterns, explains Dr. Gordon.
In general, survival rate of melanomas depends on depth of the cancer.
This depth is determined by a dermapathologist who examines a biopsy of the suspicious spot, which includes a surrounding margin of skin also taken out, under a microscope.
The rule of thumb is that the height of the melanoma above the surface of the skin is equal to its depth below the skin surface.
Dr. Gordon explains, In general, smaller lesions the thinner they are and the better outcomes people have.
Some melanomas will grow in a spreading pattern on the skin , but some will grow in a deep pattern that are more aggressive .
There is no easy way to decipher the spread of melanoma until it is biopsied and sometimes until further tests are performed.
Dr. Gordons interests include medical dermatology, particularly the treatment and prevention of melanoma and other skin cancers in athletes. For 2016, 2017 and 2018 Texas Monthly Magazine selected her as one of the Texas Super Doctors Rising Stars.
Lorra Garrick has been covering medical, fitness and cybersecurity topics for many years, having written thousands of articles for print magazines and websites, including as a ghostwriter. Shes also a former ACE-certified personal trainer.
Metastatic Behavior In Melanoma: Timing Pattern Survival And Influencing Factors
Faruk Tas
1Institute of Oncology, Istanbul University, 34390 Istanbul, Turkey
Abstract
Metastatic melanoma is a fatal disease with a rapid systemic dissemination. This study was conducted to investigate the metastatic behavior, timing, patterns, survival, and influencing factors in MM. 214 patients with MM were evaluated retrospectively. Distant metastases were the most frequent for patients initially metastatic. The median and 1-year survival rates of initially MM patients were 10 months and 41%, respectively. The median time to metastasis for patients with localized disease was 28 months. The timing of appearance of metastases varied minimally however, times to metastases for distant organs varied greatly. For the first metastatic pathway, more than half of the primary metastases were M1A . These findings were in contrast to the results compared with those with metastatic in diagnosis . The median and 1-year survival rates of all patients were 12 months and 49%, respectively. Outcome was higher in M1A than visceral metastases . In conclusion, the fact that over half of all recurrences/metastases occurred within 3 years urges us to concentrate follow-up in the early time periods following diagnosis. Because the clinical behavior of MM is variable, the factors for survival consisting of site and number of metastases should be emphasized.
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
3.1. Metastases at Presentation
3.2. Metastases during Follow-Up
| From |
4. Discussion
Also Check: What Does Stage 3 Melanoma Look Like
Melanocyte As The Source Cell Of Melanoma
Melanoma is known to be more aggressive than most other cancers. Introduction of the Ras oncogene into normal melanocytes resulted in significantly more metastasizing melanomas than similar introduction into normal fibroblasts or epithelial cells . This provides evidence that an intrinsic feature of the melanocyte might be responsible for the rapid development of metastatic disease. Since melanocytes are derived from the neural crest, they are characterized by expression of the motility-associated genes that not only mediate the neural crest but also tumor cell migration. Some of those genes are transcription factor Slug, endothelin receptor B, ERBB3, CD44 and Nodal . Alternatively, the melanogenesis process that defines the melanocyte, might be the culprit . Formation of melanin consists of transformation of l-tyrosine to melanin pigment through several oxidativereduction reactions . Melanogenesis thus forms oxidative environment and some of its intermediates are directly toxic and mutagenic. Melanin scavenges biomolecules and oxygen. All these processes might significantly enhance the effects of typical oncogenes. Inhibition of melanogenesis should therefore decrease melanoma aggressiveness and act as an enhancer of current therapy protocols . We have recently shown that the inhibition of melanogenesis by phenylthiourea and d-penicillamine enhanced cytoxicity of cyclophosphamide and IL-2-activated lymphocytes against melanoma cells .
Signs Melanoma Has Spread
Melanoma is the most dangerous type of because it spreads so quickly and so easily. That’s why it’s important to catch melanoma early. After it starts to spread, melanoma is harder to treat.
Melanoma can spread in three ways: directly through your skin, by getting into your bloodstream, and by getting into your lymphatic systempart of your immune system.
Melanoma can spread to almost any part of the body. It usually spreads on your skin, under your skin, or into your lymph nodes. If melanoma gets into your lymphatic system or your bloodstream, it can also spread to distant parts of your body. This is metastatic . Metastatic melanoma spreads most often to the lungs, brain, liver and bones.
If melanoma spreads, it usually happens within two years of getting a diagnosis. The chance that it will spread is higher if your melanoma was thick or ulcerated , if it was already in your lymph nodes at the time of diagnosis, or if you are older than 50.
Read Also: What Does Cancer Tissue Look Like
What Does Scalp Melanoma Look Like
Melanoma is one of the most serious forms of cancer, and because its appearance can closely mimic natural moles, freckles, and age spots, it can be easy to overlook. Its important to know what to look for and perform regular skin cancer screenings to ensure you receive treatment for this condition in the earliest stages. According to Dr. Gregory Walker of U.S. Dermatology Partners in Waco, Texas, Melanoma can be easily overlooked in obvious places on the body, but many people dont know that the scalp, fingernails and toenails, and other harder to see areas often hide this condition until it has progressed to more advanced stages. Patients who know what to look for and regularly screen their skin for cancers, are much more likely to receive a diagnosis in early, more treatable stages. Keep reading to hear more from Dr. Walker about what scalp melanoma looks like and how to check for this condition and prevent serious health concerns.
How Fast Does Melanoma Grow
Some types of melanoma can grow very quickly, becoming life-threatening in as little as six weeks. If left untreated it can spread to other parts of the body.
Nodular melanoma is a highly dangerous form of melanoma that looks different from common melanomas and can grow in just a few weeks. Raised and even in color, nodular melanoma are often red, pink, brown, or black. It can be life-threatening if not detected and removed quickly. See your doctor immediately if you notice any of these changes.
Its also important to note that while sun exposure is a major risk factor in melanoma, the disease can develop in parts of the body that get little or no sun exposure.
Recommended Reading: How To Tell If Skin Cancer Is Melanoma
Recommended Reading: Invasive Mammary Carcinoma Survival Rate
How Does Melanoma Make You Feel
Melanoma can cause pain in the bones where it’s spread, and some peoplethose with very little body fat covering their bonesmay be able to feel a lump or mass. Metastatic melanoma can also weaken the bones, making them fracture or break very easily. This is most common in the arms, legs, and spine.
What Is The Most Effective Treatment For Melanoma
Wide excision The main treatment for melanoma is surgical removal, or excision, of the primary melanoma on the skin. The extent of the surgery depends on the thickness of the melanoma. Most melanomas are found when they are less than 1.0 mm thick, and outpatient surgery is often the only treatment needed.
Also Check: Chances Of Squamous Cell Carcinoma Spreading
How Do You Know If Melanoma Has Spread To Lymph Nodes
The most common symptom if cancer has spread to the lymph nodes is that they feel hard or swollen. Swollen lymph nodes in the neck area can make it hard to swallow. Cancer cells can also stop lymph fluid from draining away. This might lead to swelling in the neck or face due to fluid buildup in that area.
Where In The Body Cancer Can Spread
Cancer can spread to almost every part of the body. Some types of cancer tend to spread to certain parts of the body. For example:
-
Breast cancer tends to spread to the bones, liver, lungs, chest wall, and brain
-
Lung cancer tends to spread to the brain, bones, liver, and adrenal glands
-
Prostate cancer tends to spread to the bones
-
Colon and rectal cancers tend to spread to the liver and lungs
Less frequently, cancer can spread to the skin, muscle, or other organs in the body. Cancer cells can also spread to the lining around the lungs called the pleural cavity. It can also spread to the space around the belly called the peritoneal cavity. When these cancer cells cause fluid to build up in these areas, it is called malignant pleural effusion and malignant ascites.
Read Also: How Quickly Can Melanoma Metastasis
Recommended Reading: Melanoma Stage 3 Life Expectancy
How Do You Treat Stage 4 Melanoma
The good news is that even stage 4 melanoma can be treated. The sooner the cancer is found, the sooner it can be removed and the higher your chances are for recovery. Stage 4 melanoma also has the most treatment options, but these options depend on:
- where the cancer is
- how advanced the cancer has become
- your age and overall health
How you respond to treatment also affects your treatment options. The five standard treatments for melanoma are:
- surgery: to remove the primary tumor and affected lymph nodes
- chemotherapy: a drug treatment to stop growth of cancer cells
- radiation therapy: the application of high-energy X-rays to inhibit growth and cancer cells
- immunotherapy: treatment to boost your immune system
- targeted therapy: the use of drugs or other substances to attack cancer drugs
Other treatments may also depend on where the cancer has spread to. Your doctor will discuss your options with you to help map out a treatment plan.
Dormancy In Metastatic Melanoma
The time period between removal of the primary tumor and subsequent recurrence of disease is referred to as metastatic dormancy. In melanomas, a period of dormancy may end with the emergence of recurrent disease at a metastatic site and only rarely at the site of the primary tumor. Melanomas, as well as some other cancers, such as prostate and some types of breast cancer, often have very protracted courses in which metastatic disease does not manifest until years or even decades after removal of the primary tumor. Clinically localized melanoma can recur after disease-free intervals of 10 years or more . In fact, a subset of melanomas will have ultra-long dormancy with recurrence greater than 20 years later . Other tumor types, such as lung and pancreatic adenocarcinomas tend to follow a much swifter clinical course in which discovery of the primary tumor and subsequent metastasis is often a temporally contiguous event . While these differences in metastasis patterns may in part reflect differences in detection amongst different cancer types, it has also been proposed that such observations suggest that certain tumor types might gain full metastatic competency earlier in tumor progression .
You May Like: Idc Breast Cancer Survival Rate