How To Prevent Basal Cell Cancer
To significantly minimize the basal cell skin cancer risk, you can:
- Avoid getting out in the sun during the daytime. There are many places where the suns rays are strongest between 10 am and 4 pmschedule outdoor activities for other times during the day, even in winter or in cloudy weather.
- You can use a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of a minimum of 30, even on cloudy days. Generously, apply sunscreen and reapply after two hours or more often, when swimming or sweating.
- Cover skin with tightly woven dark clothing. Covering your legs and arms with a broad-brimmed hat provides more protection than a visor or baseball cap.
- Many companies also sell sun-protective clothing. Dermatologists recommend a reputed brand. Also, dont forget to wear sunglasses. Search for those blocking both UV radiation types UVA and UVB.
- You should check your skin regularly and report changes to the doctor. Examine the skin for any new skin growth or changes in freckles, birthmarks, or bumps. Check your face, ears, scalp, and neck on mirrors.
- Dont use tanning beds. Tanning beds emit Ultra-violet rays, increasing the risk of basal cell skin cancer.
- Examine the trunk and chest and underside tops of hands or arms. Examine both the back and front of legs and feet, including spaces and ole between the toes. Also, examine your genital area and the area around your buttocks.
Treatment Options
The type of treatment would depend on any of the factors:
Identifying The Types Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
Did you know that skin cancer is the most frequently diagnosed cancer in the US and globally? Of the various kinds of skin cancer, basal cell carcinoma is the most common, with up to 4.3 million new cases discovered annually in America. The good news? In the early stages, most types of basal cell carcinoma have a high cure rate and cause very little damage.
This month, were exploring the types of basal cell carcinoma, including the causes, symptoms, and prognosis for recovery.
Recurrent Basal Cell Carcinoma
Basal cell carcinomas are the most common type of skin cancer, according to the American Cancer Society. These cancers develop within the basal cell layer of the skin, in the lowest part of the epidermis.
Patients who have had basal cell carcinoma once have an increased risk of developing a recurrent basal cell cancer. Basal cell cancers may recur in the same location that the original cancer was found or elsewhere in the body. As many as 50 percent of cancer patients are estimated to experience basal cell carcinoma recurrence within five years of the first diagnosis.
Basal cell carcinomas typically grow slowly, and it is rare for them to metastasize or spread to nearby lymph nodes or other parts of the body. But early detection and treatment are important.
After completing treatment for basal cell carcinoma, it is important to perform regular self-examinations of the skin to look for new symptoms, such as unusual growths or changes in the size, shape or color of an existing spot. Skin cancers typically develop in areas of the body that are exposed to the sun, but they may also develop in areas with no sun exposure. Tell your oncologist or dermatologist about any new symptoms or suspicious changes you may have noticed.
- Have a history of eczema or dry skin
- Have been exposed to high doses of UV light
- Had original carcinomas several layers deep in the skin
- Had original carcinomas larger than 2 centimeters
Read Also: Is Melanoma Bad
How To Spot A Bcc: Five Warning Signs
Check for BCCs where your skin is most exposed to the sun, especially the face, ears, neck, scalp, chest, shoulders and back, but remember that they can occur anywhere on the body. Frequently, two or more of these warning signs are visible in a BCC tumor.
Please note: Since not all BCCs have the same appearance, these images serve as a general reference to what basal cell carcinoma looks like.
An open sore that does not heal
A reddish patch or irritated area
A small pink growth with a slightly raised, rolled edge and a crusted indentation in the center
A shiny bump or nodule
A scar-like area that is flat white, yellow or waxy in color
What Do Basal Cell Carcinomas Look Like
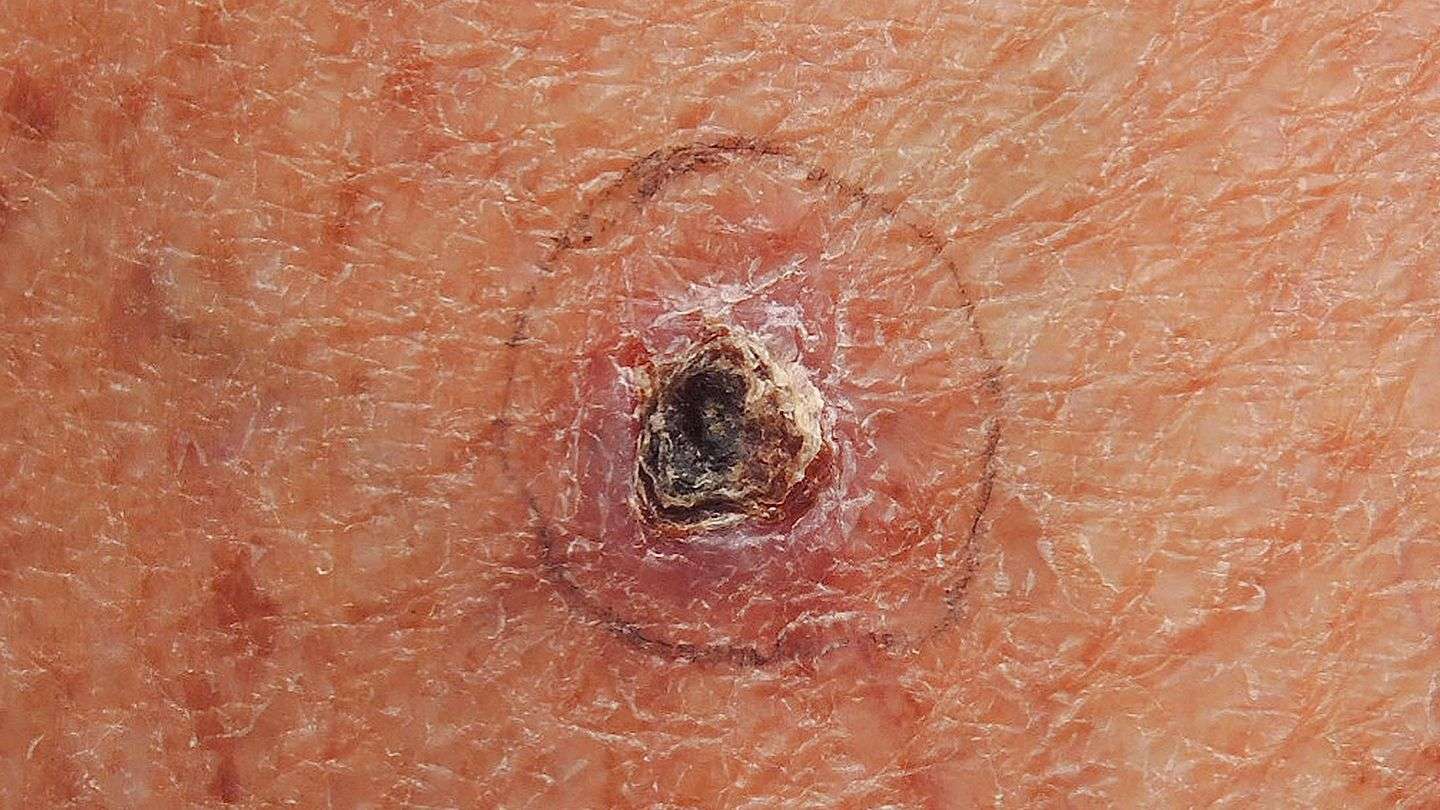
BCCs often appear as a change in your skin, such as a lump or a sore that does not heal.
The main features are:
- slow growing months to years
- a pearly white, skin-coloured or pink bump that is translucent
- waxy, small, raised lesions that may have a dent in the centre
- brown or blue-black areas, in some cases
- a scaly red flat mark on the skin, in some cases
- a tendency to bleed or turn into an ulcer
- scaly, oozing or crusted areas
- varying in size from a few millimetres to several centimetres in diameter.
You May Like: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Survival
How Can Basal Cell Carcinoma Be Prevented
The most important way to prevent BCC is to avoid sunburn. This is especially important in childhood and early life. Fair skinned individuals and those with a personal or family history of BCC should protect their skin from sun exposure daily, year-round and lifelong.
- Stay indoors or under the shade in the middle of the day
How Is Basal Cell Carcinoma Diagnosed
BCC is diagnosed clinically by the presence of a slowly enlarging skin lesion with typical appearance. The diagnosis and histological subtype is usually confirmed pathologically by a diagnostic biopsy or following excision.
Some typical superficial BCCs on trunk and limbs are clinically diagnosed and have non-surgical treatment without histology.
Recommended Reading: Stage Iii Melanoma
What Does Morpheaform Basal Cell Carcinoma Look Like
One of the defining features of morpheaform BCC is its shape. These tumors tend to be less regular and do not have well-defined edges. They often have long strands that extend off the main tumor node. This means the tumors can grow into other layers of the skin, or nearby muscles or other structures. The irregular shape of these tumors can make them difficult to treat.2
Risk Factors Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
Having a risk factor does not mean that you will get cancer not having risk factors doesnt mean that you will not get cancer. Some risk factors are out of your control, such as your complexion or family history. However, some risk factors, such as exposure to ultraviolet light, are factors you can control. People who think they may be at risk should discuss this with their doctor.
Also Check: How Many People Die From Skin Cancer
Also Check: Idc Breast Cancer Survival Rate
Treatment For Basal Cell Carcinoma
With this type of skin cancer, if your dermatologist removes the tumor for biopsy, you probably wont need any further basal cell carcinoma treatments.
If your tumor is large, or is on your face , neck or ears, your doctor will probably recommend treating basal carcinoma with Mohs surgery, which is a procedure thats designed to leave the smallest possible scar.
Either way, youll need to keep a close watch on your skin McMichael said that once youve had this type of tumor, youre at higher risk of getting another one in the next three years.
You May Like: How To Know Skin Cancer Symptoms
Diagnosing Basal Cell Carcinoma
The most common way dermatologists diagnose basal cell carcinoma is with a full body skin check.
Stevenson says during the diagnosis process dermatologists are looking for papules with skin cancer characteristics. Sometimes dermatologists will use a tool called a dermatoscope, which uses a polarized light to look for other signs of skin cancer. With their training, dermatologists should be able to tell patients if the lesion is benign or something that should be removed because of a skin cancer concern.
RELATED: Do You Need to Wear Sunscreen Indoors?
Don’t Miss: Large Cell Cancers
Nevoid Basal Cell Carcinoma Syndrome
In addition to basal cell carcinoma, this autosomal dominant disorder can result in the early formation of multiple odontogenic keratocysts, palmoplantar pitting, intracranial calcification, and rib anomalies. Various tumors such as medulloblastomas, meningioma, fetal rhabdomyoma, and ameloblastoma also can occur.
Odontogenic keratocysts, palmoplantar pitting, intracranial calcification, and rib anomalies may be seen. Mutations in the hedgehog signaling pathway, particularly the patched gene, are causative.
Go to Nevoid Basal Cell Carcinoma Syndrome to see more complete information on this topic.
What Else Could This Skin Lesion Be
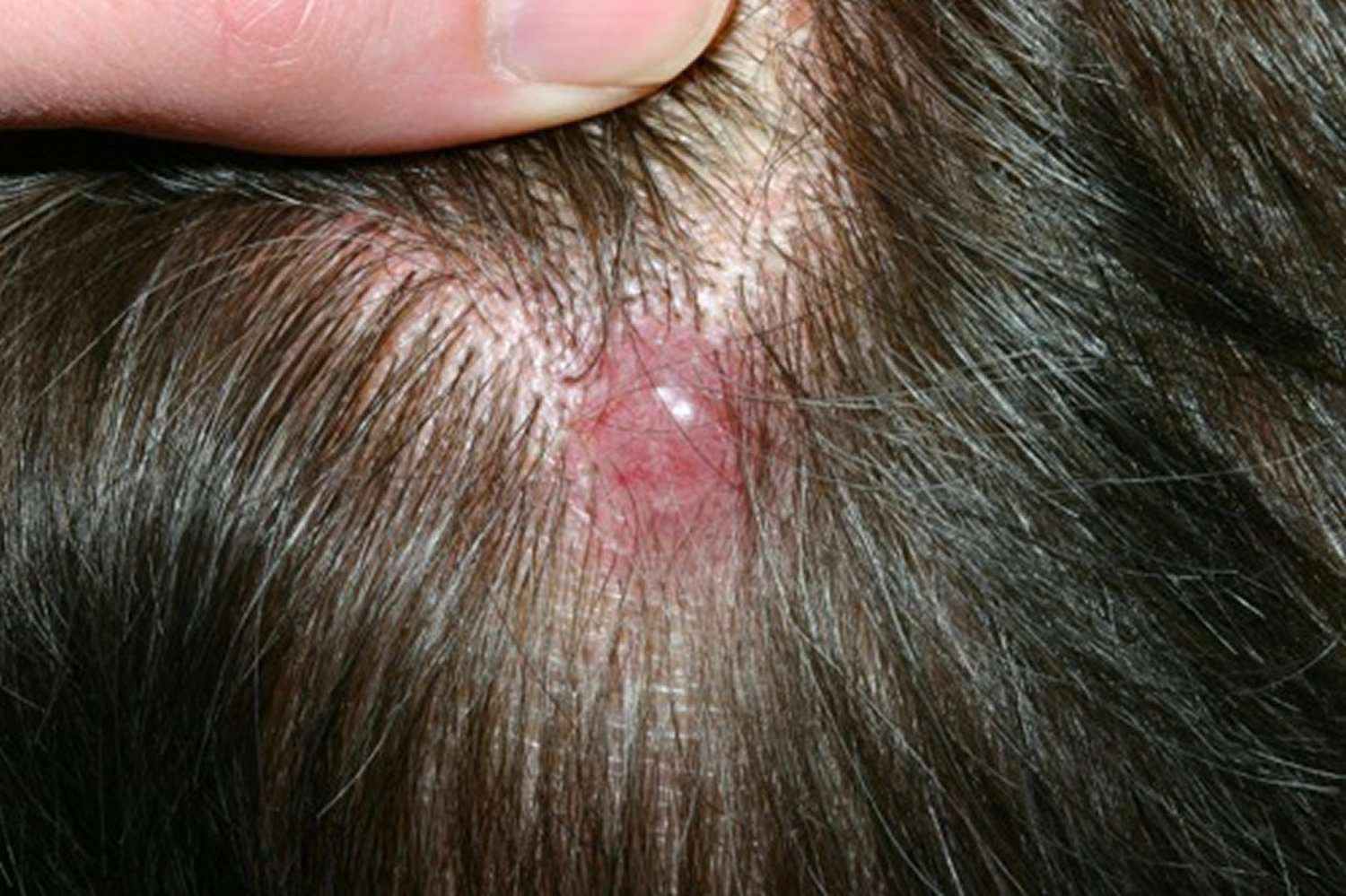
Other skin conditions may look like BCC. Nodular BCC without ulceration may look similar to:3
- Molluscum contagiosum, a viral infection that causes numerous small bumps.
- Sebaceous hyperplasia, a condition characterized by small yellow bumps.
- Intradermal melanocytic nevus, a nest of melanocytes in the dermis layer of skin.
- Fibrous papule, a firm bump that may develop on the nose.
- Other skin cancers
Ulcerated BCC may be confused with squamous cell carcinoma or keratoacantoma.
Conditions that look similar to superficial BCC include:3
Read Also: Amelanotic Melanoma Blanch
Common Side Effects People Have Besides Basal Cell Carcinoma *:
Difference Between Skin Cancer And Melanoma
Skin Cancer vs Melanoma
Melanoma is a type of highly invasive skin cancer. It is the most dangerous and most frequently heard of cancer of the skin. However, there are many other types of skin cancers, as well. This article will outline the causes, clinical features, symptoms, investigation and diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment of skin cancers, especially of melanoma.
Melanoma
Melanoma is a highly invasive carcinoma. It is an uncontrollable overgrowth of melanocytes. Melanocytes are responsible for producing skin pigments. Therefore, melanoma can arise from any part of the body where there are melanocytes. In the UK, 3500 new cases are identified per year. 800 people have died only during the last 20 years. Melanoma is commoner among Caucasians. It is commoner in females.
Prevention of exposure to UV light is thought to be preventive of melanoma. As a rule of thumb, avoiding sun exposure between 9 am and 3 pm is a good method. Sun creams and other preparations may help, but there is a risk of allergies and other skin changes with the use of these applications. Less invasive melanomas with lymph node spread have a better prognosis than deep melanomas without lymph node spread. When melanoma is spread to lymph node, the number of involved nodes is related to prognosis. Widely metastatic melanoma is said to be incurable. Patients tend to survive 6 to 12 months after diagnosis.
Skin Cancers
Layers of the skin, Author: Don Bliss, National Cancer Institute
Read Also: 2nd Stage Cancer
Apple Cider Vinegar Baking Soda And Coconut Oil
1 User Review
Cured 3 BCC with ACV and baking soda with coconut oil.
The first time I removed my bcc, I used ACV soaked in a cotton ball and taped it to my BCC every night. After a few days it turned red and after about a month I was BCC free.The second time I removed my bcc, it was close to my eyes, so I used baking soda with coconut oil 1 tbsp each mixed and made a paste and applied it to the area. After about 2 weeks I was bcc free. I had to deal with scabbing and redness but after that I’m bcc free.
Treating Basal Cell Carcinoma
Basal cell carcinomas must be removed. Methods include
- surgery
- electrosurgery
- and curettage
A painstaking procedure called Mohs surgery minimizes the amount of tissue removed. It is often performed when the cancer is located in the skin folds around the nose, at the corners of the eyes, and around the ears.
If you have had one basal cell carcinoma, you are at higher risk of developing others. Regular checkups are recommended for five years after removal of a basal cell carcinoma to make sure the cancer has not returned, and no new ones have appeared.
Recommended Reading: Melanoma On Face Prognosis
Putative Genes For Basal Cell Carcinoma
BRCA1-associated protein 1
Pathogenic variants in the BAP1 gene are associated with an increased risk of a variety of cancers, including cutaneous melanoma and uveal melanoma. Although the BCC penetrance in individuals with pathogenic variants in BAP1 is not known, there are several BAP1 families that report diagnoses of BCC. In one study, pathogenic variant carriers from four families reported diagnoses of BCC. Tumor evaluation of BAP1 showed loss of BAP1 protein expression by immunohistochemistry in BCCs of two germline BAP1 pathogenic variant carriers but not in 53 sporadic BCCs. A second report noted that four individuals from families with BAP1 germline pathogenic variants were diagnosed with a total of 19 BCCs. Complete loss of BAP1 nuclear expression was observed in 17 of 19 BCCs from these individuals but none of 22 control BCC specimens. Loss of BAP1 nuclear expression was also reported in a series of 7 BCCs from individuals with loss of function BAP1 variants, but only in 1 of 31 sporadic BCCs.
Do Some People Have A Higher Risk Of Getting Basal Cell Carcinoma
Yes. The main risk factor for getting this skin cancer is:
-
UV-damaged skin caused by the sun or tanning beds. Each time you go outdoors without protecting your skin from the sun or use a tanning bed, you increase your risk of getting skin cancer.
There are other risk factors for BCC, which include:
-
Color of your skin, hair, and eyes. This skin cancer develops in skin damaged by UV light, and skin is more easily damaged by UV light if you have one or more of the following:
- Skin that burns easily and rarely tans
- Sun-sensitive skin that freckles easily
- Naturally blonde or red hair
- Blue or green eyes
Sunburns. If youve had sunburns, especially blistering ones in your youth, you have a higher risk of developing this skin cancer.
Where you live. Living in an area that gets intense sunlight year-round, such as Florida or California, increases your risk of getting skin cancer. People who live at a high altitude also have an increased risk.
Previous skin cancer. If youve had any type of skin cancer, you have a greater risk of getting another one.
Weakened immune system. Anything that weakens your immune system increases your risk of getting this skin cancer. In fact, BCC is one of the cancers most likely to develop when the immune system weakens.If you received an organ transplant, the medication you take to prevent your body from rejecting the organ suppresses your immune system. This increases your risk of developing basal cell skin cancer greatly.
Image
Don’t Miss: Skin Cancer Pictures Mayo Clinic
How Can I Prevent Basal Cell Carcinoma From Recurring
Most basal cell carcinomas can be treated and cured. However, it is possible for these types of cancers to recur or for new skin cancers to appear.
Do the following to reduce the risk of new cancers occurring:
- Keep all follow-up appointments with your GP or skin specialist.
- Regularly check all your skin . If you see anything that is growing, bleeding or in any way changing, go and see your doctor straight away. See skin checks
- Protect your skin from the sun and avoid indoor tanning. This is essential to prevent further damage, which will increase the risk of getting another skin cancer.
Mohs Microscopically Controlled Surgery
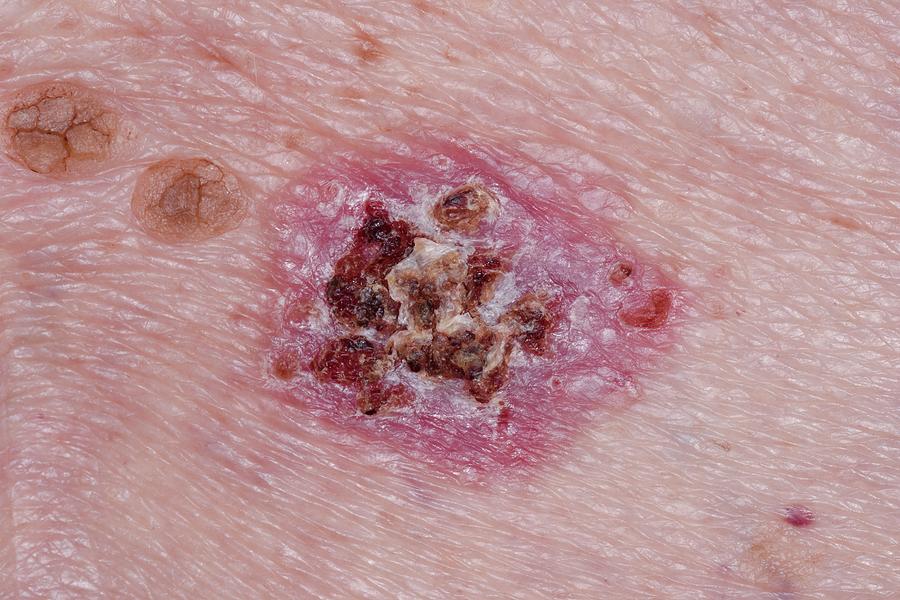
|
Because skin cancer cells often have spread beyond the edges of the visible patch on the skin, doctors sometimes use a special surgical technique to make sure they remove all of the cancer. In this technique, called Mohs microscopically controlled surgery or Mohs micrographic surgery, doctors first remove the visible tumor and then begin cutting away the edges of the wound bit by bit. During surgery, doctors examine pieces of tissue to look for cancer cells. Tissue removal from the area continues until the samples no longer contain cancer cells. This procedure enables doctors to limit the amount of tissue removed and thus is especially useful for cancers near such important sites as the eye. After removing all of the cancer, doctors decide how best to replace the skin that has been cut away. They may bring the edges of the remaining skin together with sutures or use a skin graft or skin flap. Or they may place dressings on top of the wound and let the skin heal on its own. Mohs surgery reduces recurrence rates for skin cancers. This surgery is useful for basal cell and squamous cell cancers but is less often used for melanoma. |
Also Check: Can Melanoma Be Skin Colored
You May Like: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Survival Rate Stage 4