Amount Of Exposure To Sunlight
The damaging effects of ultraviolet radiation accumulate over the years. In general, the risk of developing skin cancer increases with the amount of time spent under the sun and the intensity of radiation. The intensity of radiation varies according to the season of the year, time of day, geographic location , elevation above sea level, reflection from surfaces , stratospheric ozone, clouds, and air pollution.
Recent studies have focused on the effects of intermittent sun exposure in comparison to chronic exposure. It appears that the type of exposure may influence the type of cancer that develops. For example, intermittent solar exposure may be an important factor leading to the onset of basal cell carcinoma of the skin. Childhood sun exposure may also play an important part in the development of these cancers later in adult life. The pattern for cutaneous melanoma is similar to that for basal cell carcinoma.
In contrast, the relationship between squamous cell carcinoma and solar UVR appears to be quite different. For squamous cell tumours, high levels of chronic occupational sunlight exposure, especially in the 10 years prior to diagnosis, results in an elevated risk for this cancer in the highest exposure group.
How Does The Sun Cause Cancer
- How does the sun cause skin cancer?
1st March 2022
With the sun beginning to emerge, many will want to spend a bit more time in parks, gardens and at the beach to get that healthy glow. But did you know that this glow is radiation burn caused by exposure to ultraviolet light? While being in the sunshine supplies us with vitamin D and can improve our mood, this radiation burn also increases the risk of skin cancer.
Common Skin Cancer Symptoms And Causes
Sunlight contains ultraviolet light that is harmful to human skin cells. These energetic light waves can produce mutations in the DNA of skin cells, which in turn can lead to skin cancer. In areas close to the equator, the incidence of cutaneous cancers is dramatically higher due to the increase in sun exposure.
The most obvious skin cancer warning sign is the development of a persistent bump or spot in an area of sun-damaged skin. These spots are likely to bleed with minimal trauma and produce a superficial erosion.
Ultraviolet Light and Skin Cancer
Ultraviolet rays are classified by three types: UVA, UVB, and UVC. UVC is very dangerous, but it does not reach the earths surface due to the ozone layer. Exposure to both UVA and UVB radiation poses potential skin cancer risks.
UVA Radiation
UVA light is the most abundant source of solar radiation. Scientists think it can penetrate the top layer of skin, potentially damaging connective tissue and causing skin cancer. An estimated 50% of UVA exposure occurs in the shade. Light skin is far more vulnerable to UVA radiation: while dark skin allows only 17.5% of UVA to penetrate, light skin allows 55% of UVA light to pass through.
UVB Radiation
How Skin Cancer Develops
Recommended Reading: Lobular Breast Cancer Stage 1
What Are The Symptoms Of Skin Cancer
The most common warning sign of skin cancer is a change on the skin, typically a new mole or skin lesion or a change in an existing mole.
- Basal cell carcinoma may appear as a small, smooth, pearly or waxy bump on the face, ears or neck, or as a flat pink, red or brown lesion on the trunk or arms and legs.
- Squamous cell carcinoma can appear as a firm, red nodule, or as a rough, scaly flat lesion that may bleed and become crusty. Both basal cell and squamous cell cancers mainly occur on areas of the skin frequently exposed to the sun, but can occur anywhere.
- Melanoma usually appears as a pigmented patch or bump but can also be red or white. It may resemble a normal mole, but usually has a more irregular appearance.
When looking for melanoma, think of the ABCDE rule that tells you the signs to watch for:
- Asymmetry — the shape of one half doesn’t match the other
- Border — edges are ragged or blurred
- Color — uneven shades of brown, black, tan, red, white or blue
- Diameter — A significant change in size , although any mole that is getting larger should be brought to the attention of your dermatologist many melanomas are being diagnosed at much smaller diameters.
- Evolving — any new spot or mole that is changing in color, shape or size or itches or bleeds.
Continued
What Is The Difference Between Uva And Uvb Rays
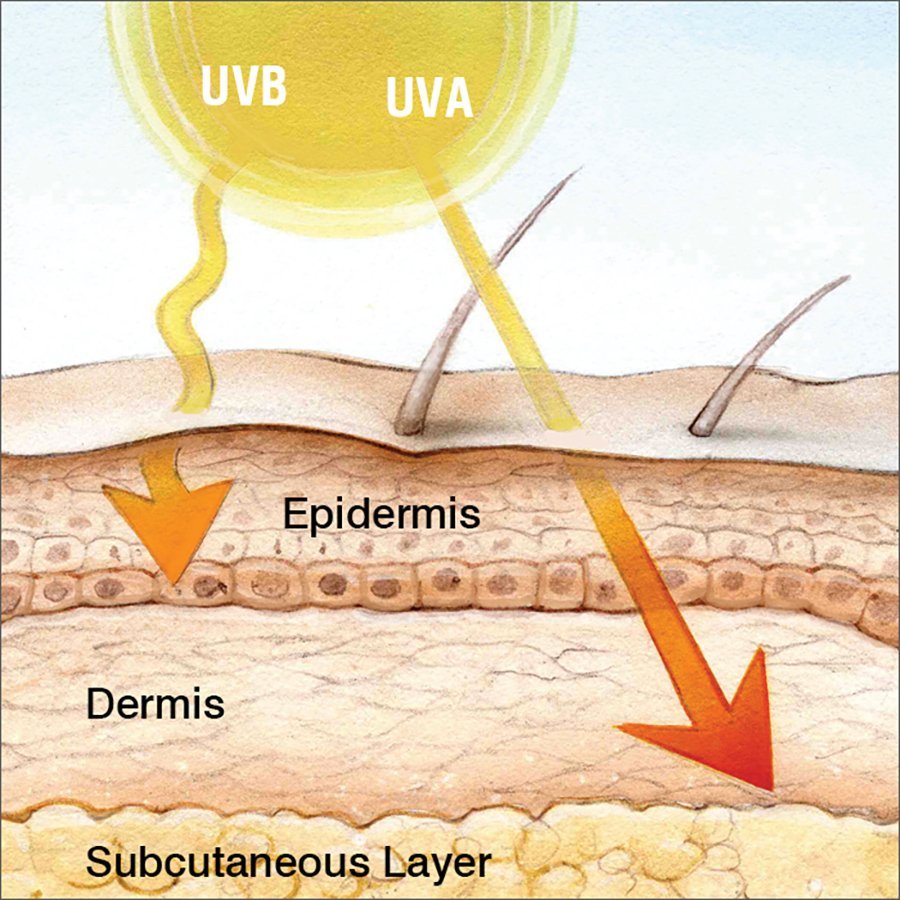
There are many different types of rays present in sunlight. The rays that are most damaging to our skin are called ultraviolet rays. There are two basic types of ultraviolet rays that reach the earths surfaceUVB and UVA. UVB rays are responsible for producing sunburn. The UVB rays also play the greatest role in causing skin cancers, including the deadly black mole form of skin cancer .
UVA rays also play a role in skin cancer formation. In addition, the UVA rays penetrate more deeply into the skin and play a greater role in premature skin aging changes including wrinkle formation . There are approximately 500 times more UVA rays in sunlight than UVB rays. Therefore, in addition to protecting your skin from the effects of UVB rays, it is also very important to protect from the damaging effects of the more numerous UVA rays. Traditional chemical sunscreen products have been more successful at blocking UVB rays than UVA rays.
You May Like: Melanoma On Face Prognosis
Risk Of Skin Cancer Among Cancer Survivors
Oncology patients and cancer survivors, whether skin cancers or other types of cancer, are at increased risk of a later diagnosis of BCC, SCC, or melanoma. Increased risk may be conferred by treatment or genetic factors such as BRCA mutations, which may increase risk of skin cancers. Additionally, immunosuppression related to the initial development of cancer or to treatment can increase risk of a later skin cancer., Organ transplant recipients are at very high risk for developing UV-induced skin tumors, especially cutaneous SCCs., An increased risk of melanoma has been documented in patients with a history of prior skin cancer, Kaposi sarcoma, female breast cancer, ocular melanoma, prostate cancer, thyroid cancer, non-Hodgkin lymphoma, and chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Patients diagnosed with chronic lymphocytic leukemia and non-Hodgkin lymphoma are at increased risk for developing particularly aggressive skin cancers associated with poorer outcomes. Childhood cancer survivors are also more likely to be diagnosed with skin cancers in adulthood.,
Warning Signs Of Basal Cell Carcinoma That You Could Mistake As Harmless
Warning sign: A pink or reddish growth that dips in the centerCan be mistaken for: A skin injury or acne scar
A pink or reddish growth that dips in the center
The BCC on this patients cheek could be mistaken for a minor skin injury.
Warning sign: A growth or scaly patch of skin on or near the earCan be mistaken for: Scaly, dry skin, minor injury, or scar
A growth or scaly patch of skin on or near the ear
BCC often develops on or near an ear, and this one could be mistaken for a minor skin injury.
Warning sign: A sore that doesnt heal and may bleed, ooze, or crust overCan be mistaken for: Sore or pimple
A sore that doesnt heal, or heals and returns
This patient mistook the BCC on his nose for a non-healing pimple.
Warning sign: A scaly, slightly raised patch of irritated skin, which could be red, pink, or another colorCan be mistaken for: Dry, irritated skin, especially if its red or pink
A scaly, slightly raised patch of irritated skin
This BCC could be mistaken for a patch of dry, irritated skin.
Warning sign: A round growth that may be pink, red, brown, black, tan, or the same color as your skinCan be mistaken for: A mole, wart, or other harmless growth.
A round growth that may be same color as your skin
Would you recognize this as a skin cancer, or would you dismiss it as a harmless growth on your face?
Read Also: Can You Die From Basal Cell Skin Cancer
Don’t Miss: What Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of The Head And Neck
Does Sunlight Cause Skin Cancer
There is evidence that sunlight causes skin cancer. Skin cancer can be treated and cured without serious consequences. However, in some cases the condition can be life-threatening if not diagnosed in time.
Skin cancer is an occupational concern for people who work under the sun. The risk however, may be reduced through awareness of the problem, and by taking measures to prevent exposure to sunlight.
Causes Of Skin Cancer
One of the main causes of skin cancer is being exposed to UV rays. UV rays are invisible, and are produced by the sun, and tanning equipment.
UV rays cause skin cancer by creating changes in the cells of your skin. In some cases, the UV rays cause direct damage to your cells. Tans and sunburns, for example, are both signs that UV rays have damaged your skin. In other cases, UV rays cause skin cancer indirectly, by weakening the immune system.
Many studies on skin cancer show that people who have suffered many severe sunburns in childhood are at greater risk of developing skin cancer. Family history, some chemical exposures, and immune dysfunction conditions can also create a greater risk of developing skin cancer.
Also Check: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Survival Rate
Common Causes Of Skin Cancer
Skin cancer is the most common type of cancer, yet its also one of the most preventable cancers. When you know what causes skin cancer, you can take steps to avoid this potentially dangerous disease.
If you develop skin cancer, you can turn to the compassionate care available at Plastic Surgery Specialists of Boca Raton. In our office, youre supported by an experienced team, and your treatment is in the skilled hands of Rafael C. Cabrera, MD, FACS, an expert in skin cancer removal and reconstruction techniques that minimize scarring.
Basal Cell Carcinoma: The Most Common Skin Cancer
Basal cell carcinoma, which is also called basal cell skin cancer, is the most common form of skin cancer, accounting for about 80 percent of all cases.
Rates of basal cell carcinoma have been increasing. Experts believe this is due to more sun exposure, longer lives, and better skin cancer detection methods.
This type of cancer begins in the skins basal cells, which are found in the outermost layer, the epidermis. They usually develop on areas that are exposed to the sun, like the face, head, and neck.
Basal cell carcinomas may look like:
- A flesh-colored, round growth
- A pinkish patch of skin
- A bleeding or scabbing sore that heals and then comes back
They typically grow slowly and dont spread to other areas of the body. But, if these cancers arent treated, they can expand deeper and penetrate into nerves and bones.
Though its rare, basal cell carcinoma can be life-threatening. Experts believe that about 2,000 people in the United States die each year from basal cell carcinoma or squamous cell carcinoma.
Some risk factors that increase your chances of having a basal cell carcinoma include:
- Being exposed to the sun or indoor tanning
- Having a history of skin cancer
- Being over age 50
- Having chronic infections, skin inflammation, or a weakened immune system
- Being exposed to industrial compounds, radiation, coal tar, or arsenic
- Having an inherited disorder, such as nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome or xeroderma pigmentosum
Don’t Miss: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Stage 2 Survival Rate
Cataracts And Other Eye Damage
Cataracts are a form of eye damage in which a loss of transparency in the lens of the eye clouds vision. If left untreated, cataracts can lead to blindness. Research has shown that UV radiation increases the likelihood of certain cataracts. Although curable with modern eye surgery, cataracts diminish the eyesight of millions of Americans and cost billions of dollars in medical care each year.
Other kinds of eye damage include pterygium , skin cancer around the eyes, and degeneration of the macula . All of these problems can be lessened with proper eye protection. Look for sunglasses, glasses or contact lenses if you wear them, that offer 99 to 100 percent UV protection.
Understanding The Uv Index
| Exposure categories | |
| 0 – 2 | Low. Low danger from unprotected sun exposure. But if you burn easily, cover up and use sunscreen with a sun protection factor of at least 30. |
| 3 – 5 | Moderate. A moderate risk of harm from unprotected sun exposure. Wear protective clothing, sunglasses, and a hat if you will be outside. Stay in shade around midday. Apply sunscreen with at least SPF 30 every 2 hours. |
| 6-7 | High. A high risk of harm from unprotected sun exposure. Wear protective clothing, sunglasses, and a hat if you will be outside. Apply sunscreen with at least SPF 30 every 2 hours. Reduce your time in the sun from 10 a.m. and 4 p.m. |
| 8-10 | Very High. A very high risk of harm from unprotected sun exposure. Wear protective clothing, sunglasses, and a hat if you will be outside. Apply sunscreen with at least SPF 30 every 2 hours. Seek shade outdoors. Try to avoid the sun between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m. |
| 11 + | Extreme. An extreme risk of harm from unprotected sun exposure. Follow all of the above suggestions to protect yourself from the sun. Wear protective clothing, sunglasses, and a hat if you will be outside. Apply sunscreen with at least SPF 30 every 2 hours. Seek shade outdoors. Try to avoid the sun between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m. |
Don’t Miss: Invasive Breast Cancer Survival Rates
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Stages
- Stage 0: Also referred to as carcinoma in situ, most cancers found on this stage is just current within the dermis and have not spread deeper to the dermis.
- Stage I: The cancer is lower than 2 centimeters, about 4/5 of an inch throughout, has not spread to close by lymph nodes or organs and has one or fewer high-risk options.
- Stage II: The cancer is bigger than 2 centimeters across, and has not spread to close by organs or lymph nodes, or a tumor of any measurement with 2 or extra excessive danger options.
- Stage III: Most cancer has spread into facial bones or 1 close by a lymph node, however to not different organs.
- Stage IV: Cancer might be any measurement and has spread to 1 or extra lymph nodes that are bigger than three cm and will have to spread to bones or different organs within the physique.
Who Is At Risk For Skin Cancer
Although anyone can get skin cancer, the risk is greatest in people who have fair or freckled skin that burns easily, light eyes and blond or red hair. Darker-skinned individuals are also susceptible to all types of skin cancer, although their risk is lower.
In addition to complexion, other risk factors include having a family history or personal history of skin cancer, having an outdoor job, and living in a sunny climate. A history of severe sunburns and an abundance of large and irregularly shaped moles are risk factors unique to melanoma.
You May Like: Lobular Breast Cancer Survival Rates
How Does Sunlight Affect The Skin
When ultraviolet radiation reaches the skin, some radiation is reflected away from the surface. The remaining radiation is scattered into the tissues just beneath the skin’s surface. A fraction of this radiation is absorbed by the skin’s living cells.
Ultraviolet radiation absorbed by living cells damages sensitive substances that influence the skin’s normal growth and appearance. Damage can result in:
- sunburn
- increased rate of aging of the skin
- skin cancer
Skin Cancer: Quick Facts From The Surgeon General
Skin cancer is a serious public health concern.
Every year, there are more than 63,000 new cases of melanoma, the deadliest form of skin cancer, resulting in nearly 9,000 deaths.
Skin cancer is the most commonly diagnosed cancer in the United States, with 5 MILLION PEOPLE treated each year.
Treatment for skin cancer costs $8.1 BILLION each year in the United States.
Anyone can get skin cancer. Although those with lighter skin are at higher risk of getting skin cancer, people with darker skin may often be diagnosed with skin cancer at a later stage, making it difficult to treat.
Most skin cancers can be preventedbut we arent doing enough.
More than 1 out of every 3 Americans reports getting sunburned each year. Sunburn is a clear sign of overexposure to UV rays, a major cause of skin cancer.
More than 400,000 cases of skin cancer, about 6,000 of which are melanomas, are estimated to be related to indoor tanning in the U.S. each year.
Tanned skin is damaged skin, yet nearly 1 out of every 3 young white women engages in indoor tanning each year.
Choose sun protection strategies that work:
- Wear a hat, sunglasses, and other protective clothing, seek shade, especially during midday hours.
- Use broad spectrum sunscreen with SPF 15+ to protect any exposed skin. Remember that sunscreen is most effective when used in combination with other methods, and when reapplied as directed.
For more information, visit: www.cdc.gov/cancer/skin
Don’t Miss: What Does Well Differentiated Squamous Cell Carcinoma Mean
Uv Light And Other Possible Causes
Much of the DNA damage in skin cells is caused by ultraviolet radiation, which is found in sunlight and tanning bed lights. But exposure to the sun does not explain the causes of skin cancer that appear on skin not commonly exposed to sunlight. This indicates that other factors may play a role in the risk of skin cancer, such as being exposed to toxic substances or having a condition that weakens the immune system.
What You Need To Know About Sunburn
- Some people are more prone to sunburn: Skin type determines your susceptibility people with fair skin run the greatest risk. But anyone can get burned.
- Even without a burn, sun exposure raises skin cancer risk. Even if you are tan or your skin type is dark and your skin does not redden, the sun can cause cellular damage that can lead to cancer.
- The UV index is a factor: The sun varies in intensity by season, time of day and geographic location. A high UV index means that unprotected skin will burn faster or more severely. Be careful, especially when the sun is strongest. But even when the index is low, the risk remains. Protect yourself every day of the year.
- You can burn on an overcast day: Be careful even when the sun isnt shining. Up to 80 percent of UV rays can penetrate clouds.
- Light pink is still bad: No matter how mild, every burn is a sign of injury to your skin that can result in premature aging and skin cancer.
Read Also: What Are The Early Stages Of Melanoma
Read Also: Melanoma Stage 3 Survival Rate