When Melanoma Can’t Be Cured
If your cancer has spread and it is not possible to cure it by surgery, your doctor may still recommend treatment. In this case, treatment may help to relieve symptoms, might make you feel better and may allow you to live longer.
Whether or not you choose to have anti-cancer treatment, symptoms can still be controlled. For example, if you have pain, there are effective treatments for this.
General practitioners, specialists and palliative care teams in hospitals all play important roles in helping people with cancer.
Signs And Symptoms Of Melanoma
The most common sign of melanoma is the appearance of a new mole or a change in an existing mole.
This can happen anywhere on the body, but the most commonly affected areas are the back in men and the legs in women.
Melanomas are uncommon in areas that are protected from sun exposure, such as the buttocks and the scalp.
In most cases, melanomas have an irregular shape and are more than 1 colour.
The mole may also be larger than normal and can sometimes be itchy or bleed.
Look out for a mole that gradually changes shape, size or colour.
Superficial spreading melanoma are the most common type of melanoma in the UK.
They’re more common in people with pale skin and freckles, and much less common in people with darker skin.
They initially tend to grow outwards rather than downwards, so they do not pose a problem.
But if they grow downwards into the deeper layers of skin, they can spread to other parts of the body.
You should see a GP if you have a mole that’s getting bigger, particularly if it has an irregular edge.
How Is Melanoma Treated
Your melanoma treatment will depend on the stage of the melanoma and your general health.
Surgery is usually the main treatment for melanoma. The procedure involves cutting out the cancer and some of the normal skin surrounding it. The amount of healthy skin removed will depend on the size and location of the skin cancer. Typically, surgical excision of melanoma can be performed under local anesthesia in the dermatologist’s office. More advanced cases may require other types of treatment in addition to or instead of surgery.
Treatments for melanoma:
- Melanoma Surgery: In the early stages, surgery has a high probability of being able to cure your melanoma. Usually performed in an office, a dermatologist numbs the skin with a local anesthetic and removes the melanoma and margins .
- Lymphadenectomy: In cases where melanoma has spread, removal of the lymph nodes near the primary diagnosis site may be required. This can prevent the spread to other areas of your body.
- Metastasectomy: Metastasectomy is used to remove small melanoma bits from organs.
- Targeted cancer therapy: In this treatment option, drugs are used to attack specific cancer cells. This targeted approach goes after cancer cells, leaving healthy cells untouched.
- Radiation Therapy: Radiation therapy includes treatments with high-energy rays to attack cancer cells and shrink tumors.
- Immunotherapy: immunotherapy stimulates your own immune system to help fight the cancer.
Recommended Reading: Skin Cancer Spreading To Lymph Nodes
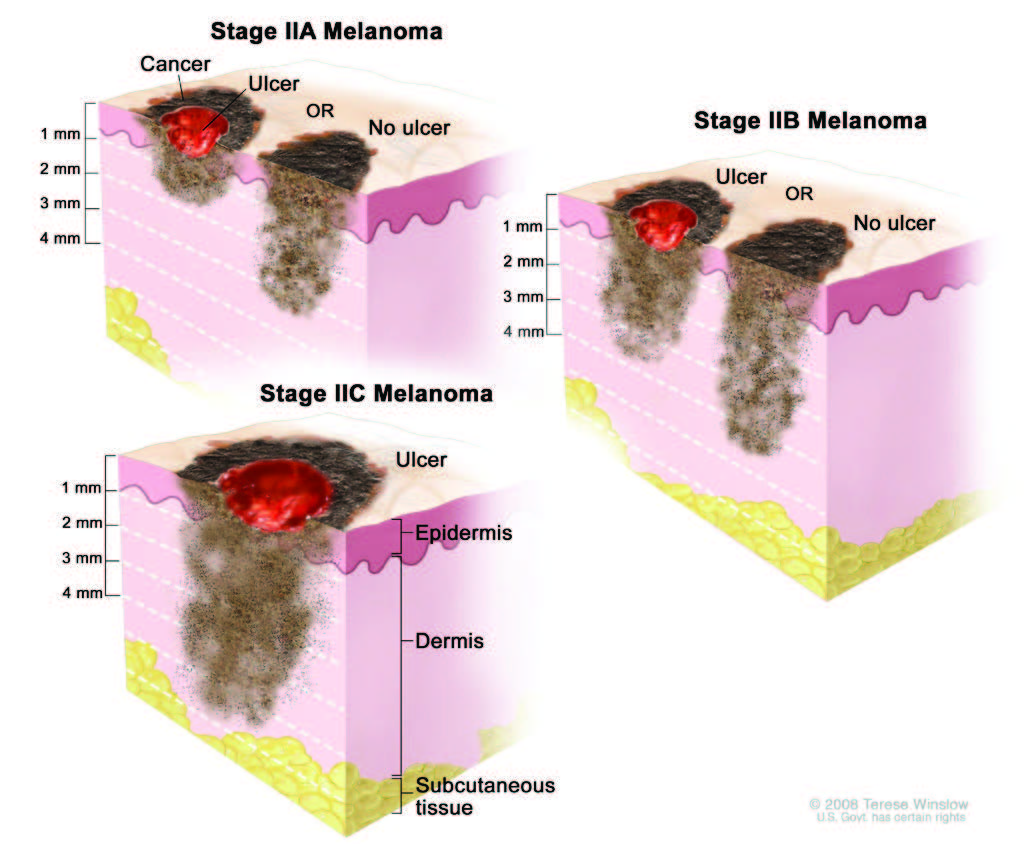
What Are The Melanoma Stages And What Do They Mean
Early melanomas
Stage 0 and I are localized, meaning they have not spread.
- Stage 0: Melanoma is localized in the outermost layer of skin and has not advanced deeper. This noninvasive stage is also called melanoma in situ.
- Stage I: The cancer is smaller than 1 mm in Breslow depth, and may or may not be ulcerated. It is localized but invasive, meaning that it has penetrated beneath the top layer into the next layer of skin. Invasive tumors considered stage IA are classified as early and thin if they are not ulcerated and measure less than 0.8 mm.
Find out about treatment options for early melanomas.
Intermediate or high-risk melanomas
Localized but larger tumors may have other traits such as ulceration that put them at high risk of spreading.
- Stage II: Intermediate, high-risk melanomas are tumors deeper than 1 mm that may or may not be ulcerated. Although they are not yet known to have advanced beyond the primary tumor, the risk of spreading is high, and physicians may recommend a sentinel lymph node biopsy to verify whether melanoma cells have spread to the local lymph nodes. Thicker melanomas, greater than 4.0 mm, have a very high risk of spreading, and any ulceration can move the disease into a higher subcategory of stage II. Because of that risk, the doctor may recommend more aggressive treatment.
Learn more about sentinel lymph node biopsy and melanoma treatment options.
Advanced melanomas
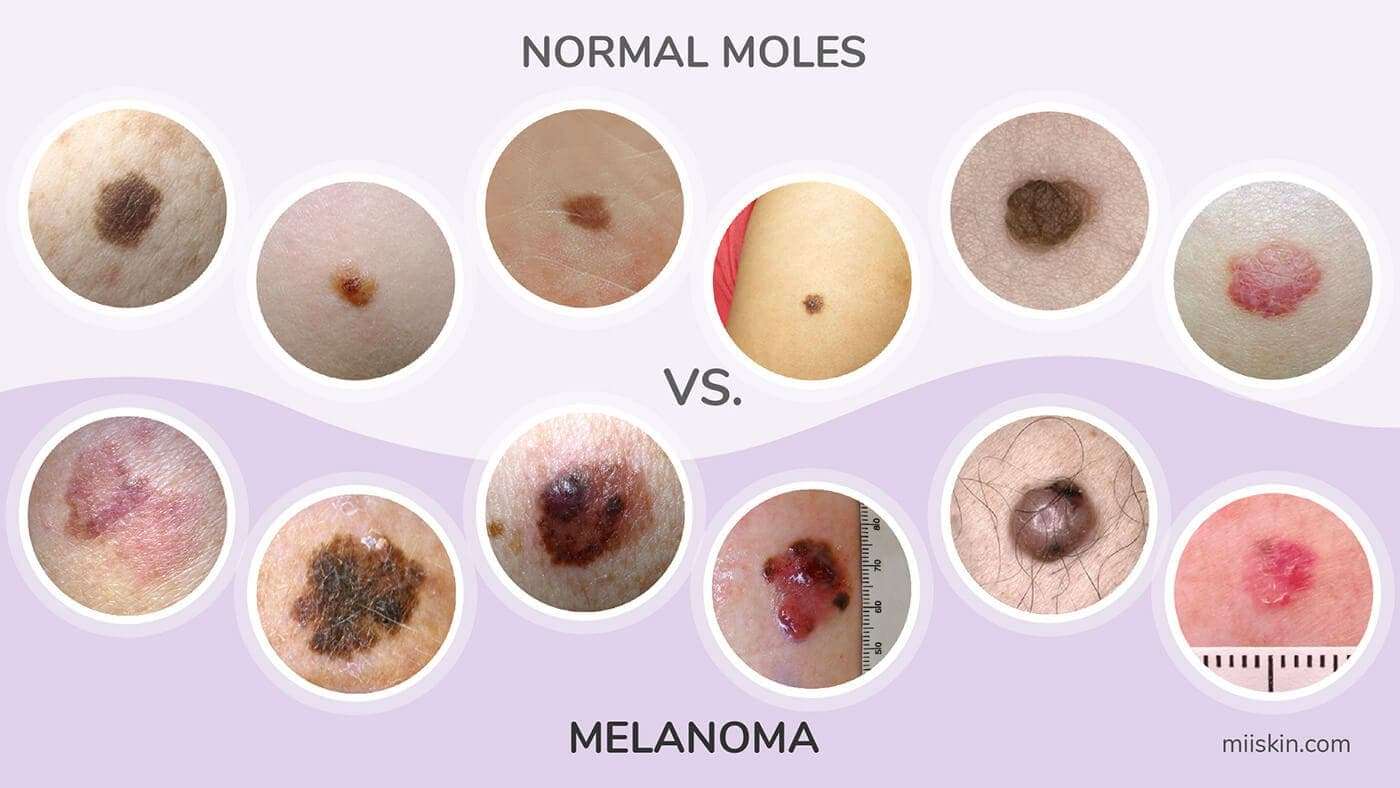
What To Watch For In Moles
- Score4.8/5
What Should I Look for When Examining My Moles?
- Asymmetry: One half of the mole does not match the other half.
- Border: The border or edges of the mole are ragged, blurred, or irregular.
- Color: The mole has different colors or it has shades of tan, brown, black, blue, white, or red.
-
Skin Cancer Screening | Symptoms, Types & Warning Signs
Watch Youtube video
Also Check: 3b Melanoma
What To Do If You Find Something Suspicious
If you do notice a new mole or spot on your skin, see any changes to any existing spots or simply have any concerns about the spots on your skin, be sure to book a visit with your GP as quickly as possible. They can identify whether a spot is harmless or needs closer attention.
âItâs so important to see your GP or skin specialist. If the lesion isnât removed or biopsied and youâre still concerned, donât be afraid to get a second opinion,â says Hamish.
Need some help understanding your risk of developing skin cancer? Take the nib skin self-assessment.
People At Higher Risk Of Melanoma
Some people have a higher than normal risk of developing melanoma. This includes people who have:
- had a melanoma in the past
- a family history of melanoma
- many moles
- had an organ transplant
If you have any of these, your doctor can refer you to a skin specialist who can show you how to check your skin each month for abnormal moles.
Some people have a much higher than normal risk of melanoma and should have regular checks by a skin cancer specialist. This includes people who:
- have 2 family members with melanoma and also have a lot of large, irregularly shaped moles
- were born with a very large mole
- have 3 or more people in their family diagnosed with melanoma or pancreatic cancer
- have had more than 1 melanoma
Your skin cancer specialist or nurse can examine your skin. They are trained to look out for moles that may be starting to become cancerous. If you have any moles that could be a melanoma, they can remove them at the clinic. By removing suspicious moles early, they can prevent an invasive melanoma developing.
-
Revised guidelines for the management of cutaneous melanoma 2010JR Marsden and others
Read Also: Invasive Ductal Breast Cancer Prognosis
What Makes A Mole Suspicious
Border that is irregular: The edges of suspicious moles are ragged, notched or blurred in outline, while healthy moles tend to have more even borders. The pigment of the mole may also spread into the surrounding skin. Color that is uneven: The mole may have various colors present, including black, brown and tan.
Less Common Skin Cancers
Uncommon types of skin cancer include Kaposi’s sarcoma, mainly seen in people with weakened immune systems sebaceous gland carcinoma, an aggressive cancer originating in the oil glands in the skin and Merkel cell carcinoma, which is usually found on sun-exposed areas on the head, neck, arms, and legs but often spreads to other parts of the body.
Recommended Reading: Is Melanoma Bad
When To See A Doctor
Many melanomas are dark brown or black and are often described as changing, different, unusual, or ugly looking. However, any skin abnormality that is growing or changing quickly and does not go away, whether colored or not, should be examined by a doctor. Bleeding may be a sign of more advanced melanoma. In addition, the appearance of a new and unusual mole is more likely to be melanoma.
If you are concerned about a new or existing mole, please talk with your family doctor or a dermatologist. Your doctor will ask how long and how often youve been experiencing the symptom, in addition to other questions. This is to help figure out the cause of the problem, called a diagnosis.
The next section in this guide is Diagnosis. It explains what tests may be needed to learn more about the cause of the symptoms. Use the menu to choose a different section to read in this guide.
Treatments For Melanoma Skin Cancer
If you have melanoma skin cancer, your healthcare team will create a treatment plan just for you. It will be based on your health and specific information about the cancer. When deciding which treatments to offer for melanoma skin cancer, your healthcare team will consider:
- the of the cancer whether it is early stage, locoregional or metastatic
- the risk that the cancer will come back
- where the cancer is located
- how treatments will affect how you look
- your personal preferences
Also Check: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Survival Rate
Can Changing My Diet Help Prevent Melanoma
The American Cancer Society advocates eating a plant-based diet over an animal-based diet as part of a healthy plan to avoid all cancers. Growing evidence suggests that plants pack a powerful punch in any fight against cancer because they’re nutritious, cholesterol-free and fiber-rich.
Theres no doubt that a healthy diet can protect your immune system. Having a strong immune system is important to help your body fight disease. Some research has shown that a Mediterranean diet is a healthy choice that may help prevent the development of cancer. Talk to your healthcare provider about the role food plays in lowering your cancer risks.
Some skin and immune-system healthy foods to consider include:
- Daily tea drinking: The polyphenols in tea help strengthen your immune system. Green tea contains more polyphenols than black tea.
- High vegetable consumption: Eating carrots, cruciferous and leafy vegetables is linked to the prevention of cutaneous melanoma.
- Weekly fish intake: Study participants who ate fish weekly seemed to avoid developing the disease when compared to those who did not eat fish weekly.
Melanoma: What To Look For
If it is discovered in its early stages, it is usually highly treatable however, if it spreads to the lymph nodes and organs, the survival rate drops dramatically.
According to statistics from the American Cancer Society, the estimated five-year survival rate for stage one melanoma is 92-97%, for stage three it is approximately 40-59% and for stage 4 it drops to only 15-20%.
The key is knowing what to look for to catch the cancer before it has a chance to spread. Read on to learn the main warning signs of melanoma so you know what to look for.
Don’t Miss: Can You Have Cancer Without A Tumor
What’s The Difference Between A Freckle And A Mole
Both moles and freckles appear as darker spots on the skin, but while moles are usually raised, freckles are flat. In both, the colour is due to melanin, which can darken with sun exposure, and moles occur when pigment-containing skin cells form a cluster. While skin cancer self-checks are important, do keep in mind that not all spots are cancerous â and most moles are harmless.
Set A Regular Scan Reminder
You wont know whats weird if you dont carve out time to look. The Cleveland Clinic recommends a monthly scan, though some doctors say you can opt for a quarterly skin check instead.
If you dont examine yourself at least once a month, you dont have a good mental memory of what you look like, so you wont be able to spot change, Dr. Halpern said.
To scan, stand in front of a full-length mirror have a hand mirror on deck for hard-to-reach places. Start systematically, from the top of your head down. Dont forget your scalp and neck, or under the nails.The Skin Cancer Foundation has a guide, and the American Academy of Dermatology Association has a video tutorial.
And remember, look for weird. If theres a mole that you think looks out of the ordinary, get it checked out. You can also take pictures of your moles so you can compare them on your next scan. If youre noticing changes, or if you develop a sore that does not heal, call a dermatologist.
Recommended Reading: Melanoma 3b
Changing The Standard Of Care For Stage Iii Melanoma Surgery
- Date:
- University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus
- Summary:
- For years, surgery for patients with stage III melanoma — melanoma that has spread to the lymph nodes — involved removing those lymph nodes along with the primary tumor. Known as completion lymph node dissection , the surgery was meant to ensure that no cancer remained after surgery. More recently, however, cancer surgeons have discovered that CLND has the potential to cause more problems than it solves. In most cases, patients do better on immunotherapy alone than they do when their surgery involves removal of the lymph nodes, due to potential complications from lymph node surgery.
For years, surgery for patients with stage III melanoma — melanoma that has spread to the lymph nodes — involved removing those lymph nodes along with the primary tumor. Known as completion lymph node dissection , the surgery was meant to ensure that no cancer remained after surgery.
More recently, however, cancer surgeons have discovered that CLND has the potential to cause more problems than it solves. In most cases, patients do better on immunotherapy alone than they do when their surgery involves removal of the lymph nodes, due to potential complications from lymph node surgery.
Better outcomes with immunotherapy
The de-escalation movement
Changing course
Story Source:
Materials provided by University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus. Original written by Greg Glasgow. Note: Content may be edited for style and length.
Should The Lymph Nodes Be Removed
If the local lymph nodes are enlarged due to metastatic melanoma, they should be completely removed. This requires a surgical procedure, usually under general anaesthetic. If they are not enlarged, they may be tested to see if there is any microscopic spread of melanoma. The test is known as a sentinel node biopsy.
In New Zealand, many surgeons recommend sentinel node biopsy for melanomas thicker than 1 mm, especially in younger persons. However, although the biopsy may help in staging cancer, it does not offer any survival advantage.
Lymph nodes containing metastatic melanoma often increase in size quickly. An involved node is usually non-tender and firm to hard in consistency.
If the melanoma is widespread, treatment is not always successful in eradicating the cancer. Some patients may be offered new or experimental treatments, such as:
- PD-1 blocking antibodies: nivolumab, pembrolizumab
Don’t Miss: What Is Stage 2 Squamous Cell Carcinoma
What Does Stage 1 Melanoma Mean
In Stage I melanoma, the cancer cells are in both the first and second layers of the skinâthe epidermis and the dermis. A melanoma tumor is considered Stage I if it is up to 2 mm thick, and it may or may not have ulceration. There is no evidence the cancer has spread to lymph nodes or distant sites .
How Are Moles Evaluated
If you find a mole or spot that has any ABCDE’s of melanoma — or one that’s tender, itching, oozing, scaly, doesn’t heal or has redness or swelling beyond the mole — see a doctor. Your doctor may want to remove a tissue sample from the mole and biopsy it. If found to be cancerous, the entire mole and a rim of normal skin around it will be removed and the wound stitched closed. Additional treatment may be needed.
Also Check: Well Differentiated Squamous Cell Carcinoma Stages
Look For New Spots Or Changes In The Skin
As youâre checking your skin in the mirror, keep an eye out for new spots, freckles or moles, as well as any changes in colour, size or shape of existing spots, bleeding spots or moles and freckles that look different to the others.
âYou are looking for the ABCDE of melanoma changes â asymmetry, border, colour, diameter and evolving,â says Hamish.
Can Melanoma Be Cured
Melanoma that’s caught early, when it’s still on the surface of the skin, can be cured.
Untreated melanoma can grow downward into the skin until it reaches the blood vessels and lymphatic system. This lets it travel to distant organs, like the lungs or the brain. That’s why early detection is so important.
Don’t Miss: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Breast Cancer Survival Rates
Know Your Risk Factors
Your skin, and your personal history, affect how often you have to check. If youre at high risk of skin cancer, you should have a different relationship to your dermatologist and your moles.
People who have a family history of melanoma are more likely to develop the disease. If youve gotten a lot of blistering sunburns, maybe five by the time youre 18, or used a tanning bed, you are at increased risk, Dr. Deborah S. Sarnoff, the president of the Skin Cancer Foundation, said. That really bumps it up, the way smoking bumps up lung cancer.
Your skin color plays a role, too. People with light skin, blond or red hair, blue eyes, or many freckles and moles are more prone to developing skin cancer than people of color its more than 20 percent more common in white people than Black people, according to the American Cancer Society. Thats because most skin cancers are sun related, and darker skin is less at risk for sun-induced cancers.
In people of all races, however, skin cancers can also present in places that do not regularly get sun exposure, like the hands or soles of their feet, the mucous membranes and the nail beds. These cancers may be more deadly, because they are often diagnosed at a later stage.