Stage I And Stage Ii Melanoma
Stage I and stage II melanoma describe invasive cancer that has grown below the epidermis to the next layer of skin, the dermis. It has not reached the lymph nodes.
Two major factors help determine the seriousness of stage I melanoma and stage II melanoma: Breslow depth and ulceration.
Breslow depth is a measurement that doctors use to describe the depth of an invasive melanoma in millimeters. It measures how far melanoma cells have reached below the surface of the skin. The thinner the melanoma, the better the chances for a cure.
Ulceration means that there is broken skin covering the melanoma. This breakage can be so small that it can only be seen under a microscope. Ulceration is an important factor in staging. A melanoma with ulceration may require more aggressive treatment than a melanoma of the same size without ulceration.
Melanoma is considered stage 1A when:
- the tumor is less than or equal to 1 millimeter thick in Breslow depth
Melanoma is considered stage IB when:
- the tumor is 1.1 to 2 millimeters thick in Breslow depth without ulceration
Melanoma is considered stage IIA when:
- the tumor is 1.1 to 2 millimeters thick in Breslow depth with ulceration
- the tumor is 2.1 to 4 millimeters thick in Breslow depth without ulceration
Melanoma is considered stage IIB when:
- the tumor is 2.1 to 4 millimeters thick in Breslow depth with ulceration
- the tumor is more than 4 millimeters in Breslow depth without ulceration
Melanoma is considered stage IIC when:
Symptoms Of Metastatic Melanomas
Melanoma usually is found in early stages, before its become metastatic. If you notice any abnormal moles or discolorations on your skin, dont hesitate to reach out to your doctor. This is especially important for those with many risk factors. Melanoma is more treatable at early stages, so early identification may prevent metastatic melanoma from developing.
Though a primary tumor is typically found, its possible that metastatic melanoma is detected elsewhere in the body and causes symptoms without any signs of a primary tumor.
Metastatic melanoma symptoms and signs may include:
- Fatigue
Treating Stage Iv Melanoma
Stage IV melanomas have already spread to distant lymph nodes or other areas of the body. Skin tumors or enlarged lymph nodes causing symptoms can often be removed by surgery or treated with radiation therapy.
Metastases in internal organs are sometimes removed, depending on how many there are, where they are, and how likely they are to cause symptoms. Metastases that cause symptoms but cannot be removed may be treated with radiation, immunotherapy, targeted therapy, or chemotherapy.
The treatment of widespread melanomas has changed in recent years as newer forms of immunotherapy and targeted drugs have been shown to be more effective than chemotherapy.
Immunotherapy drugs called checkpoint inhibitors such as pembrolizumab or nivolumab are typically the first drugs tried, especially in people whose cancer cells do not have BRAF gene changes. These drugs can shrink tumors for long periods of time in some people. Ipilimumab , a different type of checkpoint inhibitor, is not typically used by itself as the first treatment, although it might be combined with nivolumab or pembrolizumab. This slightly increase the chances that the tumor will shrink, although itâs also more likely to result in serious side effects, which needs to be considered carefully. People who get any of these drugs need to be watched closely for serious side effects..
Itâs important to carefully consider the possible benefits and side effects of any recommended treatment before starting it.
Don’t Miss: Well Differentiated Carcinoma
What If I Have Metastatic Melanoma Symptoms
Whether you have a suspicious mole or are experiencing some symptoms of advanced-stage melanoma, it is important to consult with a physician to receive an accurate diagnosis, as many other conditions can cause similar symptoms. At Moffitt Cancer Center, we provide a comprehensive range of screening, diagnostic, treatment and supportive care services for patients with melanoma and other types of cancer. Within our Cutaneous Oncology Program, our multispecialty team includes surgeons, dermatologists, medical oncologists and other experts who work together as a tumor board to ensure our patients receive the best possible treatment and care.
If you would like to schedule an appointment at Moffitt to discuss your metastatic melanoma symptoms, call or fill out a new patient registration form online. We do not require a referral to schedule an appointment.
- BROWSE
Where Else Does Melanoma Spread To
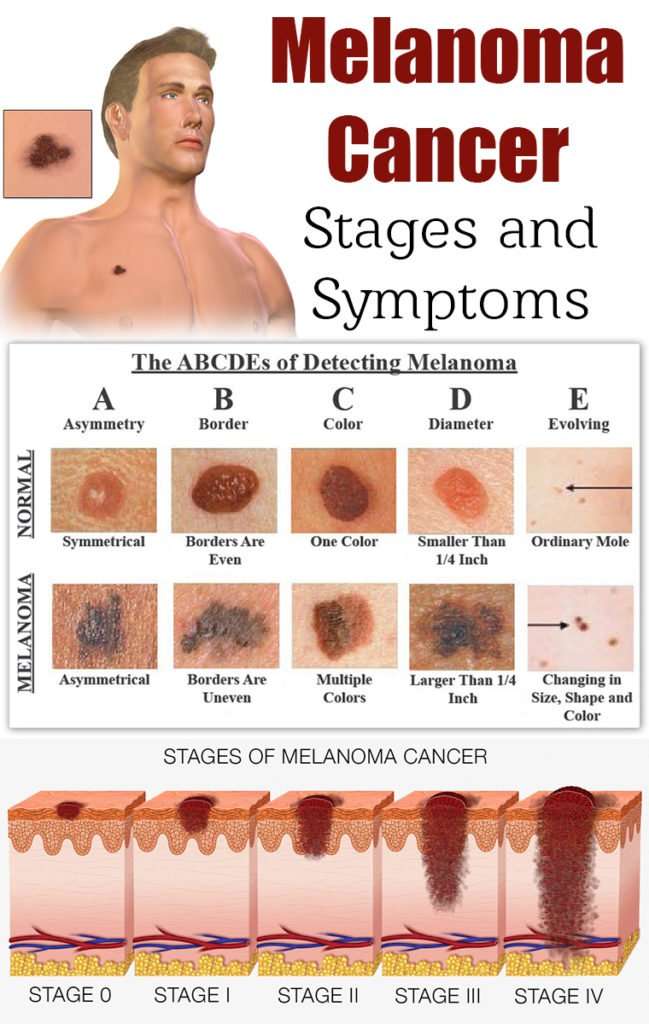
When melanoma advances to stage 3, it means the tumor has spread to the lymph nodes or the skin around the primary tumor and lymph nodes. In stage 4, the cancer has moved to other areas far beyond the lymph nodes, like your internal organs. The most common places melanoma spreads to are the:
- lungs
- brain
- stomach, or abdomen
These growths will cause different symptoms, depending on which areas it has spread to. For example, you may feel breathless or constantly cough if the cancer has spread to your lungs. Or you may have a long-term headache that wont go away if it has spread to your brain. Sometimes the symptoms for stage 4 melanoma may not appear for many years after the original tumor was removed.
Talk to your doctor if youre feeling new pains and aches or symptoms. Theyll be able to help diagnose the cause and recommend treatment options.
You May Like: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Survival Rate Stage 4
What To Ask Your Doctor About Stage I Melanoma
When your doctor tells you that you have Stage I melanoma, it can be overwhelming. But it is important to use the time with your doctor to learn as much about your cancer as you can. S/he will provide you important information about your diagnosis.
The following questions are those you may want to ask your doctor. Remember, it is ALWAYS okay to ask your doctor to repeat or clarify something s/he said so that you can better understand it. You may find it helpful to print out these questions and bring them with you to your next appointment.
Diagnosis And Staging What It Means For You
How is melanoma diagnosed?
To diagnose melanoma, a dermatologist biopsies the suspicious tissue and sends it to a lab, where a dermatopathologist determines whether cancer cells are present.
After the disease is diagnosed and the type of melanoma is identified, the next step is for your medical team to identify the stage of the disease. This may require additional tests including imaging such as PET scans, CT scans, MRIs and blood tests.
The stage of melanoma is determined by several factors, including how much the cancer has grown, whether the disease has spread and other considerations. Melanoma staging is complex, but crucial. Knowing the stage helps doctors decide how to best treat your disease and predict your chances of recovery.
You May Like: Merkel Cancer Prognosis
Characteristics Of Stage I Melanoma
Stage I melanomas are defined by two primary characteristics: tumor thickness and ulceration.
Tumor thickness : how deeply the tumor has penetrated the skin. Thickness is measured in millimeters . These comparisons will give you an idea of size:
- 1 mm = .04 inch, or less than 1/16 inchabout equal to the edge of a penny
- 2 mm = between 1/16 and 1/8 inchabout equal to the edge of a nickel
Ulceration: when the epidermis that covers a portion of the primary melanoma is not intact. Ulceration can only be seen under a microscope, not by the naked eye.
Treatments For Stage Iii Melanoma
Stage III melanoma has multiple treatment options and can include surgery , neo-adjuvant therapy, adjuvant therapy, radiation therapy, and clinical trials. You will likely see a surgical oncologist for the surgery-related treatments and a medical oncologist for the drug-related treatments. If you have any radiation treatments, you will see a radiation oncologist.
It is important to know whether all of your Stage III melanoma has been completely removed with surgery , or if it was not possible to remove all of the melanoma . These two types of Stage III melanoma are treated very differently. Unresectable Stage III patients are treated similarly to Stage IV melanoma patients. Read about Stage IV melanoma.
Order of Treatment
Patients with melanoma often receive more than one type of treatment, and certain terms are used to describe the order of treatments given. Neo-adjuvant treatment is what is given before primary treatmentin melanoma, primary treatment is generally surgeryto shrink tumors. For Stage III patients, neo-adjuvant treatment is mostly given in clinical trials. Primary treatment is the main treatment to remove cancer. Adjuvant treatment is given after primary treatment to kill any remaining cancer cells. FDA-approved adjuvant therapies for Stage III are noted below.
Surgery
The standard treatment for all primary melanoma is a surgery called wide local excision. The purpose of the surgery is to remove any cancer remaining after the biopsy of the primary tumor.
Also Check: Stage 2 Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Survival Rate
How Often Should You Follow Up With Your Doctor
After your treatment, your doctor will recommend a regular follow-up schedule to monitor your cancer. Theyll be checking to make sure the cancer hasnt come back or new cancerous lesions havent appeared. The types of follow-up include:
A yearly skin check: Skin checks are an important aspect of detecting melanoma in its earliest, most treatable stages. You should also conduct a skin check on yourself once per month. Look everywhere from the bottoms of your feet to behind your neck.
Imaging tests every three months to a year: Imaging studies, such as an X-ray, CT scan, or brain MRI, look for cancer recurrence.
Physical exam as needed: A physical exam to assess your overall health is important when you have had melanoma. For the first two years, youll want to get an exam every three to six months. Then for the next three years, the appointments can be every three months to a year. After the fifth year, the exams can be as needed. Do a monthly self-examination of your lymph nodes to check your progress.
Your doctor may recommend a different schedule based on your overall health.
What Is Stage Iii And Stage Iv Melanoma
Stage III and Stage IV melanoma is also sometimes called advanced melanoma, or secondary melanoma. This is when the melanoma has grown beyond the skin and has either spread to your lymphatic system that is, melanoma cells can be found in your lymph nodes or has spread beyond the regional lymph nodes to other parts of your body .
When the cancer spreads or metastasises to other parts of the body, away from the original site, the cells still have the characteristics of a melanoma even though they may now be growing somewhere else. The most common sites of melanoma metastases are in vital organs , bone, soft tissues and distant lymph nodes .
Don’t Miss: Does Melanoma Blanch When Pressed
Treatment Of Metastatic Melanoma
Metastatic melanomas can be difficult to treat. The five-year survival rate for people diagnosed with melanoma that has spread to nearby lymph nodes is 66 percent, according to the American Cancer Society. When cancer has spread to distant parts of the body, there may also be other metastases too small to detect by scans. For people diagnosed with stage 4 melanoma, or melanoma that has spread to distant parts of the body, the five-year survival rate is 27 percent.
For stage 3 and 4 melanomas, the following treatments may be used:
Multiple therapies can be used at any given time, and your care plan is a dynamic process. You and your care team should discuss all the options and decide on a treatment plan. Each treatment has different side effects, and its important to feel fully informed of all the associated risks. Other medications and options may help manage the symptoms of your cancer treatment, so you can live the highest quality of life possible throughout the course of your treatment and disease.
Expert
Complications Caused By Treatment
The treatments for metastatic melanoma can cause nausea, pain, vomiting, and fatigue.
Removal of your lymph nodes can disrupt the lymphatic system. This can lead to fluid buildup and swelling in your limbs, called lymphedema.
Some people experience confusion or mental cloudiness during chemotherapy treatment. This is temporary. Others may experience peripheral neuropathy or damage to the nerves from the chemotherapy. This can be permanent.
You May Like: What Is Stage 2 Melanoma Skin Cancer
I’ve Been Diagnosed With Melanomawhat Happens Next
Doctors use the TNM system developed by the American Joint Committee on Cancer to begin the staging process. Its a classification based on three key factors:
T stands for the extent of the original tumor, its thickness or how deep it has grown and whether it has ulcerated.
What Is Breslow depth?
Breslow depth is a measurement from the surface of the skin to the deepest component of the melanoma.
Tumor thickness: Known as Breslow thickness or Breslow depth, this is a significant factor in predicting how far a melanoma has advanced. In general, a thinner Breslow depth indicates a smaller chance that the tumor has spread and a better outlook for treatment success. The thicker the melanoma measures, the greater its chance of spreading.
Tumor ulceration: Ulceration is a breakdown of the skin on top of the melanoma. Melanomas with ulceration are more serious because they have a greater risk of spreading, so they are staged higher than tumors without ulceration.
N indicates whether or not the cancer has already spread to nearby lymph nodes. The N category also includes in-transit tumors that have spread beyond the primary tumor toward the local lymph nodes but have not yet reached the lymph nodes.
M represents spread or metastasis to distant lymph nodes or skin sites and organs such as the lungs or brain.
After TNM categories are identified, the overall stage number is assigned. A lower stage number means less progression of the disease.
Recognizing The Signs And Symptoms
The most noticeable sign of melanoma is the appearance of a new mole or a change in an existing mole or birthmark. People should be aware of any pigmented areas on the skin that appear abnormal in color, shape, size, or texture.
People with stage 4 melanoma may also have ulcerated skin , which is skin with tiny breaks on the surface. These ulcerations can bleed.
Another sign is swollen or hard lymph nodes, which a doctor can confirm by carrying out a physical examination. Other tests include blood tests and imaging scans to confirm the presence of cancer and check how much it has spread.
Recommended Reading: Prognosis For Skin Cancer
What Is The Outlook For Patients With Metastatic Melanoma
In most instances, it is not possible to cure metastatic melanoma entirely because it tends to spread to multiple sites. Treatment is focussed on improving the quality of life and the length of survival.
The prognosis of melanoma depends on the disease staging, which is based around characteristics of the primary tumour, nodal and distant metastases. The prognosis is poorer with higher numbers of involved nodes and with metastases to internal organs and distant sites.
What Is Metastaticmelanoma
Melanoma is a type of skin cancer that develops from the pigment-producing cells of the skin, mucosa, eye, and rarely other sites. Metastatic melanoma is melanoma that has spread to other sites of the body. The spread occurs through the lymphatic system and/or the blood vessels. Melanoma can spread to the subcutaneous tissue which lies underneath the skin, the lymph nodes, and to other organs such as the lungs, liver, bone or brain.
Metastatic melanoma can be classified into local recurrence, in transit metastasis, nodal metastasis, and haematogenous spread.
You May Like: Invasive Mammary Carcinoma Survival Rate
Treating Stage 4 Melanoma
If melanoma comes back or spreads to other organs it’s called stage 4 melanoma.
In the past, cure from stage 4 melanoma was very rare but new treatments, such as immunotherapy and targeted treatments, show encouraging results.
Treatment for stage 4 melanoma is given in the hope that it can slow the cancer’s growth, reduce symptoms, and extend life expectancy.
You may be offered surgery to remove other melanomas that have grown away from the original site. You may also be able to have other treatments to help with your symptoms, such as radiotherapy and medicine.
If you have advanced melanoma, you may decide not to have treatment if it’s unlikely to significantly extend your life expectancy, or if you do not have symptoms that cause pain or discomfort.
It’s entirely your decision and your treatment team will respect it. If you decide not to receive treatment, pain relief and nursing care will be made available when you need it. This is called palliative care.
What Is Metastatic Melanoma
Metastatic melanoma occurs when the cancerous cells from the original tumor get loose, travel through the lymph or blood circulation, and start a new tumor somewhere else. Once it spreads, or metastasizes, the disease is known as metastatic melanoma. This type of melanoma may typically occur during stage III or stage IV. Common sites for metastases include the lymph nodes, lungs, liver, bones and brain.
About 106,110 adults in the United States will be diagnosed with melanoma in 2021, according to the American Society of Clinical Oncology . Approximately 4 percent of people are diagnosed with melanomas that have spread to distant parts of the body, according to the ASCO. This is the most advanced stage of metastatic melanoma.
The percentage of people diagnosed with melanoma that has spread to nearby lymph nodes is 8.5 percent, according to the National Cancer Institute . These cases have a slightly better prognosis.
From 2014 to 2018, the incidence rate of melanoma that had spread to distant parts of the body was 0.9 per 100,000 people, according to the NCI.
Melanoma tumors that have metastasized to other parts of the body are still considered melanoma. For example, melanoma found in the lungs is called metastatic melanoma of the lung or melanoma with lung metastases.
You May Like: What Does Well Differentiated Mean