What Medication Treat Ductal Carcinoma In Situ
Tamoxifen may be prescribed for woman of all ages who have been treated for DCIS. In those women past menopause, the doctor may prescribe an aromatase inhibitor. These medications help lower the risk of DCIS or another type of cancer developing in either breast. If either is prescribed, it is suggested that these drugs be taken for five years after surgery.
Nonsurgical Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Treatment
Radiation. Radiation therapy might be part of your treatment plan if you are undergoing a lumpectomy. Studies show that lumpectomy followed by radiation can be as effective in treating IDC as mastectomy. We dont usually treat patients with radiation after a mastectomy unless theres some cancer in the lymph nodes, Wright says.
Chemotherapy. Deciding on whether to treat invasive ductal breast cancer with chemotherapy, or chemo, depends on features of the tumor cells themselves their genes and proteins. The more the doctor can learn about the characteristics of the cancer cells, the easier it is to determine what type of chemotherapy is likely to be effective.
Hormone therapy. Breast cancers with positive hormone receptors can be treated with estrogen or progesterone. These medications come in pill form, and may be prescribed for several years.
Biologic therapy. This approach uses antibodies or small molecule drugs to activate your bodys immune system to fight the invasive ductal cancer cells.
The Types Of Radiotherapy
The type of radiotherapy you have will depend on the type of breast cancer and the type of surgery you have. Some women may not need to have radiotherapy at all.
Types of radiotherapy include:
- breast radiotherapy after breast-conserving surgery, radiation is applied to the whole of the remaining breast tissue
- chest-wall radiotherapy after a mastectomy, radiotherapy is applied to the chest wall
- breast boost some women may be offered a boost of high-dose radiotherapy in the area where the cancer was removed however, this may affect the appearance of your breast, particularly if you have large breasts, and can sometimes have other side effects, including hardening of breast tissue
- radiotherapy to the lymph nodes where radiotherapy is aimed at the armpit and the surrounding area to kill any cancer that may be in the lymph nodes
Don’t Miss: Skin Cancer Metastasis To Lymph Nodes
How Grade Affects Treatment Options
Your treatment team will consider the grade of your cancer when deciding which treatment to offer you.
If you have grade 3 breast cancer, youre more likely to be offered chemotherapy. This is to help destroy any cancer cells that may have spread as a result of the cancer being faster growing.
Chemotherapy is less likely for grade 1 and grade 2 cancers.
The grade of your cancer alone will not determine what treatment youre offered. Your treatment team will consider the grade alongside all other information about your cancer when deciding on the best treatment options for you.
Recommended Reading: How To Get Rid Of Skin Cancer Naturally
Stages Of Breast Cancer
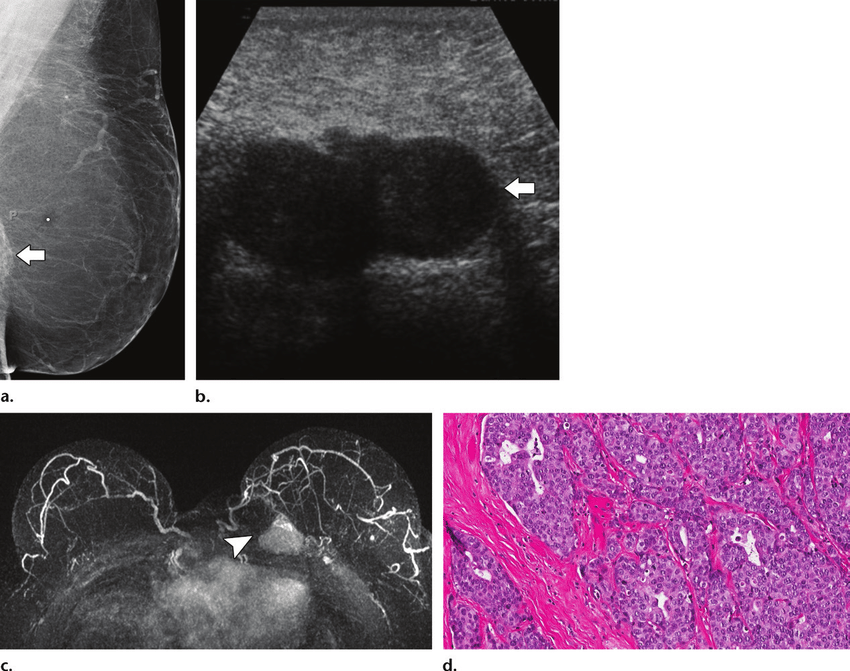
When cancer is diagnosed, a stage is assigned to it, based on how advanced it is. The stage helps doctors determine the most appropriate treatment and the prognosis. Stages of breast cancer may be described generally as in situ or invasive. Stages may be described in detail and designated by a number .
Read Also: Can You Get Cancer In The Back Of Your Neck
Recommended Reading: Skin Cancer Mayo
Clinical Stage Iii Invasive Carcinoma
This group of patients with more locally advanced disease should undergo a more extensive pre-treatment evaluation than patients with stage I or II cancers. Bone scan should be performed, and abdominal ultrasound, CT, or MRI should be considered. Even in the absence of overt findings of systemic disease , most of these patients do have microscopic metastasis beyond the axilla. Traditionally, many of these patients were considered inoperable, and mastectomy was forsaken in favor of what was considered palliative radiation therapy, often without even removing the lesion. Over the course of the past generation, however, neo-adjuvant or induction chemotherapy, currently using an anthracycline-based regimen, has produced significant down-staging in up to 8090% of these patients. Complete clinical remission is uncommon , but significant enough regression may occur using induction chemotherapy to permit wide local excision of previously large lesions. In these situations, breast conservation may be employed instead of mastectomy, including wide local excision, levels I and II axillary dissection and radiation therapy. Sentinel node biopsy in this group of patients must be considered investigational.
How Do You Differentiate Carcinoma In Situ From Invasive Cancer
Carcinoma in situ, also called in situ cancer, is different from invasive carcinoma, which has spread to surrounding tissue, and from metastatic carcinoma, which has spread throughout the body to other tissues and organs. In general, carcinoma in situ is the earliest form of cancer, and is considered stage 0.
Read Also: What Does Cancer Look Like Outside The Body
Invasive Carcinoma Of No Special Type
| Invasive carcinoma of no special type | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Invasive ductal carcinoma |
| Histopathologic types of breast cancer, with relative incidences and prognoses, with invasive ductal carcinoma at bottom left | |
| Oncology, Dermatology, Breast surgery |
Invasive carcinoma of no special type also known as invasive ductal carcinoma or ductal NOS and previously known as invasive ductal carcinoma, not otherwise specified is a group of breast cancers that do not have the specific differentiating features. Those that have these features belong to other types.
In this group are: pleomorphic carcinoma, carcinoma with osteoclast-like stromal giant cells, carcinoma with choriocarcinomatous features, and carcinoma with melanotic features. It is a diagnosis of exclusion, which means that for the diagnosis to be made all the other specific types must be ruled out.
What Are The Signs Of Invasive Breast Cancer
Breast cancer may have no signs or symptoms, especially during the early stages. As the cancer grows, you may notice one or more of the following:
- A lump or thickening in or near the breast or in the underarm that continues after your monthly menstrual cycle
- A mass or lump, which may feel as small as a pea
- A change in the size, shape, or contour of the breast
- A blood-stained or clear fluid from the nipple
- A change in the feel or appearance of the skin on the breast or nipple — dimpled, puckered, scaly, or inflamed
- Redness of the skin on the breast or nipple
- A change in shape or position of the nipple
- An area that is distinctly different from any other area on either breast
- A marble-like hardened area under the skin
You may notice changes when you do a monthly breast self-exam. By doing a regular self-check of your breast, you can become familiar with the normal changes in your breasts.
You May Like: How Do Carcinomas Spread
What Can I Expect If I Have Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
If youve been diagnosed with invasive ductal carcinoma, your healthcare provider will discuss your treatment options with you in detail. For best results, youll want to begin treatment as soon as possible.
How curable is invasive ductal carcinoma?
Invasive ductal carcinoma is quite curable, especially when detected and treated early.
What is the survival rate for invasive ductal carcinoma?
The five-year survival rate for localized invasive ductal carcinoma is high nearly 100% when treated early on. If the cancer has spread to other tissues in the region, the five-year survival rate is 86%. If the cancer has metastasized to distant areas of your body, the five-year survival rate is 28%.
Keep in mind that survival rates cannot tell you how long you will live. These numbers are based on people who have undergone breast cancer treatment in the past. For more information about your specific case, talk to your healthcare provider.
How Fast Does Dcis Progress
Grade 1 DCIS is almost always ER and PR positive and is a very slow growing form of cancer. It can take years, even decades, to see progression of the disease. In some cases, it may take such a long time to spread beyond the breast duct that it is not an event that will happen during a persons lifetime.
You May Like: Prognosis Of Skin Cancer
Don’t Miss: What Is The Survival Rate For Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
How Is Ductal Carcinoma In Situ Treated
No two patients are the same. Your doctor will customize your treatment plan based on your test results and medical history. Among other things, your doctor will consider:
- Tumor location
- Aggressiveness of the cancer cells
- Your family history of breast cancer
- Results of tests for a gene mutation that would increase the risk of breast cancer
Most women with DCIS don’t have the breast removed with a mastectomy. Instead, they have a lumpectomy.
Most common is a lumpectomy followed by radiation. The surgeon removes the cancer and a small area of healthy tissue around it. Lymph nodes under the arm donât need to be removed as they are with other types of breast cancer.
After a lumpectomy, radiation cuts the chances that the cancer will come back. If cancer does return, itâs called recurrence.
Some women may opt to have a lumpectomy only. Discuss the risks of not having radiation with your doctor before deciding against it.
You and your doctors may decide that a mastectomy to remove the breast is the best course of treatment if you have any of the following:
- A strong family history of breast cancer
- A gene mutation that makes having breast cancer more likely
- Very large areas of DCIS
- DCIS lesions in multiple areas throughout your breast
- Not being able tolerate radiation therapy
You and your treatment team may also consider the use of hormone therapy if the cancer tests positive for hormone receptors. It can cut the chance of getting another breast cancer.
Show Sources
What Are The Symptoms Of Dcis
DCIS usually has no symptoms. Most cases of DCIS are found during routine breast screening or if a mammogram is done for some other reason.
Occasionally DCIS is found when someone has a breast change such as a lump or discharge from the nipple. However, if someone with DCIS has a breast change its more likely they will also have an invasive breast cancer.
Some people with DCIS also have a type of rash involving the nipple known as Pagets disease of the nipple, although this is rare.
Read Also: How Long Does It Take For Melanoma To Spread To Organs
Treatment Of Breast Cancer By Stage
This information is based on AJCC Staging systems prior to 2018 which were primarily based on tumor size and lymph node status. Since the updated staging system for breast cancer now also includes estrogen receptor , progesterone receptor , and HER2 status, the stages may be higher or lower than previous staging systems. Whether or not treatment strategies will change with this new staging system are yet to be determined. You should discuss your stage and treatment options with your doctor.
The stage of your breast cancer is an important factor in making decisions about your treatment options. In general, the more the breast cancer has spread, the more treatment you will likely need. But other factors can also be important, such as:
- If the cancer cells have hormone receptors
- If the cancer cells have large amounts of the HER2 protein
- If the cancer cells have a certain gene mutation
- Your overall health and personal preferences
- If you have gone through menopause or not
- How fast the cancer is growing and if it is affecting major organs like the lungs or liver
Talk with your doctor about how these factors can affect your treatment options.
Stage 0 cancers are limited to the inside of the milk duct and are non-invasive .
Ductal carcinoma in situ is a stage 0 breast tumor.
Proposed Mechanisms For The Development Of Invasive Breast Cancer
Although the natural course of the intraductal process is unknown, DCIS is considered to be a non-obligate precursor of invasive breast cancer. Four evolutionary models have been proposed to describe the progression of DCIS into invasive breast cancer .
Overview of models showing four different theories of progression from ductal carcinoma in situ to invasive breast cancer
The first model is the independent lineage model. On the basis of mathematical simulations of the observed frequencies of the histological grade of DCIS and the histological grade of invasive disease in the same biopsy sample, Sontag et al. proposed that in situ and invasive cell populations arise from different cell lineages and develop in parallel and independently of each other. In support of this theory, Narod et al. state that small clusters of cancer cells with metastatic ability spread concomitantly through various routes to different organs and can therefore give rise to DCIS, invasive breast cancer and metastatic deposits simultaneously. Recent studies elucidating molecular differences between DCIS and invasive breast cancer further support the relevance of this model.
These putative models illustrate the potential complexity of the invasion process in DCIS and indicate that indolent lesions might become invasive via a combination of more than one of the proposed mechanisms.
Read Also: Idc Breast Cancer Survival Rate
Invasive Ductal Carcinomas We Treat
Apart from IDC, New Hope Unlimited offers treatment for the less common types of invasive ductal carcinoma:
Medullary Ductal CarcinomaThis rare breast cancer does not always feel like a lump. Instead, it can feel like a spongy change of breast tissue.
Mucinous Ductal CarcinomaThis disease occurs when cancer cells within the breast secrete mucus, which also contains breast cancer cells. The cells and mucus combine to form a tumor.
Tubular Breast CancerThis breast cancers name comes from its appearance under the microscope like hundreds of tiny tubes. Tubular ductal carcinoma often has an excellent prognosis.
Papillary Breast CarcinomaMany papillary tumors are benign . This rare type of invasive ductal carcinoma accounts for fewer than 1 percent of all breast cancer diagnoses.
How Can I Reduce My Risk For Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Like most cancers, knowing your family history can help you take preventative steps, such as early screenings and mammograms. Even though invasive ductal carcinoma cant be prevented altogether, there are steps you can take to lower your risk:
- Maintain a healthy body weight.
- Dont smoke.
- Eat a healthy, well-balanced diet.
- Undergo genetic testing for gene mutations if recommended based on family history.
Read Also: Can You Have Cancer Without A Tumor
Microvinvasive Breast Carcinoma Cells Are Often Comedotype
Microinvasive ductal carcinoma are frequently associated with a higher nuclear grade comedo type ductal carcinoma in situ. Other histologic subtypes of DCIS such as cribriform, papillary and solid, are thought to invade less frequently than comedo DCIS. If the microinvasive DCIS element comprises cells of either the solid, papillary, or cribriform pattern, the changes of lymph node metastasis are reduced even further.
Surgery For Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Breast cancer treatment has evolved to offer patients more options. In addition to removing breast cancer, new aesthetic surgical approaches can enhance well-being and lessen the emotional impact of losing all or part of a breast to cancer. Comprehensive breast centers with coordinated teams of oncologic and plastic surgery practitioners can offer a wider array of options.
Surgery for IDC may include one of these procedures:
- Lumpectomy is removal of part of the breast. It is also known as breast-conserving surgery. Lumpectomy may be followed by radiation treatments to treat any remaining cancer cells.
- Mastectomy is removal of the breast. Mastectomy is a treatment for patients with multiple, very aggressive, or large invasive ductal tumors. It can be followed by breast reconstruction.
Read Also: Well-differentiated Squamous Cell Carcinoma Prognosis
Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Diagnosis
IDC is usually found as the result of an abnormal mammogram. To diagnose cancer, youâll get a biopsy to collect cells for analysis. The doctor will remove a bit of tissue to look at under a microscope. They can make a diagnosis from the biopsy results.
If the biopsy confirms you have cancer, youâll likely have more tests to see how large the tumor is and if it has spread:
- CT scan. It’s a powerful X-ray that makes detailed pictures inside your body.
- PET scan. The doctor injects a radioactive substance called a tracer into your arm. It travels through your body and gets absorbed into the cancer cells. Together with a CT scan, this test can help find cancer in lymph nodes and other areas.
- MRI. It uses strong magnets and radio waves to make pictures of the breast and other structures inside your body.
- Bone scan. The doctor injects a tracer into your arm. They take pictures to find out if cancer has traveled to your bones.
- Chest X-ray. It uses low doses of radiation to make pictures of the inside of your chest.
What Is The Outlook For Idc
IDC prognosis largely depends on how far the cancer has spread. Among those with invasive breast cancer that has not metastasized, about 9 out of 10 people will live for five years or more after being diagnosed. Additionally, 84 percent will live at least 10 years.
If invasive breast cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes, the survival rates are slightly lower. About 86 percent of people will live for five years or more. Additionally, about 28 percent of people with metastatic breast cancer will live at least five years.
Other factors besides stage also affect a persons breast cancer outlook. Younger women and Black women tend to have worse outcomes when they are diagnosed with breast cancer, according to Cancer.Net. A persons overall health, as well as their cancers grade and molecular subtype, also affect prognosis. If you would like to learn more about your individual outlook, talk to your doctor, who is familiar with your cancers specific characteristics.
Recommended Reading: Stage 3 Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Survival Rate