What Is Basal Cell Carcinoma
Basal cell carcinoma is the result of DNA damage caused by UV rays. The basal cells are at the very bottom of your top living skin cell layer, which is called the epidermis.
When the harmful rays of the sun penetrate into the deepest portion of your epidermis, the basal cell DNA is damaged.
Once damaged, the cancers start to grow.
How Is Skin Cancer Treated
Treatment depends upon the stage of cancer. Stages of skin cancer range from stage 0 to stage IV. The higher the number, the more cancer has spread.
Sometimes a biopsy alone can remove all the cancer tissue if the cancer is small and limited to your skins surface only. Other common skin cancer treatments, used alone or in combination, include:
Cryotherapy uses liquid nitrogen to freeze skin cancer. The dead cells slough off after treatment. Precancerous skin lesions, called actinic keratosis, and other small, early cancers limited to the skins top layer can be treated with this method.
Excisional surgery
This surgery involves removing the tumor and some surrounding healthy skin to be sure all cancer has been removed.
Mohs surgery
With this procedure, the visible, raised area of the tumor is removed first. Then your surgeon uses a scalpel to remove a thin layer of skin cancer cells. The layer is examined under a microscope immediately after removal. Additional layers of tissue continue to be removed, one layer at a time, until no more cancer cells are seen under the microscope.
Mohs surgery removes only diseased tissue, saving as much surrounding normal tissue as possible. Its most often used to treat basal cell and squamous cell cancers and near sensitive or cosmetically important areas, such as eyelids, ears, lips, forehead, scalp, fingers or genital area.
Curettage and electrodesiccation
Chemotherapy and immunotherapy
Skin Cancer: An Overview
Skin cancer is the most common type of cancer in the United States, with more cases diagnosed annually than every other type of cancer combined. It’s so common that an estimated one in five Americans will develop one of the types of skin cancersuch as melanoma, actinic keratosis, basal cell carcinoma, or squamous cell carcinomaby age 70. People of all ages can get skin cancer, but it’s most common in people older than 50, those who have light-colored skin, who have a family history of skin cancer, or have spent lots of time out in the sun. Though a funny-looking mole is the skin cancer symptom people are most familiar with, it can present with many other symptoms as well. The good news: most skin cancers can be cured if they’re caught early.
You May Like: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Survival Rate
How Widespread Is Bcc
Basal cell carcinoma is quite common, and the number of reported cases in the U.S. has steadily increased.
- An estimated 3.6 million Americans are diagnosed with BCC each year.
- More than one out of every three new cancers are skin cancers, and the vast majority are BCCs.
- The diagnosis and treatment of nonmelanoma skin cancers, including BCC and squamous cell carcinoma , increased up to 77 percent between 1994 and 2014.
Reviewed by:
Does Skin Cancer Affect People With Skin Of Color
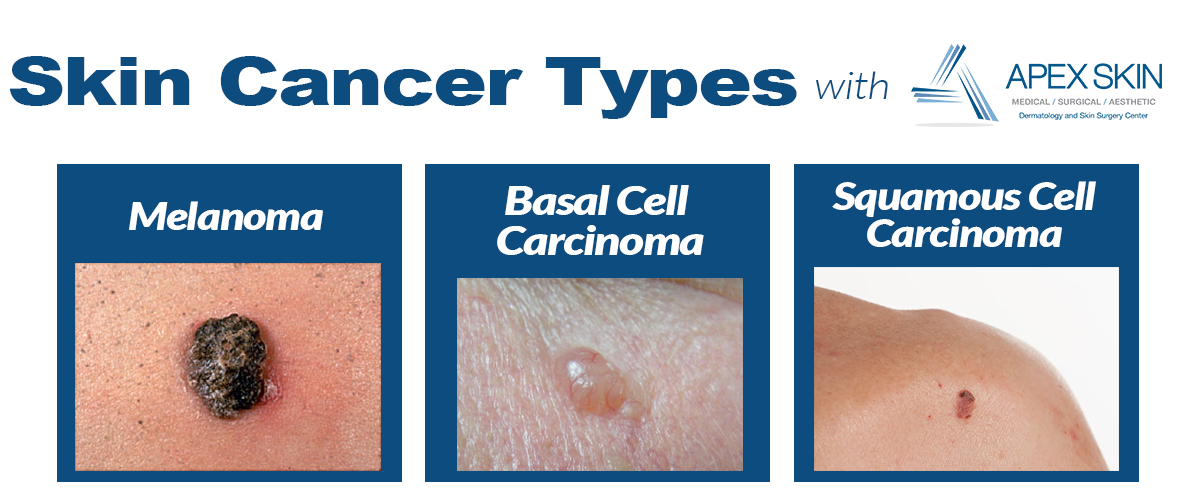
People of all skin tones can develop skin cancer. If you are a person of color, you may be less likely to get skin cancer because you have more of the brown pigment, melanin, in your skin.
Although less prevalent than in nonwhite people, when skin cancer does develop in people of color, its often found late and has a worse prognosis. If youre Hispanic, the incidence of melanoma has risen by 20% in the past two decades. If youre Black and develop melanoma, your five-year survival rate is 25% lower than it is for white people . Part of the reason may be that it develops in less typical, less sun-exposed areas and its often in late-stage when diagnosed.
Don’t Miss: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Grade 1 Survival Rate
Different Types Of Cancer Start In The Skin
Skin cancer may form in basal cells or squamous cells. Basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma are the most common types of skin cancer. They are also called nonmelanoma skin cancer. Actinic keratosis is a skin condition that sometimes becomes squamous cell carcinoma.
Melanoma is less common than basal cell carcinoma or squamous cell carcinoma. It is more likely to invade nearby tissues and spread to other parts of the body.
This summary is about basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma of the skin, and actinic keratosis. See the following PDQ summaries for information on melanoma and other kinds of cancer that affect the skin:
What Does Bcc Look Like
BCCs can look like open sores, red patches, pink growths, shiny bumps, scars or growths with slightly elevated, rolled edges and/or a central indentation. At times, BCCs may ooze, crust, itch or bleed. The lesions commonly arise in sun-exposed areas of the body. In patients with darker skin, about half of BCCs are pigmented .
Its important to note that BCCs can look quite different from one person to another. For more images and information on BCC signs, symptoms and early detection strategies, visit our BCC Warning Signs page.
Please note: Since not all BCCs have the same appearance, these photos serve as a general reference to what they can look like. If you see something new, changing or unusual on your skin, schedule an appointment with your dermatologist.
An open sore that does not heal
A shiny bump or nodule
A reddish patch or irritated area
A scar-like area that is flat white, yellow or waxy in color
A small pink growth with a slightly raised, rolled edge and a crusted indentation in the center
Read Also: How Long Does It Take Melanoma To Metastasize
Three Most Common Skin Cancers
It is estimated that one in seven people in the United States will develop some form of skin cancer during their lifetime. Although anyone can get skin cancer, people who burn easily and are fair-skinned are at higher risk. Researchers believe that one serious sunburn can increase the risk of skin cancer by as much as 50%. A yearly skin exam by a doctor is the best way to detect skin cancer early, when it is most treatable. If you have a new growth or any change in your skin, be sure to see your doctor to have it examined. Remember, protecting yourself from the sun is the best way to prevent all forms of skin cancer.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Treatment
Squamous cell carcinoma can usually be treated with minor surgery that can be done in a doctors office or hospital clinic. Depending on the size and location of the SCC, your doctor may choose different techniques to remove it.
For small skin cancers:
- Curettage and electrodessication : removing the top layer of the skin cancer then using an electronic needle to kill cancer cells
- Laser therapy: an intense light destroys the growth
- : a photosensitizing solution applied to your skin then activated with a light or daylight, or sometimes with intense pulsed light
- Cryosurgery: freezing of the spot using liquid nitrogen
For larger skin cancers:
- Excision: cutting out the cancer spot and some healthy skin around it, then stitching up the wound
- Mohs surgery: excision and then inspecting the excised skin using a microscope this requires stitching up the wound
Don’t Miss: Stage 3b Melanoma Survival Rate
The Most Common Skin Cancer
Basal cell carcinoma is the most common form of skin cancer and the most frequently occurring form of all cancers. In the U.S. alone, an estimated 3.6 million cases are diagnosed each year. BCCs arise from abnormal, uncontrolled growth of basal cells.
Because BCCs grow slowly, most are curable and cause minimal damage when caught and treated early. Understanding BCC causes, risk factors and warning signs can help you detect them early, when they are easiest to treat and cure.
The Most Common Types Of Skin Cancer
Listed in order from the most to least common, the main types of skin cancer are:
- Basal cell carcinoma By far the most frequently diagnosed type of skin cancer, basal cell carcinoma usually results from sun exposure and tends to be slow-growing. Left untreated, however, the cancerous cells can potentially spread to nearby tissues.
- Squamous cell carcinoma Squamous cell cancers often appear on parts of the body that have been exposed to sunlight, such as the face, ears, neck and hands, but can also develop on scars, mucous membranes and genitals. As compared to basal cell carcinomas, these malignancies are slightly more likely to invade fatty tissues beneath the skins surface.
- Melanoma A relatively uncommon but serious type of cancer, melanoma may develop in areas of the body that are not exposed to the sun, such as the groin, eyes and bottoms of the feet. The cancerous cells may also spread to nearby lymph nodes and metastasize to distant parts of the body.
- Merkel cell carcinoma A rare and aggressive form of skin cancer, Merkel cell carcinoma may originate in sun-exposed areas of the body, such as the face and scalp, and then spread to the bones, lungs, liver or brain.
- BROWSE
You May Like: Skin Cancer 1st Stage
Causes Of Skin Cancer
One of the main causes of skin cancer is being exposed to UV rays. UV rays are invisible, and are produced by the sun, and tanning equipment.
UV rays cause skin cancer by creating changes in the cells of your skin. In some cases, the UV rays cause direct damage to your cells. Tans and sunburns, for example, are both signs that UV rays have damaged your skin. In other cases, UV rays cause skin cancer indirectly, by weakening the immune system.
Many studies on skin cancer show that people who have suffered many severe sunburns in childhood are at greater risk of developing skin cancer. Family history, some chemical exposures, and immune dysfunction conditions can also create a greater risk of developing skin cancer.
What Is Skin Cancer
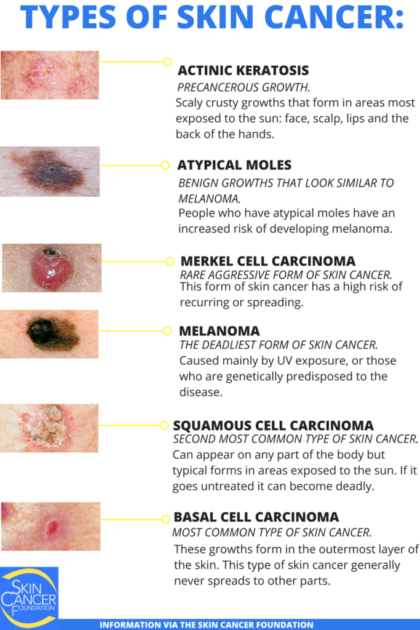
Basal cell carcinoma begins in the basal cell layer of the skin. Squamous cell carcinoma begins in the squamous layer of the skin. Melanoma begins in the melanocytes, which are the cells that make melanin, the pigment that gives skin its color.
Basal cell carcinoma begins in the basal cell layer of the skin. Squamous cell carcinoma begins in the squamous layer of the skin. Melanoma begins in the melanocytes, which are the cells that make melanin, the pigment that gives skin its color.
The skin is the bodys largest organ. Skin has several layers, but the two main layers are the epidermis and the dermis . Skin cancer begins in the epidermis, which is made up of three kinds of cells
- Squamous cells: Thin, flat cells that form the top layer of the epidermis.
- Basal cells: Round cells under the squamous cells.
- Melanocytes: Cells that make melanin and are found in the lower part of the epidermis. Melanin is the pigment that gives skin its color. When skin is exposed to the sun, melanocytes make more pigment and cause the skin to darken.
Basal and squamous cell carcinomas are the two most common types of skin cancer. They begin in the basal and squamous layers of the skin, respectively. Both can usually be cured, but they can be disfiguring and expensive to treat.
Don’t Miss: Stage 3 Melanoma Life Expectancy
Who Is Most At Risk For Skin Cancer
Although anyone can develop skin cancer, youre at increased risk if you:
- Spend a considerable amount of time working or playing in the sun.
- Get easily sunburned have a history of sunburns.
- Live in a sunny or high-altitude climate.
- Tan or use tanning beds.
- Have light-colored eyes, blond or red hair and fair or freckled skin.
- Have many moles or irregular-shaped moles.
- Have actinic keratosis .
- Have a family history of skin cancer.
- Have had an organ transplant.
- Take medications that suppress or weaken your immune system.
- Have been exposed to ultraviolet light therapy for treating skin conditions such as eczema or psoriasis.
What Does Skin Cancer Look Like
Basal cell carcinoma
-
BCC frequently develops in people who have fair skin. People who have skin of color also get this skin cancer.
-
BCCs often look like a flesh-colored round growth, pearl-like bump, or a pinkish patch of skin.
-
BCCs usually develop after years of frequent sun exposure or indoor tanning.
-
BCCs are common on the head, neck, and arms however, they can form anywhere on the body, including the chest, abdomen, and legs.
-
Early diagnosis and treatment for BCC are important. BCC can grow deep. Allowed to grow, it can penetrate the nerves and bones, causing damage and disfigurement.
Squamous cell carcinoma of the skin
-
People who have light skin are most likely to develop SCC. This skin cancer also develops in people who have darker skin.
-
SCC often looks like a red firm bump, scaly patch, or a sore that heals and then re-opens.
-
SCC tends to form on skin that gets frequent sun exposure, such as the rim of the ear, face, neck, arms, chest, and back.
-
SCC can grow deep into the skin, causing damage and disfigurement.
-
Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent SCC from growing deep and spreading to other areas of the body.
SCC can develop from a precancerous skin growth
-
People who get AKs usually have fair skin.
-
AKs usually form on the skin that gets lots of sun exposure, such as the head, neck, hands, and forearms.
-
Because an AK can turn into a type of skin cancer, treatment is important.
Melanoma
You May Like: Invasive Ductal Breast Cancer Survival Rate
Basal Cell And Squamous Cell Carcinoma
The two most common kinds of skin cancer are basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma, which are sometimes called nonmelanoma skin cancer. These cancers are carcinomas that begin in the cells that cover or line an organ.
Basal cell carcinoma accounts for more than 90 percent of all skin cancers in the United States and is the most common of all cancers. Typically, it is a slow-growing cancer that seldom spreads to other parts of the body.
Squamous cell carcinoma also rarely spreads, but does so more often than basal cell carcinoma. It is important that skin cancers are found and treated early because they can invade and destroy nearby tissue. Organ transplant recipients have a 65-fold higher risk of developing squamous cell carcinoma than others. UCSF Medical Center offers a High Risk Skin Cancer Clinic for those at high risk for non-melanoma skin cancers, such as transplant recipients.
What Happens If Precancers Go Untreated
As the name suggests, precancers are damaged skin cells that arent considered cancerous, but if they are left untreated, these lesions are at high risk to become skin cancer. There are two main types of precancerous skin conditions: actinic keratosis and dysplastic nevi. Actinic keratosis looks like a rough, scaly patch of the skin that is usually red or brown. This condition may develop into squamous cell carcinoma if left untreated.
Nevi are moles, and dysplastic nevi is a term that means a mole is abnormal. Dysplastic nevi may develop into melanoma without proper treatment. While precancerous skin cancers are not malignant on their own, the potential to develop into life-threatening forms of this condition means they need to be evaluated regularly.
You May Like: Melanoma On Face Prognosis
After Skin Cancer Treatment
Most skin cancer is cured surgically in the dermatologist’s office. Of skin cancers that do recur, most do so within three years. Therefore, follow up with your dermatologist as recommended. Make an appointment immediately if you suspect a problem.
If you have advanced malignant melanoma, your oncologist may want to see you every few months. These visits may include total body skin exams, regional lymph node checks, and periodic chest X-rays and body scans. Over time, the intervals between follow-up appointments will increase. Eventually these checks may be done only once a year.
Symptoms Of Skin Cancer
The main symptom of skin cancer is a new or changing bump, growth, lesion, mole, or rough patch of skin. Not all skin cancers look alike.
A normal mole is solid tan, brown, dark brown, or flesh colored. Its edges are well defined. Its usually smaller than 1/4 inch in diameter. It has a round or oval shape. It is flat or dome-like.
The ABCDE rule can help you remember what to look for when youre checking for moles. If you notice any of these signs, talk to your doctor right away.
- A for asymmetry Mole is not symmetrical. This means its not the same on both sides. If it was folded in half, the two halves wouldnt match.
- B for border Edges of the mole are blurry or jagged.
- C for color Changes in the color of a mole. This could be darkening, loss of color, spreading color, or multiple colors.
- D for diameter A mole more than ¼ inch in diameter.
- E for evolving Mole looks different from others or is changing in shape, size, or color.
Other signs of cancer could include:
- A mole that itches or bleeds.
- A fast-growing mole.
- A scaly or crusted growth on the skin.
- A sore that wont heal.
- A patch of skin that has changed color.
Most skin cancers occur on parts of the body that are repeatedly exposed to the sun. For men, these areas include the head, neck, face, tips of the ears, hands, forearms, shoulders, back, and chests. For women, they occur most commonly on the back and the lower legs.
Read Also: Basal Cell Carcinoma Syndrome
What Questions Should I Ask My Healthcare Provider
Questions to ask your dermatologist may include:
- What type of skin cancer do I have?
- What stage is my skin cancer?
- What tests will I need?
- Whats the best treatment for my skin cancer?
- What are the side effects of that treatment?
- What are the potential complications of this cancer and the treatment for it?
- What outcome can I expect?
- Do I have an increased risk of additional skin cancers?
- How often should I be seen for follow-up checkups?