What Are Lymph Nodes
Lymph nodes are small structures that filter substances and help fight infection. They are part of a network that runs throughout the body. Cancer that reaches the lymph nodes is concerning because cancer cells can easily spread to other parts of the body through this interconnected system.
Whether or not a melanoma spreads to one or more lymph nodes, it also may affect nearby skin. Such melanoma tumors are called satellite tumors. Theyre defined as being within 2 centimeters of the original tumor and can be seen without a microscope.
Melanoma tumors also may spread to lymphatic channels, thin tubes that resemble blood capillaries, through which lymph fluid flows.
How To Protect Yourself From Melanoma
Fortunately, most melanomas are diagnosed in early, localized stages, says Dr. González, and most patients treated for melanoma make a full recovery. But we do have patients that have ignored that funny looking mole for way too long, and its not uncommon to see cases that have metastasized to other organs, she adds.
Melanoma tends to a very aggressive form of cancer, and it can progress quickly from one stage to another. Says Dr. González: As soon as you see something unusual you should get it checked out, and as soon as you get a diagnosis, you need to be on top of the appropriate treatment.
Risk factors for melanoma include ultraviolet light exposure , having fair skin and light hair, and having a close relative whos also had melanoma. But monitoring skin for abnormal growths and changes is important for everyone, whether or not they are predisposed to skin cancer.
Going to see your board-certified dermatologist yearly and doing regular skin exams may not seem that important, Dr. González says, but these are the things that could save your life.
Recurrence In Nearby Lymph Nodes
If nearby lymph nodes werenât all removed during the initial treatment, the melanoma might come back in these lymph nodes. Lymph node recurrence is treated by lymph node dissection if it can be done, sometimes followed by adjuvant treatments such as radiation therapy and/or immunotherapy or targeted therapy . If surgery is not an option, radiation therapy or systemic treatment can be used.
You May Like: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Survival Rate Stage 1
What Are The Stages Of Melanoma
When a melanoma has been diagnosed, the pathology report provides information to determine the stage of the disease.
The prognosis of melanoma and the treatment options available depend on the stage at which the cancer is diagnosed.
One of the most common areas of confusion is the difference between the levels of melanoma and the staging of melanoma. The level of melanoma relates to the depth of the melanoma in the skin and the staging of melanoma refers to how limited or advanced the melanoma is at the time of diagnosis.
The stages of melanoma are determined by reviewing different factors including:
Dont Miss: Metastatic Melanoma Cancer Life Expectancy
Treatment Of Brain Metastasis
Melanoma that has spread to the brain accounts for 10-50% of reported deaths from melanoma. Individuals with multiple brain metastasis are treated with immunotherapy and higher dose therapy with Opdivo and Yervoy appears to produce the best results.
Patients are often treated with steroids to reduce “swelling” and its safest to discontinue steroids prior to starting immunotherapy.
A single brain metastasis can be removed with surgery – sterotactic radiation therapy should also be considered. There is a suggestion that radiation therapy in this situation improves survival and reduces recurrences. The decision to recommend surgery should be based primarily on whether the entire melanoma can be removed, and the status and number of other organs involved with metastatic lesions.
Also Check: Is Melanoma Bad
It Usually Starts With Suspicious Spot
Maybe you noticed a mole that stood out from the rest . Its edges were irregular, maybe it was asymmetrical in shape, unevenly pigmented, noticeably large , or rapidly changing . These are the spots that concern dermatologists. If you had one, your doc did a biopsy on your own ugly duckling. During this in-office procedure, your doctor either shaved off a layer of your mole, punched it out with a hole-punch-like tool, or removed it with surgical excision, along with a margin of healthy skin to check for wandering cancer cells.
What If I Have Metastatic Melanoma Symptoms
Whether you have a suspicious mole or are experiencing some symptoms of advanced-stage melanoma, it is important to consult with a physician to receive an accurate diagnosis, as many other conditions can cause similar symptoms. At Moffitt Cancer Center, we provide a comprehensive range of screening, diagnostic, treatment and supportive care services for patients with melanoma and other types of cancer. Within our Cutaneous Oncology Program, our multispecialty team includes surgeons, dermatologists, medical oncologists and other experts who work together as a tumor board to ensure our patients receive the best possible treatment and care.
If you would like to schedule an appointment at Moffitt to discuss your metastatic melanoma symptoms, call or fill out a new patient registration form online. We do not require a referral to schedule an appointment.
- BROWSE
Also Check: Ductal Invasive Carcinoma Survival Rate
What Are The Survival Rates For Melanoma
Melanoma can be treated most effectively in its early stages when it is still confined to the top layer of the skin . The deeper a melanoma penetrates into the lower layers of the skin , the greater the risk that it could or has spread to nearby lymph nodes or other organs. In recent years, clinical breakthroughs have led to new treatments that continue to improve the prognosis for people with advanced melanoma.
What Do Stage 4 Tumors Look Like
A change to an existing mole or normal skin can be the first sign that the cancer has spread. But the physical symptoms of stage 4 melanoma arent the same for everyone. A doctor will diagnose stage 4 melanoma by looking at the primary tumor, the spread to nearby lymph nodes, and whether the tumor has spread to different organs. While your doctor wont base their diagnosis only on what your tumor looks like, part of their diagnosis involves looking at the primary tumor.
Read Also: If You Have Skin Cancer How Do You Feel
What To Ask Your Doctor About Stage Iv Melanoma
When your doctor tells you that you have Stage IV melanoma, it can be frightening and overwhelming. But it is important to use the time with all of your doctors to learn as much about your cancer as you can. Your doctors will provide you important information about your diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment options.
It is often helpful to bring a friend or family member with you to your doctor appointments. This person can lend moral support, ask questions, and take notes.
The following questions are those you may want to ask your doctors. Some of the questions are for your medical oncologist, some are for your surgical oncologist, and some for your dermatologist. Remember, it is ALWAYS okay to ask your doctor to repeat or clarify something s/he has said so that you can better understand it. You may find it helpful to print out these questions and bring them with you to your next appointment.
Treating Stage I Melanoma
Stage I melanoma is typically treated by wide excision . The width of the margin depends on the thickness and location of the melanoma. Most often, no other treatment is needed.
Some doctors may recommend a sentinel lymph node biopsy to look for cancer in nearby lymph nodes, especially if the melanoma is stage IB or has other characteristics that make it more likely to have spread. You and your doctor should discuss this option.
If the SLNB does not find cancer cells in the lymph nodes, then no further treatment is needed, although close follow-up is still important.
If cancer cells are found on the SLNB, a lymph node dissection might be recommended. Another option might be to watch the lymph nodes closely by getting an ultrasound of the nodes every few months.
If the SLNB found cancer, adjuvant treatment with an immune checkpoint inhibitor or targeted therapy drugs might be recommended to try to lower the chance the melanoma will come back. Other drugs or perhaps vaccines might also be options as part of a clinical trial.
You May Like: Skin Cancer Prognosis
Stage 3 Peritoneal Mesothelioma
Peritoneal mesothelioma is the second-most common form of the disease. Instead of a formal staging system to measure progression, physicians typically use the existing Peritoneal Cancer Index to grade tumors in the abdomen. In addition, the PCI helps doctors determine the stage in many other abdominal cancers.
The PCI ranges from 0 to 39, measuring the spread of tumors across 13 different abdominal sectors. A score between 21 and 30 indicates stage 3 peritoneal mesothelioma. The characteristics of this stage are tumors localized within the abdomen, with some spread to nearby lymph nodes.
If a doctor refers to peritoneal mesothelioma as stage 3, it usually means tumors have spread throughout the abdominal lining and to nearby lymph nodes.Dr. Daniel A. LandauOncologist and hematologist
Recommended Reading: Invasive Lobular Carcinoma Grade 2 Survival Rates
Central Nervous System Changes
Patients dying of stage IV melanoma may exhibit changes in their mentation.Their activity decreases and they may sleep quite a bit. The Hospice Foundation notes that patients may not respond to conversation or questions 2. Patients with brain metastasis from the melanoma may lapse into a coma, a deep state of unconsciousness from which they cannot be aroused. Hospice states that even though patients are in a coma they may still hear what is said and feel pain. One of the last senses to go before death is hearing. As patients near death, they may experience sensory changes and hallucinate or hear things that are not there.
- Patients dying of stage IV melanoma may exhibit changes in their mentation.
- As patients near death, they may experience sensory changes and hallucinate or hear things that are not there.
Recommended Reading: Chances Of Squamous Cell Carcinoma Spreading
Stages Of Melanoma Skin Cancer
Staging describes or classifies a cancer based on how much cancer there is in the body and where it is when first diagnosed. This is often called the extent of cancer. Information from tests is used to find out the size of the tumour, which parts of the skin have cancer, whether the cancer has spread from where it first started and where the cancer has spread. Your healthcare team uses the stage to plan treatment and estimate the outcome .
The most common staging system for melanoma skin cancer is the TNM system. For melanoma skin cancer there are 5 stages stage 0 followed by stages 1 to 4. Often the stages 1 to 4 are written as the Roman numerals I, II, III and IV. Generally, the higher the stage number, the more the cancer has spread. Talk to your doctor if you have questions about staging.
When describing the stage, doctors often use the words early stage, locoregional or metastatic.
Early stage means that the cancer is only in where it started and has not spread to other parts of the body. It includes stage 0, stage 1A, stage 1B, stage 2A, stage 2B and stage 2C melanoma skin cancers.
Locoregional means the cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes, or it has spread to nearby areas of skin or lymph vessels. It includes stage 3 melanoma skin cancer.
Metastatic means that the cancer is in a part of the body farther from where it started. It includes stage 4 melanoma skin cancer.
Find out more about .
Factors Used For Staging Melanoma
To determine the stage of a melanoma, the lesion and some surrounding healthy tissue need to be surgically removed and analyzed using a microscope. Doctors use the melanomas thickness, measured in millimeters , and the other characteristics described in Diagnosis to help determine the diseases stage.
Doctors also use results from diagnostic tests to answer these questions about the stage of melanoma:
-
How thick or deep is the original melanoma, often called the primary melanoma or primary tumor?
-
Where is the melanoma located?
-
Has the melanoma spread to the lymph nodes? If so, where and how many?
-
Has the melanoma metastasized to other parts of the body? If so, where and how much?
The results are combined to determine the stage of melanoma for each person. The stages of melanoma include: stage 0 and stages I through IV . The stage provides a common way of describing the cancer, so doctors can work together to create the best treatment plan and understand a patient’s prognosis.
Don’t Miss: Survival Rates For Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Clinical Staging And Pathologic Staging
To add to the complexity of staging, the cancer also may have a clinical stage and a pathologic stage.
Clinical staging takes place before surgery, based on blood tests, physical exams or imaging tests such as X-rays, a computed tomography scan, magnetic resonance imaging or positron emission tomography scans.
What doctors discover during surgery may provide more detailed information about the cancers size and spread. Often, some tissue from the surgery will be examined afterward to provide more clues. This process is known as pathologic staging, or surgical staging.
If surgery isnt possible, doctors will use the clinical stage when determining a treatment plan.
How Often Should You Follow Up With Your Doctor
After your treatment, your doctor will recommend a regular follow-up schedule to monitor your cancer. Theyll be checking to make sure the cancer hasnt come back or new cancerous lesions havent appeared. The types of follow-up include:
A yearly skin check: Skin checks are an important aspect of detecting melanoma in its earliest, most treatable stages. You should also conduct a skin check on yourself once per month. Look everywhere from the bottoms of your feet to behind your neck.
Imaging tests every three months to a year: Imaging studies, such as an X-ray, CT scan, or brain MRI, look for cancer recurrence.
Physical exam as needed: A physical exam to assess your overall health is important when you have had melanoma. For the first two years, youll want to get an exam every three to six months. Then for the next three years, the appointments can be every three months to a year. After the fifth year, the exams can be as needed. Do a monthly self-examination of your lymph nodes to check your progress.
Your doctor may recommend a different schedule based on your overall health.
Dont Miss: How Bad Is Basal Cell Skin Cancer
Read Also: Well Differentiated Squamous Cell Carcinoma Prognosis
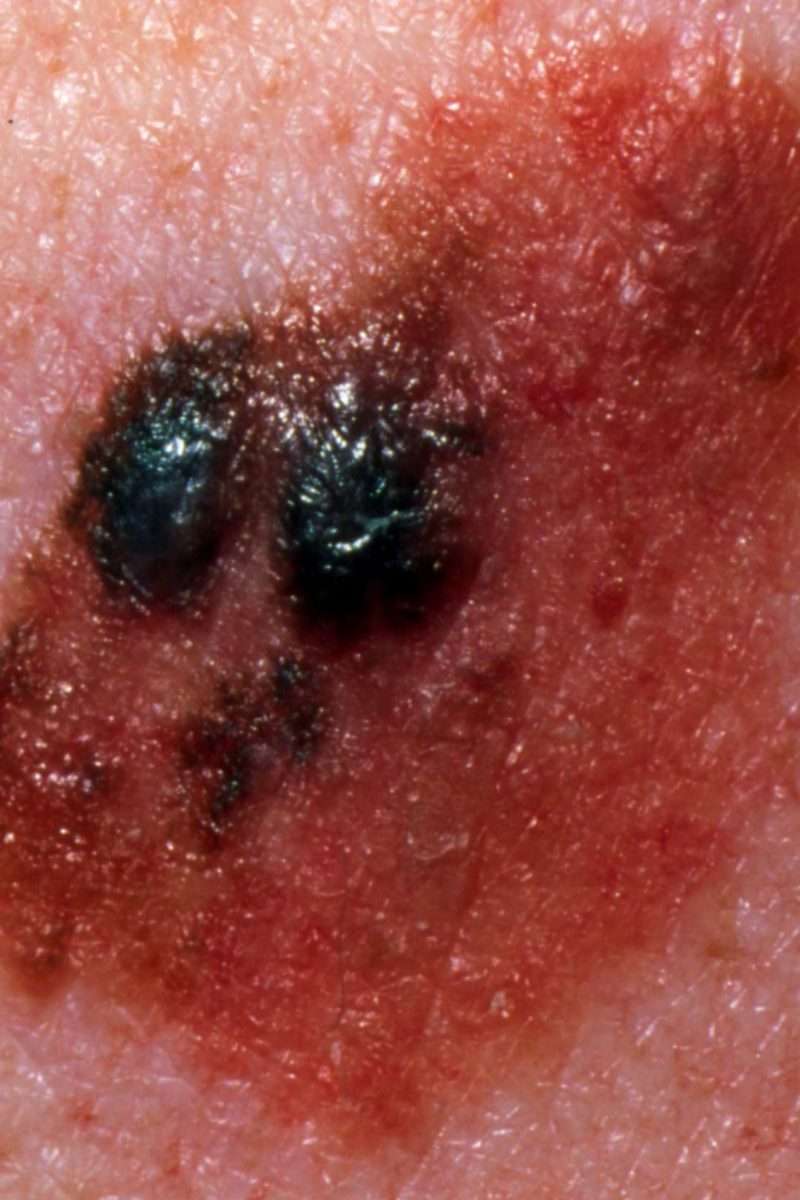
What Do Cutaneous Melanoma Metastases Look Like
Cutaneous melanoma metastases usually grow rapidly within the skin or under the skin surface dermal metastases are more common than subcutaneous. They are usually firm or hard in consistency. Cutaneous metastases may be any colour but are often black or red. They may also ulcerate and bleed.
Cutaneous metastatic melanoma
Epidermotropic metastatic melanoma is rare. In this case, the metastases develop more superficially than usual, within the epidermis. Epidermotropic metastatic melanoma is often initially misdiagnosed as the primary melanoma. The diagnosis of epidermotropic metastatic melanoma should be considered if multiple lesions arise with similar pathology.
Subcutaneous metastases are skin coloured or bluish lumps. They are usually painless.
Subcutaneous metastatic melanoma
Obstruction of lymphatic vessels due to melanoma in the lymph nodes or surgical removal of the lymph glands can result in swelling of the associated limb .
Metastatic melanoma
Treating Stage Iv Melanoma
Stage IV melanomas have already spread to distant lymph nodes or other areas of the body. Skin tumors or enlarged lymph nodes causing symptoms can often be removed by surgery or treated with radiation therapy.
Metastases in internal organs are sometimes removed, depending on how many there are, where they are, and how likely they are to cause symptoms. Metastases that cause symptoms but cannot be removed may be treated with radiation, immunotherapy, targeted therapy, or chemotherapy.
The treatment of widespread melanomas has changed in recent years as newer forms of immunotherapy and targeted drugs have been shown to be more effective than chemotherapy.
Immunotherapy drugs called checkpoint inhibitors such as pembrolizumab or nivolumab are typically the first drugs tried, especially in people whose cancer cells do not have BRAF gene changes. These drugs can shrink tumors for long periods of time in some people. Ipilimumab , a different type of checkpoint inhibitor, is not typically used by itself as the first treatment, although it might be combined with nivolumab or pembrolizumab. This slightly increase the chances that the tumor will shrink, although itâs also more likely to result in serious side effects, which needs to be considered carefully. People who get any of these drugs need to be watched closely for serious side effects..
Itâs important to carefully consider the possible benefits and side effects of any recommended treatment before starting it.
Recommended Reading: Skin Cancer Spreading To Lymph Nodes
Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy
A sentinel lymph node biopsy is a procedure to test for the spread of cancer.
It may be offered to people with stage 1B to 2C melanoma. It’s done at the same time as surgical excision.
You’ll decide with your doctor whether to have a sentinel lymph node biopsy.
If you decide to have the procedure and the results show no spread to nearby lymph nodes, it’s unlikely you’ll have further problems with this melanoma.
If the results confirm melanoma has spread to nearby nodes, your specialist will discuss with you whether further surgery is required.
Additional surgery involves removing the remaining nodes, which is known as a lymph node dissection or completion lymphadenectomy.
Treatment Of Stage I Melanoma
For information about the treatments listed below, see the Treatment Option Overview section.
Treatment of stage I melanoma may include the following:
- Surgery to remove the tumor and some of the normaltissue around it. Sometimes lymph node mapping and removal of lymph nodes is also done.
- A clinical trial of new ways to find cancercells in the lymph nodes.
Use our clinical trial search to find NCI-supported cancer clinical trials that are accepting patients. You can search for trials based on the type of cancer, the age of the patient, and where the trials are being done. General information about clinical trials is also available.
Also Check: Malignant Breast Cancer Survival Rate