Citation Doi And Article Data
Citation:DOI:Dr Ahmed AbdrabouRevisions:see full revision historySystems:
- Laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma
- Laryngeal SCC
- Squamous cell carcinomas of the larynx
Squamous cell carcinoma of the larynx is the most common primary malignant tumor that affects the laryngeal framework. Typically it is categorized by the laryngeal subsite affected, which affects presentation, treatment and prognosis.
How Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of Tongue Diagnosed
A diagnosis of Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Tongue is made by:
- Complete physical examination with detailed medical history evaluation
- Examination by a dermatologist using a dermoscopy, a special device to examine the skin
- Woodâs lamp examination: In this procedure, the healthcare provider examines the skin using ultraviolet light. It is performed to examine the change in skin pigmentation
Although the above modalities can be used to make an initial diagnosis, a tissue biopsy of the tumor is necessary to make a definitive diagnosis to begin treatment.
Tissue biopsy: A portion of the tongue tumor is removed for biopsy.
- A tissue biopsy of the tumor is performed and sent to a laboratory for a pathological examination. A pathologist examines the biopsy under a microscope. After putting together clinical findings, special studies on tissues and with microscope findings, the pathologist arrives at a definitive diagnosis. Examination of the biopsy under a microscope by a pathologist is considered to be gold standard in arriving at a conclusive diagnosis
- Biopsy specimens are studied initially using Hematoxylin and Eosin staining. The pathologist then decides on additional studies depending on the clinical situation
- Sometimes, the pathologist may perform special studies, which may include immunohistochemical stains, molecular testing, and very rarely, electron microscopic studies to assist in the diagnosis
Deterrence And Patient Education
Regarding primary prevention of HPV-related OPSCC, HPV vaccines show more than 90% efficacy in preventing vaccine-type HPV infections and their correlated anogenital precancerous lesions. Pinto et al. demonstrated that vaccination induces HPV antibodies levels at the oral cavity that correlate with circulating levels . A screening tool useful in early detection of HPV-DNA in oral rinses is promising, but very little data is available .
Safe oral sex habits should be advised. Educating the patients on the risks of betel quid chewing, alcohol use, and tobacco smoking is of the prime importance in the control and prevention of oropharyngeal cancers.
Read Also: What Is The Prognosis For Skin Cancer
What Causes Cancers Of The Head And Neck
Alcohol and tobacco use are the two most important risk factors for head and neck cancers, especially cancers of the oral cavity, hypopharynx, and voice box . People who use both tobacco and alcohol are at greater risk of developing these cancers than people who use either tobacco or alcohol alone . Most head and neck squamous cell carcinomas of the mouth and voice box are caused by tobacco and alcohol use .
Infection with cancer-causing types of human papillomavirus , especially HPV type 16, is a risk factor for oropharyngeal cancers that involve the tonsils or the base of the tongue . In the United States, the incidence of oropharyngeal cancers caused by HPV infection is increasing, while the incidence of oropharyngeal cancers related to other causes is falling . About three-quarters of all oropharyngeal cancers are caused by chronic HPV infection . Although HPV can be detected in other head and neck cancers, it appears to be the cause of cancer formation only in the oropharynx. The reasons for this are poorly understood.
Other known risk factors for specific cancers of the head and neck include the following:
Paan . The use of paan in the mouth, a common custom in Southeast Asia, is strongly associated with an increased risk of mouth cancers .
Radiation exposure. Radiation to the head and neck, for noncancerous conditions or cancer, is a risk factor for cancer of the salivary glands .
Cancer Evaluation And Staging
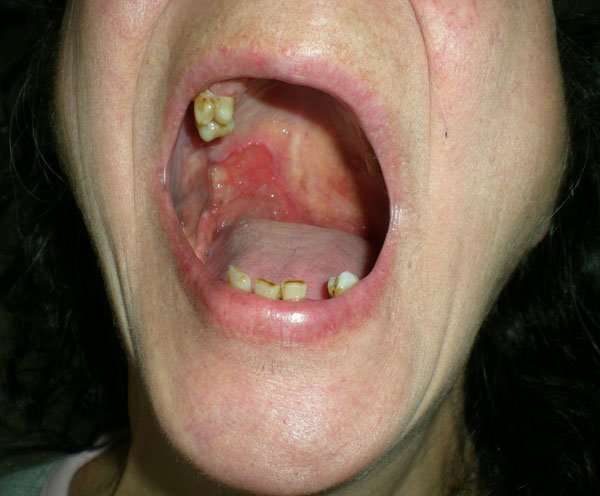
The first step in decision-making for patients with cancer of the larynx is accurate diagnosis and staging. This requires adequate tissue biopsy and histologic interpretation by a pathologist. Generally, these cancers are not difficult to diagnose by the pathologist, but if the clinical presentation is unusual , or if the appearance is not typical or the growth is too slow or too fast, a second interpretation or re-biopsy may be warranted.
Because most treatment decisions are based on the size and extent of the cancer, precise direct visualization of the cancer is required. This usually involves examination with an endoscope in the physician’s office, which allows determination of vocal cord mobility and other dynamic features and also direct laryngoscopy with a microscope under anesthesia. The exact size, shape and depth of invasion can be better determined and a search for adjacent areas of pre-malignant or malignant change can be assessed in other areas such as the oral cavity, pharynx and esophagus. The larynx is connected with the back of the tongue and the lower swallowing passageways and so these areas must also be examined thoroughly.
Also Check: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Stage 3 Survival Rate
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
An interprofessional team consisting of an oncologist, psychotherapist, dentist, a dietitian, histopathologist, surgeon, radiation oncologist, otorhinolaryngologist, a dental hygienist, and a chemotherapy nurse should work in collaboration to arrive at the best possible outcomes regarding the diagnosis and management of such patients .
These professionals are also in an optimal position to influence and advise patients on quitting smoking and limiting alcohol in addition to maintaining the healthy lifestyle habits such as eating fruits and vegetables, observing dental hygiene, and performing safe sex, that may contribute to preventing the increasing incidence of oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma.
What Are The Risk Factors For Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of Esophagus
The risk factors for Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Esophagus include the following:
Note:
- The involvement of Barrett esophagus is observed only in very rare cases
- Suspected causative factors include long-term exposure to fumes/smoke from burning and human papillomavirus infection
It is important to note that having a risk factor does not mean that one will get the condition. A risk factor increases ones chances of getting a condition compared to an individual without the risk factors. Some risk factors are more important than others.
Also, not having a risk factor does not mean that an individual will not get the condition. It is always important to discuss the effect of risk factors with your healthcare provider.
Recommended Reading: Stage 3b Melanoma Survival Rate
Genomic Alterations And Key Pathways
There is a tremendous need to identify molecular biomarkers that can be used to predict progression of pre-malignant HNSCC lesions, prognosticate survival, reveal new targets for intervention and predict response to therapeutic agents. The search for biomarkers has focused on defining the molecular abnormalities that characterize HNSCC. In this section, we highlight findings regarding genetic and epigenetic alterations, as well as dysregulation of cellular signalling pathways, which occur during HNSCC development.
Two additional members of the TP53 gene family, TP63 and TP73, are frequently altered in HNSCC. TP63 encodes two major isoforms, Np63 and TAp63 domain, respectively), and is overexpressed in a majority of HNSCC tumours. Np63 promotes HNSCC tumour growth by multiple mechanisms, including suppression of apoptosis and p16INK4A expression and induction of mitogenic signalling,,,. By contrast, TAp73, a major isoform encoded by TP73, exhibits tumour suppressor activity, and the function of TAp73 is commonly abolished in HNSCC. For example, stimulation of HNSCC cells with TNF results in the induction of REL oncoprotein that binds to Np63, displacing TAp73 from Np63TAp73 complexes and inactivating TAp73 . Phosphorylation of TAp73 by casein kinase 2 or Polo-like kinase 2 also leads to TAp73 inactivation and results in induction of NANOG, SOX2 and OCT4, promoting the stem cell-like properties of HNSCC tumour cells,.
What Is The Prognosis For People With Oropharyngeal Cancers
The prognosis for people with oropharyngeal cancer depends on your age and overall health, the HPV status of the tumor, history of smoking, and stage of cancer. Tumors that are HPV-associated have a dramatically improved cure rate, compared to tumors that are not associated with HPV. It is important for people with oral cancer or oropharyngeal cancer to have follow-up exams for the rest of their lives as cancer can occur in nearby areas. In addition, it is important to eliminate risk factors like smoking and drinking, which increase the risk for second cancers, or recurrent cancer.
According to the American Cancer Society, the five year relative survival rate is 70%. This means that if you have cancer, you are 70% as likely to live for at least five years after being diagnosed as people who dont have cancer. Keep in mind that this number does not take into account your age, general health, treatment response and HPV 16 status. The survival rate does not apply if your cancer stage changes. Also keep in mind that the survival rates are based on statistics collected five years earlier and newer treatments and management strategies are becoming available all the time.
You May Like: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Grade 2 Survival Rate
How Is Throat Cancer Diagnosed
Diagnosis of throat cancer typically begins with a physical exam conducted by your doctor to check for any signs of abnormality, such as a sore or lump in your mouth or swollen lymph nodes in your neck. Your doctor might also conduct an endoscopy, a procedure using a small camera and light. The endoscope is inserted through your nose and travels down the throat, allowing the doctor to take a closer look.
If an abnormality is spotted, your doctor will recommend a biopsy to confirm the presence of cancer. If throat cancer is diagnosed, you will likely need imaging tests to determine whether the throat cancer has spread to other areas of the body.
What Is Transoral Robotic Surgery
Transoral robotic surgery is a minimally invasive treatment method to remove difficult-to-reach oropharyngeal cancers through your mouth. With robotic surgery, your surgeon operates while seated at a console unit, while you are on a nearby operating table. Your surgeon operates using hand and foot controls to position a 3D, high-definition camera and to precisely direct surgical instruments, which are attached to robotic arms. Robotic surgery avoids the larger neck incision and lower jaw splitting required with traditional surgery. Advantages of transoral robotic surgery include a shorter hospital stay, faster recovery, less damage to surrounding tissues and swallowing muscles, avoidance of a tracheostomy breathing tube and less long-term problems with speech and swallowing.
Also Check: Melanoma On Nose Prognosis
Symptoms And Signs Of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Oral lesions are asymptomatic initially, highlighting the need for oral screening. Most dental professionals carefully examine the oral cavity and oropharynx during routine care and may do a brush biopsy of abnormal areas. The lesions may appear as areas of erythroplakia or leukoplakia and may be exophytic or ulcerated. Cancers are often indurated and firm with a rolled border. As the lesions increase in size, pain, dysarthria, and dysphagia may result.
This photo shows a close-up of the inside of the mouth in a patient with squamous cell carcinoma of the oral mucosa.
CLINICA CLAROS/SCIENCE PHOTO LIBRARY
Erythroplakia is a general term for red, flat, or eroded velvety lesions that develop in the mouth. In this image, an exophytic squamous cell carcinoma on the tongue is surrounded by a margin of erythroplakia.
Image provided by Jonathan A. Ship, DMD.
Leukoplakia is a general term for white hyperkeratotic plaques that develop in the mouth. About 80% are benign. However, in this image, squamous cell carcinoma is present in one of the leukoplakic lesions on the ventral surface of the tongue .
Image provided by Jonathan A. Ship, DMD.
Can I Do Anything To Prevent The Development Of Oropharyngeal Cancer
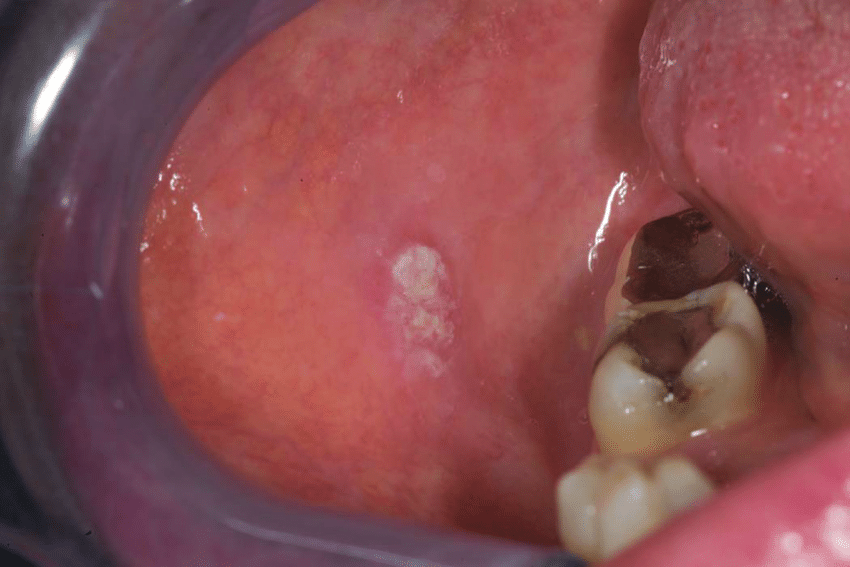
You may not be able to prevent oropharyngeal cancer, but you can take steps to lower your risk. Changes you can make include:
- Dont start smoking. If you smoke or use tobacco products, quit. Continuing to smoke greatly increased the risk of developing a second cancer in the mouth, throat or voice box or lung. Ask your healthcare provider for help. They have many resources and can put you in touch with the information need or other health professionals that can help you quit.
- Dont drink alcohol regularly or heavily. Alcohol increases the cancer-causing effects of tobacco, so its especially important to avoid this combination.
- Avoid human papilloma virus infection. Ask your doctor about the HPV vaccine. Multiple sex partners and oral sex increases your risk of HPV.
- Eat a healthy, well-balanced diet and exercise regularly.
- See your healthcare provider and dentist on a regular schedule. They can check your mouth and throat and catch any changes early in their development.
Read Also: Skin Cancer Spread To Lymph Nodes
What Is The Prognosis Of Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of Esophagus
The prognosis of Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Esophagus is generally poor.
Progression Of Throat Cancer
This type of cancerous tumor spreads by local extension, particularly into the soft palate and through the destruction of adjacent tissue. Lymphatic invasion with spread to the cervical lymph nodes is common at theime of throat cancer diagnosis. Haematogenous spread to distant sites such as the liver, bones and lungs may have occurred at the time of diagnosis of this type of throat cancer.
Don’t Miss: Stage 2 Cancer Symptoms
How Often Does Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Occur
Oral squamous cell carcinoma affects about 34,000 people in the US each year. In the US, 3% of cancers in men and 2% in women are oral squamous cell carcinomas, most of which occur after age 50. As with most head and neck sites, squamous cell carcinoma is the most common oral cancer. The chief risk factors for oral squamous cell carcinoma are.
Cancer Treatment Backed By Science And Delivered With Care
With several locations conveniently around the Greater Cincinnati area, the UC Health Head and Neck Cancer Center has experts in all areas pertaining to a patients cancer care from surgery, radiation and facial reconstruction, to nutrition, speech therapy, social work and patient navigation.
Whether early-stage or highly complex and rare, our head and neck cancer team is equipped with the latest technology and a multidisciplinary team of experts who meet weekly to discuss each and every patient case to determine the best treatment approach.
Dr. Cervenka explained, Because we have specialists from numerous areas looking at each case, we often have multiple good treatment paths that are not only backed by science, but ones that uniquely make the most sense for that patient and their life.
You May Like: Lobular Breast Cancer Stage 3
How Is Laryngeal Cancer Diagnosed
Diagnosing laryngeal cancer begins with your medical history. If you have potential cancer symptoms, your doctor will examine you carefully and begin a series of tests.
The first test performed is usually a laryngoscopy. Your doctor will use either a small scope or a series of mirrors to examine your larynx.
If your doctor sees any abnormalities, they may perform a biopsy. A laboratory can test this small tissue sample for cancer.
Imaging tests arent a common method to diagnose laryngeal cancer. However, tests such as a CT scan or MRI scan can help your doctor tell if cancer has spread.
What Are The Symptoms Of Throat Cancer
Symptoms for throat cancer can vary, depending on where the cancer is found. Generally, though, they include a sore throat that doesnt go away, pain or difficulty swallowing, persistent ear pain, a lump in the neck or throat, hoarseness or other changes in the voice, nosebleeds, headaches, coughing up blood, unexplained weight loss, sores in the throat, constant bad breath and a stiff jaw.
Recommended Reading: Stage 2 Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Survival Rate
What Fruit Is Good For Sore Throat
The Best Food And Drink For A Sore Throat
- Bananas A soft fruit that will be easy on the throat and is healthy and filling too.
- Pomegranate Juice Studies suggest pomegranate juice can reduce inflammation and fight off infection.
- Frozen Fruit Fruit sherbets and popsicles can soothe the inflammation.
Where Throat Cancer Begins
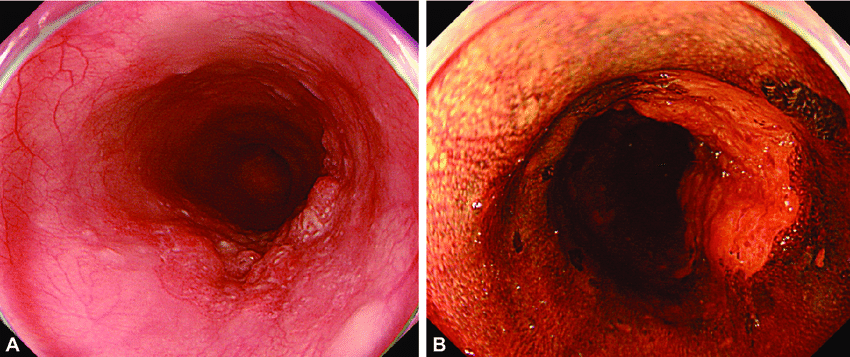
Doctors also refer to the cancer by its precise location in the throat.
The throat has two primary parts: the pharynx and the larynx.Throat cancer can begin in either place.
Knowing a little bit about the anatomy of the throat will help you talk to your doctor about your treatment options for throat cancer, which may include surgery or radiation, as well as other aspects of your care.
Recommended Reading: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Survival Rate Stage 4
Health Literacy To Empower Patients
With the right information, patients can make the best decisions about their care. By partnering with patients, healthcare providers, and hospitals, we hope to provide all patients with the tools and knowledge to understand their pathology report.
For more information about this site, contact us at .
Disclaimer: MyPathologyReport.ca is a registered not-for-profit charity . The articles on MyPathologyReport are intended for general informational purposes only and they do not address individual circumstances. The articles on this site are not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment and should not be relied on to make decisions about your health. Never ignore professional medical advice in seeking treatment because of something you have read on the MyPathologyReport site. MyPathologyReport is independently owned and operated and is not affiliated with any hospital or patient portal.
Copyright © 2021. All rights reserved. Privacy Policy
Our work is generously supported by: