Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of The Oral Cavity
More than 90 percent of mouth cancers are squamous cell carcinoma. Squamous cells are thin, flat cells that look like fish scales. They are found in the tissue that forms the surface of the skin, the lining of the hollow organs of the body, and the lining of the respiratory and digestive tracts. Carcinoma means cancer.
Squamous cell carcinoma most commonly appears on parts of the body frequently exposed to the sun, such as the face, ears, and neck. But it also arises in the mouth.
Less common cancers of the oral cavity include:
What Is Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Oral squamous cell carcinoma is the most common form of mouth cancer that is usually caused by excessive alcohol and tobacco use. Cancer of the mouth usually manifests as small discolored lesions on the tongue, gums, inner lips, or the floor or roof of the mouth. Patients do not typically experience pain, though swelling and irritation can arise in the later stages of cancer. When detected early, most cases of oral squamous cell carcinoma can be treated with surgery or radiation therapy combined with healthy lifestyle changes. Advanced carcinoma tends to spread quickly, however, and can lead to cancer in throat tissue and lymph nodes in the neck.
Squamous cells make up the outermost layer of tissue in the mouth, and are the most susceptible to oral cancer. Affected tissue can turn red or brown and emerge as elevated open lesions. Some lesions appear as white bumps that are rough to the touch. In most cases, the lesions do not cause physical pain or discomfort. As the cancer spreads, more lesions tend to appear and an individual may experience a sore throat and slight swelling and irritation of the tongue, gums, or soft palate.
After Lip And Oral Cavity Cancer Has Been Diagnosed Tests Are Done To Find Out If Cancer Cells Have Spread Within The Lip And Oral Cavity Or To Other Parts Of The Body
The process used to find out if cancer has spread within the lip and oral cavity or to other parts of the body is called staging. The information gathered from the staging process determines the stage of the disease. It is important to know the stage in order to plan treatment. The results of the tests used to diagnose lip and oral cavity cancer are also used to stage the disease.
Read Also: Mayo Clinic Pictures Of Skin Cancer
Also Check: Well Differentiated Meaning
What Are Oral Cavity And Oropharyngeal Cancers
Oral cavity cancer starts in the mouth. It might also be called oral cancer. Oropharyngeal cancer starts in the middle part of the throat just behind the oral cavity that can be seen when the mouth is open.
Cancer starts when cells in the body start to grow out of control. To learn more about how cancers start and spread, see What Is Cancer?
Tobacco And Alcohol Use Can Affect The Risk Of Lip And Oral Cavity Cancer
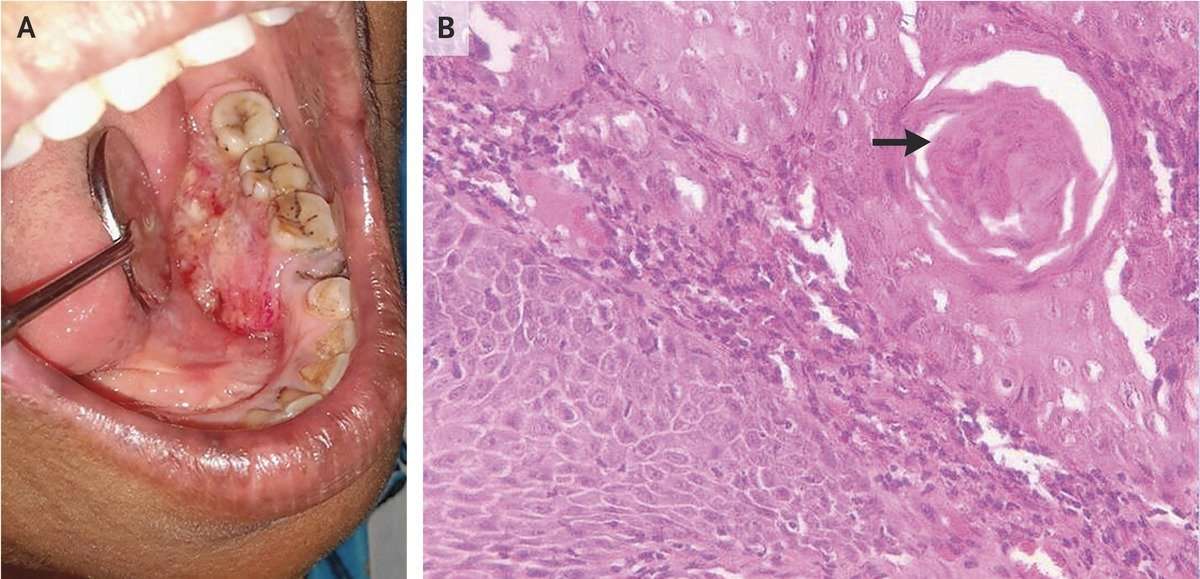
Anything that increases your risk of getting a disease is called a risk factor. Having a risk factor does not mean that you will get cancer not having risk factors doesnât mean that you will not get cancer. Talk with your doctor if you think you may be at risk. Risk factors for lip and oral cavity cancer include the following:
Recommended Reading: What Is The Survival Rate For Invasive Lobular Carcinoma
Also Check: Melanoma Forearm
Squamous Or Basal Cell Cancer: Which One Is Worse
Skin, the largest organ of the human body, protects us from infections, injuries and helps to modulate the body temperature. Also, the organ stores water and fat and is responsible for producing vitamin D. You might have studied in your school that skin is made up of three layers, i.e., the epidermis, dermis, and hypodermis. As we know, the epidermis is the outermost layer of the skin, while the dermis and hypodermis are the inner layer of the skin and the deep layer of the fat, respectively.
The abnormal growth of skin cells is known as skin cancer. It generally develops on skin exposed to the ultraviolet rays of the sun. You would be surprised to learn that more than 3 million people in the United States are diagnosed with skin cancer, making it the countrys most common type of cancer. If found at an early stage, the disease can be treated with medication, procedures provided by a dermatologist , or a surgeon.
Primarily, there are four types of skin cancer: basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, Merkel cell cancer, and melanoma, but basal and squamous cell cancer are the most common types. Lets find out more about these diseases.
How Can I Best Cope With Verrucous Carcinoma
A cancer diagnosis may feel scary, but most people with verrucous carcinoma have a good prognosis. See your healthcare provider and follow your treatment plan. Avoid tobacco products and limit the amount of alcohol you drink.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Verrucous carcinoma is a highly treatable cancer. You can reduce your risk of developing this cancer by not smoking or chewing tobacco and by drinking less alcohol. Contact your healthcare provider if you notice any lumps, growths or sores in your mouth , on your genitals or on your feet. With early diagnosis, you can get treated earlier and recover faster.
Recommended Reading: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Stage 2 Survival Rate
Other Types Of Mouth And Oropharyngeal Cancer
Other types of mouth and oropharyngeal cancer include the following.
Salivary gland cancer
There are minor salivary glands throughout the lining of the mouth and oropharynx. It is more common for a lump in this area to be non cancerous . But cancers can develop in these glands. They are mostly a type of cancer called adenocarcinoma. Adenocarcinomas are type of cancer that start in glandular tissue.
Adenoid cystic tumour
This is a rare type of tumour and can develop from glandular tissue in the salivary glands or the mouth. The parotid gland is the most common place to find this type of cancer.
These cancers develop from basal cells and can be found on the lips.
Lymphoma
Lymphomas are cancers that start from cells in the lymphatic system. The base of the tongue and tonsils are made up of lymph tissue that can develop into cancer. There are also many lymph nodes in the neck. Painless swelling of a lymph node is the most common sign of lymphoma. Treatment for lymphoma will be very different to treatment for mouth or oropharyngeal cancer.
Melanoma
Melanomas develop from the pigment producing cells that give skin its colour. Melanomas of the head and neck can occur anywhere on the skin or inside the nose or mouth . If you have a melanoma of the mouth or lip, the information about radiotherapy or surgery for mouth and oropharyngeal cancer will be useful.
How Is This Cancer Diagnosed
Fine needle aspiration or biopsy will be performed. FNA involves taking a small needle with a syringe and suctioning a sample of cells directly from the tumor and placing them on a microscope slide. A veterinary pathologist then examines the slide under a microscope.
In some cases, results from FNA may not be entirely clear and biopsy may be necessary. A biopsy is a surgical excision of a piece of the tumor. Pieces of the tumor are then examined by a veterinary pathologist under the microscope. This is called histopathology. Histopathology is not only helpful to make a diagnosis but can indicate how the tumor is likely to behave .
You May Like: Does Melanoma Blanch When Pressed
Undifferentiated Tumors: Solving The Mystery
Q. When a squamous cell carcinoma is designated as poorly differentiated, what other parameters/tests are performed to determine the tissue of origin?
A. Differentiation, for those of you who have just joined us, is a quality of tumors that has to do with how much the tumor cells resemble their tissue of origin. Well-differentiated tumors are composed of cells that closely resemble their tissue of origin, whereas poorly-differentiated tumors are composed of cells that have little resemblance to their tissue of origin. Anaplastic tumors are the least differentiated of all: they show no resemblance to their tissue of origin.
This concept is important for a couple reasons. First, the degree of differentiation of a tumor often has a bearing on prognosis. Well-differentiated tumors generally carry a better prognosis than poorly differentiated tumors. Second, when a tumor is totally undifferentiated , you have to resort to special tests in order to figure out its origin .
Back to our question: when you have a poorly-differentiated squamous cell carcinoma, how do you know its a squamous cell carcinoma ? If the tumor is poorly-differentiated, that means there are still some morphologic features that reveal the squamous nature of the tumor. If you look carefully, you should be able to find some of these features, which would then point you towards the diagnosis of squamous cell carcinoma.
Symptoms Of Squamous Cell Carcinoma In Dogs
Most SCCs tend to be localized. But there are cases in which the tumor invades the bone tissues. Tumor spread to adjacent lymph nodes may also occur. However, metastasis to distant organs is rare and usually doesnt take place until the condition is well-advanced.
The appearance of SCC tends to be variable and non-specific. The tumor may appear shallow and crusting, deeply ulcerated, red and proliferative, or cauliflower-like.
The appearance of the tumor may change as it develops. There have been cases in which the tumor has been misdiagnosed as inflammation or traumatic lesions and was prescribed antibiotics and corticosteroids.
The symptoms of SCC depend to a large extent on the location of the tumor. Dogs with digital tumors may exhibit lameness and digit ulceration. If SCC affects the nose and nasal passages, there may be facial deformity, sneezing, and nasal discharge. Dogs with oral SCC may show bleeding in the mouth, excessive salivation, loss of appetite, weight loss, bad breath, and loose teeth.
Diagnosis of Squamous Cell Carcinoma in Dogs
Early detection and diagnosis are of paramount importance so appropriate therapeutic intervention can be started immediately. This may increase the chance of long-term control or even be curative for affected dogs.
Your vet may suspect SCC based on the appearance of the growth and where its located.
Treatment Options and Prognosis
Don’t Miss: Non Invasive Breast Cancer Survival Rate
Mouth Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Invasion of OSCC into bone may occur from several routes: oral cavity occlusal route, mental or inferior alveolar foramen , secondary tumors in the neck through the lower border, cortical bone defects in an edentulous ridge, periodontal membrane in the dentate arch, and the attached gingiva.
S. Hamad Sagheer, … Nancy J. Philp, in, 2021
How To Treat Squamous Cell Carcinoma In Cats
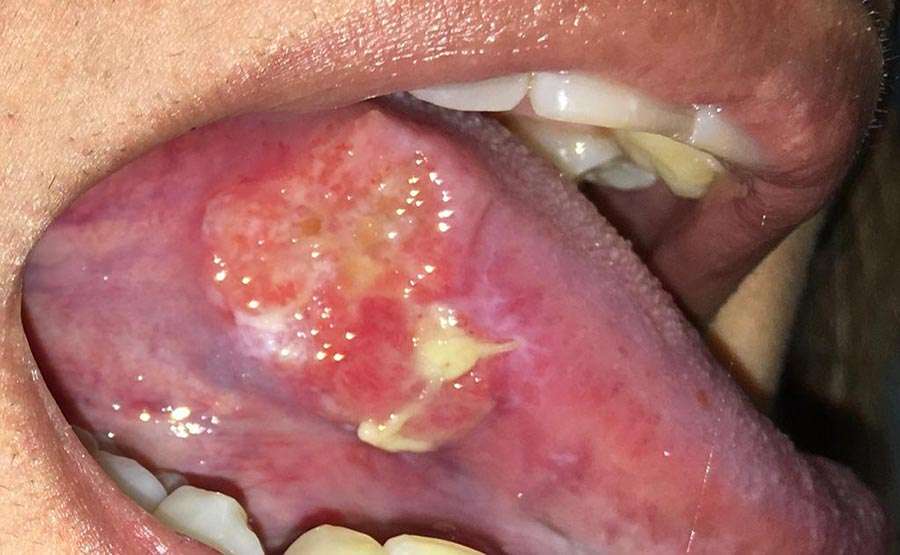
Since this is a type of cancer to spread to other parts of the body, it’s important to notify veterinary medicine professionals that you believe your cat is ill. Even if a CT scan is performed and the vet discovers that your cat doesn’t have feline oral SCC after all, it’s better to be overly cautious than too laid back about your cat’s health.
Once oral SCC is identified as the cause of your cat’s symptoms, it then becomes time for vets to intervene with a specialized treatment plan specifically designed for your pet’s circumstances. Since feline squamous cell carcinoma is a form of cancer, radiation therapy will likely be part of your cat’s treatment plan, though it might bring some unfortunate side effects.
Veterinary medicine professionals can also decide to remove the tumor causing your cat’s cancer surgically. The veterinary medicine decision to follow through with surgical removal of your cat’s tumor is taken in more severe cases of feline oral SCC.
You May Like: Survival Rates For Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
How Squamous Cell Carcinoma Is Diagnosed
Unfortunately, clinical signs are hard to detect in the earliest of stages. Since cases of feline SCC are not easily recognizable in the beginning, tumors are typically the most obvious sign.
A fine needle aspiration can be used to diagnose tumors in many areas of the body. This procedure entails taking a small, hollow tube with suction attached and sucking up some cells from the tumor before putting them on a slide for examination under an electron microscope by veterinary pathologists.
The diagnosis process may vary depending what type of skin or nail bed pathology is observed through this method such as melanoma , sarcoma or benign neoplasia which are most common founds in dogs that express outward signs like soreness at their paw pad when being palpated
To understand whether or not your affected cat has malignant tumors indicative of SCC, it’s important that the vet orders a biopsy. By looking directly at the tumor size and taking a sample to the laboratory, the vet will be able to determine whether or not the raised bump is a malignant tumor like those in cases of oral squamous cell carcinoma in cats.
Since SCC tends to be invisible until symptoms become incredibly concerning, it doesn’t hurt to check your cat’s mouth for a tumor routinely. Though you shouldn’t let the possibility rule your mind or make you feel panicked, occasionally inspecting your cat’s mouth for a tumor is a productive and proactive measure to take.
What Is Verrucous Carcinoma
Verrucous carcinoma is a type of squamous cell carcinoma . You can get this cancer in your mouth or, more rarely, on your genitals or feet.
Squamous cells are certain types of cells that are flat and thin. Theyre found in many tissues of your body, including the surface of your skin and the lining of your throat and mouth.
Also Check: Metastatic Melanoma Cancer Life Expectancy
What Are The Possible Complications Of Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of Oral Cavity
The possible complications due to Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Oral Cavity could be:
- Severe discomfort while eating, chewing, or swallowing food this can even lead to weight loss
- A partial of complete loss of taste sensation
- They can metastasize to the lymph nodes SCC of Oral Cavity has a higher chance of metastasis than if they are at other locations
- Tumors that invade into nerves have higher chances of recurrence and metastasis
- Tumors that are over 2 cm in size have a higher incidence of recurrence and metastasis, than tumors that are less than 2 cm in size
- Severe emotional and psychological stress
- Complications that arise from cancer therapy
Who Gets Oral Cancer
According to the American Cancer Society, men face twice the risk of developing oral cancer as women. Men who are over age 50 face the greatest risk. Itâs estimated that over 50,000 people in the U.S. received a diagnosis of oral cancer in 2019.
Risk factors for the development of oral cancer include:
It is important to note that over 25% of all oral cancers occur in people who do not smoke and who only drink alcohol occasionally.
Also Check: Skin Cancer Spread To Lymph Nodes
Who’s Affected By Mouth Cancer
Mouth cancer is the 6th most common cancer in the world, but it’s much less common in the UK.
Around 8,300 people are diagnosed with mouth cancer each year in the UK, which is about 1 in every 50 cancers diagnosed.
More than 2 in 3 cases of mouth cancer develop in adults over the age of 55. Only 1 in 8 happen in people younger than 50.
Men are more likely to get mouth cancer than women. This may be because, on average, men tend to drink more alcohol than women.
Mouth cancer can develop in younger adults. HPV infection is thought to be linked with the most mouth cancers that happen in younger people.
What Is An Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma
A squamous cell carcinoma is a malignant tumor of the cells that line the outer layer of the skin , and the passages of the respiratory and digestive tracts.
Squamous cell carcinoma is the most commonly reported oral tumor in cats, and the second most common in dogs. This cancer can also affect the tonsils in dogs and cats , as well as the gum line and remainder of the oral cavity .
Multicentric squamous cell carcinoma is a type of squamous cell carcinoma that occurs in both dogs and cats. The lesions are confined to the surface layers of the skin and mouth. Multicentric SCC is rare in cats and dogs.
Don’t Miss: Stage 3 Melanoma Cancer Life Expectancy
Squamous Cell Cancers Of The Mouth And Oropharynx
Squamous cell carcinoma is cancer starting in the squamous cells. Around 95 out of 100 of all oropharyngeal cancers are SCC. Most mouth cancers are also SCC. Squamous cells are the flat, skin like cells covering the inside of the mouth, nose, larynx and throat. Carcinoma means cancer.
Verrucous carcinoma is an unusual type of squamous cell carcinoma. It spreads to other parts of the body but can grow very deeply into surrounding tissues.
What Is The Prognosis Of Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of Oral Cavity
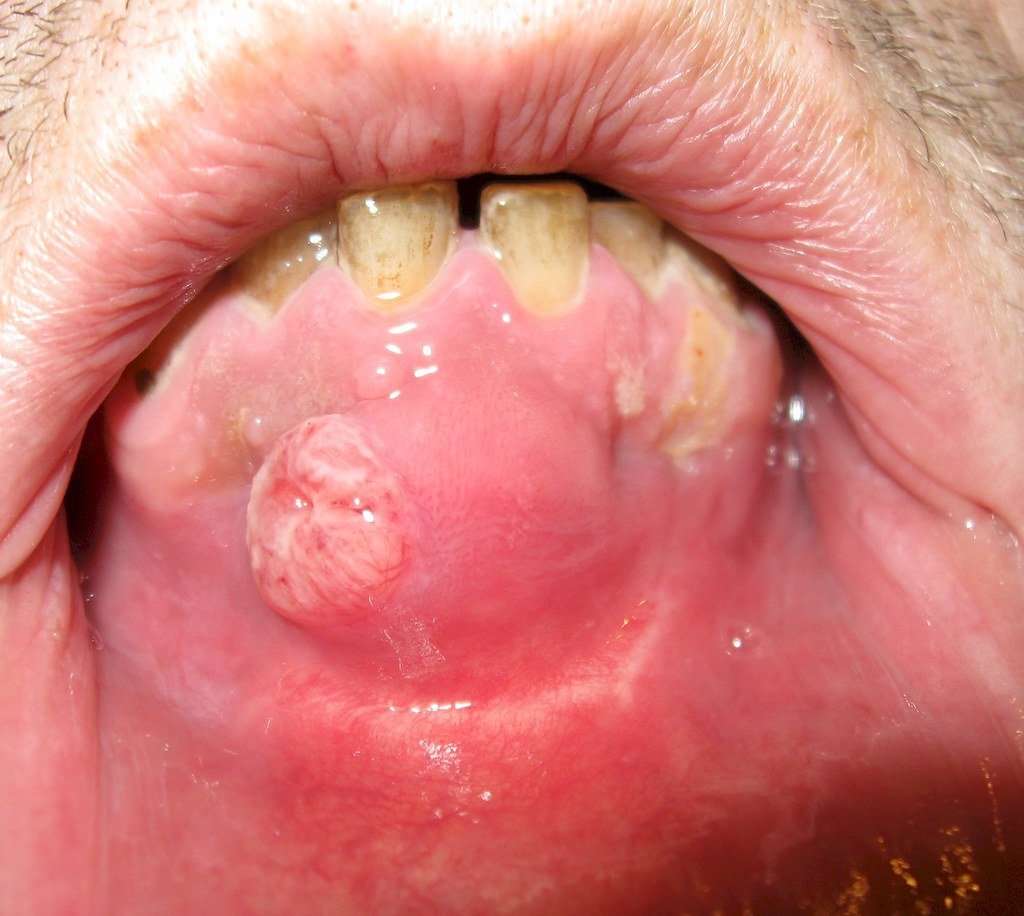
- In general, Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Oral Cavity is an aggressive form of cancer. If metastasis is observed, then the prognosis is guarded or unpredictable
- Tumors in their early stage with complete excisional treatment typically have good prognosis
- In cases of metastasis, its prognosis depends upon a set of several factors that include:
- Stage of tumor: With lower-stage tumors, when the tumor is confined to site of origin, the prognosis is usually excellent with appropriate therapy. In higher-stage tumors, such as tumors with metastasis, the prognosis is poor
- The surgical respectability of the tumor
- Overall health of the individual: Individuals with overall excellent health have better prognosis compared to those with poor health
- Age of the individual: Older individuals generally have poorer prognosis than younger individuals
- Whether the tumor is occurring for the first time, or is a recurrent tumor. Recurring tumors have a poorer prognosis compared to tumors that do not recur
- Response to treatment: Tumors that respond to treatment have better prognosis compared to tumors that do not respond so well to treatment
Don’t Miss: Clear Cell Carcinoma Symptoms