What Medications Treat Squamous Cell Carcinoma
If you have invasive squamous cell carcinoma or if treatment to remove your cancer surgically isnt right for you, your healthcare provider could offer medicine to treat your diagnosis. Medicines could include:
- Skin creams containing imiquimod or 5-fluorouracil help treat squamous cell carcinoma thats in the top layer of your skin .
- Cemiplimab-rwlc is immunotherapy to treat advanced forms of squamous cell carcinoma.
- Pembrolizumab is immunotherapy to treat squamous cell carcinoma that isnt treatable with surgery.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma In Situ
Early forms of squamous cell carcinoma, also known as Bowen disease, are classified as in situ, which means in place in Latin. This simply means that the cancer cells havent yet spread beyond the epidermis. When the carcinoma spreads deeper into the skin, into the lymph nodes or organs, it is considered to be metastasized.
Typically, Bowen disease will first appear as a red, scaly plaque of skin, often larger than 1/2 inch across. It can also sometimes appear as a hard domed bump. Both varieties typically feel rough and crusty and can bleed when scraped. Cancer usually shows up on areas of the skin that are exposed to the sun, such as the face, ears, lips, arms, legs, and tops of hands, but it can also more rarely appear on areas not exposed to the sun including the lower lip and genitals. This cancer usually develops slowly but can spread to the lymph nodes and other organs if left untreated. If caught early though, it is highly treatable.
A doctor will diagnose squamous cell carcinoma with a biopsy. Treatment of the cancer will then vary depending on location, size, severity, how far it has spread and the health of the patient.
Signs & Symptoms Of Bowens Disease Or Squamous Cell Carcinoma In Situ
- Bowens disease or Squamous Cell Carcinoma In Situ can affect any part of the skin on the body however, it commonly occurs on sun-exposed skin, such as hands, head and lower legs.
- Initially, there is appearance of red, scaly patches of around 1 to 3 cm in diameter.
- These patches can also appear as raised spots or warts.
- Patient has itchiness and the affected area can become sore.
- There can also be bleeding and scabbing.
Don’t Miss: Melanoma 3c
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Squamous Cell Carcinoma In Situ Of Anus
Squamous Cell Carcinoma In Situ of Anus signs and symptoms may include:
- The presence of a single patch-like red lesion on the anus that is poorly-defined they may be many in number, in some cases
- Itching sensation may be felt around the red patch
- They may or may not ulcerate and bleed
- Crusting of the lesions can occur
- In squamous cell carcinoma in situ, the malignancy is confined to the skin surface and no invasion or metastasis is observed
You May Like: Brain Melanoma Treatment
Ductal Carcinoma In Situ Causes
Its not clear what causes ductal carcinoma in-situ . Ductal carcinoma in-situ forms when genetic mutations occur in the DNA of breast duct cells. The genetic mutations cause the cells to appear abnormal, but the cells dont yet have the ability to break out of the breast duct.
Researchers dont know exactly what triggers the abnormal cell growth that leads to ductal carcinoma in-situ . Factors that may play a part include your lifestyle, your environment and genes passed to you from your parents.
Also Check: Survival Rates For Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Stage Of Cancer Carcinoma In Situ And Additional Terms
A common question is, What stage of cancer is carcinoma in situ? Carcinoma in situ is referred to as stage 0 cancer. At this stage, cancer is considered non-invasive. Stage 1 cancers and beyond are considered invasive, meaning that even if low, there is a potential they could spread. Other terms that may be used in defining the same thing as carcinoma in situ or stage 0 cancer include:
- Non-infiltrating
You May Like: Does Skin Cancer Burn And Itch
What Can I Expect If I Have Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Most cases of squamous cell carcinoma have a positive prognosis and an excellent survival rate if you receive an early diagnosis. Early detection and treatment prevent the tumor from growing and damaging other parts of your body.
If your healthcare provider removes your cancer, theres a chance it can return in the future. Make sure to follow up with your healthcare provider to verify youre cancer-free. Its also important to protect your skin from UV rays when outdoors.
Also Check: Skin Cancer Spreading To Lymph Nodes
Ductal Carcinoma In Situ Diagnosis
Breast imaging
Ductal carcinoma in-situ is most often discovered during a mammogram used to screen for breast cancer. If your mammogram shows suspicious areas such as bright white specks that are in a cluster and have irregular shapes or sizes, your radiologist likely will recommend additional breast imaging.
You may have a diagnostic mammogram, which takes views at higher magnification from more angles. This examination evaluates both breasts and takes a closer look at the microcalcifications to be able to determine whether they are a cause for concern.
If the area of concern needs further evaluation, the next step may be an ultrasound and a breast biopsy.
Removing breast tissue samples for testing
During a core needle biopsy, a radiologist or surgeon uses a hollow needle to remove tissue samples from the suspicious area, sometimes guided by ultrasound or by X-ray . The tissue samples are sent to a lab for analysis.
In a lab, a doctor who specializes in analyzing blood and body tissue will examine the samples to determine whether abnormal cells are present and if so, how aggressive those abnormal cells appear to be.
How Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma In Situ Of Penis Diagnosed
Some of the tests that may help in diagnosing Squamous Cell Carcinoma In Situ of Penis include:
- Complete physical examination with detailed medical history evaluation
- Examination by a dermatologist using a dermoscopy, a special device to examine the skin
- Skin or tissue biopsy: A skin or tissue biopsy is performed and sent to a laboratory for a pathological examination, who examines the biopsy under a microscope. After putting together clinical findings, special studies on tissues and with microscope findings, the pathologist arrives at a definitive diagnosis. A biopsy is performed to rule out other similar conditions too
Many clinical conditions may have similar signs and symptoms. Your healthcare provider may perform additional tests to rule out other clinical conditions to arrive at a definitive diagnosis.
Read Also: Whats Cancer Look Like
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Risk Factors
Certain things make you more likely to develop SCC:
Your doctor may refer you to a dermatologist who specializes in skin conditions. They will:
- Ask about your medical history
- Ask about your history of severe sunburns or indoor tanning
- Ask if you have any pain or other symptoms
- Ask when the spot first appeared
- Give you a physical exam to check the size, shape, color, and texture of the spot
- Look for other spots on your body
- Feel your lymph nodes to make sure they arent bigger or harder than normal
If your doctor thinks a bump looks questionable, theyll remove a sample of the spot to send to a lab for testing.
Continued
Prevention Of Bowens Disease Or Squamous Cell Carcinoma In Situ
- Observation: Bowens disease or Squamous Cell Carcinoma In Situ tends to grow very slowly, often over a period of months to years. So, if a patient has a thin patch of affected skin area which is not changing and remains constant, then just simply observing it may be all that is needed. Regular check-ups with your dermatologist need to be undertaken for close monitoring of the affected region. This option is more suitable for those patients who may have trouble with skin healing after the treatment of Bowens disease.
- Sun Protection: Is very important as if you have had a patch of Bowens disease or Squamous Cell Carcinoma In Situ then you are at an increased risk for getting a second patch. To prevent this, always use sun protection by wearing a hat, and using a sun block with a minimum SPF of 30. Always avoid stepping out when the sun is at its harshest and wear clothes which cover your body, such as trousers, leggings and long skirts to protect the legs.
| Written, Edited or Reviewed By:Pramod Kerkar, M.D., FFARCSI, DA Pain Assist Inc.This article does not provide medical advice. See disclaimerLast Modified On: July 29, 2021 |
Don’t Miss: Body Cancer Symptoms
What Are The Risk Factors For Squamous Cell Carcinoma In Situ Of Vulva
The following factors increase the risk of Squamous Cell Carcinoma In Situ of Vulva:
- Infection with human papilloma virus subtypes 16, 18, 31, 33, and 45,
- High-risk sexual behavior sexual promiscuity
- Weakened immune system as a result of HIV infection or AIDS, or due to administration of immunosuppressants
- Smoking
- Lack of proper hygiene
- Longstanding ulcerative lichen planus
It is important to note that having a risk factor does not mean that one will get the condition. A risk factor increases ones chances of getting a condition compared to an individual without the risk factors. Some risk factors are more important than others.
Also, not having a risk factor does not mean that an individual will not get the condition. It is always important to discuss the effect of risk factors with your healthcare provider.
Dont Miss: What Does Stage 3b Melanoma Mean
What Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma In Situ Of Vulva
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma In Situ of Vulva is a malignant condition affecting the skin or mucosal membranes of the vulva . The carcinoma may be present as a well-defined red patch it is frequently solitary, but sometimes are many in number
- The lesion may itch, ulcerate, or even bleed. The condition may be diagnosed definitively through a tissue biopsy
- Middle-aged and elderly women are at risk for the condition. The cause of Squamous Cell Carcinoma In Situ of Vulva is unknown, but it is influenced by factors such as HPV infection, poor immunity, high-risk sexual practices, etc.
- Any combination of radiation therapy and invasive procedures are used to treat Vulvar Squamous Cell Carcinoma In Situ. The prognosis depends upon early diagnosis and treatment that is administered
Recommended Reading: Non Invasive Breast Cancer Survival Rate
What If My Biopsy Report Mentions Margins Or Ink
When an entire tumor or abnormal area is removed, the pathologist coats the outer edges, or margins, of the tissue with ink, sometimes with different colored ink on different sides. If a cancer is found, the pathologist can then tell if it goes up to the edges of tissue removed. This is known as a positive margin. If it does, it may mean that some cancer has been left behind. Sometimes this is not a concern because the surgeon removed other tissue in that area. Still, if some cancer has been left behind, you might need more treatment, such as radiation or more surgery. Talk with your doctor about the best approach for you if cancer is found at the margins.
Bowens Disease Or Squamous Cell Carcinoma In Situ
Squamous cell carcinoma in situ is the earliest recognizable form of squamous cell skin cancer This condition is also referred to as stage 0 squamous cell carcinoma, on the scale from 0 to IV. There are typically no visible symptoms. When symptoms are present, a scaly condition may be present, and the skin may seem to catch on clothing. The presence of abnormal cells may be detected by a pathologist. Although the cancerous cells have not yet invaded the deeper layers of the skin and the condition is not considered a serious condition, treatment at this early stage is generally recommended to help prevent this condition from developing into squamous cell carcinoma. In some cases, monitoring may be prescribed.
Donât Miss: What Happens If I Have Melanoma
Also Check: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Survival Rate Stage 1
What Are The Signs Of Squamous Cell Carcinoma
There are cancerous bumps, marks or lesions that form on your skin that can be a sign of squamous cell carcinoma, including:
- A bump or lump that can feel dry, itchy, scaly or have a different color from the skin around it .
- A lesion on your lower lip where the tissue becomes pale, dry and cracked . This may have a burning sensation when youre exposed to the sun.
- White or pale spots in your mouth, on your tongue, gums or cheeks .
Health Literacy To Empower Patients
With the right information, patients can make the best decisions about their care. By partnering with patients, healthcare providers, and hospitals, we hope to provide all patients with the tools and knowledge to understand their pathology report.
For more information about this site, contact us at .
Disclaimer: MyPathologyReport.ca is a registered not-for-profit charity . The articles on MyPathologyReport are intended for general informational purposes only and they do not address individual circumstances. The articles on this site are not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment and should not be relied on to make decisions about your health. Never ignore professional medical advice in seeking treatment because of something you have read on the MyPathologyReport site. MyPathologyReport is independently owned and operated and is not affiliated with any hospital or patient portal.
Copyright © 2021. All rights reserved. Privacy Policy
Our work is generously supported by:
Recommended Reading: Invasive Breast Cancer Prognosis
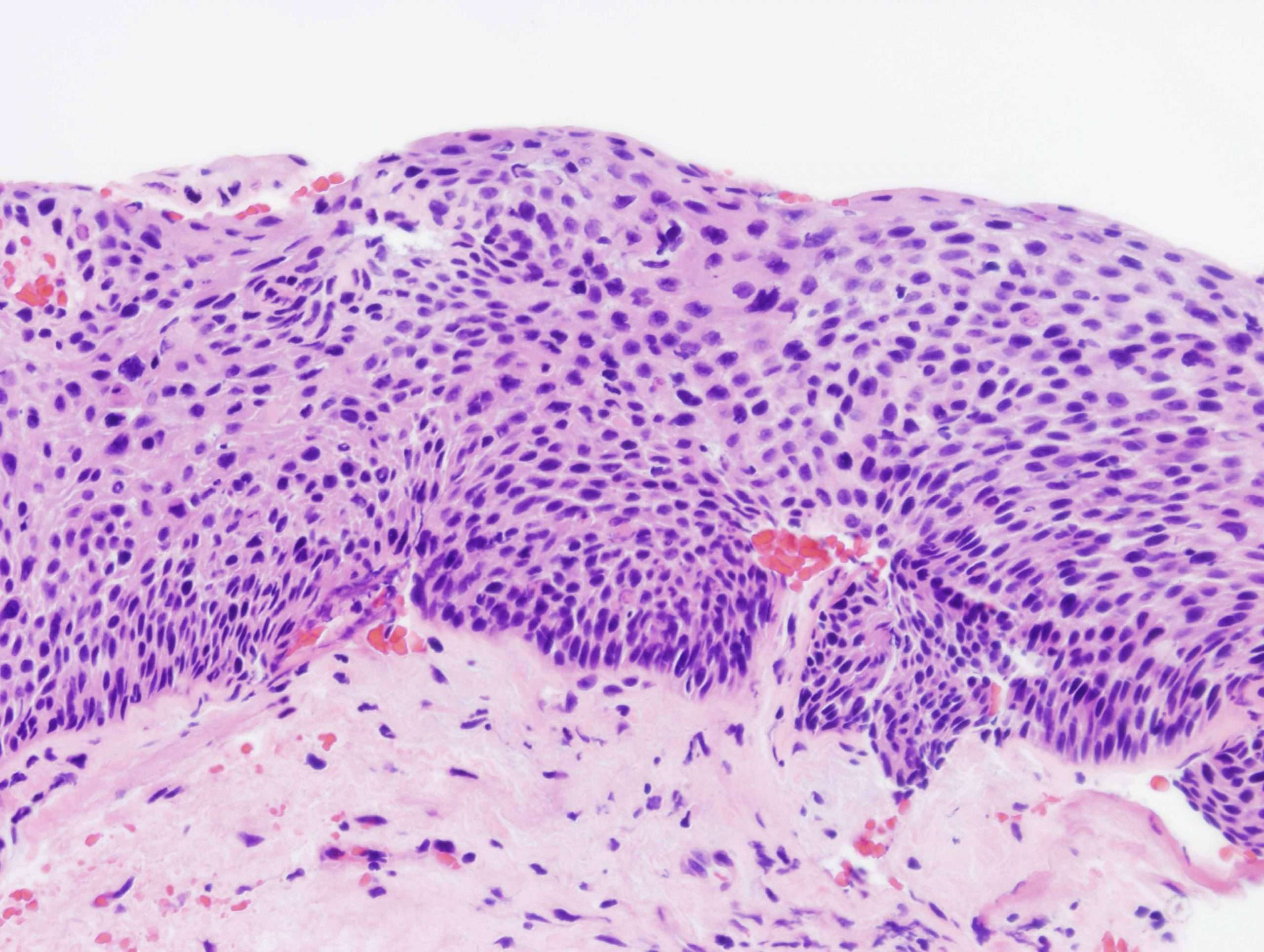
Histology Of Squamous Cell Carcinomain Situ
The scanning power view of squamous cell carcinoma in situ reveals epidermal alteration . Closer inspection reveals atypia of the keratinocytes across the full thickness of the epidermis . There is a loss of the granular layer and overlying zones of parakeratosis. Sparing of the adnexal ostial epithelium is commonly seen . The keratinocytes show cytologic atypia with disorderly maturation.
Squamous cell carcinoma in situ pathology
How Can Squamous Cell Carcinoma In Situ Of Vulva Be Prevented
Squamous Cell Carcinoma In Situ of Vulva may be prevented by following some of these measures:
- Use of condoms, avoiding multiple sexual partners, etc. to avoid sexually-transmitted infections
- Undertake immediate treatment of ulcers in the genital region
- Avoidance of smoking
- Availing vaccinations against the human papilloma virus
- Maintaining personal hygiene
You May Like: Cancer All Over Body Symptoms
Meaning Of Carcinoma In Situ
In many ways, the term âcarcinomaâ is simply equated with cancer. Roughly 85 percent of cancers are carcinomas. Carcinomas are composed of epithelial cells the type of cells that line the skin, breast ducts, and other surfaces of organs in the body.
The subtypes of carcinomas include adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, transitional cell carcinoma , and basal cell carcinoma.
Carcinoma in situ can be further defined by the tissue type in which cancer is beginning. For example, squamous cell carcinoma in situ of the cervix would represent a cancer that had started in squamous cells which line the cervix and has not yet become invasive.
Tumors such as sarcomas arise in tissues which do not have a basement membrane so that for these types of cancer there is not a stage of carcinoma in situ. In other words, tumors such as bone cancer do not have a pre-invasive stage and the cells would either be considered normal or cancer. Likewise, blood-related cancers, such as leukemias and lymphomas, do not have a preinvasive but cancerous stage for which people can be screened. For cancers that donât have a CIS stage, screening tests are not as effective in early detection, because once the abnormal cells are detected, it would already be considered invasive with the potential to spread .
How Will Your Doctor Diagnose Squamous Cell Carcinoma

Your doctor will first examine the area in question, looking for things such as: the size, whether or not the borders are clearly or poorly defined, and location, including whether or not the spot is situated on top of a previous injury. The next step is a biopsy, which is the removal of tissue for examination under a microscope. If a tumor is considered to be high-risk, your doctor might order imaging scans to determine if nearby lymph nodes are involved or if the tumor has invaded other tissue in the area.
You May Like: Idc Breast Cancer Survival Rate
Is Bowen’s Disease Serious
Bowen’s disease itself is not usually serious. It tends to grow very slowly over months or years, and there are several very effective treatments for it.
The concern is that Bowen’s disease can eventually develop into a different type of skin cancer called squamous cell skin cancer if it’s left undiagnosed or neglected.
It’s estimated this happens in up to 1 in 20 to 1 in 30 people with untreated Bowen’s disease.
Squamous cell skin cancer is often treatable, but it can spread deeper into the body and is sometimes very serious.
Carcinoma In Situ Bladder Symptoms
Bladder cancer signs and symptoms may include:
- Blood in urine
- Painful urination
- Pelvic pain
If you have hematuria, your urine may appear bright red or cola colored. Sometimes, urine may not look any different, but blood in urine may be detected during a microscopic exam of the urine.
People with bladder cancer might also experience:
- Back pain
But, these symptoms often occur because of something other than bladder cancer.
Don’t Miss: Melanoma Stage 3 Survival Rate
What Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Squamous cell carcinoma or cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma is the second most common form of skin cancer after basal cell carcinoma. It starts in squamous cells in the outer layer of your skin, the epidermis. Usually, squamous cell carcinomas form on areas of your skin that receive the most sun exposure like your head, arms and legs. Cancer can also form in areas of your body where you have mucous membranes, which are the inner lining of your organs and body cavities like in your mouth, lungs and anus.
What are the types of squamous cell carcinoma?
There are different types of squamous cell carcinoma based on where and how much cancer is in your body:
- Cutaneous: Cancer that only affects the top layer of your skin or cancer thats spread beyond the top layer of your skin.
- Metastatic: Cancer thats spread to other parts of your body beyond your skin.