Support Groups And Counseling For Small
Support groups and counseling can help you feel less alone and can improve your ability to deal with the uncertainties and challenges that cancer brings.
Cancer support groups provide a forum where patients with cancer, survivors of cancer, or both can discuss the challenges that accompany the illness and guide you to deal with your concerns.
Support groups provide an opportunity to exchange information about the disease, take advice about managing side effects, and share your feelings with others who are undergoing a similar situation.
Support groups also help your family and friends deal with the stress.
Many organizations offer support groups for people with cancer and their family members or friends of people who have cancer. You can get information about such groups from your doctor, nurse, or hospital social worker.
The following organizations can help you with support and counseling:
- The AMC Cancer Information and Counseling Line provides current medical information and counseling for cancer issues.800-525-3777
What Are The Treatments For Non
Treatment for NSCLC will depend on whether the cancer has spread to other areas of the body, your overall health and age, and the presence of certain proteins that make treatments more effective. If your NSCLC is detected early , surgery to remove the affected tissue or tumor is the treatment of choice.
Other treatments include the following:
- Radiation therapy. This uses high-energy rays to kill cancer cells and keep new ones from growing. It can be used to treat cancer that has not metastasized. It may also be used to reduce symptoms and improve your quality of life.
- Chemotherapy. This uses anti-cancer drugs administered either through injection into the vein, or orally to kill cancer cells. Chemotherapy can prolong survival and treat symptoms of NSCLC.
- Targeted therapy. This uses anti-cancer drugs to kill specific cancer cells without causing harm to normal cells. These therapies are usually given if you have specific gene mutations, as determined by genetic testing.
- Immunotherapy. This activates your bodys immune system to specifically kill cancer cells and is usually recommended for late-stage lung cancer, specifically Stage IV NSCLC. When immunotherapy was first introduced, the effects were dramatic, says Dr. Herbst. Now we are using combined therapies such as immunotherapy with chemotherapy and exploring other immunotherapy or targeted therapies in combination, and we are seeing results.
An Emerging Molecular Classification
Major genetic alterations and molecular subtypes of SCLC.
a | The inactivation of RB1 and TP53 and p53, respectively) is a near-ubiquitous event in human small-cell lung cancer tumours. Four major molecular subtypes, SCLC-A, SCLC-N, SCLC-P and SCLC-Y, have been described on the basis of high expression of the transcription factors ASCL1, NEUROD1, POU2F3 and YAP1, respectively. SCLC-P and SCLC-Y show a less neuroendocrine phenotype than SCLC-A and SCLC-N. Within the less/non-neuroendocrine category, a rare subtype with high expression of the transcription factor ATOH1 has been reported. SCLC-A tumours have been proposed to comprise two distinct subtypes , with SCLC-A2 distinguished from SCLC-A by its expression of other factors, such as HES1 . A few other genetic and epigenetic alterations have been associated with specific subtypes, including the differential expression of MYC family members and mutations in NOTCH family genes, but most recurrent mutations are found in all subtypes. b | Chromosome level copy-number alterations reported by clinical next-generation sequencing of tumours from 409 patients with SCLC. Amplified genes and homozygous deleted genes are plotted for each chromosome. Selected genes of interest, with chromosomal locations and frequency in SCLC tumours are indicated. Data in part b are from MSK-IMPACT sequencing.
Read Also: Small Blue Cell Tumor Prognosis
Preventive Implications: Developing Genetic Test And Counseling
Current data suggest that familial SCCOHT may be much more common than expected previously . An analysis on the published SCCOHT cases with SMARCA4 mutations showed that 26 were carriers of germline mutations, and 21 had no reported familial history .The under-reported familial SCCOHT cases can be explained by germline mutations arising from unaffected father or de novo. Moreover, patients carrying germline mutations appear to be younger at the time of diagnosis than non-carriers. Patients diagnosed below 18 years have a significantly high risk for a germline mutation. Germline and somatic mutations of SMARCA4 should be detected in SCCOHT patients with loss of BRG1 expression. The next-generation sequencing based platform is recommended for mutation analysis because the hotspots of SMARCA4 mutations have not been identified yet. After the confirmation of deleterious germline mutations, the genetic test and counseling should be rendered for all her family members. Male carriers are also important since their daughters may inherit these mutations although the risk of other cancers in male carriers is unclear currently.
A proposed schema for clinical and genetic management of SCCOHT
What Causes Small Cell Lung Cancer
The exact cause of lung cancer isnt known. However, its believed that precancerous changes in the lungs can lead to cancer. These changes affect the DNA of cells inside the lungs, causing lung cells to grow faster.
Too many changes can cause the cells to become cancerous. Blood vessels feed the cancer cells, allowing them to grow into tumors.
Over time, cancer cells may break away from the primary tumor and spread to other parts of the body.
Don’t Miss: Can You Get Cancer In The Back Of Your Neck
Living With Small Cell Lung Cancer
Coping with a cancer diagnosis can be difficult. Aside from experiencing grief and anxiety, people with SCLC often undergo a long period of treatment and recovery that can be physically challenging.
People who have been diagnosed with SCLC can cope with their condition in many different ways. The key to moving forward and to living a full, happy life is trying to be adaptable and optimistic.
Here are some steps you can take that you may find helpful:
- Learn more about your condition and possible treatments by talking with your doctor. You can also use online resources to increase your understanding and gain a sense of control over your situation.
- Find a healthy way to express your emotions, whether its seeing a therapist, going to art or music therapy, or keeping a journal of your thoughts. Many people also join cancer support groups so they can talk about their experiences with other people who can relate to what theyre going through. Ask your doctor about support groups in your area or visit the
Risk Factors Of Lung Cancer
The NHS says lung cancer mainly affects older people and is rare in people younger than 40. More than four out of 10 people diagnosed with lung cancer in the UK are aged 75 and older, the site explains.
Although people who have never smoked can develop lung cancer, the NHS says smoking is the most common cause, accounting for around 72% of cases.
This is because smoking involves regularly inhaling a number of different toxic substances.
Recommended Reading: Melanoma Bone Cancer Life Expectancy
What Is The Prognosis Of Small Cell Carcinoma Of Kidney
The prognosis of Small Cell Carcinoma of Kidney depends on the size and number of tumors, their localization, and spread. In general, the prognosis of this aggressive malignancy is poor.
- The most reliable prognostic factor of Small Cell Carcinoma of Kidney is dependent on whether the tumor can be completely removed through surgery with free margins or not
- The prognosis also depends upon a set of several factors, which include:
- Stage of tumor: With lower-stage tumors, when the tumor is confined to site of origin, the prognosis is usually better with appropriate therapy. In higher-stage tumors, such as tumors with metastasis, the prognosis is poor. In majority of cases, the tumor is low stage.
- The surgical respectability of the tumor
- Overall health of the individual: Individuals with overall excellent health have better prognosis compared with those with poor health
- Age of the individual: Older individuals generally have poorer prognosis than younger individuals
- Whether the tumor is occurring for the first time, or is a recurrent tumor. Recurring tumors have worse prognosis compared to tumors that do not recur
- Response to treatment: Tumors that respond to treatment have better prognosis compared to tumors that do not respond to treatment
Large Cell Neuroendocrine Carcinoma
LCNEC is a high-grade non-small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma that meets the following criteria: neuroendocrine morphology: organoid, palisading, trabecular or rosette-like growth patterns non-small cell cytological features: large size, polygonal shape, low N/C ratio, coarse or vesicular nuclear chromatin and frequent nucleoli high mitotic rate with a mean of 60 mitoses per 2mm2 frequent necrosis and at least one positive neuroendocrine immunohistochemical marker or neuroendocrine granules by electron microscopy ., It is very difficult to diagnose LCNEC based on small biopsy specimens such as needle or bronchoscopic biopsy specimens as it is usually very difficult to be certain of the neuroendocrine morphology without a substantial sampling of the tumor. However, criteria have been proposed to diagnose LCNEC based on cytology. The term large cell carcinoma, with neuroendocrine morphology can be used for tumors resembling LCNEC by light microscopy but lacking proof of neuroendocrine differentiation by electron microscopy or immunohistochemistry. The term combined LCNEC is appropriate for those tumors containing components of other histological types of NSCLC, such as adenocarcinoma or squamous cell carcinoma. The main criteria for distinguishing SCLC from LCNEC are discussed above and summarized in .
Figure 9
Don’t Miss: Cancer Lesion Pictures
Small Cell Lung Cancer Is A Disease In Which Malignant Cells Form In The Tissues Of The Lung
The lungs are a pair of cone-shaped breathing organs that are found in the chest. The lungs bring oxygen into the body when you breathe in and take out carbon dioxide when you breathe out. Each lung has sections called lobes. The left lung has two lobes. The right lung, which is slightly larger, has three. A thin membrane called thepleura surrounds the lungs. Two tubes called bronchi lead from thetrachea to the right and left lungs. The bronchi are sometimes also affected by lung cancer. Small tubes called bronchioles and tiny air sacs calledalveoli make up the inside of the lungs.
There are two types of lung cancer:small cell lung cancer andnon-small cell lung cancer.
This summary is about small cell lung cancer and its treatment. See the following PDQ summaries for more information about lung cancer:
How Will The Doctor Know If I Have Lung Cancer
Symptoms of lung cancer are cough, chest pain, and trouble breathing. The doctor will ask you questions about your health and do a physical exam.
If signs point to lung cancer, more tests will be done. Here are some of the tests you may need:
Chest x-ray: This is often the first test used to look for spots on your lungs. If a change is seen, you will need more tests.
CT scan: This is also called a CAT scan. A CT scan is a special kind of x-ray that takes detailed pictures of your insides. CT scans can also be used to do a biopsy .
PET scan: A type of sugar is put in one of your veins for this test. Then, pictures of your insides are taken with a special camera. If there is cancer, the sugar shows up as hot spots where the cancer is found. This test is helpful when your doctor thinks the cancer has spread, but doesnt know where.
Biopsy: For a biopsy, the doctor takes out a small piece of the lung tumor. Its sent to the lab to see if there are cancer cells in it. This is the best way to know for sure if you have cancer.
Bronchoscopy: A thin, lighted, flexible tube is passed through your mouth into the bronchi. The doctor can look through the tube to find tumors. The tube also can be used to take out a piece of the tumor or fluid to see if there are cancer cells.
Blood tests: Blood tests are not used to find lung cancer, but they are done to tell the doctor more about your health.
Also Check: Is A Sore That Doesn T Heal Always Cancer
Stages Of Small Cell Lung Cancer
SCLC survival rates depend, in large part, on the stage of cancer:
- Limited-stage: This is the earliest stage of the disease in which the cancer is in one lung and possibly the lymph nodes on the same side of the chest.
- Extensive-stage: At this advanced stage, cancer has metastasized to other parts of the body, such as the other lung, brain, liver, adrenal glands, and bones.
More advanced small cell lung cancer cases have poorer survival rates than earlier-stage SCLC cases.
SCLC tends to be more aggressive than the most common form of lung cancer, non-small cell lung cancer . Because it grows rapidly and often spreads before there are even symptoms of disease, most people are not diagnosed with SCLC until it is at an advanced stage.
Approximately 60% to 70% of people are already at the extensive stage of SCLC at the time of their diagnosis.
Signs And Symptoms Of Small Cell Lung Cancer Include Coughing And Shortness Of Breath
These and other signs and symptoms may be caused by small cell lung cancer or by other conditions. Check with your doctor if you have any of the following:
- Chest discomfort or pain.
- A cough that doesnt go away or gets worse over time.
- Trouble breathing.
- Blood in sputum .
- Hoarseness.
- Weight loss for no known reason.
- Feeling very tired.
- Swelling in the face and/or veins in the neck.
Don’t Miss: What Does Cancer Tumor Look Like
How Can I Prevent Small Cell Lung Cancer
Because tobacco use is the top cause of small cell lung cancer, not smoking is the best way to protect your health. When you quit smoking regardless of your age or years of tobacco use your lungs start to heal, and cancer risk diminishes. These steps may also help:
- Eat a nutritious diet.
- Test your home for radon, a natural, odorless, radioactive gas.
- Install a mitigation system to remove radon from your home, if needed.
- Protect yourself from cancer-causing chemicals at work.
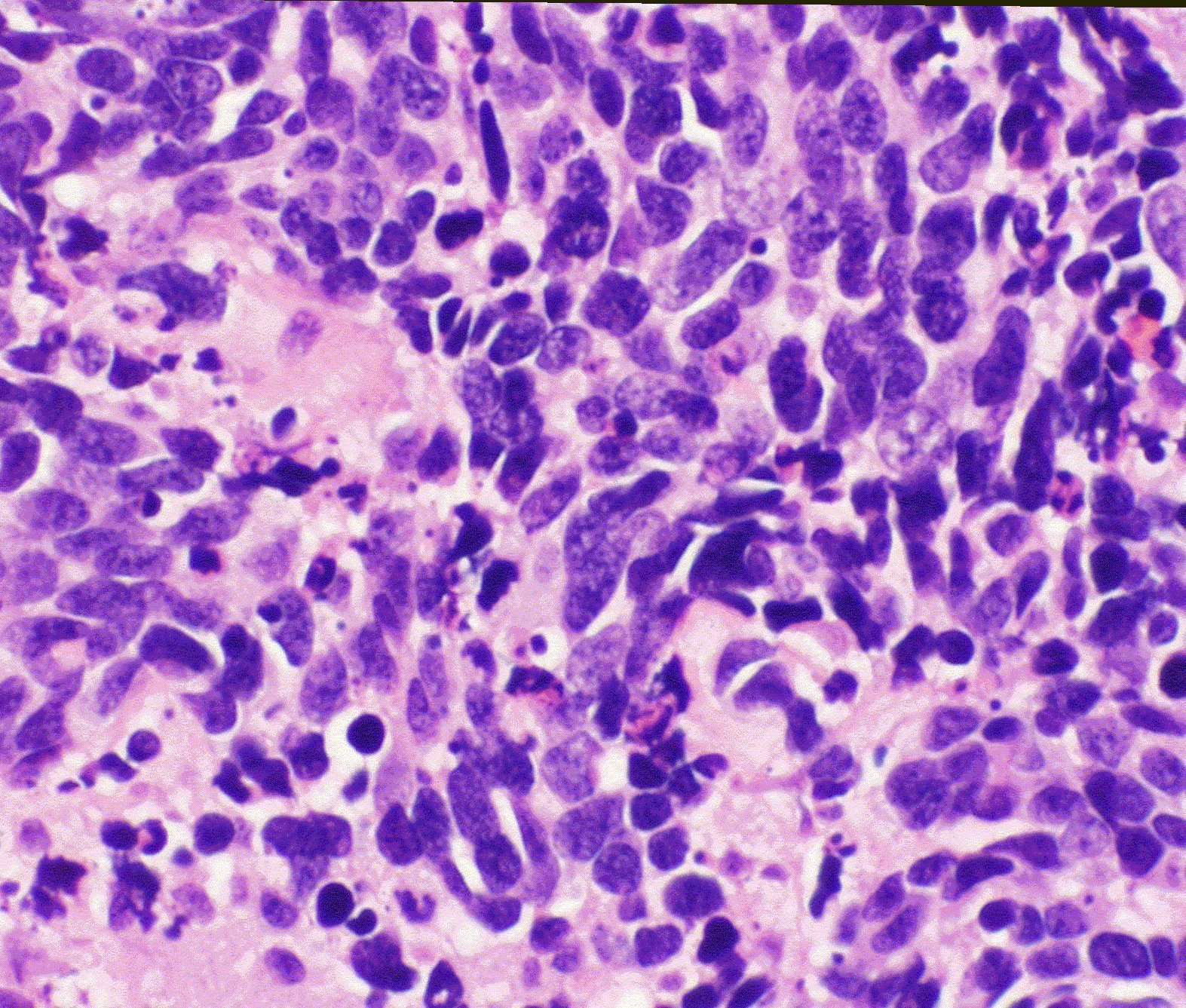
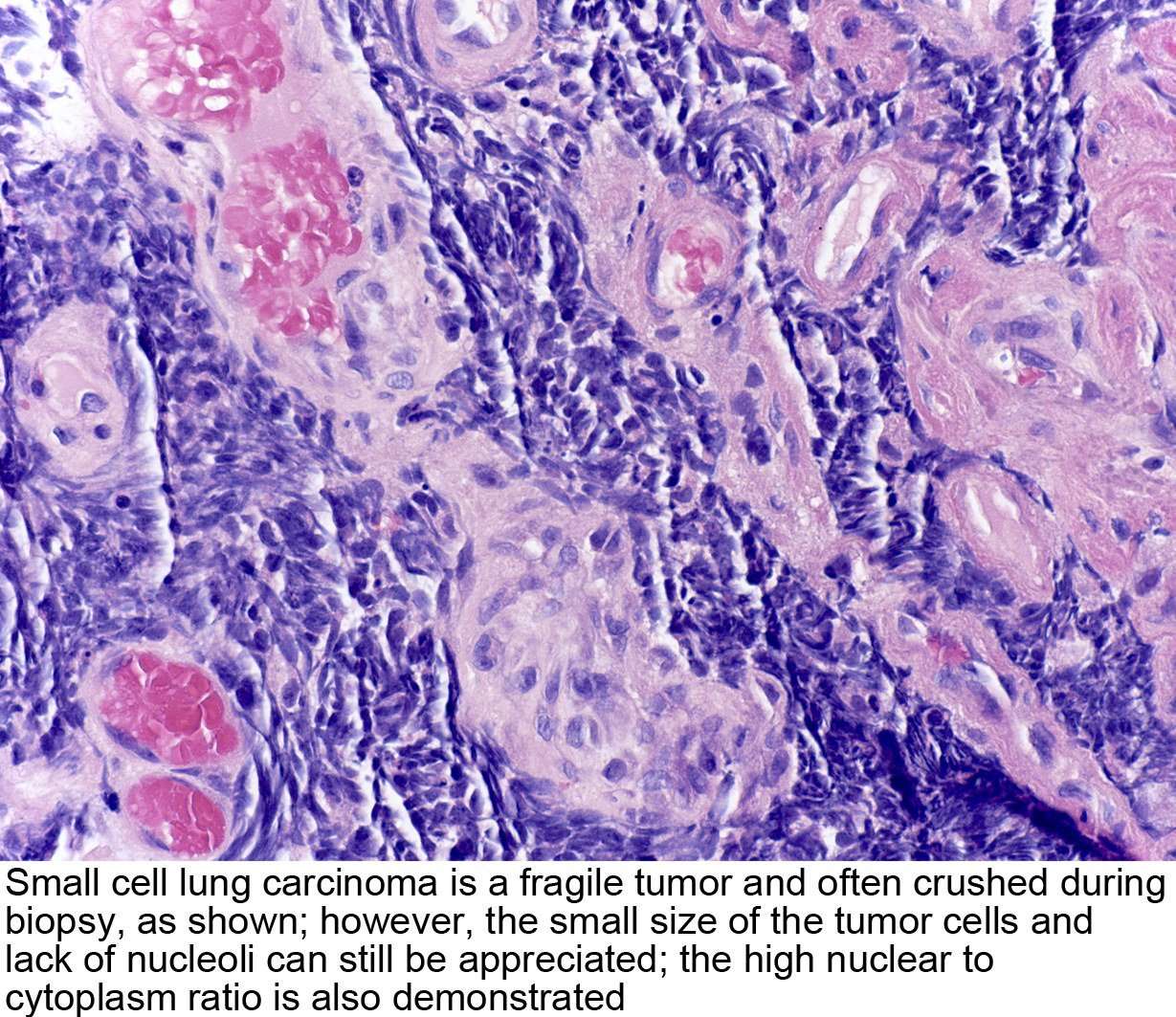
Small Cell Lung Cancer
When associated with the lung, it is sometimes called “oat cell carcinoma” due to the flat cell shape and scanty cytoplasm. Caution is required when diagnosing SCLC because small cell mesothelioma an extremely rare subtype of lung cancer can be mistaken for small cell lung cancer.
It is thought to originate from neuroendocrine cells in the bronchus called Feyrter cells .Hence, they express a variety of neuroendocrine markers, and may lead to ectopic production of hormones like ADH and ACTH that may result in paraneoplastic syndromes and Cushing’s syndrome. Approximately half of all individuals diagnosed with Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome will eventually be found to have a small-cell carcinoma of the lung.
Small-cell carcinoma is most often more rapidly and widely metastatic than non-small-cell lung carcinoma . There is usually early involvement of the hilar and mediastinal lymph nodes. The mechanisms of its metastatic progression are not well-understood.
Recommended Reading: What Is Clear Cell Carcinoma
Clinical Behavior And Treatment Of Sccoht
SCCOHT is a highly aggressive tumor. Extraovarian spread is seen in approximately half of the cases. Lymph node metastasis is present in 19/34 cases. Tumor stage remains the mainstay in the assessment of prognosis -, . Young et al. reported that one third patients at FIGO stage Ia survived free of disease 1-13 years after surgery whereas almost all patients at an advanced stage died of disease. A study from a single institution showed that 35 of 47 SCCOHT patients recurred , 30 died of disease , and 6 were alive with disease . The mean overall survival time was 35.3 months in patients at stage I, and only 3.3 months at stage IV. A combined investigation on 293 SCCOHT patients showed that patients at 40 years or older had a worse outcome than younger patients, but there was no significant survival difference between patients with and without germline SMARCA4 mutations. The 5-year overall survival rate in the NCDB cohort was 24.1% for patients with cancer- directed surgery, and only 18% and 12.3% in patients with stage III and IV respectively . Intriguingly, Ghazi A, et al. reported a SCCOHT patient that developed after two months of ovarian stimulation for in vitro fertilization and died one month after her initial symptoms. This unique case suggests the possibility of ovarian stimulation- associated cancer risk and mortal prognosis, which merits further multi-centric clinical investigation.
What Is Small Cell Carcinoma Cancer
Lung cancer is one of the most common and serious types of cancer, according to the NHS, with approximately 47,000 people diagnosed with the condition every year in the UK.
Cancer that begins in the lungs is called primary lung cancer and there are two main forms of primary lung cancer determined by the type of cells in which the cancer starts growing.
-
Non-small-cell lung cancer – This is the most common form, accounting for more than 87% of cases, according to the NHS. It can be one of three types: squamous cell carcinoma, adenocarcinoma or large-cell carcinoma.
-
Small-cell lung cancer This is the type Diamond is reported to have suffered from. It is less common than non-small-cell lung cancer and usually spreads faster. According to Cancer Research UK, around 15 to 20 out of every 100 lung cancers diagnosed are this type. It is usually caused by smoking. These cancers tend to spread quite early on.
Cancer Research UK says small-cell lung cancers are also classed as neuroendocrine tumours. Neuroendocrine tumours are rare tumours that develop in cells of the neuroendocrine system, the site explains. In small cell lung cancer, the tumour starts in the neuroendocrine cells of the lung.
Neuroendocrine cells are present in most of our organs. They make hormones which control how our bodies work. For instance, the neuroendocrine cells of the lung make hormones that control the flow of air and blood.
You May Like: What Does Well Differentiated Mean