What Are The Symptoms Of Sclc
Because SCLC grows quickly, most people with this type of cancer have symptoms at the time of diagnosis. Symptoms may worsen over weeks or days and include:
- Loss of appetite and weight loss
- Swelling of the neck or face
Other symptoms may develop if SCLC has spread outside the lungs. These may depend on where the cancer has traveled.
If it spreads to:
Tests And Procedures That Examine The Lungs Are Used To Diagnose And Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer
The following tests and procedures may be used:
What Is Small Cell Lung Cancer
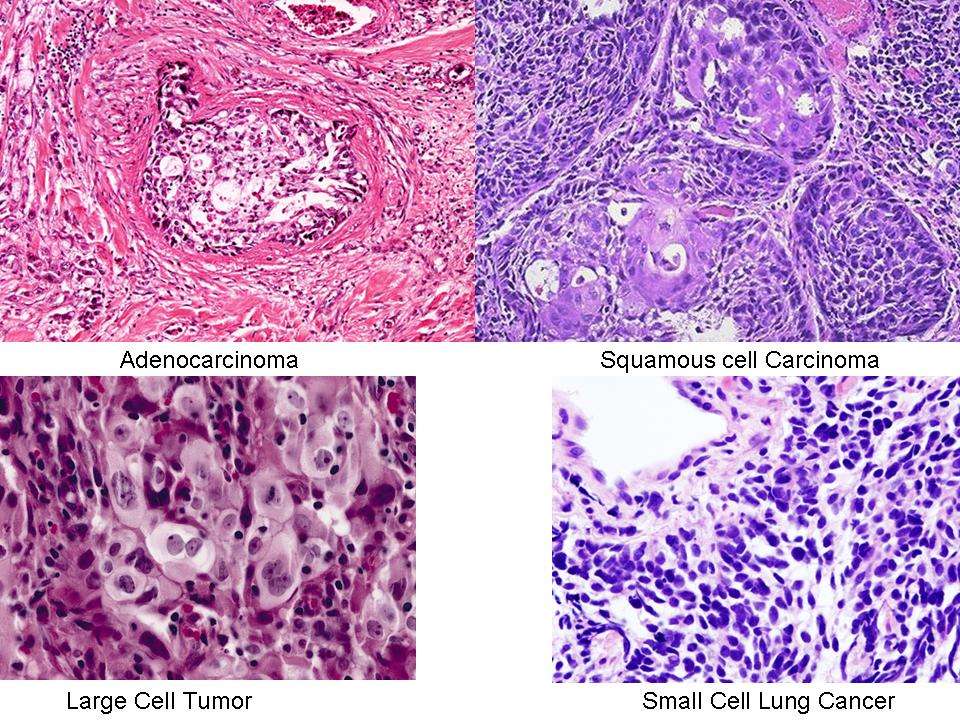
Small cell lung cancer is fast-growing lung cancer that develops in the tissues of the lungs. By the time a person gets a diagnosis, small cell lung cancer has typically spread outside of the lungs. This cancer is also more likely than other types of lung cancer to come back after treatment. Small cell lung cancer is sometimes, but not often, called oat cell cancer because the small, oval-shaped cells look like oat grains under a microscope.
Recommended Reading: What Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of The Head And Neck
The Following Stages Are Used For Small Cell Lung Cancer:
Limited-Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer
In limited-stage,cancer is in the lung where it started and may have spread to the area between the lungs or to the lymph nodes above the collarbone.
Extensive-Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer
In extensive-stage,cancer has spread beyond the lung or the area between the lungs or the lymph nodes above the collarbone to other places in the body.
Stages Of Small Cell Lung Cancer
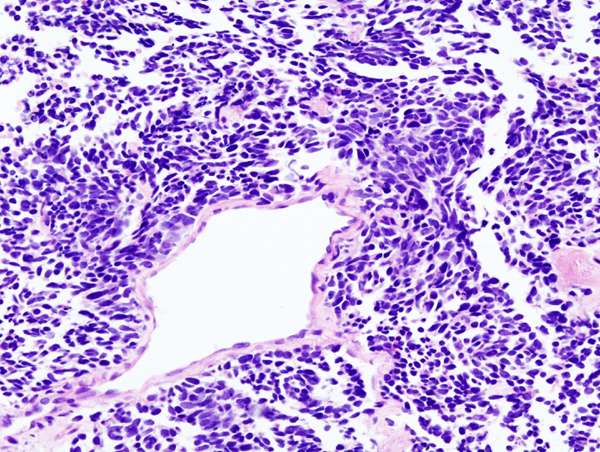
Doctors generally categorize small cell lung cancer with one of two stages:
The limited stage: This means that the cancer is on one side of the chest. It may be in one lung and, possibly, nearby lymph nodes.
The extensive stage: The cancer has spread to other parts of the chest and other organs.
Some doctors use further staging for small cell lung cancer.
Also Check: Large Cell Cancer Of The Lung
Smoking And Secondhand Smoke
Smoking is the number one cause and risk factor for lung cancer. The American Lung Association notes that smoking causes up to 90% of lung cancer cases.
Tobacco smoke contains many chemicals that act as carcinogens, which damage lung tissue and may lead to cancer. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention note that tobacco smoke contains more than 7,000 chemicals, and at least 70 are known to cause cancer.
Quitting smoking is the best thing a person can do for their lung health. Taking steps to avoid secondhand smoke is also important.
What Are The Complications Of Small Cell Lung Cancer
Metastasis, or cancer spread, is a top concern for people who have small cell lung cancer. Small cell lung cancer can grow quickly and affect the brain, bones and liver and adrenal glands . Small cell lung cancer that spreads is treatable but generally isnt curable. Other complications include:
- Pleural effusion .
- Cancer recurrence after treatment, often in the central nervous system or chest.
- Pain.
- Shortness of breath.
Don’t Miss: Lobular Carcinoma Survival Rate
What About Other Treatments I Hear About
When you have cancer you might hear about other ways to treat your cancer or treat your symptoms. These may not always be standard medical treatments. These treatments may be vitamins, herbs, diets, and other things. You may wonder about these treatments.
Some of these are known to help, but many have not been tested. Some have been shown not to be helpful. A few have even been found to be harmful. Talk to your doctor about anything you are thinking about using, whether its a vitamin, a diet, or anything else.
Macroscopic Features Of Sclc
As a highly aggressive disease, SCLC is found disseminated in the initial clinical presentation in the majority of cases, and surgery is limited to a small subgroup of patients with confined disease . Usually, these tumors undergo surgical resection only when diagnosis of SCLC has not been previously established, and it is from those infrequent surgical specimens that a macroscopic description of SCLC tumors is described. These tumors are grossly identifiable as fleshy, ranging from a white and grayish to a light tan color, soft and friable irregular masses, with necrotic cut surface areas. The majority of them are situated in hilar or perihilar areas, with less than 5% of the cases presenting in peripheral locations. Invasion into the peribronchial tissue and lymph node is often grossly identifiable, typically spreading in circumferentially along the submucosa of the bronchi.
Recommended Reading: Life Expectancy Metastatic Melanoma
How Is Small Cell Lung Cancer Diagnosed
An SCLC diagnosis begins with a thorough physical examination and medical history. Make sure to tell your doctor if you smoke.
If SCLC is suspected, your doctor will use various tests to help diagnose SCLC accurately. Once a diagnosis of SCLC is confirmed, your doctor will stage the cancer.
The symptoms of SCLC usually dont surface until the cancer has already progressed to a more advanced stage. However, SCLC is sometimes found early during diagnostic testing for a different medical condition.
SCLC can be detected by several common tests, such as:
- a chest X-ray, which produces clear, detailed images of your lungs
- a CT scan, which creates a series of cross-sectional X-ray images of your lungs
- an MRI, which uses magnetic-field technology to detect and identify tumors
- a bronchoscopy, which involves the use of a tube with an attached camera and light to view your lungs and other structures
- a sputum culture, which is used to analyze the liquid substance produced by your lungs when you cough
SCLC may also be discovered during a screening test for lung cancer. Your doctor may recommend a screening test if youre at an increased risk for lung cancer and you:
- are between 55 and 75 years old
- are in fairly good health
- smoke more than 30 packs of cigarettes each year
- are currently smoking or have quit smoking in the past 15 years
If SCLC is suspected, your doctor will perform numerous tests before making a diagnosis. These may include:
Limited Versus Extensive Stage
For treatment purposes, most doctors use a 2-stage system that divides SCLC into limited stage and extensive stage. For limited stage cancer, a person might benefit from more aggressive treatments such as chemotherapy combined with radiation therapy to try to cure the cancer. For extensive stage disease, chemotherapy alone is likely to be a better option to control the cancer.
You May Like: Skin Cancer Prognosis
Small Cell Lung Cancer Is A Disease In Which Malignant Cells Form In The Tissues Of The Lung
The lungs are a pair of cone-shaped breathing organs that are found in the chest. The lungs bring oxygen into the body when you breathe in and take out carbon dioxide when you breathe out. Each lung has sections called lobes. The left lung has two lobes. The right lung, which is slightly larger, has three. A thin membrane called thepleura surrounds the lungs. Two tubes called bronchi lead from thetrachea to the right and left lungs. The bronchi are sometimes also affected by lung cancer. Small tubes called bronchioles and tiny air sacs calledalveoli make up the inside of the lungs.
There are two types of lung cancer:small cell lung cancer andnon-small cell lung cancer.
This summary is about small cell lung cancer and its treatment. See the following PDQ summaries for more information about lung cancer:
Finding Information In Unexpected Places
Once again, tissue seems to be the issue. Typically, the diagnosis of SCLC is based on biopsy or cytology samples and not surgical specimens . As the majority of patients are unresectable at diagnosis, surgery only rarely forms part of the management of these patients. As previously mentioned, resection is indicated in the rare case of a patient presenting with a small peripheral primary lesion . It is interesting to note that comprehensive genomic characterization of SCLC is generally based on the analysis of such specimens . However, the biological features of this disease are expected to be different from the typical widespread disease we commonly encounter in clinical practice. As a rule, SCLC patients have multiple comorbid conditions that hamper their ability to undergo surgical biopsy and less invasive procedures are therefore preferred, reducing the amount of tissue that can be obtained for testing. As a result, SCLC is not included in the neoplasms studied by the Cancer Genome Atlas, as it does not meet the inclusion criteria regarding tissue availability.
Also Check: Infiltrating Ductal Carcinoma Survival Rate
What Are The Treatments For Non
Treatment for NSCLC will depend on whether the cancer has spread to other areas of the body, your overall health and age, and the presence of certain proteins that make treatments more effective. If your NSCLC is detected early , surgery to remove the affected tissue or tumor is the treatment of choice.
Other treatments include the following:
- Radiation therapy. This uses high-energy rays to kill cancer cells and keep new ones from growing. It can be used to treat cancer that has not metastasized. It may also be used to reduce symptoms and improve your quality of life.
- Chemotherapy. This uses anti-cancer drugs administered either through injection into the vein, or orally to kill cancer cells. Chemotherapy can prolong survival and treat symptoms of NSCLC.
- Targeted therapy. This uses anti-cancer drugs to kill specific cancer cells without causing harm to normal cells. These therapies are usually given if you have specific gene mutations, as determined by genetic testing.
- Immunotherapy. This activates your bodys immune system to specifically kill cancer cells and is usually recommended for late-stage lung cancer, specifically Stage IV NSCLC. When immunotherapy was first introduced, the effects were dramatic, says Dr. Herbst. Now we are using combined therapies such as immunotherapy with chemotherapy and exploring other immunotherapy or targeted therapies in combination, and we are seeing results.
Other Types Of Lung Tumors
Along with the main types of lung cancer, other tumors can occur in the lungs.
Lung carcinoid tumors: Carcinoid tumors of the lung account for fewer than 5% of lung tumors. Most of these grow slowly. For more information about these tumors, see Lung Carcinoid Tumor.
Other lung tumors: Other types of lung cancer such as adenoid cystic carcinomas, lymphomas, and sarcomas, as well as benign lung tumors such as hamartomas are rare. These are treated differently from the more common lung cancers and are not discussed here.
Cancers that spread to the lungs: Cancers that start in other organs can sometimes spread to the lungs, but these are not lung cancers. For example, cancer that starts in the breast and spreads to the lungs is still breast cancer, not lung cancer. Treatment for metastatic cancer to the lungs is based on where it started .
You May Like: What Is Clear Cell Carcinoma
What Is The Prognosis And Life Expectancy Of Small
The success of treatment depends on the stage of small-cell lung cancer.
The five-year survival rate for patients with stage I SCLC is 31%.
In approximately 65%-70% of people with small-cell lung cancer, the disease has already spread to other organs of the body by the time small-cell lung cancer is diagnosed.
The stage II SCLC survival rate is about 19%.
People with small-cell lung cancer in the advanced stage cannot be cured. They usually survive less than one year.
Treatment may be moderately successful for people with limited-stage disease. However, even with limited-stage disease, the median survival time is less than two years.
The overall five-year survival rate for people with small-cell lung cancer is less than 20%. People with small cell lung cancer have the highest rate of developing a second primary cancer, usually in 5%-10% percent of cases but as high as 30%
Normal Structure And Function Of The Lungs
Your lungs are 2 sponge-like organs in your chest. Your right lung has 3 sections, called lobes. Your left lung has 2 lobes. The left lung is smaller because the heart takes up more room on that side of the body.
When you breathe in, air enters through your mouth or nose and goes into your lungs through the trachea . The trachea divides into tubes called bronchi, which enter the lungs and divide into smaller bronchi. These divide to form smaller branches called bronchioles. At the end of the bronchioles are tiny air sacs known as alveoli.
The alveoli absorb oxygen into your blood from the inhaled air and remove carbon dioxide from the blood when you exhale. Taking in oxygen and getting rid of carbon dioxide are your lungs main functions.
Lung cancers typically start in the cells lining the bronchi and parts of the lung such as the bronchioles or alveoli.
A thin lining layer called the pleura surrounds the lungs. The pleura protects your lungs and helps them slide back and forth against the chest wall as they expand and contract during breathing.
Below the lungs, a thin, dome-shaped muscle called the diaphragm separates the chest from the abdomen. When you breathe, the diaphragm moves up and down, forcing air in and out of the lungs.
Don’t Miss: Well Differentiated Meaning
Can A Person Have Both Types
Around
After making a diagnosis, the doctor will describe the treatment options and develop a treatment plan.
Factors that affect the plan will include:- the type of cancer
- how far it has spread
- the individuals age and overall health
- the availability of therapies
Because each persons situation is different, treatment will vary accordingly.
Causes Of Small Cell Lung Cancer
Smoking tobacco is the cause of most lung cancers and the biggest risk factor. This includes smoking cigarettes, cigars and pipes. People who do not smoke can still develop lung cancer, but their risk is much lower.
If someone stops smoking, their risk of developing lung cancer gets lower over time. After about 15 years it is almost the same as a non-smoker.
Lung cancer is also more common in older people.
We have more information about the risk factors of lung cancer.
See also
If these tests show anything abnormal, your GP will refer you to a chest specialist within 2 weeks. Sometimes they will do this before getting the result of the chest x-ray.
At the hospital, the specialist will explain any other tests you need. These may include:
- PET-CT scan
A PET-CT scan combines 2 types of scan. A CT takes a series of x-rays to build up a 3D picture. A PET measures the activity of cells in the body.
- Biopsy
During a biopsy, a doctor or nurse takes samples of cells or tissue from the abnormal area. They look at the biopsy samples under a microscope to check for cancer cells. You usually have a biopsy to find out for certain if you have lung cancer. There are different ways of collecting biopsies, including:
Waiting for tests results can be a difficult time, we have more information that can help.
Also Check: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Survival Rate Stage 1
Further Tests After Diagnosis
If tests show you have small cell lung cancer, your specialist will arrange further tests. Some of these help with the staging of lung cancer.
You may have the following tests:
- Mediastinoscopy
A mediastinoscopy is sometimes done instead of an EBUS or EUS. It lets the doctor look at the area in the middle of your chest and nearby lymph nodes. You have it under a general anaesthetic.
- Thoracoscopy
A thoracoscopy lets the doctor look at the lining of the lungs . It is usually done under a general anaesthetic.
- MRI scan
An MRI scan uses magnetism to build up a detailed picture of areas of your body.
- Breathing tests
If your treatment plan involves having surgery or radiotherapy your doctor will arrange breathing tests and exercise tests. These help doctors see how well your lungs are working. You may also have tests to check how well your heart is working.
See also
After Small Cell Lung Cancer Has Been Diagnosed Tests Are Done To Find Out If Cancer Cells Have Spread Within The Chest Or To Other Parts Of The Body

The process used to find out if cancer has spread within the chest or to other parts of the body is called staging. The information gathered from the staging process determines thestage of the disease. It is important to know the stage in order to plan treatment. Some of the tests used to diagnosesmall cell lung cancer are also used to stage the disease.
Other tests and procedures that may be used in the staging process include the following:
You May Like: Invasive Ductal Breast Cancer Survival Rate